Recovery In The Hospital
After surgery, you’ll typically spend 1 or 2 days in an intensive care unit . Your heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels will be checked regularly during this time.
An intravenous line will likely be inserted into a vein in your arm. Through the IV line, you may get medicines to control blood circulation and blood pressure. You also will likely have a tube in your bladder to drain urine and a tube to drain fluid from your chest.
You may receive oxygen therapy and a temporary pacemaker while in the ICU. A pacemaker is a small device that’s placed in the chest or abdomen to help control abnormal heart rhythms.
Your doctor may recommend that you wear compression stockings on your legs as well. These stockings are tight at the ankle and become looser as they go up the leg. This creates gentle pressure up the leg. The pressure keeps blood from pooling and clotting.
While in the ICU, you’ll also have bandages on your chest incision and on the areas where an artery or vein was removed for grafting.
After you leave the ICU, you’ll be moved to a less intensive care area of the hospital for 3 to 5 days before going home.
Whats Recovery Like After Bypass Surgery
Itâs a gradual process. You may feel worse right after surgery than you did before. You might not be hungry and even be constipated for a few weeks after the surgery. You could have trouble sleeping while youâre in the hospital. If the surgeon takes out a piece of healthy vein from your leg, you may have some swelling there. This is normal.
Your body needs time to recover, but youâll feel better each day. It’ll take about 2 months for your body to feel better after surgery.
Youâll visit your doctor several times during the first few months to track your progress. Call them if your symptoms donât improve or youâre feeling worse.
Talk with your doctor about the best time to return to your normal day-to-day activities. What’s right for you will depend on a few things, including:
- Your overall health
- How many bypasses you’ve had
- Which types of activity you try
You’ll need to ease back in. Some common plans include:
Driving. Usually 4 to 6 weeks, but you need to make sure your concentration is back before you get behind the wheel.
Housework. Take it slow. Start with the simple things you like to do and have your family help with the heavy stuff for a bit while you recover.
Sex. In most cases, you should be physically good to go in about 3 weeks. But you may lose interest in sex for a while after your surgery, so it could be as long as 3 months before you’re ready to be intimate again.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
An endeavor as complex as coronary artery surgery demands attention to non-technical aspects such as teamwork, communication, human factors, culture of safety, and optimizing the operative environment. There are increasing data and consensus that focus on these issues is needed to achieve and maintain high-quality interventions.
You May Like: Dos And Don’ts After Heart Surgery
Treatment For Coronary Heart Disease
Treatment may include:
-
Modification of risk factors. Risk factors that you can change include smoking, high cholesterol levels, high blood glucose levels, lack of exercise, poor dietary habits, being overweight, and high blood pressure.
-
Medicines. Medicine that may be used to treat coronary artery disease include:
-
Antiplatelets. These decrease blood clotting. Aspirin, clopidogrel, ticlopidine, and prasugrel are examples of antiplatelets.
-
Antihyperlipidemics. These lower lipids in the blood, particularly low density lipid cholesterol. Statins are a group of cholesterol-lowering medicines, and include simvastatin, atorvastatin, and pravastatin, among others. Bile acid sequestrants–colesevelam, cholestyramine and colestipol–and nicotinic acid are other medicines used to reduce cholesterol levels.
-
Antihypertensives. These lower blood pressure. Several different groups of medicines work in different ways to lower blood pressure.
Coronary angioplasty. With this procedure, a balloon is used to create a bigger opening in the vessel to increase blood flow. Although angioplasty is done in other blood vessels elsewhere in the body, percutaneous coronary intervention refers to angioplasty in the coronary arteries to permit more blood flow into the heart. PCI is also called percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty . There are several types of PCI procedures, including:
Balloon angioplasty. A small balloon is inflated inside the blocked artery to open the blocked area.
What Happens During Bypass Surgery
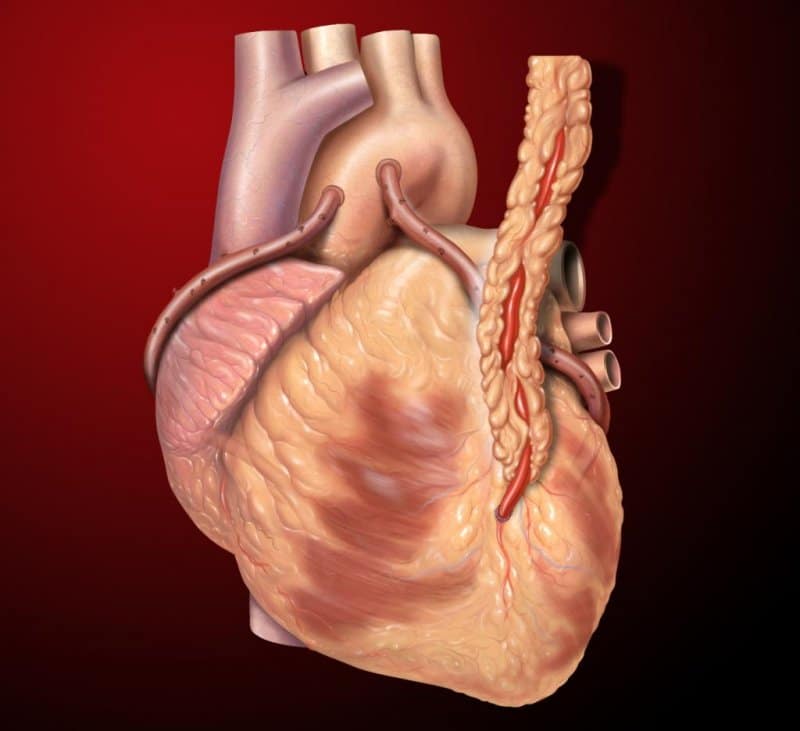
A blood vessel is grafted between the aorta and the coronary artery, or arteries leading to the heart muscle. This allows the blood to bypass blocked arteries and restores blood flow to the heart muscle. It is quite normal to need two to four grafts, otherwise known as a double, triple or quadruple bypass.
Your surgeon will then make a cut, about 25cm long, down the middle of your breastbone and will open your ribcage to reach your heart. Your surgeon may attach the new grafts while your heart is still beating, but it’s more common to temporarily stop your heart.
Your blood is then diverted to a heart-lung machine. This takes over from your heart and lungs to add oxygen to your blood and maintain your circulation.
The grafts will be attached and your heart will be restarted. Your sternum will be rejoined using wires and the skin on your chest will be closed with dissolvable stitches.
The procedure itself takes around three hours, but may take longer depending on how many grafts need to be done. If blood vessels from your leg or arm are being used for grafts, your surgeon will remove and prepare these first.
After your operation, you will be taken to the intensive care unit and will be closely monitored for about 24 hours before you go back to your ward. When you wake up you will be connected to machines that record the activity of your heart, lungs and other body systems. These might include a ventilator machine to help you breathe.
Read Also: Explain What Distinguishes A Stroke From A Heart Attack.
Nursing Allied Health And Interprofessional Team Interventions
A large team of professionals is required to not only manage the patient but to be in constant communication with each other to provide the best overall outcome. Coronary artery surgery requires a cardiothoracic surgeon, a first assistant, a pharmacist, a team of nurses, a perfusionist, an anesthesiologist or nurse anesthetist, and scrub techs in the perioperative period. As mentioned above, each of these team members plays a specific part in monitoring the patient. Though these members are crucial during the actual operation, so many more members are also vital in the pre-operative and post-operative stages of the patient.
Monitoring the patient is just as important as it is in the intra-operative stage as it is in the pre- and post-operative stages. Those involved outside of the intra-operative stage include a cardiologist, ICU, and floor nursing staff, echo techs, physical therapists, and cardiac rehabilitation specialists. Nurses are critical in the care of post-op CABG patients. They are responsible for managing all drains, lines, and educating the patient and their family regarding post-operative care. Excellent perioperative care is crucial to the success and outcomes of the patient. Interprofessional team management and interventions made collectively as a team provide the best outcomes for CABG patients.
Results Compared To Stent Placement
CABG or stent placement is indicated when medical management â anti-angina medications, statins, antihypertensives, smoking cessation, and/or tight blood sugar control in diabetics â do not satisfactorily relieve ischemic symptoms.
A 2018 meta-analysis with over 4000 patient cases found hybrid coronary revascularization to have significant advantages compared with conventional CABG. Reduced incidence of blood transfusion, reduced hospital stay duration and reduced intubation duration were all reported. In contrast, HCR was found to be significantly more expensive compared to CABG.
Also Check: Can Diabetes Cause Heart Palpitations
Other Factors That Affect Coronary Artery Disease
Other factors also may contribute to CAD. These include:
- Sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is a disorder in which your breathing stops or gets very shallow while you’re sleeping. Untreated sleep apnea can raise your chances of having high blood pressure, diabetes, and even a heart attack or stroke.
- Stress. Research shows that the most commonly reported “trigger” for a heart attack is an emotionally upsetting event-particularly one involving anger.
- Alcohol. Heavy drinking can damage the heart muscle and worsen other risk factors for heart disease. Men should have no more than two drinks containing alcohol a day. Women should have no more than one drink containing alcohol a day.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease?
A common symptom of coronary artery disease is angina. Angina is chest pain or discomfort that occurs when your heart muscle doesn’t get enough oxygen-rich blood.
Angina may feel like pressure or a squeezing pain in your chest. You also may feel it in your shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back. This pain tends to get worse with activity and go away when you rest. Emotional stress also can trigger the pain.
Another common symptom of CAD is shortness of breath. This symptom happens if CAD causes heart failure. When you have heart failure, your heart can’t pump enough blood throughout your body. Fluid builds up in your lungs, making it hard to breathe.
What Are Some Types Of Heart Surgery
There are many types of heart surgery. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, which is part of the National Institutes of Health, lists the following as among the most common coronary surgical procedures.
In addition to these surgeries, a minimally invasive alternative to open-heart surgery that is becoming more common is transcatheter structural heart surgery. This involves guiding a long, thin, flexible tube called a catheter to your heart through blood vessels that can be accessed from the groin, thigh, abdomen, chest, neck, or collarbone. A small incision is necessary. This type of surgery includes transcatheter aortic valve implantation to replace a faulty aortic valve with a valve made from animal tissue, MitraClip® placement for mitral valve abnormalities, and WATCHMAN® placement for nonvalvular atrial fibrillation patients.
Also Check: When To Go To The Hospital For Rapid Heart Rate
What Is Heart Bypass Surgery
Heart bypass surgery is when a surgeon takes blood vessels from another part of your body to go around, or bypass, a blocked artery. The result is that more blood and oxygen can flow to your heart again.
Imagine youâre on a highway. An accident causes traffic to pile up ahead. Emergency crews redirect cars around the congestion. Finally, youâre able to get back on the highway and the route is clear. Heart bypass surgery is similar.
It can help lower your risk for a heart attack and other problems. Once you recover, youâll feel better and be able to get back to your regular activities.
Youâll still need a healthy diet, exercise, and probably medicine to prevent another blockage. But first, youâll want to know what to expect from the surgery, how to prepare, what complications can happen, and what the recovery is like.
Why Do I Need Heart Bypass Surgery
Bypass surgery treats symptoms of coronary artery disease. That happens when a waxy substance called plaque builds up inside the arteries in your heart and blocks blood and oxygen from reaching it.
Your doctor may suggest heart bypass surgery if:
- You have severe chest pain that your doctor thinks happens because several of the arteries that supply blood to your heart are blocked.
- At least one of your coronary arteries has disease that’s causing your left ventricle — the chamber that does most of your heart’s blood pumping — to not work as well as it should.
- There’s a blockage in your left main coronary artery, which gives your left ventricle most of its blood.
- You’ve had other procedures, and either they haven’t worked or your artery is narrow again.
- You have new blockages.
Coronary artery disease can lead to a heart attack. It can cause a blood clot to form and cut off blood flow. Bypass surgery can give your ticker a big health boost.
Read Also: Rapid Heart Rate While Sleeping
What Happens During This Procedure
CABG is a complicated procedure that takes several hours to complete . The following steps happen for most of these surgeries.
Anesthesia and life support
Like most major surgeries, the first step to this surgery is to put you into a state of deep sleep. This keeps you from feeling pain during the surgery. It also helps relax you for other steps in the preparation.
Because CABG involves work on your heart, it usually involves multiple types of life support. These include:
Blood vessel harvesting
CABG involves creating a bypass for blood to use to reach blocked areas of your heart. A bypass is like a detour for your blood to use to get around an obstacle. Creating that bypass involves taking a blood vessel from somewhere else in your body, such as your leg, arm or chest, and using it to craft the detour around the blockage. In cases where theres more than one blocked artery, multiple bypasses may be necessary. These are double , triple and quadruple bypasses.
Surgery
To reach your heart to perform the surgery, a cardiothoracic surgeon will make an incision in the center of your chest. Theyll also split your breastbone down the middle, then spread and lift your rib cage to make it easier to access your heart.
Once the bypass is in place, the surgeon can restart your heart and get your blood flowing again. Theyll then lower your rib cage back into place and wire it together so it can heal. Theyll then close the incision in your chest with staples and sutures .
Number Of Arteries Bypassed
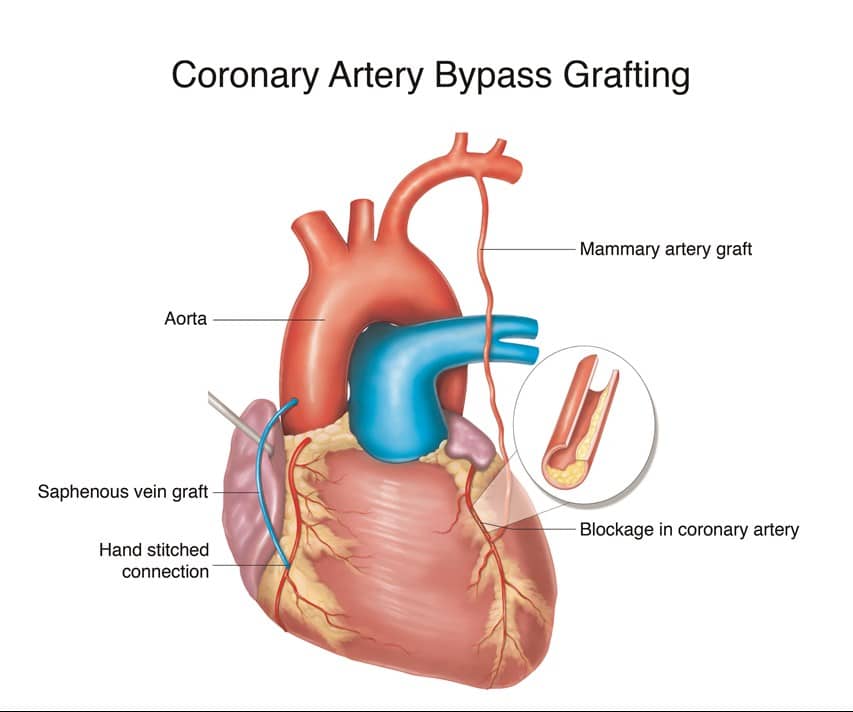
| Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| This section needs to be . Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. |
The terms single bypass, double bypass, triple bypass, quadruple bypass and quintuple bypass refer to the number of coronary arteries bypassed in the procedure. In other words, a double bypass means two coronary arteries are bypassed coronary artery and right coronary artery ) a triple bypass means three vessels are bypassed ) a quadruple bypass means four vessels are bypassed while quintuple means five. Left main coronary artery obstruction requires two bypasses, one to the LAD and one to the LCX.
A coronary artery may be unsuitable for bypass grafting if it is small , heavily calcified, or located within the heart muscle rather than on the surface. A single obstruction of the left main coronary artery is associated with a higher risk for a cardiac death and usually receives a double bypass.
The surgeon reviews the coronary angiogram prior to surgery and identifies the number of obstructions, the percent obstruction of each, and the suitability of the arteries beyond the obstruction as targets. The presumed number of bypass grafts needed as well as the location for graft attachment is determined in a preliminary fashion prior to surgery, but the final decision as to number and location is made during surgery by direct examination of the heart.
You May Like: Heart Attack Symptoms In Men
Current Research Funded By The Nhlbi
Our Division of Cardiovascular Sciences, the Atherothrombosis and Coronary Artery Disease Branch of its Adult and Pediatric Cardiac Research Program, and the Center for Translation Research and Implementation Science oversee much of the research on coronary heart disease we fund.
Find funding opportunities and program contacts for research on coronary heart disease.
What Are The Coronary Arteries
Coronary arteries supply blood to the heart muscle. Like all other tissues in the body, the heart muscle needs oxygen-rich blood to function, and oxygen-depleted blood must be carried away. The coronary arteries run along the outside of the heart and have small branches that supply blood to the heart muscle.
Don’t Miss: What Is Peak Heart Rate
Coronary Angiography And Cardiac Catheterization
Your doctor may ask you to have coronary angiography if other tests or factors show that you’re likely to have CAD. This test uses dye and special x rays to show the insides of your coronary arteries.
To get the dye into your coronary arteries, your doctor will use a procedure called cardiac catheterization . A long, thin, flexible tube called a catheter is put into a blood vessel in your arm, groin , or neck. The tube is then threaded into your coronary arteries, and the dye is released into your bloodstream. Special x rays are taken while the dye is flowing through your coronary arteries.
Cardiac catheterization is usually done in a hospital. You’re awake during the procedure. It usually causes little to no pain, although you may feel some soreness in the blood vessel where your doctor put the catheter.
How Is Coronary Artery Disease Treated?
Treatment for coronary artery disease may include lifestyle changes, medicines, and medical procedures. The goals of treatments are to:
- Relieve symptoms
- Reduce risk factors in an effort to slow, stop, or reverse the buildup of plaque
- Lower the risk of blood clots forming, which can cause a heart attack
- Widen or bypass clogged arteries
- Prevent complications of CAD
Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery
and Minimally Invasive Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
What the Procedure Does
An alternative to standard bypass surgery . Small incisions are made in the chest. Chest arteries or veins from your leg are attached to the heart to “bypass” the clogged coronary artery or arteries. The instruments are passed through the ports to perform the bypasses. The surgeon views these operations on video monitors rather than directly. In PACAB, the heart is stopped and blood is pumped through an oxygenator or “heart-lung” machine. MIDCAB is used to avoid the heart-lung machine. It’s done while the heart is still beating. Requires several days in the hospital.
Reason for the Procedure
- Manages blockage of blood flow to the heart and improves the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart.
- Reduces risk of heart attack.
- Improves ability for physical activity.
You May Like: High Reating Heart Rate
