How Does Blood Flow Through The Heart
The right and left sides of the heart work together. The pattern described below is repeated over and over, causing blood to flow continuously to the heart, lungs, and body.
Right side of the heart
- Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium.
- As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your right atrium into your right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve.
- When the ventricle is full, the tricuspid valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the right atrium while the ventricle contracts.
- As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the pulmonic valve, into the pulmonary artery and to the lungs, where it is oxygenated. The oxygenated blood then returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins.
Left side of the heart
- The pulmonary veins empty oxygen-rich blood from the lungs into the left atrium.
- As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your left atrium into your left ventricle through the open mitral valve.
- When the ventricle is full, the mitral valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the atrium while the ventricle contracts.
- As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the aortic valve, into the aorta and to the body.
What Blood Vessel Carries Blood To The Heart
Who are the experts?Our certified Educators are real professors, teachers, and scholars who use their academic expertise to tackle your toughest questions. Educators go through a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team.
Ph.D. from Oregon State University
Educator since 2017
Our heart acts as a pump to circulate the blood to different parts of our body. Blood vessels carry oxygen poor blood to heart, from where it is sent to the lungs to get fresh oxygen supply. Oxygen rich blood is sent back to heart and from there it is…
What Makes The Heart Pump
Your heart has a special electrical system called the cardiac conduction system. This system controls the rate and rhythm of the heartbeat. With each heartbeat, an electrical signal travels from the top of the heart to the bottom. As the signal travels, it causes the heart to contract and pump blood.
Read Also: How Long Do People Live With Congestive Heart Failure
Components Of The Aorta
The aortic arch contains peripheral baroreceptors and chemoreceptors that relay information concerning blood pressure, blood pH, and carbon dioxide levels to the medulla oblongata of the brain. This information is processed by the brain and the autonomic nervous system mediates the homeostatic responses that involve feedback in the lungs and kidneys. The aorta extends around the heart and travels downward, diverging into the iliac arteries. The five components of the aorta are:
Blood Vessels Arteries Capillaries Veins Vena Cava Central Veins
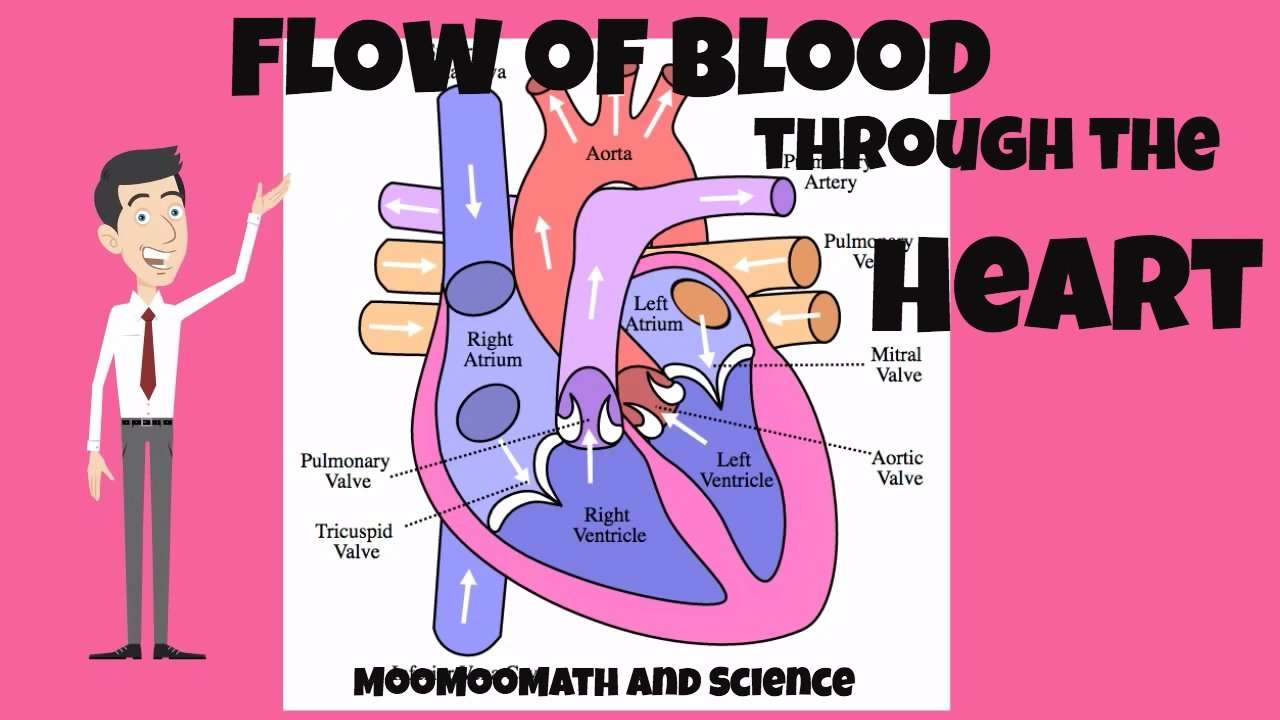
Image 1: Blood Vessels. Arteries carry oxygen rich blood from the left side of the heart to the tissues and organs. After oxygen leaves the blood and moves into the tissues, the level of oxygen in the blood becomes low. The veins carry blood that has a low level of oxygen back to the right side of the heart. Blood from the veins is pumped from the right side of the heart through the blood vessels of the lungs, where new oxygen is picked up. This oxygen rich blood flows from the lungs to the left side of the heart.
Recommended Reading: Why Does Left Arm Go Numb During Heart Attack
Where Are Your Blood Vessels Located
There are blood vessels throughout your body. The main artery is your aorta, which connects to the left side of your heart. It runs down through your chest, diaphragm and abdomen, branching off in many areas. Near your pelvis, your aorta branches into two arteries that supply blood to your lower body and legs.
The main vein in your body is the vena cava. The superior vena cava is in the upper right part of your chest. It carries blood from your head, neck, arms and chest back to your heart. The inferior vena cava is near the right side of your diaphragm. It brings blood from your legs, feet, abdomen and pelvis back to your heart.
What Conditions And Disorders Affect The Blood Vessels
A wide range of problems can affect your blood vessels, including:
- Aneurysm, a bulge in a weak or damaged portion of an artery. Aneurysms can occur anywhere in your body. If they rupture , they may cause life-threatening internal bleeding.
- Arterial diseases, including coronary artery disease, carotid artery disease and peripheral artery disease . These diseases cause arteries to narrow, usually due to atherosclerosis.
- Atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque inside your arteries. It can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
- Blood clots, or clumps of blood that form inside veins or arteries. Clots block blood flow and can lead to deep vein thrombosis , pulmonary embolism, stroke or occlusion of an artery.
- High blood pressure, or hypertension, occurs when theres too much force against the walls of your arteries.
- Raynauds disease, which causes arteries that supply blood to your skin to get very narrow in response to cold temperatures.
- Varicose veins, or twisted and enlarged veins that usually form in the legs or feet.
- Vascular malformations, which are abnormal clusters or connections between blood vessels. Conditions such as arteriovenous malformations are often congenital .
- Vasculitis, which is blood vessel inflammation. Blood vessel walls can thicken and narrow, which prevents blood from flowing freely.
Read Also: How Does High Blood Pressure Affect The Heart
What Kind Of Blood Comes Back Into The Heart & Then Goes To The Lungs
The heart consists of four chambers in which blood flows. Blood enters the right atrium and passes through the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs where it becomes oxygenated. The oxygenated blood is brought back to the heart by the pulmonary veins which enter the left atrium.
How Does Blood Move Through The Heart
Blood comes into the right atrium from the body, moves into the right ventricle and is pushed into the pulmonary arteries in the lungs. After picking up oxygen, the blood travels back to the heart through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium, to the left ventricle and out to the body’s tissues through the aorta.
Read Also: How Do Nsaids Cause Heart Attacks And Strokes
Difference Between Blood Vessels And Veins
There are multiple functions going on in our bodies simultaneously. For smooth functioning and better coordination between organs, each work inside the body is differentiated so that the whole body works flawlessly.
One of the main functions of our body is the transportation of blood to and from the heart. There are two types of blood vessels; arteries and veins in the circulatory system involved in carrying blood to the heart and away from the heart.
Arteries and veins, though they belong to the circulatory system, differs in their functionality and speciality. In this article, we will be looking at what exactly arteries and veins are and what are their significant differences.
Recommended Reading: Is Your Pulse And Heart Rate The Same Thing
How Do The Heart And Blood Vessels Work
The heart works by following a sequence of electrical signals that cause the muscles in the chambers of the heart to contract in a certain order. If these electrical signals change, the heart may not pump as well as it should.
The sequence of each heartbeat is as follows:
- The sinoatrial node in the right atrium is like a tiny in-built ‘timer’. It fires off an electrical impulse at regular intervals. This controls your heart rate. Each impulse spreads across both atria, which causes them to contract. This pumps blood through one-way valves into the ventricles.
- The electrical impulse gets to the atrioventricular node at the lower right atrium. This acts like a ‘junction box’ and the impulse is delayed slightly. Most of the tissue between the atria and ventricles does not conduct the impulse. However, a thin band of conducting fibres called the atrioventricular bundle acts like ‘wires’ and carries the impulse from the AV node to the ventricles.
- The AV bundle splits into two – a right and a left branch. These then split into many tiny fibres which carry the electrical impulse throughout the ventricles. The ventricles contract and pump blood through one-way valves into large arteries:
- The arteries going from the right ventricle take blood to the lungs.
- The arteries going from the left ventricle take blood to the rest of the body.
Don’t Miss: Does Fever Increase Heart Rate
What Is The Vascular System
The vascular system, also called the circulatory system, is made up of the vessels that carry blood and lymph through the body. The arteries and veins carry blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body tissues and taking away tissue waste matter. The lymph vessels carry lymphatic fluid . The lymphatic system helps protect and maintain the fluid environment of the body by filtering and draining lymph away from each region of the body.
The vessels of the blood circulatory system are:
-
Arteries. Blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body.
-
Veins. Blood vessels that carry blood from the body back into the heart.
-
Capillaries. Tiny blood vessels between arteries and veins that distribute oxygen-rich blood to the body.
Blood moves through the circulatory system as a result of being pumped out by the heart. Blood leaving the heart through the arteries is saturated with oxygen. The arteries break down into smaller and smaller branches to bring oxygen and other nutrients to the cells of the body’s tissues and organs. As blood moves through the capillaries, the oxygen and other nutrients move out into the cells, and waste matter from the cells moves into the capillaries. As the blood leaves the capillaries, it moves through the veins, which become larger and larger to carry the blood back to the heart.
The Heart And Blood Vessels
Oxygen is vital to life as it provides fuel for all the body’s functions. The heart’s role is to pump oxygen-rich blood to every cell in the body. The blood vessels a network of interconnecting arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins provide the pathway in which blood travels.
Arteries are the passageways through which the blood is delivered, the largest of which is the aorta. The aorta branches off the heart and divides into many smaller arteries, which have muscular walls that adjust their diameter to increase or decrease blood flow to a particular body area. Capillaries are thin walled, highly branched vessels that feed the tissues and collect wastes to be carried back to the lungs, liver, or kidney for elimination. Capillaries empty into the venules, which in turn drain into the veins that lead back to the heart. Veins carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs to pick up more oxygen, and then back to the heart once again.
Don’t Miss: How Long Can Heart Attack Last
Introduction To The Major Blood Vessels Of The Heart:
The major blood vessels of the heart are the larger arteres and veins that attach to the atria and ventricles and transport blood to and from the
Blood is delivered to the right atrium from the systemic circulatory system by two veins:
- The superior vena cava transports oxygen-depleted blood from the upper extremities, head, and neck.
Learning about the cardiovascular system? You may like this cardiovascular system revision guide complete with diagrams, quizzes and free worksheets.
What Is The Name Of The Blood Vessels That Carry Blood To And From The Lungs
pulmonary arterypulmonary
Refering to the common carotid artery supplies blood to the head and face. The blood vessel that carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. It is the only artery that carries deoxygenated blood.
Also, what is the blood vessel that carries blood to the heart called? blood vessels: Blood moves through many tubes called arteries and veins, which together are called blood vessels. The blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart are called arteries. The ones that carry blood back to the heart are called veins.
People also ask, what carries blood away from the lungs?
Key terms
Read Also: How To Slow Down My Heart Rate
Students Who Viewed This Also Studied
S L – General Biology .pdf
Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico
SCIENCE BIOLOGY
Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico
SCIENCE BIOLOGY
S L – General Biology .pdf
Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico
SCIENCE BIOLOGY
S L – General Biology .pdf
Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico
SCIENCE BIOLOGY
Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico
SCIENCE BIOLOGY
Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico
SCIENCE BIOLOGY
Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico SCIENCE BIOLOGY
S L – General Biology .pdf
Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico SCIENCE BIOLOGY
S L – General Biology.pdf
Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico SCIENCE BIOLOGY
S L – General Biology .pdf
Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico SCIENCE BIOLOGY
S L – General Biology .pdf
Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico SCIENCE BIOLOGY
PROP&ECO38
Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico SCIENCE BIOLOGY
fotosintesis ppt corr.ppt.1.pdf
Anatomy Of The Heart And Blood Vessels
Reviewed byDr Jacqueline Payne
The heart is a muscular pump that pushes blood through blood vessels around the body. The heart beats continuously, pumping the equivalent of more than 14,000 litres of blood every day through five;main types of blood vessels: arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules and veins.
Read Also: Is 116 Heart Rate High
What Are The Effects Of Vascular Disease
Because the functions of the blood vessels include supplying all organs and tissues of the body with oxygen and nutrients, removal of waste products, fluid balance, and other functions, conditions that affect the vascular system may affect the part of the body supplied by a particular vascular network, such as the coronary arteries of the heart.
Examples of the effects of vascular disease include:
-
Coronary artery disease. Heart attack, angina
-
Cerebrovascular disease. Stroke, transient ischemic attack
-
Peripheral arterial disease. Claudication , critical limb ischemia
-
Vascular disease of the great vessels. Aortic aneurysm , coarctation of the aorta , Takayasu arteritis
-
Thoracic vascular disease. Thoracic aortic aneurysm
-
Abdominal vascular disease. Abdominal aortic aneurysm
-
Peripheral venous disease. Deep vein thrombosis , varicose veins
-
Lymphatic vascular diseases. Lymphedema
-
Vascular diseases of the lungs. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis , angiitis , hypertensive pulmonary vascular disease
-
Renal vascular diseases. Renal artery stenosis , fibromuscular dysplasia
-
Genitourinary vascular diseases. Vascular erectile dysfunction
Classification & Structure Of Blood Vessels
Blood vessels are the channels or conduits through which blood is distributed to body tissues. The vessels make up two closed systems of tubes that begin and end at the heart. One system, the pulmonary vessels, transports blood from the right ventricle to the lungs and back to the left atrium. The other system, the systemic vessels, carries blood from the left ventricle to the tissues in all parts of the body and then returns the blood to the right atrium. Based on their structure and function, blood vessels are classified as either arteries, capillaries, or veins.
Also Check: What Do You Do If Someone Is Having A Heart Attack
Do All Arteries Carry Oxygen
The first and most important difference between the two is that all arteries carry blood away from the heart, and all veins carry blood to the heart from outlying areas. Most arteries carry oxygenated blood, and most veins carry deoxygenated blood; the pulmonary arteries and veins are the exceptions to this rule.
Which Side Is A Woman’s Heart
Although most of us place our right hand on our left chest when we pledge allegiance to the flag, we really should be placing it over the center of our chest, because that’s where our hearts sit. Your heart is in middle of your chest, in between your right and left lung. It is, however, tilted slightly to the left.
Don’t Miss: Does Magnesium Help With Heart Palpitations
Which Is A Large Blood Vessel That Carries Blood Away From The Heart To The Lungs
3.9/5major blood vesselsheartarterymore about it
aorta : The aorta is the major blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart to the rest of the body.
what type of artery carries blood away from the heart? Arteries. Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Pulmonary arteries transport blood that has a low oxygen content from the right ventricle to the lungs. Systemic arteries transport oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body tissues.
Herein, which vessel carries blood from heart to lungs?
The pulmonary artery channels oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle into the lungs, where oxygen enters the bloodstream. The pulmonary veins bring oxygen-rich blood to the left atrium.
What carries blood back to the heart?
The circulatory system is made up of blood vessels that carry blood away from and towards the heart. Arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry blood back to the heart. The circulatory system carries oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to cells, and removes waste products, like carbon dioxide.
