What Are The Symptoms Of Diastolic Heart Failure
In the earliest stages of diastolic heart failure, you may not notice any symptoms. But as the condition progresses, some of the following symptoms will likely develop:
- shortness of breath when lying down or when doing activities that you used to do with no problem
2016 study notes that diastolic heart failure is now the most common form of heart failure. It also suggests that the key to successful treatment is aggressive management of contributing factors. That means treating diastolic heart failure also involves proper treatment of any other conditions you may have, as listed above.
More specifically, treating diastolic heart failure usually involves some combination of the following therapies:
What Are The Main Causes Of Heart Failure
Heart failure can have many causes. The most common causes are:
- Coronary heart disease this is where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become clogged up with fatty substances called atherosclerosis which may cause symptoms of chest discomfort called angina or heart damage from a heart attack.
- Hypertension high blood pressure can put extra strain on the heart, which over time can lead to heart failure.
- Cardiomyopathy conditions affecting the heart muscle and can be hereditary or acquired condition that causes the changes in the heart muscle tissue leading to failure of function.
- Arrhythmias heart rhythm problems such as atrial fibrillation which impairs the contraction strength of the heart by the persistent fast heart rate is one of the many rhythm disturbances causing the heart to pump less efficiently.
- Heart valve disease valve defects and damage will increase volume and strain on the heart and weaken it.
- Congenital heart disease birth defects that affect the normal workings of the heart.
- Metabolic hyperthyroid with overactive thyroid and diabetes are endocrine causes of heart failure.
- Toxicity alcohol and certain chemotherapy drugs can be toxic to the muscle cells and damage their function.
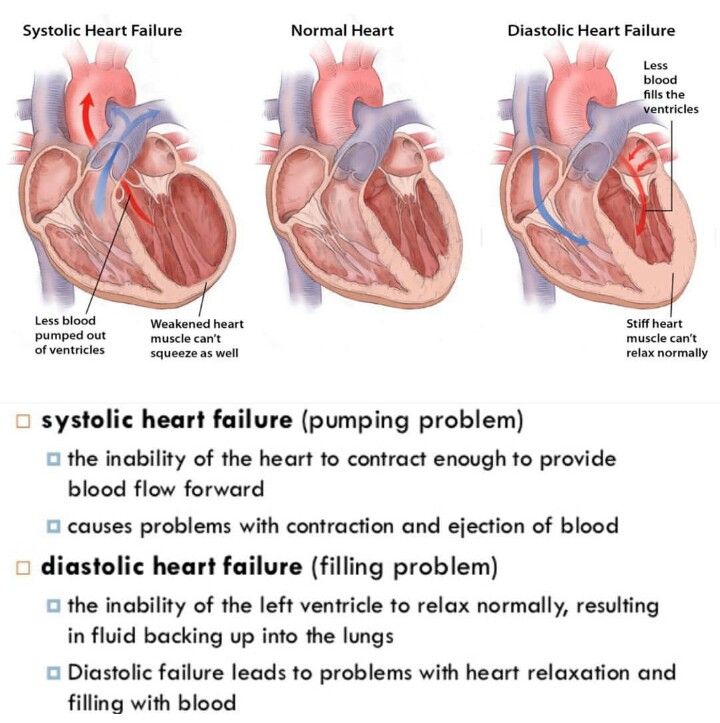
What Is The Difference Between Diastolic And Systolic
Diastolic and systolic are the two numbers on a blood pressure reading. Every time your heart squeezes, it pumps out blood to the network of blood vessels known as the circulatory system. The force or pressure of that squeeze is called systolic blood pressure. When your heart rests between beats, the pressure in the arteries is the diastolic blood pressure. This is why your blood pressure has two numbers:
- The top number is the systolic blood pressure.
- The bottom number is the diastolic blood pressure.
You May Like: How To Know If You Have A Heart Attack
Treating Chf In Louisiana
For patients suffering from CHF, skilled medical treatment is critical to managing the condition and maintaining health. Cardiovascular Institute of the South is home to many renowned and respected cardiologists. Our physicians are experienced and highly-qualified in the treatment of congestive heart failure, along with all other forms of cardiovascular disease. To request an appointment at any one of our locations across south Louisiana and Mississippi, click the button below.
Heart Failure And My Future
There is no cure for heart failure. This can be upsetting and raise concerns about your life expectancy. If this is something youre worried about, talk to your GP or a specialist heart failure team. They will explain what to expect during your treatment and give you the advice and support you need.
Conversations about life expectancy and death are difficult. You may need to discuss things like care, finances and wills. Sorting these things out when you feel well enough to do so can help give you and your loved ones peace of mind. Take the first steps with our short guide to talking about death and dying.
Read Also: Right Sided Heart Failure Edema
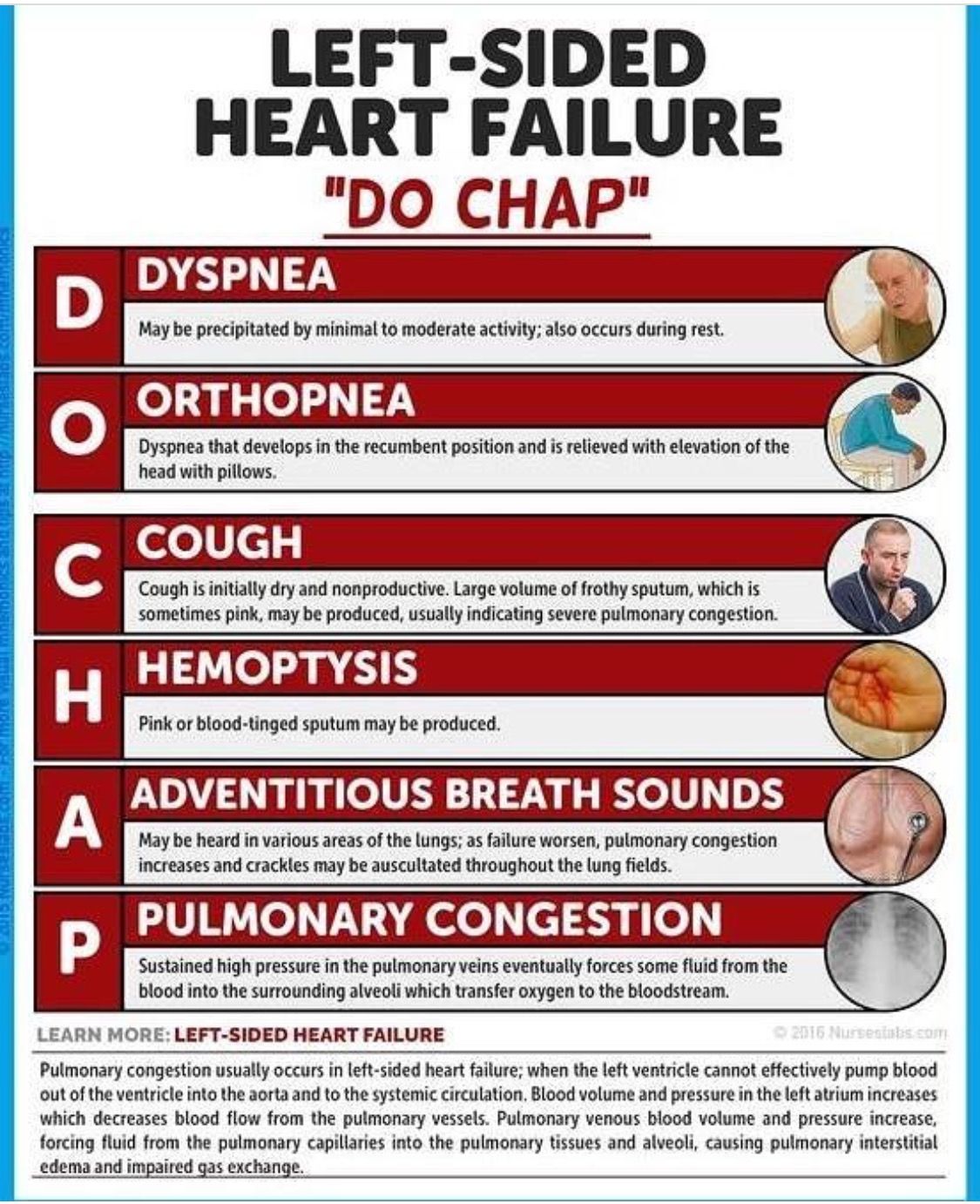
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Failure
When your heart isnt pumping blood as well as it should, it means youre not getting enough oxygen. This affects how your body works, including your breathing and muscles. This causes some of the main symptoms of heart failure, like:
- fainting or feeling lightheaded
- feeling increasingly tired or weak at rest which gets worse with movement
- new persistent cough
- shortness of breath when youre active or resting
- swelling in your feet and ankles which can spread to your lower body.
You should see your GP as soon as you can if you experience any of these symptoms. If you are struggling to breathe or have chest pain, call 999 for immediate medical assistance.
Take Care Of Your Mental Health Too
While stress is never pleasant, it can be especially hard on your heart. Anger management is also an important aspect of heart health.
Talking with a therapist or joining a support group can help with keeping your stress levels down and giving you accountability for the lifestyle changes youre making.
Also Check: How Does Blood Flow Through The Heart Step By Step
What Is Heart Failure
The term heart failure can be frightening. It doesnt mean the heart has failed or stopped working. It means the heart doesnt pump as well as it should.
Heart failure is a major health problem in the United States, affecting about 5.7 million Americans. About 550,000 new cases of heart failure occur each year. Its the leading cause of hospitalization in people older than 65.
If you have heart failure, youll enjoy better health and quality of life if you take care of yourself and keep yourself in balance. Its important to learn about heart failure, how to keep in good balance, and when to call the doctor.
How Do I Manage My Heart Failure
Its important to follow the advice from your doctor and take the medicines youre prescribed. Making changes to your lifestyle is another way to improve your health. Changes you could try are:
- keeping active which has been proven to boost energy and improve sleep and quality of life
- keeping to a healthy weight and diet this will help your overall health and prevent extra strain on your heart
- limiting how much alcohol you drink – lowering your chance of getting abnormal heart rhythms, high blood pressure and diseases such as stroke, liver problems and some cancers
- stopping smoking and using other tobacco products – reducing your risk of developing heart and circulatory diseases
- watching the amount of fluid you have each day if advised by your medical team
- weighing yourself regularly sudden weight gain may mean too much fluid is building up in your body and will need treated.
Living a healthier lifestyle can be hard at first, but its important for your overall quality of life. Visit our healthy living hub to start eating healthier and manage things like smoking and stress today.
Also Check: Does Anxiety Increase Heart Rate
How Can I Reduce My Risk Of Diastolic Heart Failure
The best way to reduce your risk of developing diastolic heart failure is to adopt healthy habits. These habits can improve your overall heart health. They decrease your risk of heart problems.
You can reduce your risk of diastolic heart failure by:
- Limiting alcohol intake and avoiding smoking.
- Managing conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
How Much Water Should You Drink With Heart Failure
Heart failure can cause fluid retention.
Those who are diagnosed with heart failure are usually instructed to limit their daily fluid intake to 2,000 to 2,500 milliliters or 2 to 2.5 liters per day. This includes all types of fluid intake, not just water.
However, too little fluid intake can increase dehydration and the risk of problems such as damage to the kidneys.
Your optimal fluid intake goal should be based on multiple factors, such as:
- the type of heart failure you have
- whether you take a diuretic medication
- your kidney function
- your sodium intake
- whether youve been hospitalized in the past for fluid retention
Based on these factors, you and your doctor can decide what your ideal fluid intake should be.
Dr. Kohli is an internationally recognized researcher and noninvasive cardiologist who specializes in preventive cardiology. She received two undergraduate Bachelor of Science degrees in biology and brain and cognitive science with a concentration in economics. She graduated with a perfect GPA, receiving the most outstanding academic record distinction. She went on to Harvard Medical School for her MD degree and again graduated at the top of her class with a distinction. She completed her internal medicine residency at Harvard Medical School/Brigham & Womens Hospital in Boston.
Don’t Miss: Acute Diastolic Congestive Heart Failure
Stages C And D With Preserved Ef
Treatment for patients with Stage C and Stage D heart failure and reserved EF includes:
- Treatments listed in Stages A and B.
- Medications for the treatment of medical conditions that can cause heart failure or make the condition worse, such as atrial fibrillation, high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, coronary artery disease, chronic lung disease, high cholesterol and kidney disease.
- Diuretic to reduce or relieve symptoms.
YOU ARE THE MOST IMPORTANT PART OF YOUR TREATMENT PLAN!
It is up to you to take steps to improve your heart health. Take your medications as instructed, follow a low-sodium diet, stay active or become physically active, take notice of sudden changes in your weight, live a healthy lifestyle, keep your follow-up appointments, and track your symptoms. Talk to your healthcare team about questions or concerns you have about your medications, lifestyle changes or any other part of your treatment plan.
C Laboratory Tests To Monitor Response To And Adjustments In Management
Repeat echocardiography after initial treatment can be helpful in determining therapeutic efficacy in terms of reversing or normalizing the cardiac structural or functional abnormality which led to the diagnosis of stage B HF. However, all tests, including echocardiography, should only be done with clear diagnostic or therapeutic rationale.
We advise against the use of echocardiography for routine monitoring. For example, in a patient with known LV systolic dysfunction, after initial treatment and re-evaluation, there is no need for annual echocardiograms to evaluate LV ejection fraction unless there is a change in symptoms or a specific clinical question that needs to be answered.
Laboratory testing can be helpful in the monitoring of medications, particularly ACE-inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, and diuretics. Patients on these drugs should undergo routine laboratory evaluation of electrolytes and renal function.
Some patients will develop worsening symptoms after the initiation of beta-blockers. Etiologies of clinical worsening in response to beta-blockers include: negative inotropy in patients with severe LV systolic dysfunction, and chronotropic incompetence. In these patients, beta-blockers should be down-titrated and additional testing may be warranted .
Read Also: How To Get Heart Attack
Physical Examination Maneuvers That Are Likely To Be Useful In Diagnosing The Cause Of This Problem
Physical examination is necessary to identify signs that suggest heart failure as an underlying cause for the patientâs symptoms. However it does not aid in distinguishing systolic from diastolic heart failure.
The general exam should emphasize evaluation of volume status, assessing lower extremity, sacral and scrotal edema, elevated jugular venous pulsations, and abdominal distention and dullness to percussion.
Cardiac auscultation often reveals a third sound in acute exacerbations. A fourth heart sound is present in patients with longstanding uncontrolled hypertension with significant LV hypertrophy, along with a laterally displaced point of maximal impulse .
Pulsus alternans is not a typical feature found in diastolic heart failure. Examination of the right-sided jugular venous waveforms offers insight into the underlying pathophysiologic process, with large right-sided v waves in septal rupture and tricuspid regurgitation, and rapid x and y descents seen with constrictive pericarditis .
Auscultation of lung fields may also reveal basilar crackles indicative of pulmonary edema.
Initial Stages Of Chf
In the initial, mild stage A, there are underlying high-risk factors for CHF such as smoking or high blood pressure. However, the affected person has no symptoms or limitations at rest or with physical activity and there are no signs of CHF on evaluation by a doctor.
In stage B, the person develops mild symptoms of fatigue, shortness of breath, or heart palpitations with routine physical activity. There are minor signs of heart dysfunction on a doctors evaluation. There might also be a mild, intermittent collection of fluid, known as edema, in the ankles and feet.
Don’t Miss: Stage 5 Congestive Heart Failure
Resources For Coping With Heart Failure
Living with heart failure usually means making some changes to your lifestyle. To thrive with heart failure, you need to do more than eat nutritious foods, exercise, and follow your doctors other advice. Youll also need to know the signs that your physical and mental health may be changing due to heart failure.
If youre a caregiver for someone with heart failure, you should learn about what to expect to prepare you for this role.
The following articles can help you learn more about heart failure and what to expect moving forward:
Progression To Overt Hf
In its natural history, ALVDD may deteriorate and progress to heart failure with preserved ejection fraction or even to HF with reduced EF. The prognostic significance of this evolution extends further as evidenced by the association of worsening ALVDD with decreased survival. The rate of both progression to overt disease and associated mortality is determined by a variety of factors, among which the profile of comorbidities is of particular importance. A meta-analysis of several studies including asymptomatic patients with diastolic dysfunction revealed a 70% increased risk of progressing to HF, which was lower than that for asymptomatic LV systolic dysfunction. The major predictors of transition to stage C included age, diabetes, and elevated blood pressure and body mass .
Data from the Framingham Heart Study provided evidence that in addition to established HF risk factors, the presence of noncardiac abnormalities such as renal impairment, pulmonary limitation, or anemia was each associated with a 30% increased risk of incident HF . The association of superimposed clinical events, such as poorly controlled blood pressure, new onset atrial fibrillation, or infections with incident HF, was revealed in a similar community-based population with preserved EF .
Also Check: Man Heart Attack Symptoms
Trouble Arises When The Heart Can’t Properly Relax
Relaxation is every bit as important for your heart as it is for the rest of you. If for some reason the heart has trouble relaxing between beats, then it can’t fill completely. Less blood pumped with each contraction sets the stage for a type of heart failure that goes by many names: diastolic heart failure, heart failure with normal ejection fraction, heart failure with preserved systolic function, and others.
Diastolic heart failure isn’t really new. It’s just that doctors now have tools that let them see how this form of heart failure differs from “regular” heart failure. At least half of the people who develop heart failure each year have diastolic heart failure. Both types of heart failure result in the same thing the heart has trouble supplying the body’s organs and tissues with the oxygen-rich blood they need.
|
Key points
|
Stiffening and bulking up
What to do
In the meantime, the American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology recommend controlling:
How Is Diastolic Heart Failure Treated
Your healthcare provider may advise you to make specific lifestyle changes. Healthy habits can improve your cardiovascular health and help your heart work more efficiently. You may feel better if you:
- Wear a CPAP machine if you have sleep apnea.
- Exercise for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Quit smoking and using tobacco products. Ask your provider for help with quitting if needed.
Your treatment plan may also include prescription medications. Its important to take the medication exactly as directed.
Many people with HFpEF take medications for other heart conditions. Your provider might prescribe medications specifically for diastolic heart failure that include:
- Diuretics to help your body get rid of excess sodium and water.
- Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists to help your body get rid of extra sodium while keeping potassium.
- Medications to lower blood pressure.
You May Like: What Is A Dangerous Heart Rate For A Woman
Mood And Heart Failure
Some people find it very difficult to live with the uncertainty of having heart failure. Learning about your condition and getting involved in making decisions about your treatment will help you feel more in control and may help to relieve anxiety. Its also important to discuss your worries with your family and close friends and your heart failure team so they can support you.
Stress affects different people in different ways. People who dont manage their stress well may turn to unhealthy habits such as smoking, drinking alcohol, or snacking on unhealthy foods.
Knowing what triggers the stress can help you to tackle the problem. Finding healthy ways of coping with stress and learning to relax can help you manage your heart failure. Read more about coping with stress.
Pathophysiology Congestive Heart Failure
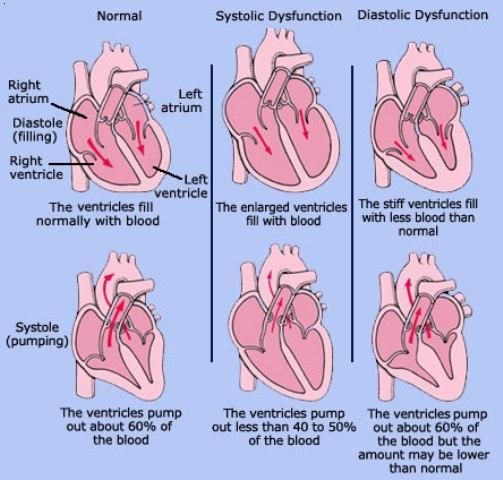
Diastolic dysfunction occurs when the left ventricular myocardium is noncompliant and not able to accept blood return in a normal fashion from the left atrium. This can be a normal physiologic change with aging of the heart or result in elevated left atrial pressures, leading to the clinical manifestations of diastolic congestive heart failure.
Although there is some degree of activation of the sympathetic nervous system and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in states of diastolic HF, it is not as dramatic as seen with systolic HF. Also, these neurohormonal systems do not exert the same negative remodeling effect on the heart during diastolic heart failure as occurs during systolic congestive HF.
Below is a schematic of the neurohormal mechanisms present in congestive heart failure:
Don’t Miss: Is 105 Heart Rate High
