What Happens During Cardiac Ablation
Cardiac ablations take place in a special room known as an electrophysiology laboratory. Your healthcare team may include a cardiologist, a technician, a nurse, and an anesthesia provider. The procedure typically takes between three to six hours to complete. It may be done under general anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation.
First, your anesthesia provider gives you medication through an intravenous line in your arm that will make you drowsy and may cause you to fall asleep. Equipment monitors your hearts electrical activity.
Your doctor cleans and numbs an area of skin on your arm, neck, or groin. Next, they thread a series of catheters through a blood vessel and into your heart. They inject a special contrast dye to help them see areas of abnormal muscle in your heart. The cardiologist then uses a catheter with an electrode at the tip to direct a burst of radiofrequency energy. This electrical pulse destroys small sections of abnormal heart tissue to correct your irregular heartbeat.
The procedure may feel a bit uncomfortable. Make sure to ask your doctor for more medication if it becomes painful.
After the procedure, you lie still in a recovery room for four to six hours to help your body recover. Nurses monitor your heart rhythm during recovery. You may go home on the same day, or you may need to stay in the hospital overnight.
Risks include bleeding, pain, and infection at the catheter insertion site. More serious complications are rare, but may include:
What Is Cardiac Ablation Purpose Procedure And Recovery
Home Blog What is cardiac ablation? Purpose, procedure and recovery
Welcome to London Heart Clinics cardiac ablation patient guide. Read this guide to find out:
- If you are at risk from abnormal heart rhythms
- How cardiac ablation works
- The benefits and risks of ablation
- How to prepare and recover.
Youll find explainer videos on key topics throughout this guide. Watching these will help you make an informed choice about your care.
Contents:
What Is Cardiac Ablation
This procedure uses energy to make small scars in your heart tissue. They stop unusual electrical signals that move through your heart and cause an uneven heartbeat . Cardiac ablation can also treat atrial fibrillation , a type of irregular heartbeat. If this is the case, your doctor might call it atrial fibrillation ablation.
The doctor may try cardiac ablation if medications and resetting your heartbeat — also known as cardioversion — donât work.
Don’t Miss: Can Squirrels Have Heart Attacks
Ablation: What To Expect On The Day Of The Procedure
An ablation is technically a minimally invasive surgical procedure. Your experience on the day of your procedure will depend a lot on the type of ablation you will have and how well your body handles it.
Ablation can be done on an outpatient basis. For more delicate ablationslike a cardiac ablationyour healthcare provider may want to keep you overnight for observation.
This article looks at some common types of ablation and how they work. It takes a step-by-step approach on what you can expect, including potential complications.
Heart Ablation For Svt

SVT is short for supraventricular tachycardia, a common cause of palpitations with a fast heart rate. An SVT can be thought of as a short circuit within the heart, usually near one of the pacemakers of the heart. An impulse can get enter the short circuit and essentially get trapped in there, basically firing off heartbeats in a fast and regular fashion. In a heart ablation for SVT, burning an area through the circuit preventing it from conducting the impulses disrupts the short circuit. Heart ablation for SVT is a successful procedure with a low risk of recurrence.
Recommended Reading: Low Heart Rate With Afib
The Cardiac Ablation Procedure
For some patients, doctors can perform an ablation without changing your heart’s rhythm. However, more commonly, your doctor will use several catheters to cause your heart to beat quickly.
This will help your doctor create an electrical map of your heart. This map helps your doctor identify what type of arrhythmia you have and where the problem. Then they can find and ablate damaged cells inside your heart.
After ablating the cells that are causing problems inside your heart tissue, your doctor will prompt your heart to start beating quickly again. If your heartbeat is regular and slower, then the ablation was successful. If your heart starts beating quickly and irregularly again, you may need more ablation.
Read more about what happens during cardiac ablation.
Cardiac Ablation Success Rate
Catheter ablation is a low-risk procedure. The outcome is successful in most people who have the treatment. Its routinely offered to people with symptomatic atrial fibrillation , for example.
Although theres variation between countries, a study in the British Journal of Cardiology showed catheter ablation is effective in at least 80% of AF cases.
Sometimes patients need an additional ablation treatment. The reported success rate was 95% after a second ablation.
Its also a highly successful alternative to antiarrhythmic drug therapy, with about 70% of AF patients not needing antiarrhythmic medication after ablation treatment.
In this video, Dr Syed Ahsan explains the success rates for cardiac ablation:
Don’t Miss: Do All Heart Attacks Require Surgery
What Is Atrial Fibrillation
- In atrial fibrillation, also called AF, abnormal electrical signals cause the upper chambers of the heart to quiver instead of beating normally. AF is serious and requires treatment.
- increases the risk of stroke significantly, requiring patients to take blood thinners for the long term.
- can cause heart failure because it interferes with the hearts efficiency as a pump, forcing it to work harder. The heart can become enlarged as a result.
- is, like high blood pressure, a general health risk.
AF patients who dont respond well to medication often require cardiac ablation, a class of procedures that strategically creates lines of scar tissue to block transmission of the abnormal electrical signals that underlie atrial fibrillation. Cardiologists generally direct their AF patients to catheter-based ablations. However, patients with non-paroxysmal or chronic AF often require multiple procedures, and the abnormal rhythm frequently comes back.
At Stanford, we offer atrial fibrillation patients comprehensive options focused on minimally invasive approaches that provide more durable results than catheter ablation alone.
Benefits Of The Minimally Invasive Cox Maze Procedure
- Minimally invasive Cox Maze procedures are done through a 5-cm thoracotomy incision. This approach reduces the risk of complications.
- Average hospital stay with the minimally invasive procedure is just 5-7 days, versus 9 days with median sternotomy. Recovery time is also faster.
- Patients who arent eligible for the minimally invasive procedure can count on Stanfords experience with the traditional “open” Cox Maze. We have specialized expertise in this successful procedure as well.
Whether hybrid cardiac ablation, minimally invasive Cox Maze or traditional Cox Maze surgery is right for you, Stanford provides important advantages.
Stanford Health Care has been identified by U.S. News & World Report as one of the top hospitals in the country, year after year. Our cardiac care doctors have adopted newer teamwork approaches. Ablation experts regularly collaborate with other cardiac surgeons to perform surgical ablations when patients are already undergoing more invasive procedures. Our arrhythmia surgeons work closely with our electrophysiologists to provide the best, personalized care for every patient.
“Patients can get conflicting information on whether they should have a catheter ablation or Cox Maze surgery. Because the Stanford electrophysiology section and I work so closely together, we can help patients find treatment options that balance aggressively treating the disease and conservatively minimizing the patients risk.”
Anson Lee, MD
You May Like: Does Gabapentin Affect Your Heart Rate
How Do You Prepare For Ablation
Your medical team will probably tell you to:
- Stop eating or drinking the night before the procedure.
- Stop taking medications to treat arrhythmia several days before.
- Ask the doctor if you should stop any other medications.
- Ask the doctor about precautions if you have a pacemaker or implanted defibrillator.
The doctor will give you any other specific instructions.
Recovery From A Cardiac Ablation
After ablation, youll see bruising and feel tender around the catheter insertion point.
Hospital staff monitor you after the procedure to ensure it was successful. Youll need to lie down and keep still in a recovery area for a few hours for observation. Depending on your condition, you can usually go home the same day.
How long it takes to heal after heart ablation varies according to the type of arrhythmia and its treatment. You should rest for a few days and not drive for two days.
After a week, the tenderness around the catheter insertion site should decrease.
In the first few days after the ablation you should avoid heavy lifting and other physical exertion. You can take cool showers but avoid bathing and swimming until the incisions heal.
It usually helps to gradually increase your amount of physical exercise. Brisk walking by the second week is normal.
You may still feel some heart symptoms for a few weeks, such as palpitations.
Within the first two months your doctor will discuss whether the ablation is successful and if you can stop taking any of your medications.
For surgical ablation, you will spend up to about a week in hospital, with the first day or two in an intensive care unit.
The recovery time will also be longer and depends on the exact surgical procedure. It takes several weeks to get back to normal, or in the case of open-heart surgery, up to six months.
In this video, Dr Syed Ahsan explains how long it takes to know if your ablation was successful:
You May Like: What Cause A High Heart Rate
Heart Ablation For Ventricular Tachycardia
VT is a dangerous heart rhythm that can lead to sudden death if not treated. The treatment of VT depends on the underlying cause. There is increasing use of catheter ablation for VT, particularly in those who have not responded to medicines. In a VT ablation, the area of the heart where the dangerous rhythm is starting is identified and then energy applied to that area to prevent it from occurring.
What Happens During Ablation
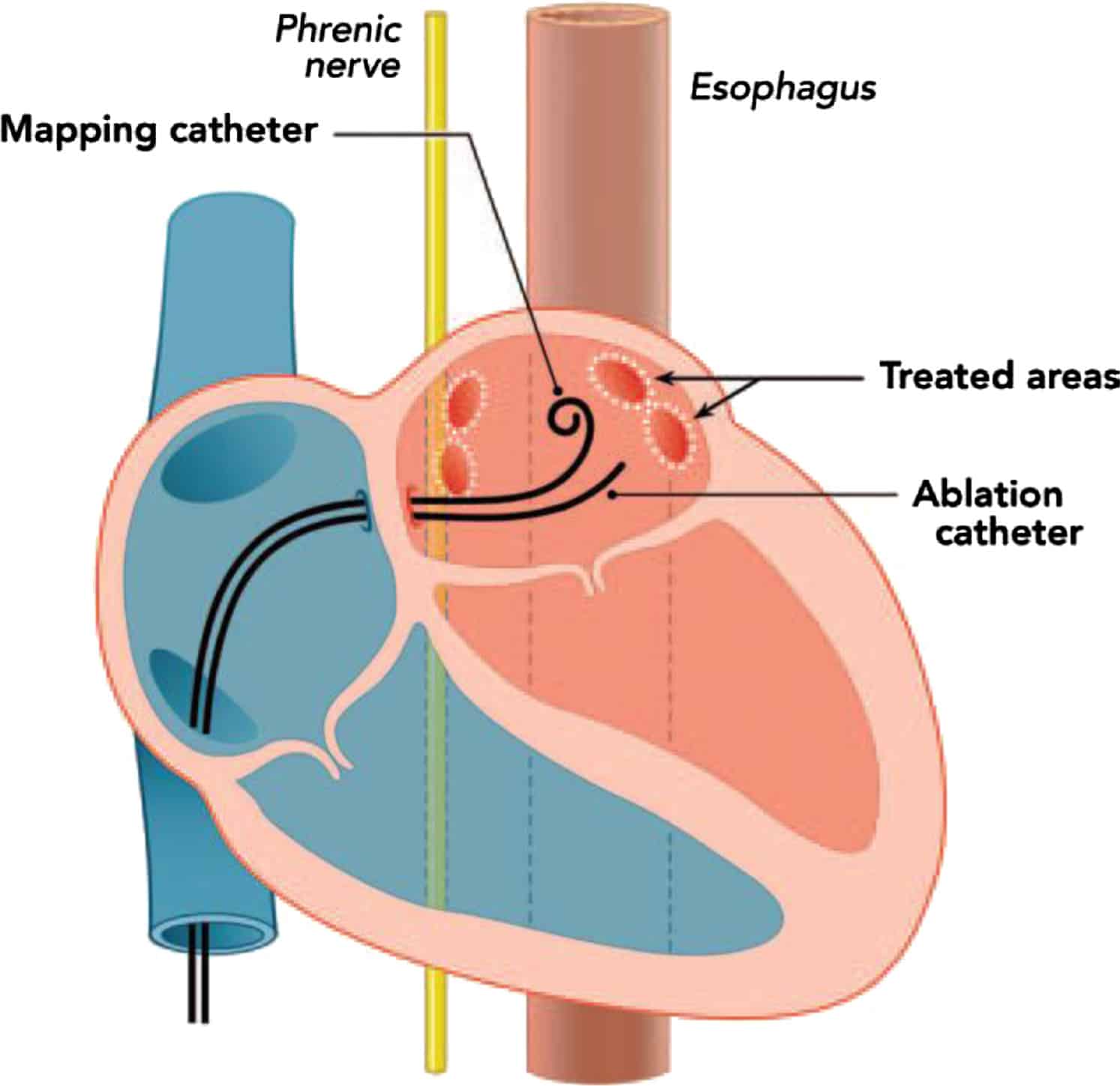
Talk with your doctor about what to expect during your ablation. The procedure usually takes 3 to 6 hours. A cardiologist and a special team of nurses and technicians will do the ablation. During the procedure:
- You may have a local anesthetic applied to your skin where the team will make a small incision .
- Or, you may receive a general anesthetic with a breathing tube inserted to make you sleep through the surgery.
- Your doctor will make several small holes in a vessel here. He or she will put a few tapered tubes called sheaths through this hole.
- Your doctor will put a series of electrode catheters through the sheaths and into your blood vessel. The team will then advance the tubes to the correct place in your heart.
- Next, the doctor will locate the abnormal tissue using special technology. He or she will do this by sending a small electrical impulse through the catheter. Other catheters will record the hearts signals to find the abnormal sites.
- The doctor will place the catheter at the site where the abnormal cells are. He or she will then scar the abnormal area . This might cause slight discomfort.
- The team will remove the tubes. They will close your vessel with firm pressure.
- The team will close and bandage the site where the doctor inserted the tubes.
You May Like: How To Improve Heart Rate Variability
What Happens After Heart Ablation
Catheter ablation generally requires less recovery time than surgical ablation. Depending on which procedure youve had, you can expect the following:
Catheter ablation
Catheter ablation takes two to four hours to complete. After the procedure, your provider removes the catheter and sheath from your vein.
You move to a recovery room and stay there for several hours . A nurse monitors your condition as you recover.
When its time to go home, youll receive detailed instructions about at-home care. Your provider may prescribe aspirin or other blood-thinning medication for several months. These drugs help prevent blood clots while you recover.
Surgical ablation
After surgical ablation, youll move to the ICU. Youll stay in the ICU for several hours up to a few days. The length of stay depends on how invasive your surgery was.
Once you leave the ICU, youll remain in the hospital for a few more days until you recover enough to return home.
While recovering at home, you may continue taking aspirin or other blood-thinning medication. These help prevent blood clots during your several months of healing.
Benefits Of A Catheter Ablation
There are many benefits of having a catheter ablation with the Norton Heart & Vascular Institute team. They include:
- Performed by a board-certified electrophysiologist whose training includes three years additional training beyond board certification in cardiology
- May reduce or even eliminate the symptoms of your heart arrhythmia
- Does not require stitches
- For many patients, long-term reduction in the number of symptomatic episodes and severity of symptoms
- Typically, return to normal life and activities after the procedure
- For many patients, reduced medications following a successful catheter ablation
- No chest incisions or ports
- Short hospital stay or go home the same day
Also Check: How To Get Your Heart Rate
Catheter Ablation Treatment For Heart Arrhythmias
If youve been diagnosed with a heart arrhythmia, you may feel like your heart is skipping a beat or fluttering in your chest. Youre not alone. Millions of Americans are diagnosed with heart arrhythmias. If medications do not help you once you have a diagnosis, your provider may suggest a catheter ablation procedure to treat your heart arrhythmia.
How Do I Prepare For An Ablation
Talk with your doctor about what you should do to prepare for your atrial fibrillation ablation. Avoid eating or drinking anything before midnight of the day of your procedure. Follow your doctors instructions about what medicines to take before the procedure. Dont stop taking any medicine unless your doctor tells you to do so.
Your doctor might order some tests before your procedure. These might include:
- Electrocardiogram , to analyze the heart rhythm
- Echocardiography , to evaluate heart structure and function
- Stress testing, to see how the heart responds to exercise
- Cardiac catheterization or coronary angiography, to get more information about the coronary arteries
- Cardiac CT or MRI, to further evaluate your heart anatomy
Let your doctor know if you are pregnant before having the procedure. Ablation uses radiation, which may be a risk to the fetus. If you are a woman of childbearing age, your doctor may want a pregnancy test to make sure you arent pregnant.
Someone will shave your skin above the area of operation . About an hour before the operation, you will be given medicine to help you relax.
Also Check: How Does Aspirin Help During A Heart Attack
What Happens After I Get Home
Follow the instructions your nurse or doctor gave you. Most people can return to their normal activities on the day after they leave the hospital.
- Dont drive for 24 hours after you leave the hospital.
- Dont drink alcohol for 24 hours after you leave the hospital.
- Avoid heavy physical activity for three days. Ask your doctor when you can return to strenuous exercise.
- A small bruise at the puncture site is normal. If the site starts to bleed, lie flat and press firmly on top of it. Have someone call the doctor or hospital.
When Can I Go Back To Work And Resume Other Activities
If you have catheter ablation, youll likely feel ready to return to work a day or two after your procedure. If your job requires physical labor, you may need a few extra days before returning to work.
After catheter ablation, you should avoid heavy lifting and strenuous exercise for at least three days. Talk with your provider about when its safe to return to physical activity.
After surgical ablation, youll spend about a week in the hospital. Once at home, you may need several more weeks to recover enough to return to work. Recovery will be quicker if youve had a less-invasive surgical procedure instead of an open-heart ablation.
Don’t Miss: Heart Rate For Afib
What Is Catheter Ablation
Catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure in which the doctor advances a flexible thin tube through the blood vessels to your heart to ablate abnormal electrical pathways in the heart tissue.
The following animation demonstrates how the catheter ablation process works.
Catheter Ablation Treatment Animation –
Watch this animation to see the differences between radiofrequency and cryoablation procedures to treat atrial fibrillation.
If you have atrial fibrillation that has not responded to medication, your doctor may recommend catheter ablation.
Types Of Cardiac Ablation

While there are two approaches to performing cardiac ablation , there are different types of heart ablation techniques. Depending on your arrhythmia condition your doctor may recommend radiofrequency or heat, and Cryo or cold, including:
- Supraventricular Tachycardia Ablation: This type of ablation uses hot or cold energy to destroy the tissue causing abnormal heart rhythms.
- Atrial Flutter Ablation: If you have a fluttering heartbeat, this type of ablation may be best for you as it creates scar tissue to stop the arrhythmia.
- Ventricular Tachycardia Ablation: This type of ablation is meant for hearts that are beating rapidly and inconsistently. This ablation will help stop the signals from creating abnormal heartbeats.
Don’t Miss: How To Calm Heart Rate
Heart Ablation For Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is a common heart rhythm problem and can lead to palpitations and associated symptoms, and increases the risk of stroke. In those patients with symptoms, especially in those who have not found anti-arrhythmic medications to be helpful, catheter heart ablation can be useful. The main triggers for atrial fibrillation are felt to arise from the veins known as the pulmonary veins that empty into the heart. Heart ablation is usually performed in those areas to prevent the triggers that start the atrial fibrillation. In carefully selected patients this can be a remarkably effective treatment. In some cases, heart ablation for atrial fibrillation is performed as part of a surgical open-heart procedure, usually when mitral valve surgery is also being performed.
