Types Of Heart Attacks
A heart attack, also known clinically as myocardial infarction, is a form of acute coronary syndrome . It occurs when a significant blockage in the coronary arteries restricts blood flow to the heart.
The main types of heart attacks include:
- Non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction
- ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
Tests For Acute Heart Failure
Your doctor will assess your medical history and perform a physical exam. Theyll listen to your heart and lungs with a stethoscope to detect any congestion or abnormal heart rhythms. Your doctor may also check for fluid buildup in your abdomen, legs, and the veins in your neck.
In addition, your doctor might request tests such as:
- Blood tests. These could include a BNP test, which measures a hormone related to heart failure.
- Electrocardiogram . During this test, your doctor will attach electrodes to your skin and record your hearts electrical activity.
- Stress test. This test measures your heart activity during physical exercise. Its not typically recommended if you already have signs and symptoms of heart failure.
Imaging tests that a doctor can use to help diagnose heart failure include:
- Chest X-ray. This test allows your doctor to better examine your heart and lungs.
- Echocardiogram. This test uses sound waves to form a live, moving image of your heart so your doctor can see which areas of your heart are affected.
- Angiogram. If your doctor thinks you may have a blocked artery, they will insert a thin tube into your groin or arm and into your coronary arteries. After injecting dye through a catheter, your doctor can see an image of your arteries.
When needed, other imaging tests can be used to look for underlying causes of heart failure:
Together, your physical exam and test results can help your doctor learn about the health of your heart.
What Is The Importance Of Ejection Fraction
Your ejection fraction is one way to measure the severity of your condition. If its below normal, it can mean that you have heart failure. Your ejection fraction tells your healthcare provider how good of a job your left or right ventricle is doing at pumping blood. Usually, your EF number is talking about how much blood your left ventricle is pumping out because its your heart’s main pumping chamber.
Several non-invasive tests can measure your EF. With this information, your healthcare provider can decide how to treat you or find out if a treatment is working as it should.
A normal left ventricular ejection fraction is 53% to 70%. An LVEF of 65%, for example, means that 65% of the total amount of blood in your left ventricle is pumped out with each heartbeat. Your EF can go up and down, based on your heart condition and how well your treatment works.
Recommended Reading: What Should My Heart Rate Be While Working Out
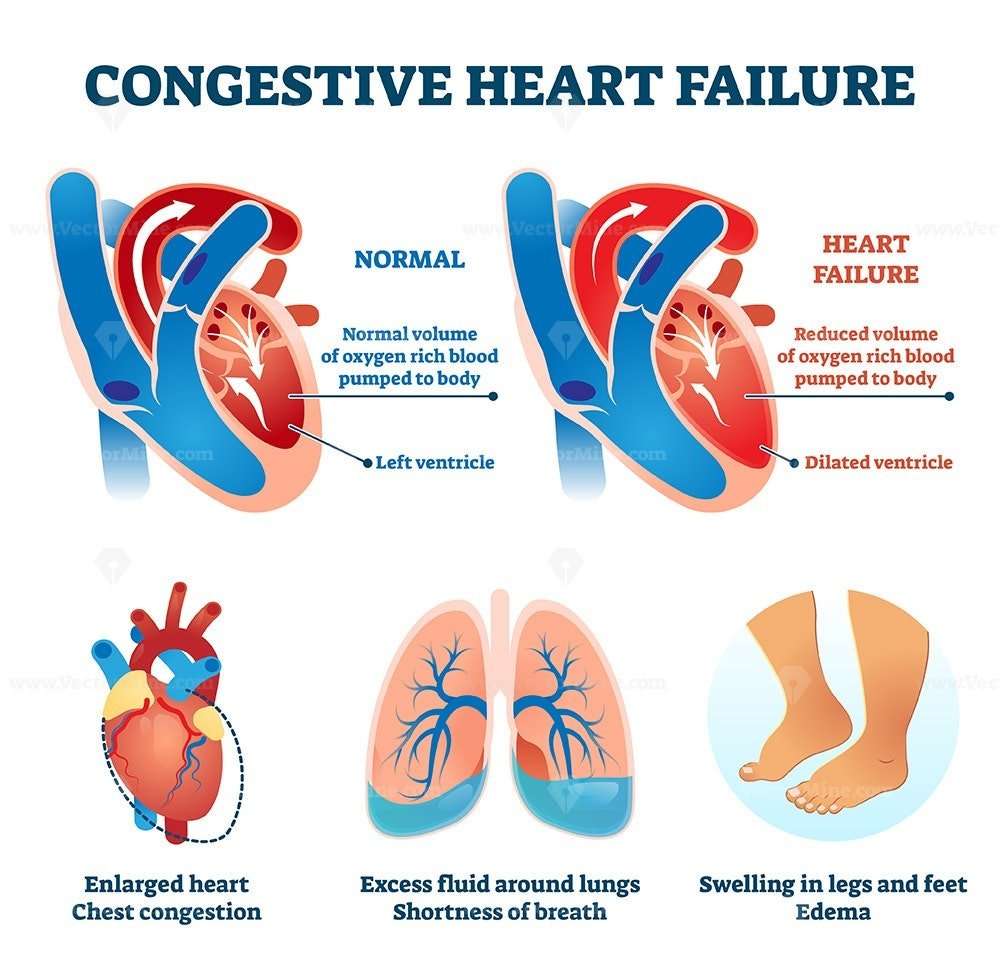
Heart Failure Vs Congestive Heart Failure: What’s The Difference
Heart failure affects people of all ages, from children and young adults to the middle-aged and older adults. About 6.2 million adults in the United States are currently living with heart failure, and over 64 million people are dealing with some form of heart failure worldwide.
Approximately 550,000 new cases are diagnosed in the United States each year, but many more remain undiagnosed as the initial symptoms of heart failure can be subtle and mimic similar symptoms seen in other conditions.
Congestive heart failure refers to the inadequate functioning of the heart muscle such that fluid builds up in the lungs, abdomen, feet, and arms . The condition can either be acute or chronic .
Untreated heart disease can be aggressive and fatal. The five-year survival rate is about 50% for all stages. In 2018, heart failure led to nearly 400,000 deaths, according to death certificate data, with the highest prevalence of disease primarily in the South and Midwest.
How Is Congestive Heart Failure Treated
Doctors will assess the current health status of the patient to establish a baseline, and develop a long-term health plan. This may involve the optimization of medicines and therapies, adding new medication, or possibly enrollment in a clinical trial.
Stabilizing and/or reversing a patients condition often involves long-term, collaborative follow-up with a referring cardiologist or physician.
In serious situations, advanced therapies, which include mechanical solutions, a heart transplant, or hospice, may be offered.
Read Also: Pima Heart Surgery Center
Drugwatchcom Has Been Empowering Patients For More Than A Decade
Drugwatch.com has provided reliable, trusted information about medications, medical devices and general health since 2008. Weve also connected thousands of people injured by drugs and medical devices with top-ranked national law firms to take action against negligent corporations.
Our team includes experienced medical writers, award-winning journalists, researchers and certified medical and legal experts. Drugwatch.com is HONCode certified. This means the high-quality information we provide comes from credible sources, such as peer-reviewed medical journals and expert interviews.
The information on Drugwatch.com has been medically and legally reviewed by more than 30 expert contributors, including doctors, pharmacists, lawyers, patient advocates and other health care professionals. Our writers are members of professional associations, including American Medical Writers Association, American Bar Association, The Alliance of Professional Health Advocates and International Society for Medical Publication Professionals.
Heart Failure Treatment Is A Team Effort
Heart failure management is a team effort, and you are the key player on the team. Your heart doctor will prescribe your medications and manage other medical problems. Other team members — including nurses, dietitians, pharmacists, exercise specialists, and social workers — will help you achieve success. But it is up to YOU to take your medications, make dietary changes, live a healthy lifestyle, keep your follow-up appointments, and be an active member of the team.
If you notice anything unusual, don’t wait until your next appointment to discuss it with your doctor. Call them right away if you have:
- Unexplained weight gain
- Swelling in your ankles, feet, legs, or belly that gets worse
- Shortness of breath that gets worse or happens more often, especially if you wake up feeling that way
- Bloating with a loss of appetite or nausea
- Extreme fatigue or more trouble finishing your daily activities
- A lung infection or a cough that gets worse
- Fast heart rate
- New irregular heartbeat
Also Check: When Do Heart Attacks Occur
Hypertension And Congestive Heart Failure
Editor’s Note: This article was originally written by Charles Whitcomb, M.D.
Congestive heart failure is one of the most common reasons for hospital admission in the United States and most Western European countries. The most common cause is coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction . Hypertension and what is called hypertensive heart disease is next on the list. Patients with congestive heart failure have a markedly increased for death.
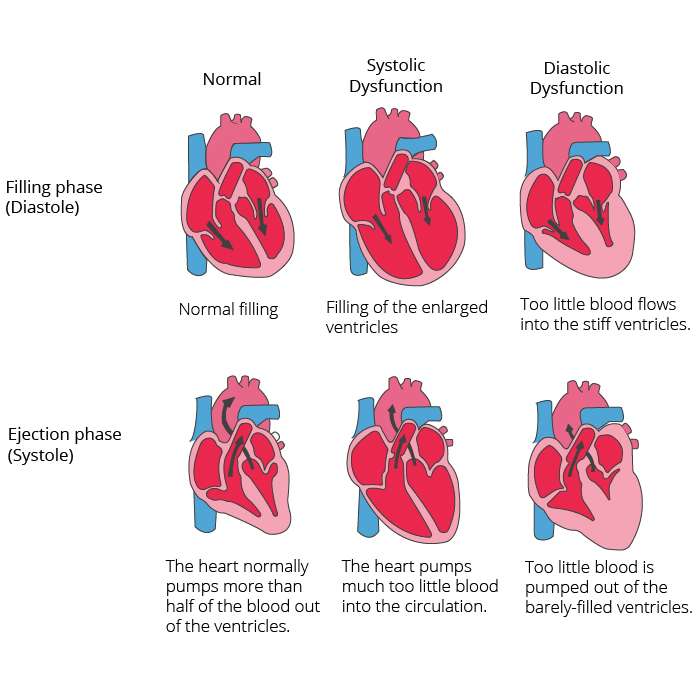
Patients with CHF usually present to the hospital with signs of fluid overload. They become short of breath due to the buildup of excess fluid in the lung. The fluid excess interferes with the transfer of oxygen from air to blood. Classically this has been attributed to abnormal heart muscle function where the heart muscle is weakened and can no longer pump blood efficiently. In the last two decades it has become apparent that many patients do not have weak heart muscle. Rather their heart is stiff and requires higher pressure to fill it between heartbeats.
The period between heartbeats when the heart fills is called diastole, and this form of heart muscle disease is called diastolic heart failure. Much less is known about this form of CHF in spite of the fact that up to half of the heart failure treated in hospital in diastolic CHF. The most common identifiable cause of diastolic heart failure by far is hypertension.
Diagnosis Congestive Heart Failure
The diagnosis of congestive heart failure is predominantly by history and physical, though echocardiography and cardiac catheterization can be beneficial.
Physical examination during systolic congestive HF will reveal a S3 heart sound if significant left ventricular dilation is present. A S4 heart sound can be present in diastolic HF. The point of maximal impulse, or PMI, will be laterally displaced and, at times, the S3 can even be palpable. Cardiac murmurs will be present if valvular heart disease is present, contributing to the HF such as aortic stenosis or mitral regurgitation.
Physical examination in states of right heart failure may reveal elevated jugular venous pressure including hepatojugular reflux, lower extremity pitting edema and ascites. Pleural effusions may be present and more prominent on the right compared to the left.
Echocardiography is indicated in all patients with a new diagnosis of congestive HF to help determine the etiology. The LV systolic function can be measured, including ejection fraction. Diastolic function assessment can help determine the left heart pressures. The cardiac valves can be interrogated for significant regurgitant or stenotic lesions.
Recommended Reading: Is Green Tea Good For Heart Attack Patients
How Can I Improve My Quality Of Life With Heart Failure
There are several things you can do to improve your quality of life if you have heart failure. Among them:
- Eat a healthy diet. Limit your consumption of sodium to less than 1,500 milligrams each day. Eat foods high in fiber. Limit foods high in trans fat, cholesterol, and sugar. Reduce total daily intake of calories to lose weight if necessary.
- Exercise regularly. A regular cardiovascular exercise program, prescribed by your doctor, will help improve your strength and make you feel better. It may also decrease heart failure progression.
- Don’t overdo it. Plan your activities and include rest periods during the day. Certain activities, such as pushing or pulling heavy objects and shoveling may worsen heart failure and its symptoms.
- Prevent respiratory infections. Ask your doctor about flu and pneumonia vaccines.
- Take your medications as prescribed. Do not stop taking them without first contacting your doctor.
- Get emotional or psychological support if needed. Heart failure can be difficult for your whole family. If you have questions, ask your doctor or nurse. If you need emotional support, social workers, psychologists, clergy, and heart failure support groups are a phone call away. Ask your doctor or nurse to point you in the right direction.
How To Prevent Acute Heart Failure
Some risk factors, such as aging, cant be avoided. The key to preventing heart failure is to reduce the risk factors that you can control.
Many of the lifestyle measures recommended for heart failure recovery can also reduce or eliminate conditions that lead to heart failure. These conditions include high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
If youre at risk for heart failure, you should consider these measures to promote heart health:
- maintain a healthy weight, if overweight or obesity is a concern
- get regular physical activity
Also Check: Is Blood Pressure And Heart Rate The Same Thing
Anemia And Iron Deficiency
Anemia is common among patients with chronic heart failure and is frequently multifactorial. Anemia is associated with worse symptoms and outcomes in HF and so reversible causes should be sought and treated. Iron deficiency Iron Deficiency Anemia Iron deficiency is the most common cause of anemia and usually results from blood loss malabsorption, such as with celiac disease, is a much less common cause. Symptoms are usually nonspecific… read more is among the most common causes of anemia in HF, and iron replacement therapy should be considered once treatable causes such as blood loss have been excluded. Oral iron replacement is often less effective due to poor absorption and other reasons, thus intravenous iron replacement is preferred.
When To Get Emergency Help
Heart failure is not the same thing as a heart attack. But, like a heart attack, acute heart failure can be a life threatening event. Someone with acute heart failure will typically need emergency hospital care. If your symptoms are sudden or severe, call 911 or your local emergency services for help.
If not treated, heart failure can lead to serious complications. These complications can include cardiac arrest, which is when your heart stops beating.
Some people with heart failure may have several health conditions. If thats the case, it can be hard to know whats causing your symptoms.
But when it comes to symptoms of heart failure, its best to get them checked by a doctor right away. According to a 2017 study, fast treatment of acute heart failure can lead to better outcomes.
You May Like: Why Use A Heart Rate Monitor
How Can You Prevent Heart Failure
Some lifestyle measures can help treat heart failure and prevent the condition from developing. Maintaining a moderate weight and exercising regularly can significantly decrease your risk of heart failure. Reducing the amount of salt in your diet can also lower your risk.
Other habits that may prevent heart failure include:
- limiting alcohol intake
What Are The Different Types Of Chf
Heart failure can occur on the left side of the heart, the right side, or both. Most commonly, it begins in the heart’s primary pumping chamber – the left ventricle. Each specific type of CHF is accompanied by its own distinct characteristics:
- Right-sided CHF – Right-sided CHF develops when the right ventricle struggles to deliver blood to the lungs. As blood backs up into the blood vessels, the body begins to retain fluid in the abdomen and lower body.
- Left-sided CHF – Left-sided CHF is the most common form of CHF and begins when the left ventricle cannot effectively deliver blood throughout the body. Eventually, this can lead to fluid retention throughout the body, particularly around the lungs.
Cases of left-sided CHF can be further classified into one of two sub-types, characterized by the manner in which the ventricle is affected:
- Systolic CHF – Systolic CHF occurs when the left ventricle is unable to contract with enough force to circulate blood properly.
- Diastolic CHF – Diastolic CHF occurs when the heart muscle becomes stiff. Because the chamber must relax in order to fill with blood between contractions, this stiffness means that an inadequate amount of blood is available to pump out to the rest of the body.
Also Check: Does Heart Rate Increase After Eating
Congestive Heart Failure And Congenital Defects
The purpose of the heart is to pump blood to the body in order to nourish it. Heart failure doesn’t mean that the heart has stopped working, but that it just isn’t able to pump enough blood to meet the needs of the body.
This may occur when the heart muscle is weak or when the heart valves are leaky. When the heart does not circulate blood normally, the kidneys receive less blood and filter less fluid out of the circulation into the urine. The extra fluid in the circulation builds up in the lungs, the liver, around the eyes, and sometimes in the legs. This is called fluid “congestion” and for this reason doctors call this “congestive heart failure”.
Older children with congestive heart failure may be tired and have problems keeping up with their friends on the playground. Infants with congestive heart failure usually have symptoms during feeding including sweating, fast breathing and fatigue. These infants also may have problems gaining weight. Fluid may also build up in the rest of the body, causing swelling of the feet, the legs or around the eyes.
Medicines called diuretics , e.g., furosemide , help get rid of the extra fluid by increasing urination. To help the body rid itself of the extra fluid, a low-sodium diet may sometimes be necessary. Blood vessel relaxing medications, such as captopril or enalapril, may be used to make it easier for the heart to pump. Another medication, digoxin, may help the heart contract with more force.
Last Reviewed: Mar 22, 2022
What Are The Treatments For Heart Failure
Your treatment will depend on the type of heart failure you have and how serious it is. There’s no cure for heart failure. But treatment can help you live longer with fewer symptoms.
Even with treatment, heart failure usually gets worse over time, so you’ll likely need treatment for the rest of your life.
Most treatment plans include:
You may need heart surgery if:
- You have a congenital heart defect or damage to your heart that can be fixed.
- The left side of your heart is getting weaker and putting a device in your chest could help. Devices include:
- A biventricular pacemaker .
- A mechanical heart pump or a total artificial heart).
As part of your treatment, you’ll need to pay close attention to your symptoms, because heart failure can worsen suddenly. Your provider may suggest a cardiac rehabilitation program to help you learn how to manage your condition.
Recommended Reading: What Is Good Heart Rate Recovery
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Treating Congestive Heart Failure Unique
Yale Medicines team comprises heart failure cardiologists and cardiac surgeons, dedicated advanced-practice, registered nurses and nurse coordinators, dietitians, exercise physiologists, financial counselors, immunologists specializing in transplants, psychologists, and specialists in palliative care.
With a multidisciplinary approach, Yale Medicine physicians include the patients desires as well as input from the family to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that’s right for them.
Outlook For Heart Failure
Heart failure is a serious long-term condition that will usually continue to get slowly worse over time.
It can severely limit the activities you’re able to do and is often eventually fatal.
But it’s very difficult to tell how the condition will progress on an individual basis.
It’s very unpredictable. Lots of people remain stable for many years, while in some cases it may get worse quickly.
Don’t Miss: How To Calculate Your Maximum Heart Rate
Facts About Heart Failure In The United States
- About 6.2 million adults in the United States have heart failure.1
- In 2018, heart failure was mentioned on 379,800 death certificates .1
- Heart failure costs the nation an estimated $30.7 billion in 2012.2 This total includes the cost of health care services, medicines to treat heart failure, and missed days of work.
