What Happens After A Tilt
You may feel tired and a little sick to your stomach right after the test. You may stay in a recovery area for 30 to 60 minutes so nurses can keep track of your blood pressure and heart rate. After recovery, most people can drive home and return to their normal activities. However, if you lose consciousness during the test, you may need to have more observation and testing. Dont drive home if you have fainted.
Tips For Heart Attack Prevention
The goal after your heart attack is to keep your heart healthy and lower your risk of having another heart attack. Take your medications as directed, make healthy lifestyle changes, see your doctor for regular heart checkups, and consider a cardiac rehabilitation program.
Why do I need to take drugs after a heart attack?
You might take certain drugs after a heart attack to:
- Prevent blood clots
What Do You Do If You Have A Heart Attack
If you have any of the listed symptoms:
- tell someone and ask them to get help right away
The faster you get help, the better your chances of surviving a heart attack. Half of heart attack deaths happen within 2 hours of the first signs.
On average, Canadians wait almost 5 hours before getting medical help. Many people find it hard to believe that they are having a heart attack. They convince themselves that the symptoms are something else and that they will go away.
Not getting help for your symptoms could lead to death. New therapies and drugs can reduce damage and save your life if treatment begins soon enough. Your health care provider will work with you to determine treatment and recovery needs.
If you have suffered a heart attack, having important health information close by can help medical staff treat you. Carry personal health information with you at all times and have it posted by your phone. You may not be able to tell medical staff this information yourself, depending on your condition.
Your list should include:
- telephone and health care number
- medical history
- current medications
- health care provider
- health insurance number for expenses that are not covered under provincial health insurance plans, such as:
- ambulance services
Recommended Reading: What Are The Early Signs Of Congestive Heart Failure
Why Even Mild Heart Attacks Should Be Taken Seriously
Even if your heart comes through unscathed, a heart attack should be viewed as a wake-up call. You are at increased risk for another heart attack or a stroke. Its time to get serious, Dr. Campbell says.
Your physician will make a plan for preventing another heart attack. But its you who must carry it out.
It is extremely important to understand that how you live your life and manage your risk factors going forward will impact what happens to you next, he says. We urge you to recognize a mild heart attack as an important event and use it to make changes that positively impact your health.
This article first appeared in Cleveland Clinic Heart Advisor.
Silent Heart Attack Treatment
Normally, silent heart attacks are found long after the heart attack is over. Treatment will mostly involve taking medicines. These medicines help improve blood flow to your heart, prevent clotting, and reduce the risks of having another heart attack. They include:
- aspirin
- ACE inhibitors
- fish oil
Your doctor will prescribe the medicines that are right for you. If you have had a heart attack, your doctor will also talk to you about lifestyle changes. You can make these changes to prevent more heart problems.
Don’t Miss: How Does Atropine Increase Heart Rate
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- I feel discomfort in my chest. Could I be having a silent heart attack?
- How much risk do I have for having a silent heart attack?
- How serious was my heart attack?
- What happens now?
- Will I have to take medicine for the rest of my life?
- What is my risk of having another heart attack? Will it be more harmful than the first one?
- What lifestyle changes can I make to prevent another heart attack?
What Is A Cardiac Risk Assessment
This is a group of tests and health factors that have been proven to indicate your chance of having a cardiovascular event such as a heart attack or stroke. They have been refined to indicate the degree of risk: borderline, intermediate, or high risk.
Perhaps the most important indicators for cardiac risk are your personal health history. These include:
- Age
- Diabetes
- Pre-existing heart disease, or already having had a heart attack
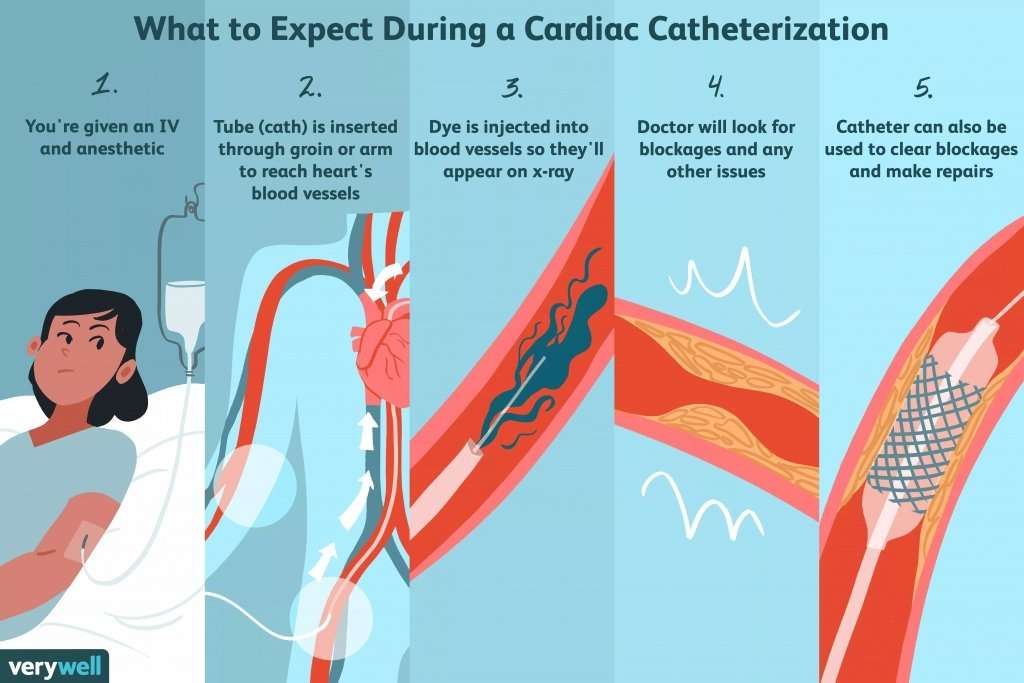
There are some imaging tests that may be used in cardiac risk assessment. Non-invasive tests may include, for example, an electrocardiogram or a stress test, also called ECG stress test or metabolic stress test. Invasive tests may also be used to evaluate for the presence of cardiovascular disease , but they are usually used for diagnostic purposes in people with signs and symptoms and not for risk assessment. Examples include an angiography/arteriography and cardiac catheterization.
The lipid panel is the most important blood test for cardiac risk assessment.
You May Like: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
Advanced Lipid Profile And Lipoprotein Test
How They Work: Unlike the traditional cholesterol blood test, which measures total cholesterol, HDL, LDL, and triglycerides, the advanced test also looks at particle size. This is important because some particles are big and fluffy, so they tend to bounce off artery walls as they travel through the body. Others are small and dense, meaning they can penetrate the artery lining and form clumps of plaque. The Lp blood test analyzes a specific type of cholesterol that can triple heart risk.
Cost: $19 each
Duration: 5 minutes
Why They’re Heart Smart: Sizing up your particles gives a clearer picture of heart risk than the conventional test: Having a lot of large particles cuts risk, while small ones raise it. The more Lp you have, the worse it is tooit makes LDL particles extra sticky, so they cling to the lining of blood vessels, causing plaque and clots.
Get Them If: You have a family history of heart disease.
What the Results Mean: “You do not want more than 15% of your particles to be the small, dense type,” says Dr. Agatston. For Lp, levels above 30 mg/dl put you at increased risk.
Next Steps: If you have small particles, your doctor may prescribe a drug to increase their size, most likely a fenofibrate or niacin , along with a healthy diet and exercise. Niacin is also among the best treatments for high Lp.
How Are The Procedures Performed
Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring The technologist will position you on the CT examination table lying flat on your back. Straps and pillows may be used to help you maintain the correct position and to help you remain still during the exam. You will be asked to raise your arms over your head. Electrodes will be attached to your chest and to an electrocardiography machine that records the electrical activity of the heart. You will then be instructed on how and when to hold your breath. The examination table will move multiple times as the CT scanner obtains the images.
Coronary CT angiography A nurse will insert an intravenous line into a vein in your arm. You may be given a medication, either by mouth or through the IV, to help slow your heart rate. You may also receive nitroglycerin to enlarge your coronary arteries . You will be positioned on an examination table and electrodes will be attached to your chest and to an electrocardiography machine that records the electrical activity of the heart. You will be asked to raise your arms over your head for the duration of the exam. You will then be instructed on how and when to hold your breath. The examination table will move multiple times as the CT scanner obtains the images. During the exam, contrast material will be given through your IV.
Also Check: What Are The Early Signs Of Congestive Heart Failure
How Are Silent Heart Attacks Diagnosed
Many times, silent heart attacks are found during a routine check-up. If your doctor thinks you may have had one, he or she may order imaging tests. These could include an electrocardiogram , which is a special ultrasound, or a CT scan or MRI of your heart.
These tests can show if your heart muscle has been damaged, signaling that youve had a heart attack. If youve gone to the emergency room with silent heart attack symptoms, the doctor may order blood tests.
How Do Doctors Know What Kind Of Heart Attack Youve Had
You cant predict the outcome of a heart attack by your symptoms or how severe they are. Thats why symptoms that suggest a possible heart attack should never be ignored.
How well you fare after a heart attack depends on how quickly you act, Dr. Campbell says. The sooner you get emergency care, the better the chance you will suffer less permanent damage to your heart.
If you go to the ER with heart-attack symptom, youll be treated right away. Your blood will be examined for any enzymes indicating theres been damage to your hearts muscle. And a noninvasive echocardiogram is performed to see how well your heart is pumping.
Still it may take several hours to determine whether youve had a heart attack and what kind of treatment is needed. That means, if youre not sure what your symptoms mean, the thought of spending several hours in the ER might discourage you from seeking care. Dont let it! Dr. Campbell advises that its much wiser to err on the safe side.
Its better you spend several hours in the ER than learn the damage has been done, and your heart cant be fixed, he says.
You May Like: Does Tylenol Lower Blood Pressure
What A Mild Heart Attack Means
A mild heart attack is a common way of referring to what physicians call a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction, or NSTEMI. .
In this type of heart attack, blood flow through one of the coronary arteries was partially blocked, limiting the supply of oxygenated blood to the heart muscle.
If you were told youve had a mild heart attack, it probably means your heart didnt suffer much damage and still pumps normally, Dr. Campbell says.
What Other Tests May Be Used To Assess Cardiac Risk
Some other tests that may be used to assess cardiac risk include:
- High-sensitivity C-reactive protein : Studies have shown that measuring CRP with a high sensitivity test can help identify risk of CVD. This test is different from the regular CRP test, which detects elevated levels of CRP in people with infections and inflammatory diseases. The hs-CRP test measures CRP that is in the normal range for healthy people. It can be used to distinguish people with low normal levels from people with high normal levels. High normal levels of hs-CRP in otherwise healthy individuals have been found to be predictive of the future risk of heart attack, stroke, sudden cardiac death, and peripheral arterial disease, even when lipid levels are within acceptable ranges. Several groups have recommended that this test be used for people with moderate risk of heart attack over the next 10 years. However, there is not a consensus on how the test should be used otherwise, nor on how frequently the test should be repeated.
- Lipoprotein A ): Lp is a lipoprotein consisting of an LDL molecule with another protein ) attached to it. Lp is similar to LDL-C but does not respond to typical strategies to lower LDL-C such as diet, exercise, or most lipid-lowering drugs. Since the level of Lp appears to be genetically determined and not easily altered, the presence of a high level of Lp may be used to identify individuals who might benefit from more aggressive treatment of other risk factors.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does End Stage Heart Failure Last
What Does The Test Show
When your heart muscle has been damaged, which can happen during a heart attack, your body releases substances into your blood. Blood tests can measure the levels of these substances and show if, and how much of, your heart has been damaged.
The most common blood test after a heart attack will check levels of a protein called troponin in your blood.Blood tests are also done to measure the level of other substances in your blood, such as blood fats and minerals.
The blood test can also show how your bodys organs are functioning, such as your kidneys, liver or hormone-producing glands. This information helps to guide treatment and diagnosis.
When Do I Do If Someone Else Has A Heart Attack
An easy-to-use device called an AED is available in many public places and can be used by almost anyone to treat cardiac arrest. This device works by shocking the heart back into a normal rhythm.
Hereâs how to use an AED:
1. Check responsiveness
- For an adult or older child, shout and shake the person to confirm whether theyâre unconscious. Do not use AED on a conscious person.
- For an infant or young child, pinch their skin. Never shake a young child.
- Check breathing and pulse. If absent or uneven, prepare to use the AED as soon as possible.
2. Prepare to use AED
- Make sure the person is in a dry area and away from puddles or water.
- Check for body piercings or outline of an implanted medical device, such as a pacemaker or implantable defibrillator.
- AED pads must be placed at least 1 inch away from piercings or implanted devices.
3. Use AED
For newborns, infants, and children up to age 8, use a pediatric AED, if possible. If not, use an adult AED.
- Turn on the AED.
- Plug in connector, if necessary.
- Make sure no one is touching the person.
- Push the âAnalyzeâ button.
- If a shock is advised, check again to make sure no one is touching the person.
- Push the âShockâ button.
- Start or resume continue compressions.
- Follow AED prompts.
4. Continue CPR
Read Also: Dangers Of Exceeding Maximum Heart Rate
How Is The Test Done
Blood tests follow this procedure:
- Your arm is first cleaned with an antiseptic
- A tourniquet or a blood pressure cuff is placed around the top part of your arm. This causes the veins in your lower arm to fill with blood.
- A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in a vial or syringe.
Once your blood is taken, the needle is removed, gentle pressure is put on the area to stop any bleeding, and then a small covering is applied. The whole procedure usually only takes a few minutes.
The Blood Test That Confirms A Heart Attack
In the Enhanced Cardiac Access Suite at Capital Cardiology Associates is a sign that reads, When its your heart it just cant wait.
Many heart attacks surface a month in advance, the symptoms go undetected until the individual experiences common indicators like chest pain or pressure. Our ECA Suite is located on the 4th floor of our Corporate Woods office and is the only Capital Region walk-in cardiac clinic. It was specifically designed to serve patients and non-patients who need attention for chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, or rapid heart rate.
You May Like: Esophagus Palpitations
Risk Factors You Can’t Control
Risk factors that you can’t control include:
- Age. The risk of heart disease increases for men after age 45 and for women after age 55 .
- Family history of early heart disease. Your risk increases if your father or a brother was diagnosed with heart disease before 55 years of age, or if your mother or a sister was diagnosed with heart disease before 65 years of age.
- Preeclampsia . This condition can develop during pregnancy. The two main signs of preeclampsia are a rise in blood pressure and excess protein in the urine. Preeclampsia is linked to an increased lifetime risk of heart disease, including CHD, heart attack, heart failure, and high blood pressure.
- Infections. Watch our video on how SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, may affect the heart. Additionally, we offer information and resources on how we are working hard to support necessary COVID-19 research.
Key Tests After A Heart Attack
Tests May Predict Death, Cardiac Arrest in Heart Attack Survivors
Dec. 3, 2007 — Canadian scientists today reported that two tests may help predict heart-related death or cardiac arrest after a heart attack.
The tests don’t require surgery or other invasive methods. Instead, the patient simply gets a special EKG .
One test checks the heart’s nervous system. The other test checks the heart’s electrical system.
Combining the results of both tests, given 10-14 weeks after a heart attack, was the study’s best predictor of heart-related death or cardiac arrest requiring resuscitation.
The study included 322 Canadian heart attack survivors who were in their early 60s, on average. Their hearts showed a weakened ability to pump blood.
The patients took both tests twice. They were first tested two to four weeks after their heart attack. They were retested 10 to 14 weeks after their heart attack.
One of the EKG tests took about half an hour. The other test took all day, but patients didn’t have to spend that time in the doctor’s office the EKG kept tabs on them for 18-24 hours.
The patients were followed for nearly four years. During that time, 30 patients died . Seven others had to be resuscitated when their hearts stopped .
Those patients tended to have poor scores on both tests 10-14 weeks after their heart attack.
Show Sources
SOURCES: Exner, D. Journal of the American College of Cardiology,Dec. 11, 2007 vol 2275-2284. News release, JAMA/Archives.
Also Check: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
How Can I Learn More About Tilt
Talk with your doctor. Here are some good questions to ask:
- Why are you using this test instead of a different test?
- Will I feel any effects of the test after it is over?
- What will it feel like when I get medicine during the second part of the test?
- What does it mean if I have a negative test?
- What does it mean if I have a positive test?
- What do you think is causing me to feel lightheaded or faint?
- What can I do to prevent fainting spells?
Written by American Heart Association editorial staff and reviewed by science and medicine advisers. See our editorial policies and staff.
Last Reviewed: Jul 31, 2015
