What Is Congestive Heart Failure In Dogs
Congestive heart failure refers to the inability of the heart to pump blood adequately throughout the body. As a result, blood backs up into the lungs and fluid accumulates in the body cavities further constricting both the heart and lungs, and preventing sufficient oxygen flow throughout the body. In dogs, there are two main types of CHF:
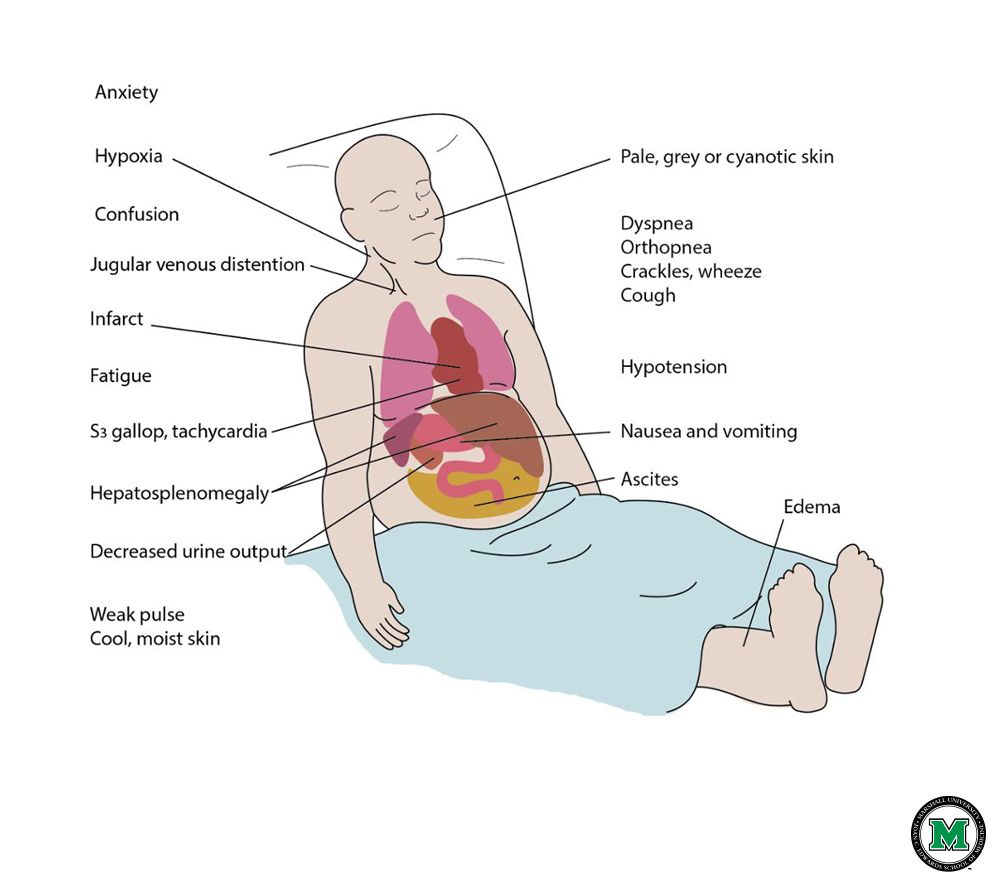
- Right-sided congestive heart failure . This occurs when a heart contraction causes some blood to leak into the right atrium from the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve rather than being pushed through the lungs and becoming oxygenated. As a result, the main circulation system becomes congested with backed up blood, and fluid accumulates in the abdomen, interfering with proper organ function. Excess fluid might also build up in the limbs and cause swelling known as peripheral edema.
- Left-sided congestive heart failure . The most common type of CHF in dogs, this occurs when blood from the left ventricle leaks back into the left atrium through the mitral valve rather than getting pumped into the bodys systemic circulation when the heart contracts. It is a state of diminished cardiac function as a result causes volume or pressure overload to the left side of the heart. As a result, fluid leaks into the tissue of the lungs, causing swelling known as pulmonary edema, which leads to coughing and difficulty breathing.
How It Affects Quality Of Life
You can have hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and live a normal, active life. It depends on the severity of your disease and symptoms. You may need to make lifestyle changes if they aggravate your symptoms. And you may be told to avoid competitive, contact sports.
As the disease progresses it can lead to other health problems includingatrial fibrillation, which can result in blood clots, stroke, and other heart-related complications.
The life expectancy of someone with the disease is actually very good with proper treatment, its normal, says Dr. Kaibas.
It’s Easy To Get The Care You Need
See a Premier Physician Network provider near you.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a genetic condition that causes the walls of your hearts left ventricle to contract harder and become thicker than normal. Once the walls are thicker and stiff, it reduces the amount of blood taken in and pumped out with every heartbeat. There are varying degrees of the disorder, and not everyones heart is affected in the same area, explains Aaron Kaibas, DO, a specialist in cardiovascular diseases.
The disease is inherited , and is most often diagnosed in middle age.
You May Like: How Much Aspirin Do You Take For A Heart Attack
Inherited Heart Disease Treatment
If youre diagnosed with an inherited heart disease, well help you and your family understand all the treatments available. And if you need a surgical procedure, our specialists are experts in minimally invasive techniques to help you get back on your feet as quickly as possible.
To manage an inherited heart disease, we may recommend one or more treatments. Your care plan will depend on your condition, but may include:
- Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss or exercise to help prevent or minimize the effects of heart disease
- Healthy living, like avoiding smoking, alcohol, caffeine and high-fat foods to improve your health
- Medication to help regulate the way your heart works or minimize the chance of blood clots
- Cardiovascular surgery to repair or replace damaged valves, vessels or other parts of your heart.
Women are just as likely as men to develop heart failure, but there are some differences:
- Women tend to develop heart failure later in life compared with men.
- Women tend to have heart failure caused by high blood pressure and have a normal EF .
- Women may have more shortness of breath than men do. There are no differences in treatment for men and women with heart failure.
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Treating Congestive Heart Failure Unique
Yale Medicines multidisciplinary team comprises heart failure cardiologists and cardiac surgeons, dedicated advanced-practice, registered nurses and nurse coordinators, dietitians, exercise physiologists, financial counselors, immunologists specializing in transplants, psychologists, and specialists in palliative care.
With a multidisciplinary approach, Yale Medicine physicians include the patients desires as well as input from the family to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that’s right for them.
Also Check: What Does Jaw Pain Heart Attack Feel Like
Causes Of Heart Failure And Congestive Heart Failure
Heart failure and CHF are typically caused by other conditions that damage the heart. Some of these conditions are:
When the heart is weakened, it has difficulty pumping blood forward, so blood and fluid back up into the lungs. Fluid in the lungs can cause shortness of breath, a common symptom of congestive heart failure.
If the heart is having serious difficulty with pumping, then you might experience edemaa buildup of blood fluid in the feet, ankles, and legs.
What Is The Outlook With Heart Failure
With the right care, congestive heart failure wont stop you from doing the things you enjoy. Your prognosis, or outlook for the future, will depend on:
- How well your heart muscle is working.
- Your symptoms.
- How well you respond to your treatment plan.
- How well you follow your treatment plan.
One study says that people with heart failure have a life span 10 years shorter than those who dont have heart failure. Another study showed that the survival rates of people with chronic heart failure were 80% to 90% for one year, but that dropped to 50% to 60% for year five and down to 30% for 10 years.
A different study found that people who had heart failure and were discharged from the hospital had expected life spans ranging from three to 20 years, depending on various factors like age and gender. Its important to look at your specific situation when considering your prognosis.
Read Also: How Soon Can I Fly After Heart Bypass Surgery
Can Congestive Heart Failure Be Prevented
Unfortunately, when cats are diagnosed with congestive heart failure many will succumb to their heart disease within one year of the initial diagnosis. However, if heart disease can be identified BEFORE congestive heart failure develops, your cat has the potential remain your faithful companion for several years if their heart disease responds well to treatment. As the only person who sees your cat daily, your close attention is paramount. Closely monitor your cats weight, as both an increase or a drop in weight can be related to heart disease in cats. Ensure that your cat receives a well-balanced diet, as nutrition plays a large part in feline heart disease as well. There are therapeutic cat foods available for cats with heart disease to slow the diseases progression.
Annual exams and routine blood work are also recommended, as this allows your vet to watch for trends of creeping blood values before they are outside the normal ranges. If you have an at-risk purebred cat or a cat who you know has a history or heart disease in their family, an annual heart ultrasound to screen for early signs of heart disease should also be discussed with your veterinarian. There are also genetic tests for HCM available and your veterinarian can discuss whether or not these may be appropriate for your pet.
Understanding The Types Of Genetic Heart Disease
There are many kinds of inherited heart diseases that can run in families. The most common include:
- Bicuspid aortic valve disease, when your heart valve has only two flaps instead of three, causing it to leak or narrow
- Cardiomyopathy, in which your heart muscle becomes enlarged, thick or stiff. This includes hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, which can cause cardiac arrest in younger people, especially young athletes.
- , which damages the connective tissues in your heart and blood vessels, making you more prone to aneurysms
Also Check: What Branch Of Medicine Deals With Heart Disease
Also Check: How Do You Lower Your Heart Rate
What Are The Complications Of Heart Failure
Some of the complications from heart failure include:
- Irregular heartbeat.
- History of taking drugs that can damage your heart muscle, such as some cancer drugs.
Stage B
Stage B is considered pre-heart failure. It means your healthcare provider has given you a diagnosis of systolic left ventricular dysfunction but youve never had symptoms of heart failure. Most people with Stage B heart failure have an echocardiogram that shows an ejection fraction of 40% or less. This category includes people who have heart failure and reduced EF due to any cause.
Stage C
People with Stage C heart failure have a heart failure diagnosis and currently have or previously had signs and symptoms of the condition.
There are many possible symptoms of heart failure. The most common are:
- Shortness of breath.
- Need to urinate while resting at night.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats .
- A dry, hacking cough.
- A full or hard stomach, loss of appetite or upset stomach .
There may be times that your symptoms are mild or you may not have any symptoms at all. This doesn’t mean you no longer have heart failure. Symptoms of heart failure can range from mild to severe and may come and go.
Unfortunately, heart failure usually gets worse over time. As it worsens, you may have more or different signs or symptoms.Its important to let your doctor know if you have new symptoms or if your symptoms get worse.
Congestive Heart Failure Procedures And Interventions
Other treatment or procedures may be offered, depending on the underlying cause of the heart failure.
Angioplasty: This is an alternative to coronary bypass surgery for some people whose heart failure is caused by coronary artery disease and may be compounded by heart damage or a previous heart attack. Angioplasty is performed to treat narrowing or blockage of a coronary artery that supplies the left ventricle with blood. The narrowing or blockage is caused by cholesterol deposits.
- Angioplasty begins with the cardiac catheterization procedure during which a long, thin tube called a catheter is inserted through the skin, into a blood vessel, and threaded into the affected artery. This procedure is performed while the person is under local anesthesia.
- At the point of the atherosclerotic narrowing or blockage, a tiny balloon and/or an expandable metal stent, attached to the end of the catheter, is inflated and/or deployed.
- The expanded stent pushes aside the cholesterol deposits that are blocking the artery so that blood can flow through in a more normal manner.
Pacemaker: This device controls the rate of the heartbeat. A pacemaker may keep the heart from going too slow, increasing heart rate when the heart is not increasing enough with activity. It also helps sustain regular rates when the heart is not beating in a coordinated way. Or, the pacemaker performs some combination of these.
Recommended Reading: How Does Aspirin Help During A Heart Attack
What Is The Importance Of Ejection Fraction
Your ejection fraction is one way to measure the severity of your condition. If its below normal, it can mean that you have heart failure. Your ejection fraction tells your healthcare provider how good of a job your left or right ventricle is doing at pumping blood. Usually, your EF number is talking about how much blood your left ventricle is pumping out because its your heart’s main pumping chamber.
Several non-invasive tests can measure your EF. With this information, your healthcare provider can decide how to treat you or find out if a treatment is working as it should.
A normal left ventricular ejection fraction is 53% to 70%. An LVEF of 65%, for example, means that 65% of the total amount of blood in your left ventricle is pumped out with each heartbeat. Your EF can go up and down, based on your heart condition and how well your treatment works.
Causes Of Heart Failure
The heart is a double pump made up of four chambers. Deoxygenated blood from the veins enters the right upper chamber , is passed to the right lower chamber , and then pumped to the lungs.
Oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the left upper chamber and then enters the left lower chamber . The blood is then pumped around the body, under pressure, via arteries.
In a person with heart failure, one or both ventricles dont empty properly. This leads to increased pressure in the atria and the nearby veins. This backlog of blood can affect the kidneys and lungs interfering with their function and leading to a build-up of fluid in the lungs, abdominal organs and legs.
In some people with heart failure, rather than failed pumping of the blood from the ventricle, there is failed relaxation of the ventricle.
If the heart is not pumping and becomes stiff and unable to relax, it can cause the blood to pool in the hearts ventricles. This can cause pressure build up and can put strain on the heart.
Heart failure can be caused by several conditions, including:
Recommended Reading: Diets For Congestive Heart Failure
What Is Heart Failure
Heart failure, or congestive heart failure, is a long-term condition that gets worse over time. Although the name sounds like your heart has stopped working, heart failure means your heart isnt able to pump blood as well as it should. When your heart has less pumping power, that can damage your organs and fluid can collect in your lungs.
Is Congestive Heart Failure Genetic
While congestive heart failure itself doesnt appear to be genetic, the chances of developing risk factors such as high cholesterol and hypertension tend to run in families. There are also a number of other heart diseases related to congestive heart failure that have a genetic component. Three of the most commonly inherited heart diseases are familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, familial dilated cardiomyopathy, and familial hypercholesterolemia.
All of these diseases may lead to heart failure. Other factors that contribute to the risk of developing heart failure are hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, and coronary artery disease.
Is congestive heart failure hereditary? Most of the cases documented are not, but some inherited heart conditions are considered a risk factor and can run in families.
Did you know you can test for heart health at home? Learn more about home heart health tests and home cholesterol tests on our blog.
Also Check: How To Slow Your Heart Rate When Nervous
Is Congestive Heart Failure Hereditary
Congestive heart failure can be passed on from generation to generation. Several hereditary factors put people at higher risk if their family members have congestive heart failure, such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy, and complications from diabetes. A number of conditions can also lead to congestive heart failure, including diseases that directly affect the heart like rheumatic fever and infections such as endocarditis or myocarditis.
What Is Genetic Testing
Genetic testing involves looking for the fault in the genes known to cause familial DCM. It is a long and difficult task that has been likened to looking for a single spelling mistake in an encyclopaedia set. This is because most families have their own unique gene fault that may exist in one of the genes we have already identified, or even in a gene not yet discovered to be involved in this condition. To date over 30 genes have been found to cause DCM, however these genes account for a small proportion of disease. Genetic testing in DCM is expensive and at the moment there is only a small chance of finding the gene fault causing disease. Genetic testing for familial DCM is therefore not routinely offered at present, however this may change in the near future as the technology for carrying out the tests improves. In some cases, particularly in families where there is also a history of conduction disease, then genetic testing is expected to be more informative.
Will a diagnosis of familial dilated cardiomyopathy change my lifestyle?
There are certain Dos and Donts that we advise people about when they are diagnosed with this condition. These guidelines help to reduce the risk of the most devastating outcome sudden cardiac death.
Recommended Reading: How To Tell Heart Attack
Measurements Of Cardiac Function Cardiac Morphology Biomarker For Hf And Genetic Factors
The genetic analysis of all-cause HF was very challenging. On the other hand, genetic analysis using individual cardiac parameters as an outcome variable not only gives more statistical power , but also provides various suggestions regarding cardiac function. Newly, Aung et al. in 2019, Pirruccello et al. in 2020 performed GWAS using parameters obtained from cardiac MRI, which are closely related to cardiac function. They identified 57 new susceptibility loci, 45 of which were novel and had not been reported in previous genomic analyses. In addition, familial cardiomyopathy genes such as BAG3, FLNC, TTN, GATA4, MYH6, MYH7, NKX2-5, PLN, RBM20, and RYR2 were found to be significantly enriched in the susceptibility loci, suggesting an association between genetic factors that define cardiac function in healthy individuals and cardiomyopathy-related genes. They also showed that polygenic risk scores derived from the cardiac MRI GWAS were significantly correlated with HF and DCM was the most correlated). They also showed that these genetic loci also influence cardiac function in patients with cardiomyopathy with low penetrance. Collectively, they demonstrated the association of myocardial measurements with cardiomyopathy genes.
Genes And Familial Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Our body is made up of millions of cells, including brain cells, liver cells and heart cells. Each cell contains 46 chromosomes chromosomes contain genetic information that guides our bodys growth and development. These 46 chromosomes are grouped into 23 pairs, one of each pair coming from mum and the other from dad. One of these pairs is known as the sex chromosomes, and these decide whether we are male or female.
If you imagine a chromosome as being like a ball of wool, you could stretch it out into one long strand, which is known as the DNA. Along the length of DNA there are regions called genes. As there are two copies of every chromosome, there are also two copies of every gene . Genes act as recipes to make certain things in the body, and each recipe is unique based on the order of units it is made up of. If there is a mistake in one of these genes it may lead to the development of disease. This mistake is known as a gene fault.
In the case of familial DCM, we know a single fault in any one of 30 genes can cause the disease.
Recommended Reading: What Should Your Heart Rate Be
