Treatment Options For Heart Failure
Once your vet has diagnosed your dog with congestive heart failure with a physical exam and diagnostic imaging, there will be a few treatment options that can offer your dog more time.
These management options will only be a band aid for your dogs heart disease, but can offer them much needed comfort as the condition progresses.
Some of the most common treatment options for dogs with CHF include:
B: Delivery Of Health Care
B1: Perceptions regarding care
B1.a: Appropriateness of care
The interviewed patients assessment of the quality of medical and nursing care varied depending on whether they thought the treatment was appropriate, necessary and met their needs. If decisions about medical treatment, prescriptions and home visits made by the professionals do not meet a patients expectations, they may be perceived as inadequate or wrong. Treatment of pain was particularly highlighted: The fact that patients often perceive pain as an expression of complete suffering not attributable to any particular cause leads to a type of indifference that makes any medical help inconceivable. The following quotation clearly illustrates this perception of ubiquitous suffering, which the patient repeatedly mentioned in every interview.
Patient HD12, T2 : I only want to feel better. But it seems its not to be, nothing good. Being ill, theres nothing wanted, nothing needed, its always the same. I dont need anything, I can be quite alone. Pain everywhere
Patient HD06, T1 : So you know, if a patient is really ill, yes, its good when you have someone who looks after you. I mean, I do not want too much care, it would be too much responsibility for me, you know. But if youre not feeling well, its good to have someone.
B1.b: Continuity of care
B2: Interpersonal relationships
B2.a: Interaction in the processes of care
B2.b: Specific aspects in physician-patient interaction
B3: Meaning of family
What Determines Life Expectancy
Some things that affect your life expectancy with heart failure are out of your control, such as your age. Others, such as a healthy lifestyle, are not.
Things that may affect life expectancy include:
Ejection fraction. To get a better picture of your heart health, your doctor will check how well an area of your heart called the left ventricle pumps out blood. An echocardiogram is one test thatâs often used. It scans the heart and takes measurements to find out what percentage of your blood is being pumped out with each heartbeat. For instance, an ejection fraction of 55% means that 55% of your blood is being pushed out with each thump. A normal result usually falls between 50% and 70%, according to the American Heart Association.
People with a reduced ejection fraction have one type of the condition. Itâs called heart failure with reduced left ventricular function. With the other type, heart failure with preserved left ventricular function, the percentage isnât below normal. But there are other changes, such as the heart becoming stiffer. âAfter the heart squeezes and pumps blood forward, it has to relax to fill with blood,â Lampert says. âWhen the heart muscle is stiff or unable to relax as blood is trying to rush in and fill it, itâs not very compliant, and so you can get that same results of fluid backing up into the lungs and other parts of the body.â
Staging. There are four stages of heart failure, which indicate how serious your condition may be.
Also Check: How To Slow Your Heart Rate
Caring For Someone With Heart Failure Towards The End Of Life
Please be aware – this;information is for healthcare professionals.;We also have;information for the public.;
You can use our My Learning form ; to reflect on how this page has helped with your continuing professional development.
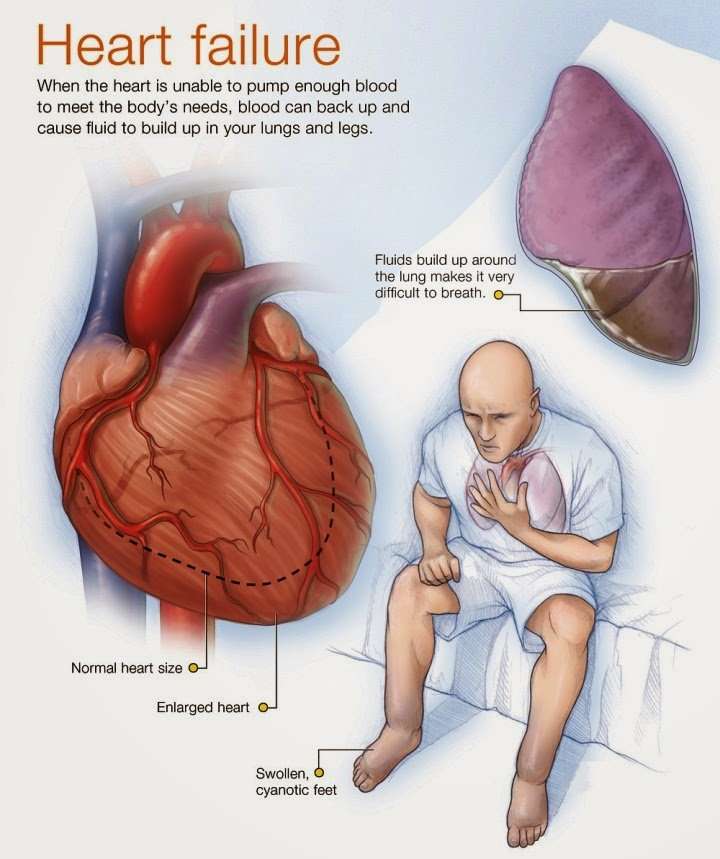
Someone with heart failure may experience symptoms such as fatigue, breathlessness, oedema and pain. Towards the end of life, health and social care professionals can support the person by helping to manage their symptoms and talking to them about how they want to be cared for, now and in the future.
On this page:
Initial Stages Of Chf
In the initial, mild stage A, there are underlying high-risk factors for CHF such as smoking or high blood pressure. However, the affected person has no symptoms or limitations at rest or with physical activity and there are no signs of CHF on evaluation by a doctor.
In stage B, the person develops mild symptoms of fatigue, shortness of breath, or heart palpitations with routine physical activity. There are minor signs of heart dysfunction on a doctor’s evaluation. There might also be a mild, intermittent collection of fluid, known as edema, in the ankles and feet.
Recommended Reading: Why Does Your Heart Rate Go Up When You Exercise
Women And Heart Failure
Women are just as likely as men to develop heart failure, but there are some differences:
- Women tend to develop heart failure later in life compared with men.
- Women tend to have heart failure caused by high blood pressure and have a normal EF .
- Women may have more shortness of breath than men do. There are no differences in treatment for men and women with heart failure.
Heart Failure Life Expectancy Calculator
The heart failure life expectancy calculator is a simple, yet effective, tool for predicting the 1-year and 3-year survival odds of someone with congestive heart failure.
In the article below, we will focus on congestive heart failure/CHF prognosis, the estimates on how long can you live with congestive heart failure, and the average CHF life expectancy for a given stage of the disease.
Recommended Reading: How Do I Lower My Heart Rate
Causes Of Heart Failure
Heart failure is often the result of a number of;problems affecting the heart at the same time.
Conditions that can lead to;heart failure;include:
- coronary heart disease where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become clogged up;with fatty substances , which may cause angina or a heart attack
- high blood pressure this can put extra strain on the heart, which over time can lead to heart failure
- cardiomyopathy conditions affecting;the heart muscle
- heart rhythm problems;, such as;atrial fibrillation
- damage or other problems with the heart valves
- congenital heart disease;;birth defects that affect the normal workings of the heart
Sometimes anaemia, drinking too much alcohol, an overactive thyroid or high pressure in the lungs can also lead to heart failure.
How Is Heart Failure Treated/managed
Treatment of heart failure depends on the underlying cause and this will direct the main treatment to prevent further deterioration. Heart failure can be cured if it has a treatable cause.
If the causes are due to coronary heart disease then the patient may require coronary stents or . If there is a heart valve cause, then the defective valve will need surgery to repair or replace the valve.
All heart failure patients will need:;
- Lifestyle changes; including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and stopping smoking and watching fluid intake and reduce alcohol consumption.
- Medicine; a range of medicines can help; many people need to take three to four;different types which have evidence to show they strengthen the heart and improve prognosis. This includes beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, ARNI and SGLT2 inhibitors. Other medicines, such as diuretics, may be used to help with the symptoms.
In cases where patients are seen to be experiencing;continued deteriorating heart function despite the best and optimal medication, the following may be considered:
- Cardiac resynchronising therapy; In very severe heart failure conditions, a specialised type of pacemaker has shown to benefit and improve symptoms as well as prolonging life by resynchronising the contractility of the two main pumping chambers of the heart.;
- Cardiac transplant; If there is no scope for recovery and the condition deteriorates then in suitable patients, a heart transplant may be considered.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Hormonal Heart Palpitations
How Can I Prevent Heart Failure
You can prevent heart failure by preventing coronary heart disease and heart attack. The best way to do this is to reduce or eliminate the risk factors that lead to heart failure. You could:
- drink alcohol in moderation
- reduce stress and look after your mental wellbeing
If you have had a heart attack, its even more important to manage your risk factors and follow your treatment plan. Make sure you check in frequently with your healthcare team.
Some risk factors such as your age, whether you have other health conditions, or your genes may be outside your control. Speak with your doctor if you have concerns about developing heart failure, and how you can manage it.
Chf Is Not A Death Sentence
While serious, congestive heart failure diagnosis doesnt mean your life is over. Its important to understand how manageable it is. By taking the right steps, patients can learn to live a happy and fulfilling life.
Will there be necessary lifestyle changes? Certainly. But it doesnt mean you have to stop what youre doing. Do regular physical exercises like walking, swimming, biking, and light-weight exercises. Avoid activities such as running in very hot or very cold weather or doing heavy lifting. Stick to a diet thats low in sodium and avoid processed foods.
Consult a doctor for the best steps to combat your CHF.
Patient Experiences
Recommended Reading: What Does It Mean If Your Heart Rate Is High
Symptoms That Occur First
- Small appearance;
- Puffiness around the eyes;
However, theres a slight problem when a child is suffering from congestive heart failure. The symptoms mentioned above can very likely be mistaken for a repertory infection or colic. This makes it difficult to diagnose congestive heart failure in children and infants when compared to adults.
If you have any of these symptoms, visit your doctor immediately.;
Managing Congestive Heart Failure: How To Live Longer And Better With Congestive Heart Failure

The term heart failure is something of a misnomer. It makes it sound like the heart has stopped working, but that isnt really the case. What congestive heart failure means is that the heart isnt pumping efficiently enough to keep up with the bodys needs. Heart inefficiency might be a better term. With the proper treatment and lifestyle changes, many people with congestive heart failure can lead active lives for many years.
Read Also: How Long Does End Stage Heart Failure Last
What Is The General Prognosis Of Congestive Heart Failure
The congestive heart failure is a progressive disease and is demarcated into four classes. With the progression to the next class, the condition of the patient is seen to deteriorate.
Class I The heart failure is mostly not symptomatic apart from the complaint of weakness by the patient.
Class II Patients of congestive heart failure avoid strenuous activities as such lead to heart palpitation and fatigue.
Class III Patients with Class III congestive heart failure are pretty symptomatic where most activities get limited due to the weakness.
Class IV The CHF is characterized by severe symptoms where the patient cannot even carry out basic life activities and experience severe heart palpitations and shortness of breath.
The general prognosis of the disease primarily varies from patient to patient because an amalgamation of factors leads to the disease. Nevertheless what can be definitely said is if the symptoms are brought to notice at an earlier stage, which is followed by early diagnosis. The prognosis will be much better as compared to late diagnosis.
Early diagnosis and early treatment is effective in reducing the symptoms so that the patient can live a quality life.
What Is Heart Failure
Heart failure is a term used to describe a set of signs that suggest the heart isnt pumping blood around the body as efficiently as it should.
Its most commonly caused by:
- damage to the heart muscle, for example as the result of a heart attack
- cardiomyopathy
- high blood pressure.
;It can also be caused by:
- heart valve problems
- a viral infection affecting the heart muscle
- an abnormal heart rhythm
- excess alcohol or recreational drugs.
Heart failure can be chronic or acute:
Acute heart failure is when the symptoms of heart failure come on suddenly, when heart failure is diagnosed for the first time, or if symptoms suddenly become worse during long-term heart failure.
Chronic heart failure is when someone has heart failure as a long-term condition.
Read Also: Heart Rate When Having A Heart Attack
How Long Can You Live With A Heart Failure
Heart failure is often mistaken as the end of life. Though the term sounds very alarming, it is just an indication of an urgent situation that tends to show that the heart is not working as well as it should be. It also indicates that if proper measures are not taken in order to slow down the condition or prevent the condition from worsening further, it might take a toll on your life.
What Are The Survival Rates For Heart Failure
Survival rates are based on studies of large groups of people with certain diagnoses and generally presented as a 5-year survival rate, which is the percentage of people who lived for at least 5 years after diagnosis.
You can find online calculators that ask you to submit information to get a life expectancy prediction. However, these calculators are not always accurate since they are based on studies of certain population groups over a period of time .
Table: Survival rates for patients with heart failure
| Survival | |
|---|---|
| 10 | About 24.5% on average |
For example, the 5-year survival rate for patients with heart failure is about 76%. This means that about 76 out of 100 people who were diagnosed with heart failure could live for at least 5 years.
Generally, young patients with heart failure have a better prognosis than older patients. Early diagnosis and treatment help increase life expectancy as well.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Average Heart Rate Per Minute
What Are The 4 Stages Of Heart Failure
There are four stages of heart failure;-;stage A, B, C and D -;which;range from high risk of developing heart failure to advanced heart failure.
The four;stages of heart failure are different to the four classes of heart failure symptoms also described in New York Heart Association , which illustrates the severity of symptoms, ranging from class one; to the most severe, which is class four .
Ejection Fraction And Its Importance
Ejection Fraction is a key indicator of a healthy heart and is frequently used by physicians to determine how well your heart is functioning as a pump. Ejection fraction is the percentage of blood that is pumped out of the heart during each beat. In a healthy heart, 50-75 percent of the blood is pumped out during each beat. Many people with heart disease pump out less than 50% and many people with Heart Failure pump out less than 40%.
Ejection Fraction is one of the many ways doctors classify the type and severity of Heart Failure and damage to the heart muscle.
Ejection Fraction ranges
- An Ejection Fraction above 50% indicates that your heart is pumping normally and is able to deliver an adequate supply of blood to your body and brain.
- An Ejection Fraction that falls below 50% could indicate that the heart is no longer pumping efficiently and is not able to meet the bodys needs.
- An Ejection Fraction of 35% or less indicates a weakened heart muscle. The heart is pumping poorly, which can significantly increase a persons risk for sudden cardiac arrest.
Measuring your Ejection Fraction
For Heart Failure patients, knowing your ejection fraction is just as important as knowing your blood pressure and your cholesterol. Ejection fraction is often measured using an echocardiogram, a simple and painless test often performed right in the doctors office. Ejection faction can also be measured with other tests including:
- Echocardiography
- Nuclear stress testing
Recommended Reading: What Does A Slow Heart Rate Mean
How Can I Approach A Hospice Discussion With Family Members And Loved Ones
The final months of life are frequently marked by strong emotions and hard decisions. Talking about hospice, even with those closest to you, can be difficult. Here are some tips to get the discussion started.
For patients speaking to families
Education is key. Educate yourself first. By now, youve probably done some research online. It may be helpful to read and share “Considering Hospice: A Discussion Guide for Families” at HospiceCanHelp.com. This discussion guide is a tool for you to print out and use in a family discussion.
Determine what your family members know. Before bringing up hospice, make sure your family members and caregivers have a clear understanding of your health status. People handle difficult information in different ways. If family members do not accept or understand your prognosis, ask your physician, clergy, a VITAS social worker or a trusted friend to speak with them on your behalf.;
Discuss your goals for the future, as well as theirs. As a patient, your greatest concern might be to live without pain, to stay at home or not to be a burden. Ask your family members/caregivers about their concerns as they consider the coming days, weeks and months. Explain that hospice is not giving up. It is an active choice to ensure that everyones needs are met.
For families speaking to patients
Stage Of Heart Failure And Life Expectancy:
The lower your stage of heart failure is, the longer you will live. People with Stage A of heart failure, may live for about 20 years, if they check their lifestyle, eat healthy, drink healthy and exercise properly. People with Stage B may not realize the signs and symptoms as they take rest. However, while taking a flight of stairs, or while walking or running, they might feel breathless or tired. They will live slightly shorter than people with Stage A heart failure.
However, research studies, as published in Circulation Research journal, in the August 2013 issue, have shown that about 50% of heart failure patients have lived for more about 5 years. About 10% of all their subjects have lived for about 10 years. However, in case the patient is in the Stage D, 90% of the patients will die within a year. That is how the stage of the heart failure is important in determining the life expectancy of the patients.
Don’t Miss: Does Baby Aspirin Help Prevent Heart Attacks
