How It Is Done
The health professional drawing your blood will:
- Wrap an elastic band around your upper arm to stop the flow of blood. This makes the veins below the band larger so it is easier to put a needle into the vein.
- Clean the needle site with alcohol.
- Put the needle into the vein. More than one needle stick may be needed.
- Attach a tube to the needle to fill it with blood.
- Remove the band from your arm when enough blood is collected.
- Apply a gauze pad or cotton ball over the needle site as the needle is removed.
- Put pressure on the site and then put on a bandage.
Low Bnp Levels In Up To 16% Of Heart Failure Patients
By Jamie L. W. Kennedy, MD, FACC
Associate Professor, Division of Cardiology, Advanced Heart Failure & Transplant Cardiology, University of California, San Francisco
SYNOPSIS: In patients with clinical heart failure and low B-type natriuretic peptide levels, the authors found these patients usually are young and obese, with higher ejection fraction and better renal function.
: Bachmann KN, Gupta DK, Xu M, et al. Unexpectedly low natriuretic peptide levels in patients with heart failure. JACC Heart Fail 2021 9:192-200.
Interestingly, there is a subset of patients with clear heart failure with normal or even low BNP values. To further evaluate this phenomenon, Bachmann et al queried a de-identified version of their institutions electronic medical record to find patients with measured BNP values and heart failure based on echo or hemodynamic criteria or hospitalized with heart failure. Echo criteria included left ventricular ejection fraction 35% or lower or left ventricular hypertrophy based on estimated left ventricular mass . BNP measurement was required within 90 days of the study.
The authors identified 47,970 adult patients with a measured BNP value: 9,153 were associated with a heart failure hospitalization, 7,041 met echo criteria, and 363 met hemodynamic criteria . BNP levels below 50 pg/mL were present in 4.9% of patients hospitalized for heart failure, 14% of patients with abnormal echoes, and 16.3% of patients with abnormal hemodynamics.
What Does The Test Result Mean
Higher-than-normal results suggest that you have some degree of heart failure, and the level of BNP or NT-proBNP in the blood may be related to its severity. Higher levels of BNP or NT-proBNP are often associated with an increased need for aggressive therapy. In some individuals with chronic heart failure, the markers may remain elevated and cannot be used to monitor response.
Normal results indicate that signs and symptoms are likely due to something other than heart failure.
You May Like: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Why Is Bnp Released In Heart Failure
BNPreleasedheartheart failurecardiac problemsheart failureheart failure
. Moreover, why is BNP high in heart failure?
Increases in BNP levels may be caused by intrinsic cardiac dysfunction or may be secondary to other causes such as pulmonary or renal diseases . BNP level is a strong predictor of risk of death and cardiovascular events in patients previously diagnosed with heart failure or cardiac dysfunction.
Beside above, can BNP be elevated without heart failure? BNP predicts mortality, even in patients without heart failure. The results suggest that an elevated B-type natriuretic peptide level in a patient without heart failure may warrant additional investigation, including assessment of cardiac structure and function, study authors said.
Similarly one may ask, what BNP level indicates heart failure?
BNP levels go up when the heart cannot pump the way it should. A result greater than 100 pg/mL is abnormal. The higher the number, the more likely heart failure is present and the more severe it is. Sometimes other conditions can cause high BNP levels.
How sensitive is BNP for heart failure?
A BNP cutoff of 100 pg/mL was found to be the optimal level for the diagnosis of heart failure with a sensitivity of 90% and a specificity of 76% the negative predictive value was 89% . BNP was the single most reliable predictor with an accuracy of 83%.
What Tube Is An Ammonia Level Drawn In
Lavender-top tube EDTA is the only acceptable anticoagulant.
How do you collect ammonia samples?
Blood should be collected into EDTA or heparin tubes, separated immediately and the plasma kept on ice until analysis. Ammonia is stable in plasma for a maximum of 3 hours under these conditions.
When do you draw ammonia levels? Your doctor will probably order an ammonia test if you have neurological changes, like sudden confusion or you fall into a coma for no reason. For a newborn, your doctor might order an ammonia test if they have the following symptoms within the first few days after birth: Seizures. Vomiting.
How do you collect blood from ammonia?
The ammonia test measures the level of ammonia in a blood sample. Blood is drawn from a vein , usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe.
Read Also: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
Why Do I Need A Natriuretic Peptide Test
You may need a BNP test or an NT-proBNP test if you have symptoms of heart failure. These include:
If you are being treated for heart failure, your health care provider may order one of these tests to see how well your treatment is working.
Bnp In The Management Of Heart Failure
- the NICE clinical guideline on CHF the use of BNP as a diagnostic tool for heart failure
-
refer patients with suspected heart failure and previous myocardial infarction urgently, to have transthoracic Doppler 2D echocardiography and specialist assessment within 2 weeks
- refer people with suspected heart failure and an NT-proBNP level above 2,000 ng/litre urgently, to have specialist assessment and transthoracic echocardiography within 2 weeks – because very high levels of NT-proBNP carry a poor prognosis
- refer people with suspected heart failure and an NT-proBNP level between 400 and 2,000 ng/litre to have specialist assessment and transthoracic echocardiography within 6 weeks
- review alternative causes for symptoms of heart failure in people with NTproBNP levels below 400 ng/litre. If there is still concern that the symptoms might be related to heart failure, discuss with a physician with subspeciality training in heart failure
- perform transthoracic echocardiography to exclude important valve disease, assess the systolic function of the ventricle, and detect intracardiac shunts
- if a poor image is produced by transthoracic echocardiography
- consider alternative methods of imaging the heart
Notes:
Recommended Reading: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
The Role Of Bnp Testing In Heart Failure
JENNY DOUST, B.M.B.S., FRACGP, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
RICHARD LEHMAN, B.M.B.C.H., MRCAP, Banbury, Oxfordshire, United Kingdom
PAUL GLASZIOU, M.B.B.S., PH.D., FRACGP., University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
Am Fam Physician. 2006 Dec 1 74:1893-1900.
Brain natriuretic peptide levels are simple and objective measures of cardiac function. These measurements can be used to diagnose heart failure, including diastolic dysfunction, and using them has been shown to save money in the emergency department setting. The high negative predictive value of BNP tests is particularly helpful for ruling out heart failure. Treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin-II receptor blockers, spironolactone, and diuretics reduces BNP levels, suggesting that BNP testing may have a role in monitoring patients with heart failure. However, patients with treated chronic stable heart failure may have levels in the normal range . Increases in BNP levels may be caused by intrinsic cardiac dysfunction or may be secondary to other causes such as pulmonary or renal diseases . BNP tests are correlated with other measures of cardiac status such as New York Heart Association classification. BNP level is a strong predictor of risk of death and cardiovascular events in patients previously diagnosed with heart failure or cardiac dysfunction.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
BNP = brain natriuretic peptide.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
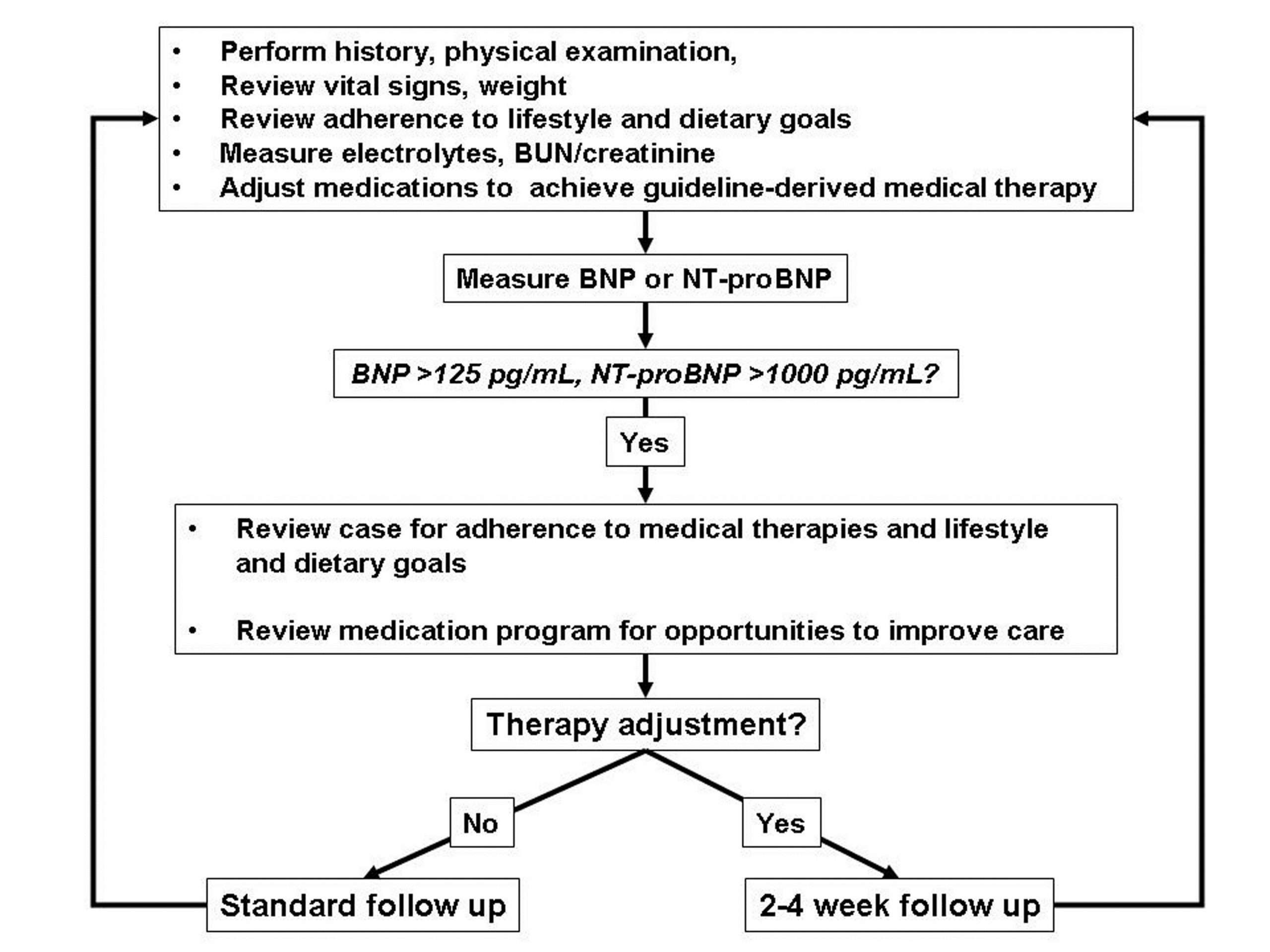
Monitoring Patients With Heart Failure
BNP measurement is a potential tool for monitoring treatment response in patients with heart failure because of the tests ability to diagnose heart failure, predict prognosis, and correlate with more invasive clinical measures .36 Prognostic studies have shown that BNP levels measured after treatment took effect were more predictive of the risk of death or further cardiovascular events than those initiated at first presentation.37,38
Ideally, randomized trials would offer definitive evidence however, only two small trials have evaluated BNP-guided treatment.39,40 The first trial showed a nearly twofold decrease in cardiovascular events,39 and the second trial showed a decrease in BNP levels with BNP-guided treatment.40 However, according to the ACC/AHA guideline on the management of heart failure, the value of serial BNP measurements in guiding therapy for patients with heart failure is not well established.32 Larger randomized controlled trials are needed before routine BNP monitoring of heart failure can be recommended.
Read the full article.
- Get immediate access, anytime, anywhere.
- Choose a single article, issue, or full-access subscription.
- Earn up to 6 CME credits per issue.
You May Like: Typical Resting Heart Rate For A Healthy Individual
Is There Anything Else I Should Know
BNP and NT-proBNP levels decrease in most people who are taking drug therapies for heart failure, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, beta blockers, and diuretics.
Levels of both BNP and NT-proBNP tend to increase with age in the absence of disease.
Levels of NT-proBNP and BNP may be increased in persons with kidney disease due to reduced clearance. Obese individuals may have lower concentrations of BNP or NT-proBNP.
While both BNP and NT-proBNP will rise with left ventricle dysfunction and either can be measured for diagnosis or monitoring therapy, they are not interchangeable and the results cannot be directly compared.
Natriuretic Peptide Measurement In Heart Failure
Summary
This paper is an up-to-date account of research and current clinical practice guideline recommendations. Chris Higgins summarizes the recommendations of 2 new guidance documents on the use of natriuretic peptides in heart failure. The first document is a systematic review of published research on the role of biomarkers in heart failure conducted by an expert group on behalf of the American Heart Association . The second document is the 2017 update of 2013 American College of Cardiology /AHA Guideline for Management of Heart Failure. The article begins with brief overviews of BNP/NT-proBNP and heart failure.
Measurement of circulating natriuretic peptide concentration has been a routine part of the clinical assessment of patients with suspected heart failure for close to 15 years following discovery that heart failure is associated with increased concentration of both peptides. Voluminous research over this 15-year period has sought to refine and extend the clinical utility of the two tests and allow evidence-based guidelines for their clinical use in heart failure.
The focus of, and impetus for this article is two recently published, potentially influential papers . Together they provide current group expert view of the value of BNP, NT-proBNP testing in heart failure. The first is a systematic review of published research on the role of biomarkers in heart failure conducted by an expert group on behalf of the American Heart Association .
Recommended Reading: What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
Why It Is Done
The brain natriuretic peptide test is used to:
- Check your risk for getting heart failure.
- Check for heart failure. A doctor may think you have heart failure if you are having problems such as trouble breathing and swelling in the arms or legs.
- Find out how severe heart failure is.
- Check the response to treatment for heart failure.
Why The Test Is Performed
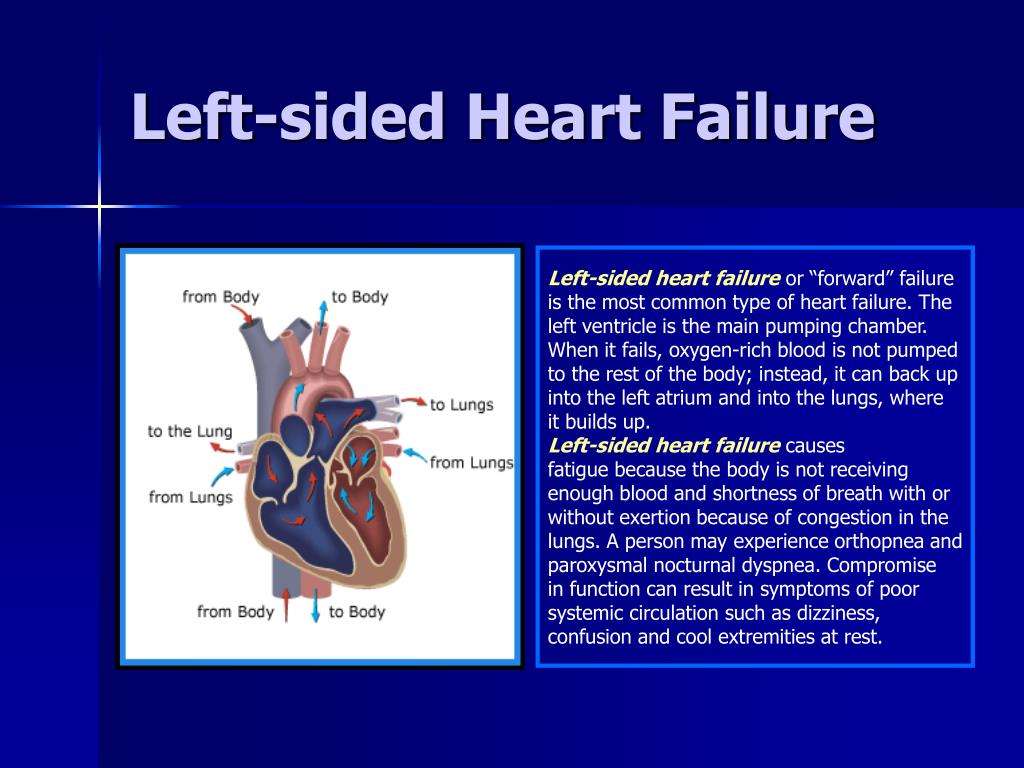
You may need this test if you have signs of heart failure. Symptoms include shortness of breath and swelling of your legs or abdomen. The test helps make sure the problems are due to your heart and not your lungs, kidneys, or liver.
It is unclear if repeated BNP tests are helpful in guiding treatment in those already diagnosed with heart failure.
You May Like: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
Bnp As A Prognostic Biomarker In Hf Patients
There are several studies performed to evaluate prognostic significance of natriuretic peptide. The predictive value of BNP/NT-proBNP was evaluated in the following trials of large cohort of patients with symptoms of HF.
Prognostic value in patients with LV systolic dysfunction
In a larger study of 452 patients with LVEF < 35%, Berger et al. found that BNP levels were a strong independent predictor of sudden death . The prospective Copenhagen Hospital Heart Failure study showed that measurements of NT-proBNP add additional prognostic information independent of LVEF, and is a strong predictor of 1-year mortality in hospitalized patients with HF regardless of systolic dysfunction . The COPERNICUS NT-proBNP substudy investigated the prognostic value of NT-proBNP in a large number of patients with severe CHF. NT-proBNP was consistently associated with increased risk for all-cause mortality and or hospitalization for HF in patients with severe CHF .
Prognostic value in patients with chronic HF and preserved LV systolic function
Although some studies have shown the promising results of the BNP/NT-proBNP assay in patients with chronic HF and preserved LV systolic function for the prediction of adverse cardiovascular incidence, its prognostic value is still not well established because there are scarce evidence in this group of patients.
How Common Is Heart Failure
According to the American Heart Association, more than 6 million people in the United States are living with heart failure and the number is growing. It is estimated that one in five American adults age 40 and older will develop heart failure in their lifetime. You may be at increased risk of developing heart failure if you have conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure, or diabetes, or if you have had a heart attack. Other risk factors include tobacco use, alcohol use, and obesity.
You May Like: Afrin Heart Palpitations
What Do High Or Low Bnp Levels Mean
Low BNP levels mean you likely dont have heart failure. Your doctor can rule that diagnosis out and look at other reasons why you may have symptoms such as shortness of breath.
High levels mean that your doctor may make a diagnosis of heart failure. Also, levels are higher when heart failure is worse, and they go down when the heart is stable.
If you have high BNP but the doctor rules out heart failure, the levels may point to other conditions such as:
Bnp Blood Test Overview
If your doctor orders a BNP test, you are probably showing symptoms of heart failure. The test measures a hormone called brain natriuretic peptide.
During heart failure, pressure builds up in the chambers of your heart and creates BNP. When the heart works harder and doesnt pump blood well, it releases this hormone in large amounts. BNP widens your blood vessels to help improve circulation. Thats why higher levels may be a sign of heart failure.
Emergency departments can get your BNP test results in about 15 minutes.
Here is information you can use to get a clearer understanding of heart failure and the value of this test. It will help you understand what the results mean and how you can use them to help improve your health.
You May Like: What Is A Dangerously High Heart Rate When Exercising
Clinical Information Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
B-type natriuretic peptide is a 32-amino acid-ringed peptide secreted by the heart to regulate blood pressure and fluid balance. BNP is stored in, and secreted predominantly from, membrane granules in the heart ventricles and is continuously released from the heart in response to both ventricle volume expansion and pressure overload.
The natriuretic peptide system and the renin-angiotensin system counteract each other in arterial pressure regulation. When arterial pressure decreases, the kidneys release renin, which activates angiotensinogen resulting in increased peripheral resistance of the arterioles, thus increasing arterial pressure.
The natriuretic peptides counteract the effects of renin secretion, causing a reduction of blood pressure and extracellular fluid volume. Both BNP and atrial natriuretic peptide are activated by atrial and ventricular distension due to increased intracardiac pressure. These peptides have both natriuretic and diuretic properties: they raise sodium and water excretion by increasing the glomerular filtration rate and inhibiting sodium reabsorption by the kidney.
The New York Heart Association developed a functional classification system for congestive heart failure consisting of 4 stages based on the severity of the symptoms. Various studies have demonstrated that circulating BNP concentrations increase with the severity of CHF based on the NYHA classification.
Is There Anything Else I Need To Know About A Natriuretic Peptide Test
Your health care provider may order one or more of the following tests in addition to or after you’ve had a BNP or NT-proBNP test:
- Electrocardiogram, which looks at heart’s electrical activity
- Stress test, which shows how well your heart handles physical activity
- Chest x-ray to see if your heart is larger than normal or if you have fluid in your lungs
You may also get one or more of the following blood tests:
- ANP test. ANP stands for atrial natriuretic peptide. ANP is similar to BNP but it is made in a different part of the heart.
- Metabolic panel to check for kidney disease, which has similar symptoms to heart failure
- Complete blood count to check for anemia or other blood disorders
You May Like: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Ask A Laboratory Scientist
This form enables patients to ask specific questions about lab tests. Your questions will be answered by a laboratory scientist as part of a voluntary service provided by one of our partners, American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science. Please allow 2-3 business days for an email response from one of the volunteers on the Consumer Information Response Team.
