Anaesthetic And Operative Technique
Anaesthetic technique and heparin management were standardised and have previously been reported . In the on-pump group, cardiopulmonary bypass was instituted using ascending aortic cannulation and two-stage venous cannulation of the right atrium. A standard circuit was used a Bard tubing set, which included a 40-m filter and a hollow fibre membrane oxygenator . The extracorporeal circuit was primed with 1000 mL of Hartmann’s solution, 500 mL of Gelofusine, 0.5 g/kg mannitol, 7 mL of 10% calcium gluconate, and 6000 IU of heparin. Non-pulsatile flow was used and flow rates throughout bypass were 2.4 L/m2/min. Systemic temperature was kept between 34 and 36°C. Myocardial protection was achieved with intermittent anterograde hyperkalaemic warm blood cardioplegia .
In the off-pump group, we used two methods of exposure and stabilisation of the heart previously described . Briefly, the target vessel was exposed and snared above the anastomotic site using a 4-0 prolene suture with a soft plastic snugger to prevent coronary injury. The coronary target area was stabilised with a reusable stabiliser . An intra-coronary shunt was used only in case of relative electrocardiographic or haemodynamic instability or excessive bleeding during the anastomosis.
What Are Stat Categories
STAT categories classify heart surgeries into groups based on how risky or complex they are. The STAT 1 category indicates surgeries with the lowest risk of death, while the STAT 5 category indicates the surgeries with the highest risk of death. A hospital that has a high survival rate for STAT 5 cases indicates success at handling unpredictable situations during the operation and during recovery.
What we measure:
STAT 5 neonatal survival measures the percentage of babies with the most complex heart defects who survive their surgery and have been discharged from the hospital.
What it means:
At Childrens Colorado, our surgical team specializes in some of the most complex cardiovascular procedures, with special expertise in surgical repair during the newborn period. Having a high STAT 5 survival rate means that the newborn babies we treat are more likely to survive their operation than the national average, even though we accept many more complex patients.
Recommended Reading: How To Lower Heart Rate During Exercise
Studies: Open Heart Surgery Ok For 80
Eighty-year-olds with clogged arteries or leaky heart valves used to be sent home with a pat on the arm from their doctors and pills to try to ease their symptoms. Now more are getting open-heart surgery, with remarkable survival rates rivaling those of much younger people, new studies show.
Years ago, physicians “were told we were pushing the envelope” to operate on a 70-year-old, said Dr. Vincent Bufalino, a cardiologist at Loyola University in Chicago. But today “we have elderly folks who are extremely viable, mentally quite sharp,” who want to decide for themselves whether to take the risk, he said.
Even 90-year-olds are having open-heart surgery, said Dr. Harlan Krumholz, a Yale University cardiologist who has researched older heart patients.
“Age itself shouldn’t be an automatic exclusion,” he said. Not every older person can undergo such a challenging operation, but the great results seen in the new studies show that doctors have gotten good at figuring out who can.
The studies were reported at an American Heart Association conference this week in New Orleans.
People 75 and older are the fastest-growing segment of the U.S. population this group is projected to more than quadruple over the next 50 years. Forty percent have heart disease, and half will die from it.
But open-heart surgery is another thing splitting open an aged chest and putting a patient on a heart-lung machine while doctors repair fragile blood vessels and weak valves.
Read Also: How To Reduce Heart Rate
An Octogenarian Success Story
Case in point: 89-year-old Albert Carlsen, a retired engineer who divides his time between homes in Idaho and Rancho Mirage, Calif. Carlsen underwent a double bypass operation in November at The Heart Hospital of the Desert in Rancho Mirage and has since resumed walking, gardening, and golfing.
“There’s obviously some risk when you get up where I am,” says the strapping, square-jawed Carlsen. “But heckfire, I went through that operation with flying colors. I was up in three days, dressed, and ready to go home.”
The St Pauls Rehabilitation Experience
Located conveniently near you, St. Pauls Senior Community offers comprehensive senior rehabilitation services to provide support for you and your loved one through any upcoming medical procedures, injury recovery, or other health concerns. We know youre likely to have questions, and wed be happy to answer them for you. To get more information, please contact us. Our team is ready to help!
You May Like: How To Figure Out Your Heart Rate
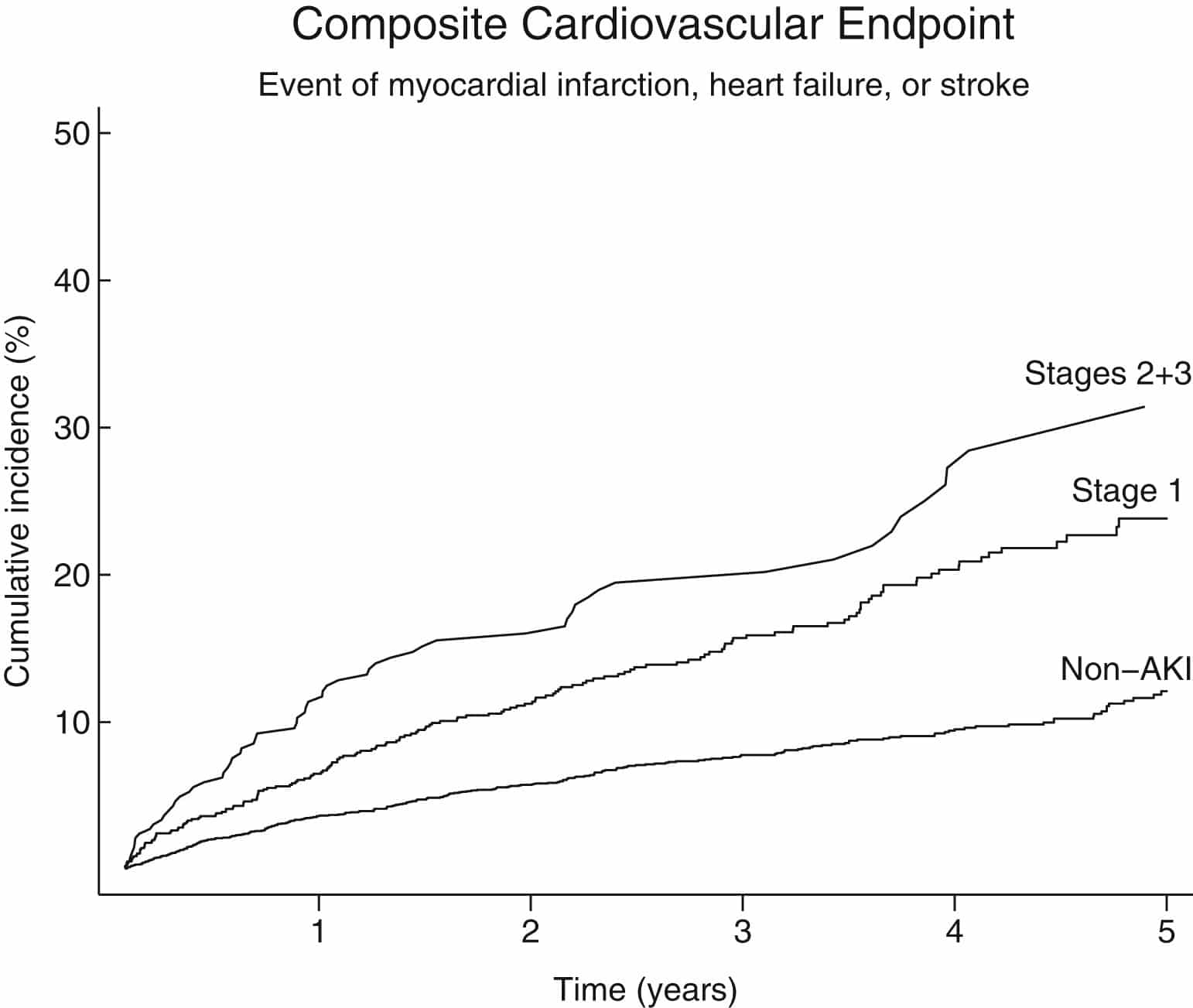
Comparison With Existing Literature
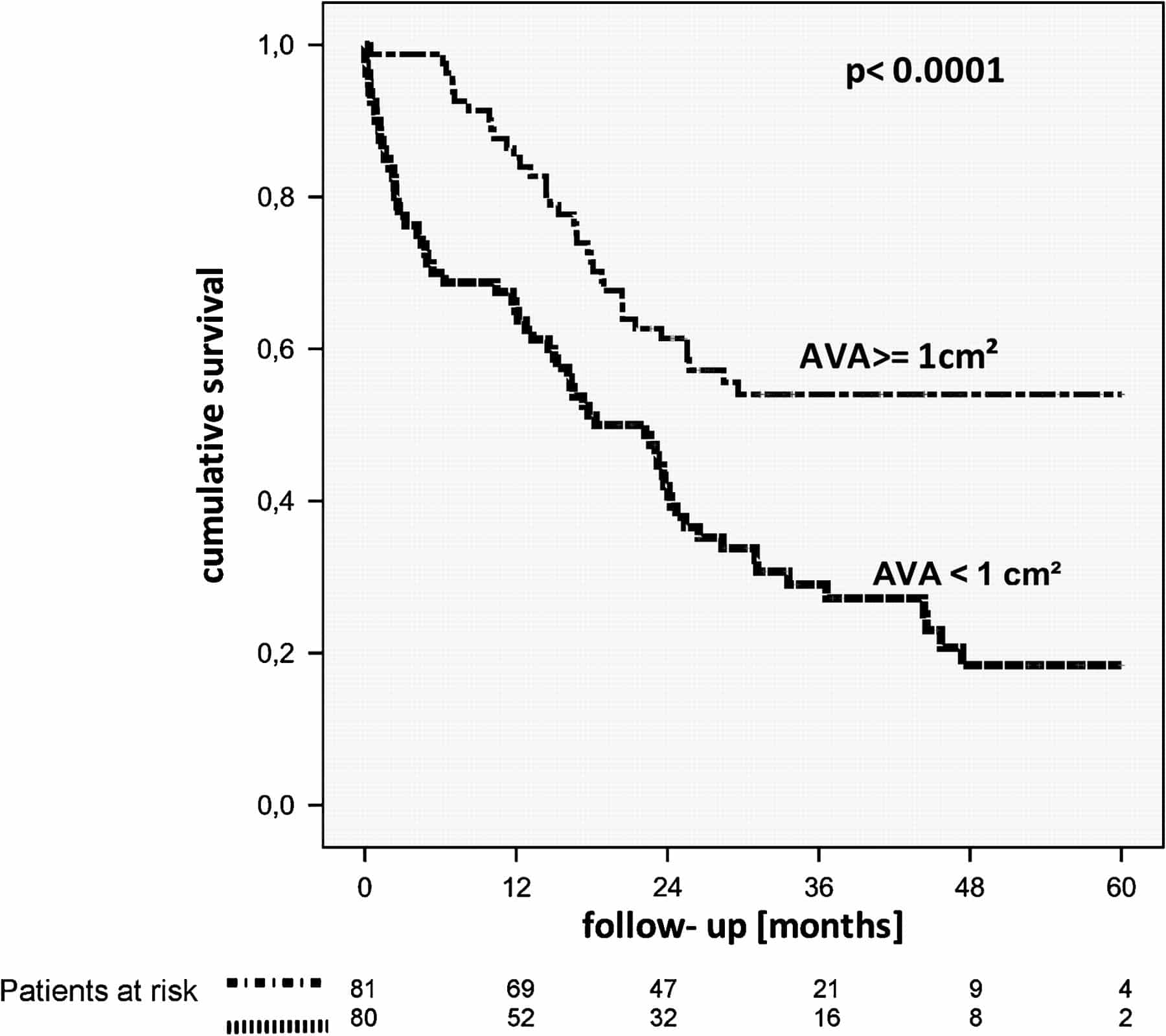
The expected survival of symptomatic patients with severe AS who do not have surgery is 14years., Surgical AVR improves this dismal prognosis and, as we have shown in the present study, restores survival to that expected of an age-matched and gender-matched general population without AS at least up to 8years of follow-up.
Our findings are consistent with previous reports by high-volume centres undertaking AVR in elderly patients. A report published using the Society of Thoracic Surgeons Adult Cardiac Surgery Database of over 145000 patients from over 1000 US centres found a median survival of 13, 9 and 6years in patients undergoing isolated AVR aged 6569, 7079 and 80years of age, respectively. For patients undergoing AVR+CABG, median survival for the same age groups was 10, 8 and 6years. Similarly, baseline CKD, severely impaired LVF and being a current smoker have all been associated with poor long-term survival following surgical AVR.,
Open Heart Surgery Survival Rate By Age
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Don’t Miss: What Should My Resting Heart Rate Be
Characteristics Of The Study Population
The mean age of all patients was 74.5 years at the time of surgery . Fifty percent of the patients were between 70 and 75 years, 45% between 75 and 80 years, and 5% between 80 and 93 years of age. Males represented 58.9% of the study population. Overall, 82% had coronary artery bypass grafting only. Only 8.2% had valve surgery and 9.8% had a combined procedure. Regarding urgency of operation, 38.2% were considered elective, 48.1%
Patient Selection And Data Collection
Data were collected prospectively using the Patient Analysis and Tracking Systems for all patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery between April 1996 and December 2000 . The dataset includes five different sections to be filled in consecutively by anaesthetist, surgeon, intensive care unit, high dependency unit, and ward nurses. Data were extracted for consecutive elderly patients who had undergone coronary revascularisation during the study period.
Allocation to on- and off-pump surgery was on the basis of the preference and expertise of the surgeons carrying out the operations and, also, during the early part of data collection when experience was still being gained with off-pump techniques, the allocation was based on coronary anatomy and number of grafts required. The decision about which surgical method to use was taken after opening the chest, when the anatomy of the coronary vessels could be explored.
Don’t Miss: How To Decrease Resting Heart Rate
What Do We Mean By Survival Statistics
The NHS monitors childrens heart surgery in the UK by reviewing each hospitals 30-day survival rate. The 30-day survival rate is the percentage of operations where the child survived to at least 30 days after their heart surgery. Ireland also submits its data to the same audit body, NCHDA.
Approximately 3500 children under the age of 16 have heart surgery each year in the United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland.
Routinely Performed Coronary Artery Bypass Surgeries
Recommended Reading: Why Did My Heart Rate Spike
Preparing For The Surgery
Preparation for open heart surgery starts the night before. A person should eat an evening meal as usual but must not consume any food or drink after midnight.
It is a good idea to wear loose, comfortable clothing to assist with restricted movement following surgery, but wear whatever is comfortable.
Be sure to have all personal medical information on hand. This might include a list of medications, recent illness, and insurance information.
It is normal to feel anxious before an anesthetic, and people should not hesitate to seek reassurance from the healthcare team.
The doctor may request that the person washes their upper body with antibacterial soap. A member of the healthcare team may need to shave the persons chest area before they can have the anesthetic.
The doctors may also need to run tests before surgery, such as monitoring the heart or taking blood samples. A doctor or nurse might place a line into a vein to enable the delivery of fluids.
After the medical team has completed the preliminary tasks, the anesthesiologist will administer general anesthesia.
You May Like: How Much Does Bypass Heart Surgery Cost
What Do We Do If The Bypasses Close Off
So far we have said that while LIMA-LAD grafts are an excellent option with great long term results, vein grafts are unfortunately no so good, and have an almost 1 in 2 chance of going down within several years of surgery. The good news is that the LIMA-LAD graft is the most important. And although the vein grafts may go down more frequently, if they do go down the chance of needing another heart operation is very, very low. If required, treatment can typically be undertaken using minimally invasive methods such as using stents.
The decision to treat blocked bypasses depends on many factors. Often the blockage may be silent and without symptoms, in which case no specific treatment is needed. Some bypass graft blockages will present with symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath or heart failure, in which case further evaluation can be undertaken and the decision made on the best treatment depending on the results of tests such as stress tests and angiograms. Finally some of these bypass blockages may present as a heart attack in which case often the blockages can be treated through the use of stents and medicines.
Also Check: What Is A Typical Resting Heart Rate
Heart Surgery Survival Rates By Type Of Procedure
The Cardiac Center team performs more than 850 pediatric heart surgeries a year, including open heart and closed heart procedures and heart transplants. Open heart procedures, which represent a major portion of our volume, require cardiopulmonary bypass and are usually the most complicated and complex procedures.
Pediatric heart surgery survival rates reflect the number of patients who survived within 30 days of the surgery or until the time they were discharged, whichever period is longer.
We track outcomes from common procedures as Quality Indicators for congenital heart surgery. The following data shows CHOPâs outcomes for these procedures.
The cardiac surgery indicators are included in the Society of Thoracic Surgeons Congenital Heart Surgery Database and in the National Quality Forum standards for pediatric heart surgery. The STS Congenital Heart Surgery Database contains data from over 100 congenital heart surgery centers in North America. The NQF is a nonprofit organization that sets or endorses standards to measure quality in healthcare.
Recommended Reading: Stroke After Open Heart Surgery
What Is Bypass Surgery
Coronary artery bypass graft surgery or bypass surgery is heart surgery that reroutes blood around obstructed arteries to enhance blood flow and oxygen to the heart.
- A graft vein or artery is extracted from a healthy blood vessel in the body during bypass surgery. After that, the graft is surgically implanted to bypass the obstruction or blockage in the occluded or poorly performing artery.
- Following surgery, blood will flow via the graft vessel, bypassing the blocked channel and delivering oxygen and nutrients to the tissue beyond the obstruction.
The most common reason for bypass surgery is to avoid or circumvent a blockage by a clot or plaque in a coronary artery due to atherosclerosis. If the blockage is not removed, the heart muscle beyond the obstruction is deprived of oxygen and nutrients, resulting in cardiac damage.
Also Check: Is Heart Attacks Hereditary
Cardiac Surgery Survival By Procedure
Cardiac surgery programs can also report survival rates by each specific operation. These are called benchmark operations, and they are one of the ways surgical centers can compare outcomes. Note that these data do not include a patients specific risk factors prior to surgery.
In the table below, we report the total number of benchmark operations at Childrens Colorado, as well as the survival rates here compared to the national average.
What we measure:
Index case survival shows the percentage of patients who received a specific operation and were alive 30 days after their operation. It also includes patients who needed to be in the hospital longer than 30 days who were alive and successfully able to go home.
Index case survival
| 98.8% |
What it means:
For the majority of the open-heart surgeries listed above, our survival rates are higher than the national average.
It is challenging to compare outcomes by procedure alone. The procedure-alone data does not include important health-related factors such as age, other health conditions , and genetic conditions that can make procedures riskier. This is why pediatric heart surgery programs should report a wide range of outcomes, including how well patients do when they are at higher risk due to other health conditions.
Recommended Reading: How Do I Know If I M Having Heart Attack
What Is The Survival Rate Of Heart Surgery
Heart surgery survival rates vary based on the type of surgery and how many problems are repaired during the operation. Survival rates are:
- Mitral valve repair for mitral valve prolapse: 100%.
- Aortic valve replacement: 98.1%.
- Coronary artery bypass surgery : 97.8%.
Heart surgery is generally riskier for people who are very ill or have other medical conditions.
You May Like: How To Get Your Heart Rate
Risk Factors And The Prediction Model
Univariate analysis was used to analyze potential risk factors for the development of postoperative pneumonia and showed that many aspects, including demographics, comorbidities, cardiac anatomy and function, laboratory values, operative time, and blood transfusion, were significantly different between patients with and without postoperative pneumonia .
Table 1
In the multivariate analysis, 13 independent risk factors for postoperative pneumonia were identified, including age > 60 years, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, smoking history, COPD, BMI 24 kg/m2, renal insufficiency, heart surgery history, NYHA class III-IV, preoperative anemia, hypoalbuminemia, CPB time > 120 minutes and blood transfusion . Odds ratios with corresponding 95% confidence intervals and assigned points are presented. A simplified point-based risk score used to predict the risk of postoperative pneumonia was then generated . There were 32 possible points in the composite risk index, with scores ranging from 0 to 27 in this study with a median of 9 . The predicted rate of postoperative pneumonia ranged from 0.61% for those with a score of 0, to 93.4% for those with a score of 32.
Table 2Figure 2Figure 3Table 3
What Happens After Heart Surgery
After your heart surgery is done, youll be moved to the intensive care unit . Youll recover in the ICU for at least one day. Youll then move to a regular hospital room for continued rest and care.
How long you stay in the hospital depends on the surgery you had and how your body responds to it. Each persons recovery is different. Your hospital team will keep a close eye on you and make sure youre healing as you should. Theyre also prepared to notice and respond to any problems that come up.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Heart Palpitations At Night
Good Survival Rates Found In Heart Surgery For Aged
-
Send any friend a story
As a subscriber, you have 10 gift articles to give each month. Anyone can read what you share.
Give this article
NEW ORLEANS Eighty-year-olds with clogged arteries or leaky heart valves used to be sent home with a pat on the arm from their doctors and pills to try to ease their symptoms. Now more are getting open-heart surgery, with remarkable survival rates rivaling those of much younger people, two new studies show.
Years ago, physicians were told we were pushing the envelope to operate on a 70-year-old, said Dr. Vincent J. Bufalino, a cardiologist at Loyola University Chicago. But today we have elderly folks who are extremely viable, mentally quite sharp, who want to decide for themselves whether to take the risk, said Dr. Bufalino, one of those who reviewed the studies for the American Heart Association.
Even 90-year-olds are having open-heart surgery, said Dr. Harlan M. Krumholz, a Yale cardiologist who has done other research on older heart patients. Age itself shouldnt be an automatic exclusion, Dr. Krumholz said.
Not every older person can undergo such a challenging operation, but the results seen in the new studies show that doctors have become good at figuring out who can.
