What Are The Symptoms Of A Panic Attack
A panic attack is a sudden attack of overwhelming fear or anxiety. Panic attacks are not life-threatening, but they interfere with your quality of life and mental well-being.
People who have regular or frequent panic attacks may have a panic disorder, a type of anxiety disorder. But an isolated panic attack can happen to anyone, even without a panic disorder diagnosis.
- Feeling of squeezing or, says Dr. Miller, like an elephant sitting on your chest.
- Achy or burning sensation, like heartburn.
Panic attacks often cause:
- Sharp or stabbing pain .
- Heart racing or chest discomfort thats hard to describe.
The triggers
Heart attacks tend to happen after physical strain or exertion a sign not found in panic attacks. A heart attack might happen after shoveling snow or walking up a long flight of stairs, Dr. Miller says. But you wouldnt have a panic attack after exercise unless there was an emotional stress trigger with it.
But what if the symptoms hit you at night? Both panic attacks and heart attacks can wake you from sleep. But theres a key difference: People who have nighttime, or nocturnal, panic attacks usually have daytime panic attacks, too.
So if you wake up with chest pain or other symptoms, and you dont have a history of panic attacks, that might be a sign of a heart attack.
How long it lasts
Panic attack symptoms last a few minutes or up to an hour. Then, the symptoms disappear, and you feel better. But a heart attack wont let up.
They Tend To Happen To Different Groups Of People But This Isnt An Exact Science
Heart attacks and panic attacks can affect anyone at any age, but some patterns hold true for everyone. Men and older people are more likely to have a heart attack, whereas women and younger people are more likely to have a panic attack.
That said, it depends on the individual. A person who has a mental health condition, like anxiety, depression, or post-traumatic stress disorder, is more likely to have panic attacks than is someone without one. But it is possible to have panic attacks and have heart disease. Likewise, a person can have a heart attack out of the blue, without having any known risk factors.
By signing up, I agree to GoodRx’sterms of service andprivacy policy, and to receive marketing messages from GoodRx.
Medical History Provides Clues
Your medical history may offer hints as to whether you’re experiencing a panic attack or afib. Often panic attacks are precipitated by some anxiety or depression or another psychiatric difficulty. Also, whether you’ve had a panic attack in the past could be a clue. Dr. Sobel said the presence of one panic attack increases the likelihood of another. Likewise, he said, a family history of cardiac disease and arrhythmias may point in a different direction.
Women may have atypical symptoms of a heart attack or other heart condition, such as a burning sensation in the upper abdomen, an upset stomach, or sweating. Doctors don’t always consider a heart attack or heart arrhythmia when women come to the ER with those symptoms, said Michelle B. Riba, MD, a professor and associate chair for integrated medical and psychiatric services at the University of Michigan.
Recommended Reading: Does Tylenol Raise Blood Pressure And Heart Rate
Additional Heart Attack Clues
If you have been diagnosed with cardiovascular disease, you already know that you should take the symptoms listed above seriously and call for help. But if you don’t have a diagnosis or haven’t had a heart attack, there are additional symptoms that often accompany a heart attack but typically not a panic attack. They include:
- Pain in one or both arms
- Pain in the jaw, back, shoulders, neck or upper abdomen
- Heartburn
Chest Pain In Anxiety Attacks
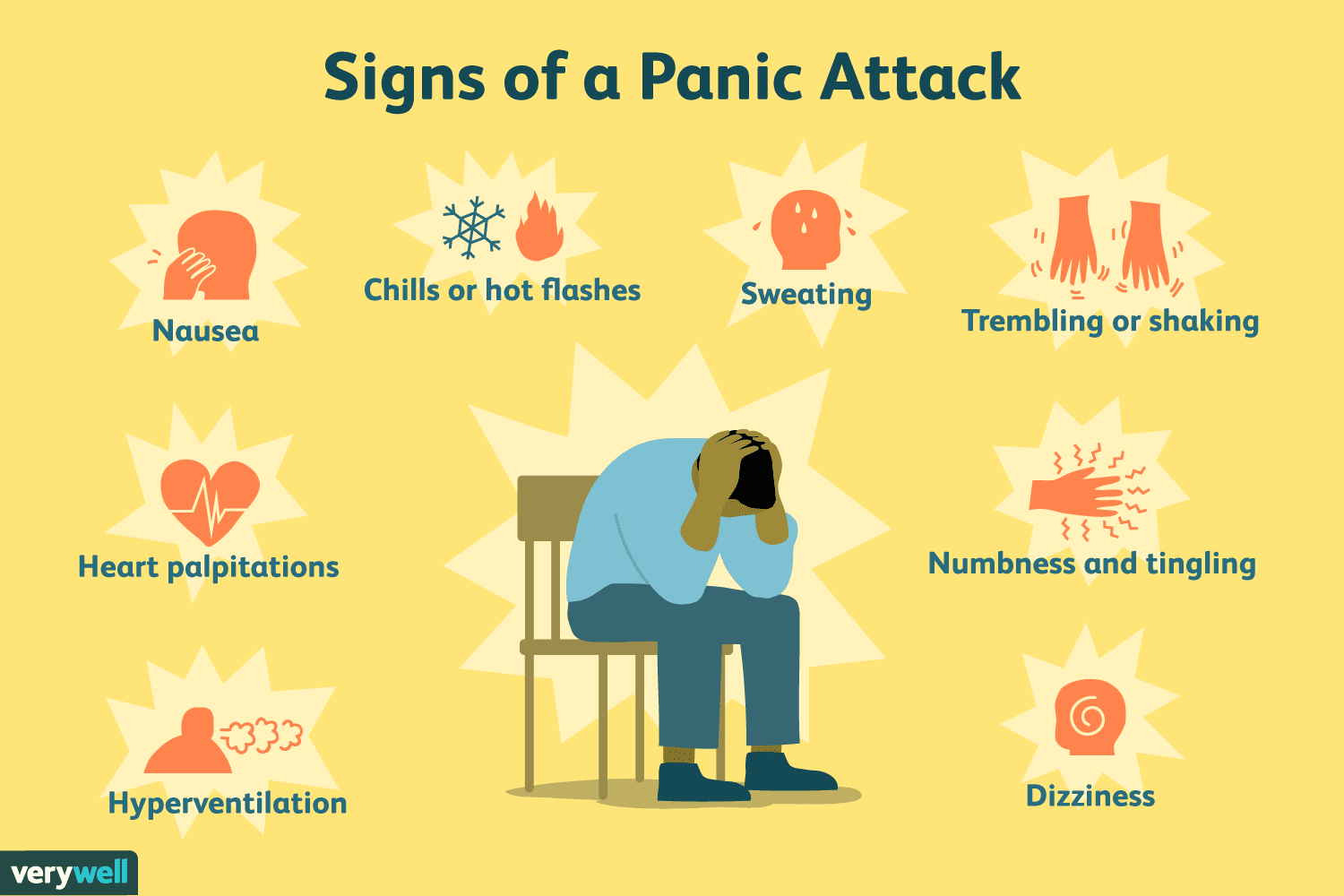
The chest pain experienced by people who are having panic attacks can be quite severe and frightening. The pain is often fleeting and sharp, and it can even be experienced as a catch that interrupts a breath.
It is most likely a form of chest wall pain caused by the muscle contractions that may occur with anxiety. In fact, because of these intense muscle contractions, the chest can remain sore for hours or days after a panic attack.
The severity of chest pain is often magnified by the intense fear associated with a panic attack.
Not surprisingly, chest pain is the symptom that often sends people having panic attacks to the emergency room.
Read Also: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
Differences Between Anxiety And Heart Problems
As you can see, anxiety and heart problems have remarkably similar symptoms!
While not as accurate a professional diagnosis, there are subtle differences between anxiety and heart problems which you may be able to determine at home.
- The chest pain from an anxiety attack is sharper and more localized, while the pain from a heart attack is duller and radiates more
- Anxiety attacks stem from a mental and not a physical cause
- Anxiety attacks rarely cause vomiting
- Heart attack pain may occur in the back or shoulders, while anxiety pain does not
And remember anxiety and heart problems can happen to people who have never had issues with either.
If you have any doubts at all about whether you are experiencing anxiety or heart problems, contact your doctor. They will be able to determine which you are experiencing and advise you as to what to do next.
Panic Attack Vs Heart Attack: How To Tell The Difference
Heartmail
Your heart suddenly begins racing. You feel pain in your chest and you are short of breath.
Are you having a heart attack? Or could it be a panic attack?
“Any of these symptoms can be extremely frightening,” says Patricia Tung, MD, of Arrhythmia Services at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Although they share a number of similarities, the two conditions result from very different disease processes. Panic attacks arise when stress hormones trigger the body’s “fight or flight” response, often resulting in racing heart, chest pain and shortness of breath.
In the case of a heart attack, a blockage in a coronary artery may result in the same symptoms. “Chest pain, rapid heartbeat and breathlessness may result when an insufficient amount of blood reaches the heart muscle,” says Tung.
One of the key distinctions between the two is that a heart attack often develops during physical exertion, whereas a panic attack can occur at rest.
A heart attack is more likely to develop when the work load of the heart increases, for example while a person is shoveling snow or running up the stairs, especially in people who do not routinely engage in physical exertion.
Another difference is duration: Panic attacks tend to gradually subside and resolve on their own within about 20 minutes. A heart attack, however, will often continue and may worsen over time.
When Your Heart Skips a Beat
Heart Attack
Read Also: Can Too Much Vitamin D Cause Heart Palpitations
Key Differences Between Panic Attacks And Heart Attacks
So how do you know if youre having a panic attack or a heart attack? Sometimes, it can be hard to tell. The difference between heart attacks and panic attacks can be subtle.
When someone is having a heart attack with chest pain, that pain is usually described as crushing. Its a pain that tends to begin in the middle of the chest but can travel down the left arm and into the back. In some cases of heart attack, the pain even extends into the neck and jaw.
This pain remains for about five minutes and can be accompanied by a tingling sensation in the left arm. It isnt unusual for someone in the middle of an attack to break into a cold, clammy sweat or feel sick to their stomach and vomit. Anyone who experiences these symptoms should call 911 immediately.
People who are having a panic attack can feel chest pain, shortness of breath, numbness or tingling sensations, nausea, and sweating. These symptoms usually peak after about 10 minutes. It is important to note that the chest pain is not crushing like the pain described by heart attack sufferers. Additionally, any tingling or numbness can be felt in both arms, not just the left. Some people even notice these sensations in their legs and toes.
When it comes to panic attack vs. heart attack, those who are having panic episodes focus on their fears, such as losing control, while people having a heart attack usually focus on the crushing pain.
What Does Anxiety Attack Mean
Anxiety attacks often have triggers, although they can be triggered by nothing at all. Some people experience anxiety attacks during periods of intense anxiety, but many others experience them out of nowhere, usually as a response to a physical sensation. For example, its not uncommon to have your first anxiety attack simply because your heartbeat speeds up, because anxiety has caused you to be hypersensitive to these changes.
The causes of anxiety attacks are everything from severe stress to hyperventilation to a need to regain control. It differs for different people, which is why treating it has a great deal to do with identifying triggers. Once youve experienced an anxiety attack, the fear of another anxiety attack may actually trigger an attack, because those that are afraid of getting a panic attack again often pay too much attention to their own body, and react to any changes in sensations.
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Resting Heart Rate
Want To Beat Depression For Yourself Or A Friend
W. Nate Upshaw, MD
Dr. William Nathan Upshaw is the Medical Director of NeuroSpa TMS®. Since receiving training from the inventor of TMS Therapy nearly a decade ago, Dr. Upshaw has been a pioneer, champion and outspoken advocate of TMS Therapy. Dr. Upshaws holistic experience in the field has transformed him into Floridas leading advocate for widespread accessibility to TMS Therapy.
When you are experiencing high levels of anxiety or panic, there is an undoubtable fear about your safety and wellbeing. However, while there may be similar physical and emotional sensations between these events, there are distinctive differences in these terms, what they mean, and how they are experienced. There is a difference between a panic attack vs anxiety attack, and a very stark difference between those two events, and a heart attack.
A panic attack is an intense period of fear and anxiety that can have environmental triggers, but may also occur without any known warning. These attacks last for about 15-20 minutes on average but can feel a lot longer than that if you are experiencing one. Someone may experience any number of these symptoms when having a panic attack:
- Increased heart rate.
- Feeling that you might be choking.
- Dizziness.
- Fear that youre dying or going crazy.
- Numbness.
- A feeling that whats happening around you isnt real.
Emotions During A Heart Attack
Of course, if youre having a heart attack youll almost certainly experience fear, toobut you may also be focused on the very real symptoms that are happening in real time, with survival being your only goal. According to the American Heart Association , people tend to struggle emotionally after surviving a heart attack. Thats when loss of control, worry about the future, and uncontrolled anxiety are common. Depression, loneliness, and even anger can occur, too. If you need help coping, contact the AHA for support.
Don’t Miss: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
How To Recognize A Heart Attack
Despite the widespread misconception, a panic attack can occur in the most ordinary of circumstances.
- The symptoms of a panic attack usually reach their peak after 10 minutes.
- The pain is concentrated in the region of thechest and has an undulating character to it: it rises then falls.
- The prickly feeling and numbness that can occur during a panic attack are not restricted to the leftarm but can also appear in the rightarm, legs, and fingers.
- During panic attacks, people experience irrationalfears, such as the fear they’re suffocating or going insane.
If you can’t work out whether you’re experiencing a panic attack or a heart attack, see a doctor immediately. Waiting is not the best solution in either case. If it turns out that you’re having a heart attack, you could die if you don’t receive medical help. A lack of medical support during a panic attack can make the symptoms worse and lead to the attacks occurring more often. Timely examination and care from a specialist could improve the quality of your life as well as your life expectancy.
What Are Anxiety Attacks
Anxiety attacks, also called panic attacks, are episodes of intense fear and emotional distress that usually occur suddenly and without warning, and typically last from several minutes up to an hour.
These attacks may have a discrete trigger, but they also can occur without any identifiable cause. Anxiety attacks are often recurrent and are very distressing to the people who experience them, as well as their loved ones.
People who have panic attacks typically spend a lot of time worrying about having more attacks and often make seemingly unreasonable lifestyle changes in an attempt to avoid circumstances that will trigger future attacks.
They may avoid situations that, they feel, have precipitated previous episodes or environments where they would not be able to escape easily if another attack should occur.
These avoidance adaptations can become quite extensive to the point where a person who suffers from panic attacks can become nearly housebound or otherwise withdraws from normal life experiences. These individuals are said to suffer from agoraphobia.
In addition to an intense feeling of fright, anxiety attacks also commonly produce real physical symptoms. These often include:
- Severe dyspnea
- Abdominal cramping
During an anxiety attack, tachycardia and tachypnea also are often present.
Recommended Reading: Fitbit Charge 2 Heart Rate Accuracy
Panic Or Heart Attack How To Know The Difference
The human body is really good at signaling when something is wrong. Unfortunately, it’s not very good at diagnosing itself. In fact, many of the signals it sends are virtually the same for a wide variety of conditions. And we tend to minimize our symptoms. So, if your body is telegraphing chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea and lightheadedness, you may be inclined to chalk it up to stress or anxiety. Chances are, you’ll rule out anything more serious despite the fact that these can also be symptoms of a heart attack. So how can you tell if you’re having a panic or heart attack? Knowing the difference and acting fast could save your life.
Are You Having An Anxiety Attack Or A Heart Attack
People who suffer from panic attacks often say their acute anxiety feels like a heart attack, as many of the symptoms can seem the same. Both conditions can be accompanied by shortness of breath, tightness in the chest, sweating, a pounding heartbeat, dizziness, and even physical weakness or temporary paralysis.
Perhaps most powerful, though, is the sense of dread that overshadows both events. The fear itself can lead to an increase in these symptoms.
To learn more about living a heart-healthy lifestyle and what to do when anxiety feels like a heart attack, contact UPMCs Heart and Vascular Institute today.
Also Check: Afrin Heart Palpitations
Diagnosing And Treating Anxiety
Its important to differentiate normal anxiety from the more severe type. Does the anxiety interfere with your family life or keep you from being productive in your professional life? Does it restrict you from engaging in the activities you like? If the answer is yes, then its the kind of anxiety that may require some degree of therapy or medical attention.
Depending on the duration, severity, and type of anxiety, treatment can include therapy, medication, or a combination of both. A common and effective method of treatment is cognitive behavioral therapy , which involves three main components:
If A Heart Attack Is Ruled Out Medically But Panic Attack Symptoms Continue
Consider visiting your primary care doctor if:
- The panic attacks are beginning to interfere with your daily life or ability to function at work, school, home or in important relationships
- The fear or anxiety of future panic attacks negatively impacts any of the above areas
- You find you’re actively avoiding doing certain things or going places for fear of having another panic attack
- You’re interested in learning how to manage your panic attacks or panic-related anxiety better
“With treatment, you can learn how to recognize the signs of an oncoming panic attack, learn skills to de-escalate the panic and break the anxiety cycle,” says Dr. Walker. “While treatment can’t necessarily prevent panic attacks from happening, they can improve your ability to manage the severity, frequency and duration of these attacks so that they’re not as disruptive or distressful.”
If you think you are experiencing a panic attack, Dr. Walker has some helpful advice. “Self-talk is important when having a panic attack. Sometimes it’s helpful to remind yourself out loud something like I’m not dying. I’m having a panic attack. It’s uncomfortable, but I’m OK. This will pass.’ Keeping a level head can be difficult when anxiety tries to hijack your thinking, but the more we can talk ourselves through it, the easier it can be to feel like you’re in control.”
Need help with frequent panic attacks?402.836.9292
Read Also: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
The Cause Of The Symptoms Is Different
One of the major differences between a heart attack and a panic attack is the cause of the symptoms, or what actually happens in your body to trigger the attack. During a heart attack, there isnt enough blood flowing to your heart. This strains the heart muscle and can lead to permanent damage. The reduced blood flow causes symptoms like chest pain and shortness of breath, and, with time, it can damage the heart muscle. Other common symptoms of a heart attack include nausea, pain in the left arm or jaw, and lightheadedness.
There are medical tests and procedures that can look at your heart to determine whether you are having a heart attack and whether your heart muscle has been damaged.
Although the symptoms of a panic attack can feel very similar to a heart attack, they are not related to decreased blood flow to the heart. In fact, the blood flow to your heart may be completely normal during a panic attack. Instead, panic attacks are caused by an exaggerated response of intense fear to things in the environment that would not normally cause that kind of reaction. Because the symptoms are not due to decreased blood flow to the heart, the results of medical tests during a panic attack are typically normal.
