What Are The Stages Of Heart Failure
Each type of heart failure is classified into stages. There are four stagesA, B, C, and Dand once you progress from one stage to another, there is no going back. The key to managing heart failure is to make changes and adhere to treatment strategies that stop or slow the progression of your heart failure from one level to the next.
A number of medications may be used to increase the function of your heart. For right-sided heart failure, the following may be prescribed:
- Medications for correcting problems that caused the heart failure, like hypertension
- Diuretics like furosemide to reduce fluid buildup and swelling
- Anticoagulants like warfarin to reduce clotting in stagnant blood that backs up in the right atrium
- Medications to increase the pumping ability or elasticity of the heart
- Implanted devices that help the heart pump more effectively
Left-sided heart failure requires slightly different treatments, including:
- Diuretics to reduce swelling
- Medications to control high blood pressure
- Inotropic medications that can help your heart pump more effectively
- Medications that reduce the strain on the heart and help it pump better like digoxin
- Implanted devices or a pump to help supplement the work of the heart
As your heart failure progresses, you may need additional treatments to manage the complications of heart failure, including medications to help support your kidney function or lifestyle changes to cope with the fatigue and weakness that heart failure can cause.
Treatment Of Common Causes Of Heart Failure
Treatment of heart failure is based on the severity of the condition. Early treatment improves symptoms of HF fairly quickly. However, the patient still gets regular testing in every three to six months. The Early stage of HF is treated with medications to help relieve symptoms and prevent the conditions from getting worse. Some medications used for individuals with heart failure include ibuprofen and naproxen. Some people with HF will be recommended for surgery. The most common surgery is coronary the bypass to allow blood to bypass the damaged or blocked artery and flow through the new one.
How Is Heart Failure Diagnosed
Tell your healthcare provider about your health history and the medicines you take. Tell him or her if you have a family history of heart failure or cardiomyopathy. He or she will ask about your shortness of breath and other symptoms. Your provider will make a diagnosis based on your physical exam, symptoms, and tests. The diagnosis may be left-sided or right-sided heart failure, or heart failure that affects both sides. You may need any of the following:
You May Like: Pima Heart Surgery Center
What Are The Symptoms
Your feet, legs, and ankles will likely to swell because blood is backing up in your veins. This symptom is called edema.
- If it backs up into your stomach or liver, you may notice that your abdomen is distended, too.
- You might find that you have to go to the bathroom more, especially at night. This is caused by fluid buildup, too.
As your heart failure gets worse, you may also see some of these symptoms:
- Itâs hard to breathe.
- Your neck veins are swollen.
- Your pulse is fast or feels âoff.â
- Your chest hurts.
- Youâre gaining weight from excess fluid.
- You donât feel like eating.
- Your skin is cold and sweaty.
- Youâre very tired.
When To See A Doctor
Its a good idea to speak with your doctor to check your heart health if you:
- Notice swelling in your legs
- Become winded easily with normal activities
There is no cure for heart failure. Still, with treatment, you can slow the progression of it and stay feeling better for longer.
You should seek immediate medical attention or call 911 if you or a loved one is experiencing:
- Sudden shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, or chest pain
- Trouble breathing and blood-tinged phlegm
- Fainting or loss of consciousness
You May Like: How To Tell The Difference Between Heartburn And Heart Attack
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide And B
ANP and BNP are endogenously generated peptides activated in response to atrial and ventricular volume/pressure expansion. ANP and BNP are released from the atria and ventricles, respectively, and both promote vasodilation and natriuresis. Their hemodynamic effects are mediated by decreases in ventricular filling pressures, owing to reductions in cardiac preload and afterload. BNP, in particular, produces selective afferent arteriolar vasodilation and inhibits sodium reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule. It also inhibits renin and aldosterone release and, therefore, adrenergic activation. ANP and BNP are elevated in chronic heart failure. BNP especially has potentially important diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications.
For more information, see the Medscape Drugs & Diseases article Natriuretic Peptides in Congestive Heart Failure.
Diagnosis Of Heart Failure
A clinical suspicion of heart failure is confirmed through the following investigations.
This includes FBC, liver biochemistry, cardiac enzymes released in acute cardiac failure and BNP.
- Electrocardiogram
- Cardiac MRI. This is also called CMR
- Cardiac biopsy. This is carried out only when a cardiac myopathy is suspected
- Cardiopulmonary exercise testing
Also Check: End Stage Heart Failure Symptoms Death
What Is Congestive Heart Failure Right
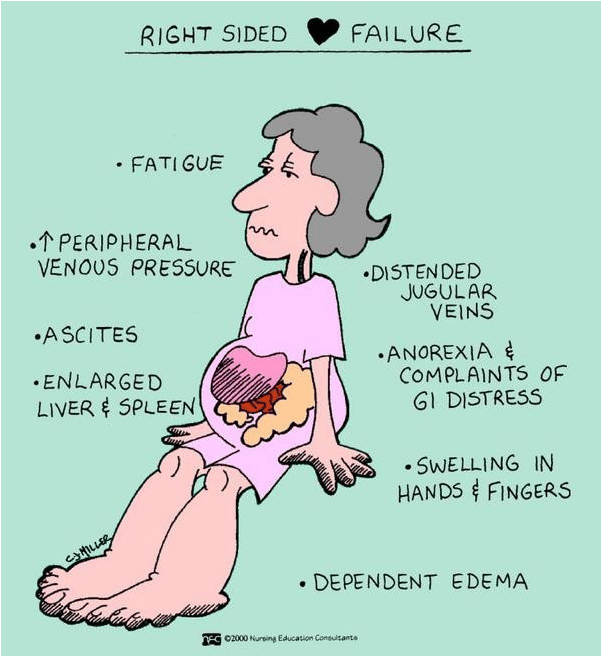
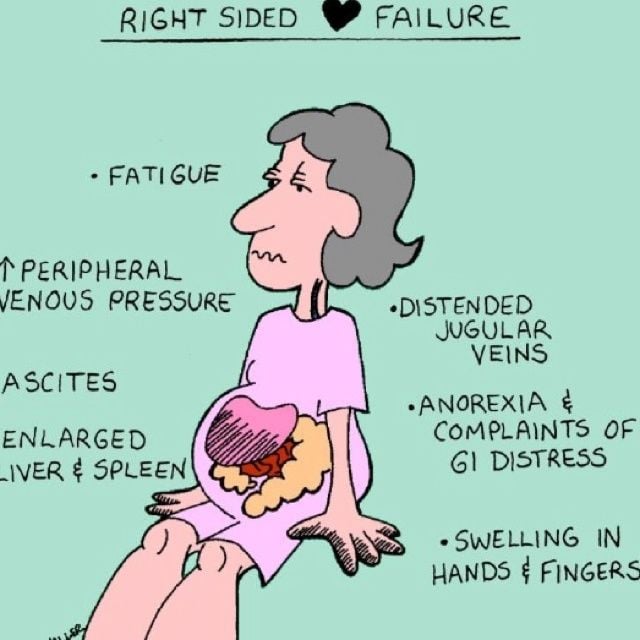
Right-sided Congestive Heart Failure occurs when the right ventricle of the heart has difficulty pumping blood into your lungs. As a result, blood backs up in your blood vessels, that triggers fluid retention in the lower abdomen, extremities, and other vital organs. Right sided congestive heart failure can occur on its own, for example when triggered due to lung disease or heart valve disease. In severe cases, hepatomegaly can happen resulting in altering liver function, coagulopathy and jaundice.
Recommended Reading: What If My Heart Rate Is Over 100
Clinical Features Of Heart Failure
Most of the clinical features of left and right heart failure are similar to each other. As explained before, left heart failure is most often the cause of right heart failure. Thus, the concurrent presence of both conditions gives a clinical picture with a plenty of shared symptoms and signs. The frequently seen symptoms that give the physicians a clue about the disease are,
- Fatigue and faintishness
- Edema in the dependent regions of the body such as ankles. In bed bound patients, edema will be seen in the sacral regions. This is more pronounced in the right sided heart failure due to the decrease in the venous return which leads to the pooling of blood in the dependent regions of the body.
Figure 02: Major Signs and Symptoms of Heart Failure
This is also due to venous congestion. Consequently, features of organomegaly are seen in right heart failure or when the right heart failure is present together with the left heart failure. Liver enlargement is associated with the abnormal distension of the stomach, the appearance of veins around the umbilicus and failure of the liver functions.
You May Like: What Is A Normal Resting Heart Rate For Adults Over The Age 18
What Causes Heart Failure
Heart failure can start suddenly after a medical condition or injury damages your heart muscle. But in most cases, heart failure develops slowly from long-term medical conditions.
Conditions that can cause heart failure include:
Anemia And Iron Deficiency
Anemia is common among patients with chronic heart failure and is frequently multifactorial. Anemia is associated with worse symptoms and outcomes in HF and so reversible causes should be sought and treated. Iron deficiency Iron Deficiency Anemia Iron deficiency is the most common cause of anemia and usually results from blood loss malabsorption, such as with celiac disease, is a much less common cause. Symptoms are usually nonspecific… read more is among the most common causes of anemia in HF, and iron replacement therapy should be considered once treatable causes such as blood loss have been excluded. Oral iron replacement is often less effective due to poor absorption and other reasons, thus intravenous iron replacement is preferred.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Heart Palpitations
How Common Is Right
More than 6 million Americans have heart failure. Each year, more than 900,000 people receive a heart failure diagnosis.
Heart failure is rare in people younger than 50. With age, it becomes increasingly common. Studies have shown that around 2% of the population younger than 54 years old have heart failure. The number increases to around 8% about 1 in 12 for people over 75.
What Can I Do To Manage Swelling From Extra Fluid
- Elevate your legs above the level of your heart. This will help with fluid that builds up in your legs or ankles. Elevate your legs as often as possible during the day. Prop your legs on pillows or blankets to keep them elevated comfortably. Try not to stand for long periods of time during the day. Move around to keep your blood circulating.
- Limit sodium . Ask how much sodium you can have each day. Your healthcare provider may give you a limit, such as 2,300 milligrams a day. Your provider or a dietitian can teach you how to read food labels for the number of mg in a food. He or she can also help you find ways to have less salt. For example, if you add salt to food as you cook, do not add more at the table.
- Drink liquids as directed. You may need to limit the amount of liquid you drink within 24 hours. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much liquid to have and which liquids are best for you. He or she may tell you to limit liquid to 1.5 to 2 liters in a day. He or she will also tell you how often to drink liquid throughout the day.
- Weigh yourself every morning. Use the same scale, in the same spot. Do this after you use the bathroom, but before you eat or drink. Wear the same type of clothing each time. Write down your weight and call your healthcare provider if you have a sudden weight gain. Swelling and weight gain are signs of fluid buildup.
Read Also: Best Food For Heart Failure
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Right heart failure is a systemic disorder that can affect many organs and hence is best managed by an interprofessional team. The outcomes of patients with RVF is worse than those with LVF, but it does depend on the cause and other comorbidities. Patients with persistently elevated pulmonary artery pressures have the worst outcomes. Many of these patients require repeat admissions and also have prolonged stays. Despite the various therapies for RVF, the outcomes have not greatly improved over the past two decades. While heart transplant is the ideal treatment for patients with no lung pathology, the shortage of donors is a limiting factor.
When Should I See A Healthcare Provider About Right Heart Failure
If you have chest pains or suspect you may be having a heart attack, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room.
Get in touch with your healthcare provider if you experience:
- Shortness of breath.
What else should I ask my provider?
If you have right-sided heart failure, ask your provider:
- What treatment is best for me?
- Is there a special diet I should follow?
- Should I go to cardiac rehab?
- Will I need surgery?
- Will I need a heart transplant?
- What can I do to stop heart failure from progressing?
- What medications will I need?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Right-sided heart failure means the right side of the heart can no longer pump blood efficiently. Fluid builds up in tissues, causing swelling. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms so the disease doesnt worsen. Healthy lifestyle habits, along with cardiac rehab, improve symptoms for many people. Other treatment options include cardiac devices and surgery. If you have shortness of breath, swelling or chest discomfort, talk to your healthcare provider.
Also Check: How Low Does Heart Rate Go When Sleeping
Whats The Outlook For People With Right
For many people, the right combination of therapies and lifestyle changes can slow or stop the disease and improve symptoms. They can lead full, active lives.
About 1 in 10 American adults who live with heart failure have advanced heart failure. That means treatments arent working, and symptoms are getting worse. You may feel symptoms, such as shortness of breath, even when youre sitting. If you have advanced heart failure, talk with your care team about important care decisions and next steps.
Summary Right Sided Vs Left Sided Heart Failure
When the heart fails to pump blood adequately to the body tissues, owing to the decrease in the pumping capacity of right heart chambers, that condition is identified as the right heart failure. On the other hand, when the heart failure is due to the faltering of the pumping capacity of the left heart chambers, it is known as left sided heart failure. Thus, the difference between right sided and left sided heart failure is that in right heart failure, the function of right heart chambers is impaired whereas the function of left heart chambers is impaired in the left heart failure.
Read Also: Why Does Heart Rate Increase During Running
Read Also: Which Statement Describe A Relationship Between Protein/amino Acids And Heart Disease
What Are The Different Types Of Chf
Heart failure can occur on the left side of the heart, the right side, or both. Most commonly, it begins in the heart’s primary pumping chamber – the left ventricle. Each specific type of CHF is accompanied by its own distinct characteristics:
- Right-sided CHF – Right-sided CHF develops when the right ventricle struggles to deliver blood to the lungs. As blood backs up into the blood vessels, the body begins to retain fluid in the abdomen and lower body.
- Left-sided CHF – Left-sided CHF is the most common form of CHF and begins when the left ventricle cannot effectively deliver blood throughout the body. Eventually, this can lead to fluid retention throughout the body, particularly around the lungs.
Cases of left-sided CHF can be further classified into one of two sub-types, characterized by the manner in which the ventricle is affected:
- Systolic CHF – Systolic CHF occurs when the left ventricle is unable to contract with enough force to circulate blood properly.
- Diastolic CHF – Diastolic CHF occurs when the heart muscle becomes stiff. Because the chamber must relax in order to fill with blood between contractions, this stiffness means that an inadequate amount of blood is available to pump out to the rest of the body.
About Heart And Vascular Institute
The UPMC Heart and Vascular Institute has long been a leader in cardiovascular care, with a rich history in clinical research and innovation. As one of the first heart transplant centers in the country and as the developer of one of the first heart-assist devices, UPMC has contributed to advancing the field of cardiovascular medicine. We strive to provide the most advanced, cutting-edge care for our patients, treating both common and complex conditions. We also offer services that seek to improve the health of our communities, including heart screenings, free clinics, and heart health education. Find an expert near you.
Tags
Also Check: How To Make Heart Palpitations Go Away
Precipitating Causes Of Heart Failure
A previously stable, compensated patient may develop heart failure that is clinically apparent for the first time when the intrinsic process has advanced to a critical point, such as with further narrowing of a stenotic aortic valve or mitral valve. Alternatively, decompensation may occur as a result of the failure or exhaustion of the compensatory mechanisms but without any change in the load on the heart in patients with persistent, severe pressure or volume overload. In particular, consider whether the patient has underlying coronary artery disease or valvular heart disease.
The most common cause of decompensation in a previously compensated patient with heart failure is inappropriate reduction in the intensity of treatment, such as dietary sodium restriction, physical activity reduction, or drug regimen reduction. Uncontrolled hypertension is the second most common cause of decompensation, followed closely by cardiac arrhythmias . Arrhythmias, particularly ventricular arrhythmias, can be life threatening. Also, patients with one form of underlying heart disease that may be well compensated can develop heart failure when a second form of heart disease ensues. For example, a patient with chronic hypertension and asymptomatic LV hypertrophy may be asymptomatic until an MI develops and precipitates heart failure.
- Profound anemia
You May Like: Who Performed The First Open Heart Surgery Successful
Left Side Of The Heart
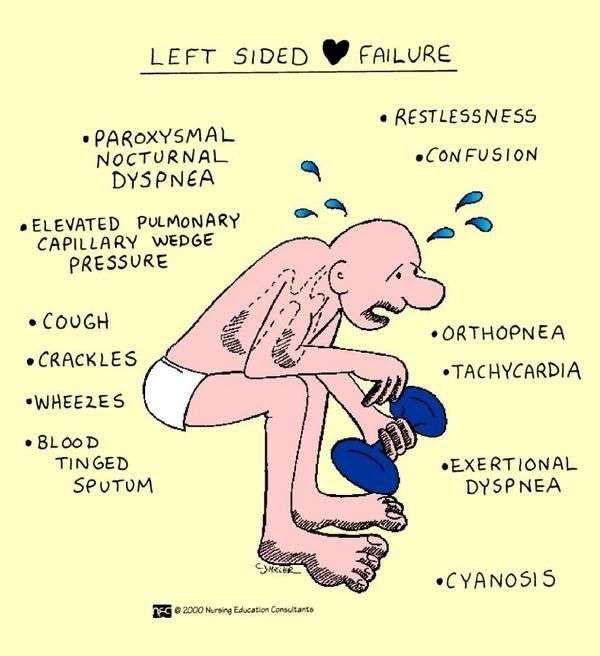
The job of the heart muscle is to transport oxygenated blood coming from the lungs to the left atrium and on through to the left ventricle. The left ventricle is the main pumping portion of the heart. It is larger than the other chambers and plays a fundamental role in normal heart function. When there is HF on the left side of the heart, the heart muscle has to work harder to squeeze out the same volume of blood. This is referred to as left ventricular heart failure. It is the most common type of HF.1
Also Check: What Should My Heart Rate Be While Working Out
You May Like: Can Zinc Cause Heart Palpitations
Types Of Heart Failure
divides heart failure into one of three categories based on the part of your heart thats affected:
- Diastolic failure. This means your left ventricle doesnt relax properly due to stiffness and your heart doesnt fill with enough blood between beats, or the pressure for the heart to function is very high.
- shortness of breath when lying down
- sleeping on extra pillows at night
