What Kind Of Blood Comes Back Into The Heart & Then Goes To The Lungs
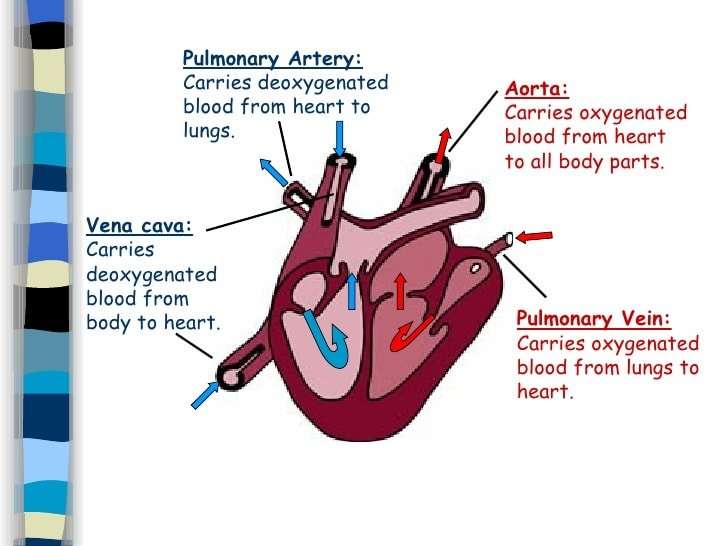
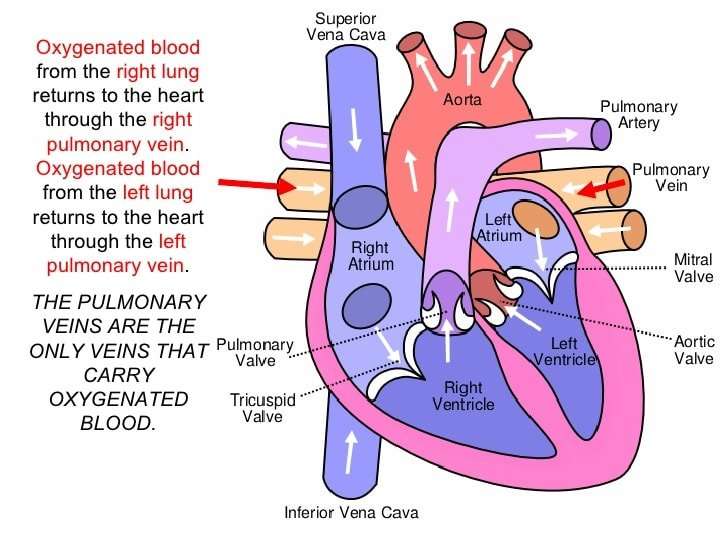
The heart consists of four chambers in which blood flows. Blood enters the right atrium and passes through the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs where it becomes oxygenated. The oxygenated blood is brought back to the heart by the pulmonary veins which enter the left atrium.
Arteries And Your Circulatory System
Arteries carry blood away from the heart in two distinct pathways:
- The systemic circuit. In this pathway, oxygen-rich blood is carried away from the heart and toward tissues of the body.
- The pulmonary circuit. In the pulmonary circuit, oxygen-depleted blood is carried away from the heart and into the lungs where it can acquire fresh oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide.
Arteries can also be divided into elastic and muscular arteries based off of the material of their tunica media or middle layer.
Elastic arteries
- are closer to the heart where blood pressure is highest
- contain more elastic fibers, which allows them to both expand and contract with the surges of blood that occur when the heart beats
Muscular arteries
- are further from the heart where blood pressure is lower
- contain more smooth muscle tissue and less elastic fibers
Classification & Structure Of Blood Vessels
Blood vessels are the channels or conduits through which blood is distributed to body tissues. The vessels make up two closed systems of tubes that begin and end at the heart. One system, the pulmonary vessels, transports blood from the right ventricle to the lungs and back to the left atrium. The other system, the systemic vessels, carries blood from the left ventricle to the tissues in all parts of the body and then returns the blood to the right atrium. Based on their structure and function, blood vessels are classified as either arteries, capillaries, or veins.
Read Also: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
What Are The Coronary Arteries
Like all organs, your heart is made of tissue that requires a supply of oxygen and nutrients. Although its chambers are full of blood, the heart receives no nourishment from this blood. The heart receives its own supply of blood from a network of arteries, called the coronary arteries.
Two major coronary arteries branch off from the aorta near the point where the aorta and the left ventricle meet:
- Right coronary artery supplies the right atrium and right ventricle with blood. It usually branches into the posterior descending artery, which supplies the bottom portion of the left ventricle and back of the septum with blood.
- Left main coronary artery branches into the circumflex artery and the left anterior descending artery. The circumflex artery supplies blood to the left atrium, side, and back of the left ventricle, and the left anterior descending artery supplies the front and bottom of the left ventricle and the front of the septum with blood.
These arteries and their branches supply all parts of the heart muscle with blood.
When the coronary arteries narrow to the point that blood flow to the heart muscle is limited , a network of tiny blood vessels in the heart that aren’t usually open called collateral vessels may enlarge and become active. This allows blood to flow around the blocked artery to the heart muscle, protecting the heart tissue from injury.
What Is The Vascular System
The vascular system, also called the circulatory system, is made up of the vessels that carry blood and lymph through the body. The arteries and veins carry blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body tissues and taking away tissue waste matter. The lymph vessels carry lymphatic fluid . The lymphatic system helps protect and maintain the fluid environment of the body by filtering and draining lymph away from each region of the body.
The vessels of the blood circulatory system are:
-
Arteries. Blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body.
-
Veins. Blood vessels that carry blood from the body back into the heart.
-
Capillaries. Tiny blood vessels between arteries and veins that distribute oxygen-rich blood to the body.
Blood moves through the circulatory system as a result of being pumped out by the heart. Blood leaving the heart through the arteries is saturated with oxygen. The arteries break down into smaller and smaller branches to bring oxygen and other nutrients to the cells of the body’s tissues and organs. As blood moves through the capillaries, the oxygen and other nutrients move out into the cells, and waste matter from the cells moves into the capillaries. As the blood leaves the capillaries, it moves through the veins, which become larger and larger to carry the blood back to the heart.
Also Check: Thrz Calculator
The Constant Pumping Of The Heart Maintains Blood Pressure And Supply Throughout The Body
The blood moving through the circulatory system puts pressure on the walls of the blood vessels. Blood pressure results from the blood flow force generated by the pumping heart and the resistance of the blood vessel walls. When the heart contracts, it pumps blood out through the arteries. The blood pushes against the vessel walls and flows faster under this high pressure. When the ventricles relax, the vessel walls push back against the decreased force. Blood flow slows down under this low pressure.
What Does The Heart Do
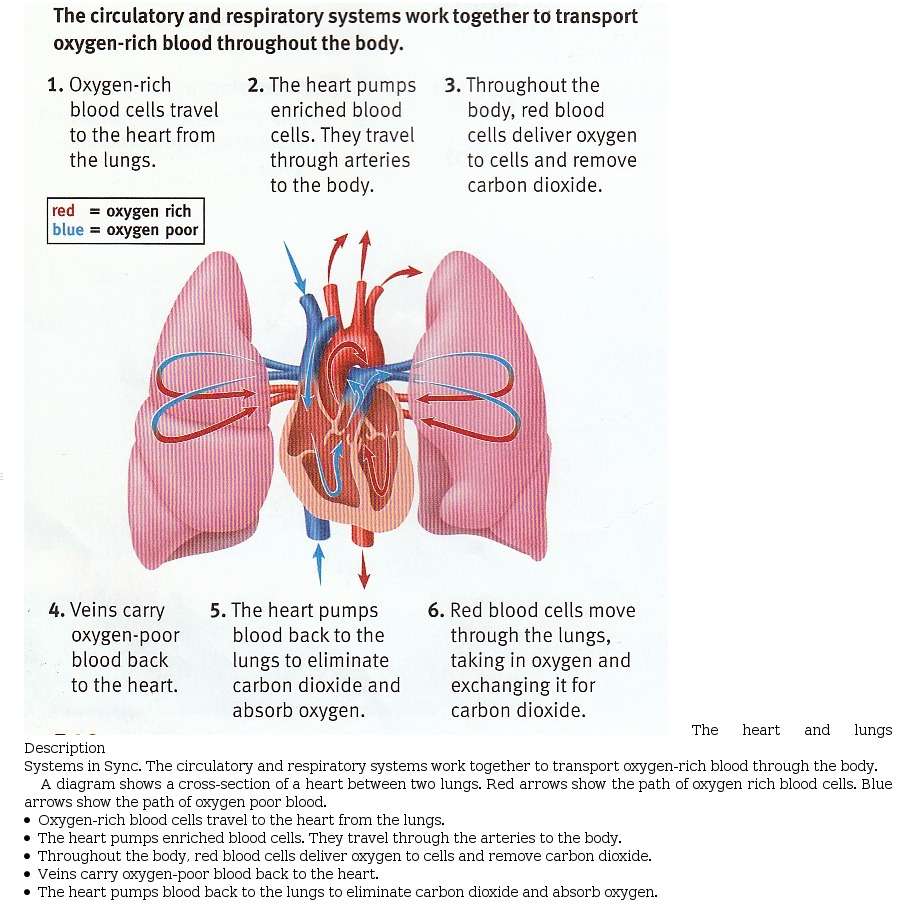
The heart is a pump, usually beating about 60 to 100 times per minute. With each heartbeat, the heart sends blood throughout our bodies, carrying oxygen to every cell. After delivering the oxygen, the blood returns to the heart. The heart then sends the blood to the lungs to pick up more oxygen. This cycle repeats over and over again.
Read Also: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Arteries In Systemic Circulation
The main artery of the systemic circulation is the aorta. It is attached to the left ventricle of the heart and carries oxygenated blood. The aorta branches into arteries that go to different organs and parts of the body. You can feel your pulse in an artery such as the carotid artery in the neck or the radial artery in the wrist.
The pulmonary artery differs from the others in that it is attached to the heart’s right ventricle and carries blood that is poor in oxygen to the lungs. There, it branches into arterioles and capillaries so the blood can take on oxygen before returning to the heart via the pulmonary vein. This oxygenated blood enters the left atrium and is pumped to the left ventricle and out through the aorta.
The Blood Supply To The Heart
Like any other muscle, the heart muscle needs a good blood supply. The coronary arteries take blood to the heart muscle. These are the first arteries to branch off the large artery which takes blood to the body from the left ventricle.
- The right coronary artery mainly supplies the muscle of the right ventricle.
- The left coronary artery quickly splits into two and supplies the rest of the heart muscle.
- The main coronary arteries divide into many smaller branches to supply all the heart muscle.
You May Like: How Much Can Marijuana Increase A Person’s Heart Rate
How Does Blood Travel Through The Heart
As the heart beats, it pumps blood through a system of blood vessels, called the circulatory system. The vessels are elastic tubes that carry blood to every part of the body.
Blood is essential. In addition to carrying fresh oxygen from the lungsand nutrients to your body’s tissues, it also takes the body’s waste products, including carbon dioxide, away from the tissues. This is necessary to sustain life and promote the health of all the body’s tissues.
There are three main types of blood vessels:
- Arteries. They begin with the aorta, the large artery leaving the heart. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to all of the body’s tissues. They branch several times, becoming smaller and smaller as they carry blood farther from the heart.
- Capillaries. These are small, thin blood vessels that connect the arteries and the veins. Their thin walls allow oxygen, nutrients, carbon dioxide, and other waste products to pass to and from our organ’s cells.
- Veins. These are blood vessels that take blood back to the heart this blood lacks oxygen and is rich in waste products that are to be excreted or removed from the body. Veins become larger and larger as they get closer to the heart. The superior vena cava is the large vein that brings blood from the head and arms to the heart, and the inferior vena cava brings blood from the abdomen and legs into the heart.
Blood flows continuously through your body’s blood vessels. Your heart is the pump that makes it all possible.
What Are The Heart And Blood Vessels
Blood vessels form the living system of tubes that carry blood both to and from the heart. All cells in the body need oxygen and the vital nutrients found in blood. Without oxygen and these nutrients, the cells will die. The heart helps to provide oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues and organs by ensuring a rich supply of blood.
Not only do blood vessels carry oxygen and nutrients, they also transport carbon dioxide and waste products away from our cells. Carbon dioxide is passed out of the body by the lungs most of the other waste products are disposed of by the kidneys. Blood also transports heat around your body.
Anatomy of the heart and blood vessels
Don’t Miss: Does A Higher Heart Rate Burn More Calories
What Are The Different Coronary Arteries
The 2 main coronary arteries are the left main and right coronary arteries.
-
Left main coronary artery . The left main coronary artery supplies blood to the left side of the heart muscle . The left main coronary divides into branches:
-
The left anterior descending artery branches off the left coronary artery and supplies blood to the front of the left side of the heart.
-
The circumflex artery branches off the left coronary artery and encircles the heart muscle. This artery supplies blood to the outer side and back of the heart.
Right coronary artery . The right coronary artery supplies blood to the right ventricle, the right atrium, and the SA and AV nodes, which regulate the heart rhythm. The right coronary artery divides into smaller branches, including the right posterior descending artery and the acute marginal artery. Together with the left anterior descending artery, the right coronary artery helps supply blood to the middle or septum of the heart.
Smaller branches of the coronary arteries include: obtuse marginal , septal perforator , and diagonals.
What Happens When Blood Travels From Arteries To Veins
Capillaries connect the arteries to veins. The arteries deliver the oxygen-rich blood to the capillaries, where the actual exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs. The capillaries then deliver the waste-rich blood to the veins for transport back to the lungs and heart. Veins carry the blood back to the heart.
Read Also: Does Benadryl Increase Heart Rate
What Is The Difference Between An Artery And A Vein
- carry blood from the tissues of the body back to the heart
- are usually positioned closer beneath the surface of the skin
- are less muscular than arteries, but contain valves to help keep blood flowing in the right direction, usually toward the heart
- would collapse if blood flow stops.
- carry blood away from the heart to the tissues of the body
- are usually positioned deeper within the body
- are more muscular than veins, which helps in transporting blood that is full of oxygen efficiently to the tissues
- would generally remain open if blood flow stopped, due to their thick muscular layer.
You may have been told that you had a heart attack or a stroke because of a blocked artery. What exactly is an artery?
Arteries, like veins, are tube-shaped vessels that carry blood in the body. The chief difference between arteries and veins is the job that they do. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body, and veins carry oxygen-poor blood back from the body to the heart.
Your body also contains other, smaller blood vessels. Here is how blood travels in vessels through the body:
What Are The Parts Of The Circulatory System
Two pathways come from the heart:
- The pulmonary circulation is a short loop from the heart to the lungs and back again.
- The systemic circulation carries blood from the heart to all the other parts of the body and back again.
In pulmonary circulation:
- The pulmonary artery is a big artery that comes from the heart. It splits into two main branches, and brings blood from the heart to the lungs. At the lungs, the blood picks up oxygen and drops off carbon dioxide. The blood then returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins.
In systemic circulation:
Read Also: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Blood Vessels Leading Into And Out Of The Heart
There are four main blood vessels that take blood into and out of the heart.
Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart .
The main artery is the aorta.
The main vein is the vena cava.
How Does Blood Flow Through Your Lungs
Once blood travels through the pulmonic valve, it enters your lungs. This is called the pulmonary circulation. From your pulmonic valve, blood travels to the pulmonary artery to tiny capillary vessels in the lungs.
Here, oxygen travels from the tiny air sacs in the lungs, through the walls of the capillaries, into the blood. At the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, passes from the blood into the air sacs. Carbon dioxide leaves the body when you exhale. Once the blood is purified and oxygenated, it travels back to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
Read Also: How Does Heart Disease Affect The Skeletal System
What Is Vascular Disease
A vascular disease is a condition that affects the arteries and veins. Most often, vascular disease affects blood flow, either by blocking or weakening blood vessels, or by damaging the valves that are found in veins. Organs and other body structures may be damaged by vascular disease as a result of decreased or completely blocked blood flow.
How Arteries And Veins Work Together
âArteries and veins work together to keep blood flowing throughout your body smoothly. They connect through structures called capillaries. Capillaries are small webs of thin tubes that connect to an artery on one side and a vein on the other.â
You have capillaries throughout your body. Some parts of your body have more capillaries depending on how much energy they need. For example, your muscles use a lot more energy than your skin, which is why your muscles have more capillaries than your outer skin.
You May Like: Afrin Heart Palpitations
What Causes Clogged Arteries
Clogged arteries are caused by a buildup of plaque in your arteries. Plaque is usually made up of a few substances, including minerals like calcium, or fats and cholesterol. High cholesterol levels can lead to this buildup of plaques.
In some cases, high cholesterol is genetic, but it is mostly linked to diet and lifestyle choices.
What Are The Different Types Of Arteries
There are three types of arteries. Each type is composed of three coats: outer, middle, and inner.
- Elastic arteries are also called conducting arteries or conduit arteries. They have a thick middle layer so they can stretch in response to each pulse of the heart.
- Muscular arteries are medium-sized. They draw blood from elastic arteries and branch into resistance vessels. These vessels include small arteries and arterioles.
- Arterioles are the smallest division of arteries that transport blood away from the heart. They direct blood into the capillary networks.
There are four types of veins:
- Deep veins are located within muscle tissue. They have a corresponding artery nearby.
- Superficial veins are closer to the skins surface. They dont have corresponding arteries.
- Pulmonary veins transport blood thats been filled with oxygen by the lungs to the heart. Each lung has two sets of pulmonary veins, a right and left one.
- Systemic veins are located throughout the body from the legs up to the neck, including the arms and trunk. They transport deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Use this interactive 3-D diagram to explore an artery.
Use this interactive 3-D diagram to explore a vein.
Also Check: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
How Do The Heart And Blood Vessels Work
The heart works by following a sequence of electrical signals that cause the muscles in the chambers of the heart to contract in a certain order. If these electrical signals change, the heart may not pump as well as it should.
The sequence of each heartbeat is as follows:
- The sinoatrial node in the right atrium is like a tiny in-built ‘timer’. It fires off an electrical impulse at regular intervals. This controls your heart rate. Each impulse spreads across both atria, which causes them to contract. This pumps blood through one-way valves into the ventricles.
- The electrical impulse gets to the atrioventricular node at the lower right atrium. This acts like a ‘junction box’ and the impulse is delayed slightly. Most of the tissue between the atria and ventricles does not conduct the impulse. However, a thin band of conducting fibres called the atrioventricular bundle acts like ‘wires’ and carries the impulse from the AV node to the ventricles.
- The AV bundle splits into two – a right and a left branch. These then split into many tiny fibres which carry the electrical impulse throughout the ventricles. The ventricles contract and pump blood through one-way valves into large arteries:
- The arteries going from the right ventricle take blood to the lungs.
- The arteries going from the left ventricle take blood to the rest of the body.
