What Happens During Catheter Ablation
A doctor with special training performs the procedure along with a team of nurses and technicians. The procedure is done in a hospital EP or cath lab.
NOTE: During this procedure, the tip of a catheter is guided to the area of heart tissue that is producing abnormal electrical signals. Then the catheter emits a pulse of painless radiofrequency energy that destroys the abnormal tissue and corrects the irregular heartbeat.
What Happens After Heart Surgery
After your heart surgery is done, youll be moved to the intensive care unit . Youll recover in the ICU for at least one day. Youll then move to a regular hospital room for continued rest and care.
How long you stay in the hospital depends on the surgery you had and how your body responds to it. Each persons recovery is different. Your hospital team will keep a close eye on you and make sure youre healing as you should. Theyre also prepared to notice and respond to any problems that come up.
Ablation After The Procedure
When your procedure is finished, all the tubes and wires are removed. Sometimes there can be a small amount of bleeding from the groin area when they are taken out. Pressure will be put on the area for a short while to stop any bleeding. Some bruising and tenderness is not uncommon.
You will be kept lying flat on your back for a few hours and may be kept in hospital overnight. Many people feel tired afterwards, but within a few days you should feel back to normal.
You May Like: How Does A Heart Attack Affect The Body
The Pros Of Ablation For Atrial Fib
1. There is a greater chance of reducing symptoms with this procedure. Ablation works by destroying the abnormal heart tissues that are causing the muscle to beat in an irregular way. Through the use of radio frequencies, the tissue is either burned or frozen. This means it is very possible for someone to feel much better almost immediately after the procedure has been completed.
2. The procedure has a high success rate. When all patients are considered, the success rate of ablation falls between 70-80% for reliving symptoms. When only patients who are younger and have no heart disease that could be causing the issue are considered, the chances of success rise to at least 95%. Older patients with heart disease may have a success rate as low as 40%. Experienced doctors who perform this procedure on a regular basis tend to see the best success rates.
3. There are few complications that result from ablation. Fewer than 5% of people who undergo this procedure develop any problems after it has been completed. A catheter is used to reach the heart so the abnormal tissue can be destroyed, so the most common issue is to have vessel damage occur. This may cause bleeding or an infection. The chances of heart failure or stroke are listed as being lower than 1% during the procedure.
Progression And Regression Of Atrial Fibrillation
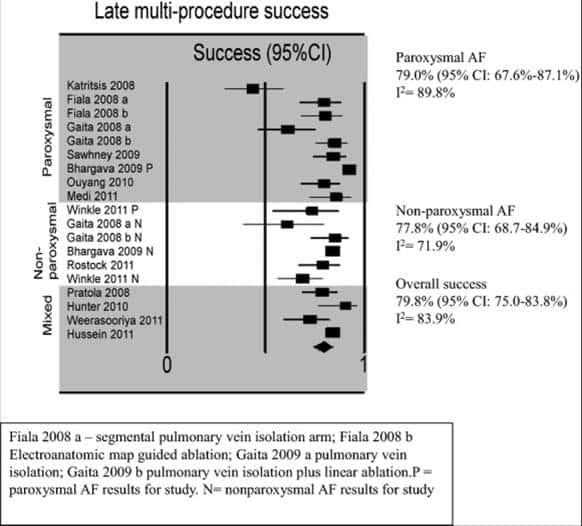
Several studies have described the natural progression from PAF to chronic forms of AF over time.,,,, Progression rates ranging from 5 to 20% per annum have been reported, while risk factors for AF progression are summarized and included in the HATCH score., In contrast, a reduction in the rate of progression could be demonstrated after catheter ablation of PAF and when compared with medical treatment only. In the present study, the rate of progression from PAF to persistent AF over a FU period of 37 ± 20 months was only 5.6%. The rates of regression from persistent AF to PAF and from long-standing persistent AF to PAF were 21 and 20%, respectively. Hence, even in the very elderly, if catheter ablation proves unsuccessful in maintaining SR, the conversion of non-paroxysmal types of AF to PAF may benefit some patients.
Don’t Miss: How Does Sleep Number Measure Heart Rate
Related: This Team Is On The Verge Of Creating A Beating Band
He considers it telling that off-pump coronary bypass surgeries in the U.S. dropped from 23 percent in 2002 to 17 percent in 2012.
The vast majority of cardiac surgeons dont want to hurt their patients, and while they want to be innovative, I think when they stop doing this operation, you know that theres got to be a problem, he said.
Repeat Procedures Due To Recurrence Of Atrial Arrhythmia
In patients with recurrent atrial arrhythmias during follow-up , a repeat procedure was recommended. During the repeat procedure, previously isolated PVs were assessed for re-conduction. If PV re-conduction was present, repeat PVI was performed as described above. In case of failure to restore SR after PVI by ECV, or if the PVs were still isolated, CFAE ablation was performed and/or linear lesion sets were placed as described above. In patients presenting with an AT, activation and entrainment mapping and focal ablation or ablation of linear lesion sets was performed followed by repeat PVI, if necessary.
You May Like: How To Calculate Your Target Heart Rate Zone
What Are The Risks Of Catheter Ablation
There are few risks. The most common problems result from the use of the catheters long, thin tubes doctors insert into your arteries or veins. Inserting the tubes can occasionally damage your blood vessel or cause bleeding or infection. These problems are rare.
“I was in the emergency department every few days with SVT. I felt awful and the medicines just werent working. After catheter ablation I can go to work and exercise without SVT.” Bill, age 61.
What Happens After The Procedure
After the procedure you will wake up in a hospital ward called the recovery area. When you are completely awake you will be transferred to the normal hospital ward. You will have to lie flat for approximately 4- 6 hours after the procedure. During this time, it is important to keep your legs straight and your head relaxed on the pillow. You will have a compression clamp on the groin area which stays in place for 4-6 hours. You will need to stay in hospital overnight after the procedure connected to the heart monitor. You will be reviewed by the Arrhythmia team the following day prior to your discharge.
Whilst in hospital you will either continue your blood thinning medications or commence blood thinning injections.
It is common to have a sore throat and some mild chest discomfort after the procedure. You will also have some discomfort and bruising in the groin after the procedure. This should usually improve over several days. Because it takes several weeks for the areas of ablation to heal and form scars, it is not uncommon to experience abnormal or irregular heart beat or rhythm for up to 4 weeks after the procedure.It is important that you monitor your groin for signs of bleeding and have adequate rest at home to help recover.
You May Like: What Are The Signs Of A Woman Having A Heart Attack
Is Catheter Ablation The Best Option For Your Svt
The cardiologists consider ablation a curative therapy with a success rate of over 90%. The ideal candidate for ablation must meet one or more conditions such as:
- a highly symptomatic patient with frequent episodes of arrhythmias
- somebody who does not tolerate medical therapy or has severe adverse drug reactions
- arrhythmia can no longer be treated with medication from various reasons
- the patient has been diagnosed with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome and presents a family history of sudden cardiac death
- the patient presents with ectopic beats that affect the quality of his/her life
- if abnormal electrical activity of the heart increases the risk of ventricular fibrillation
For patients who have rare episodes of tachycardia or can control these symptoms through various techniques and medication, for them, ablation might not be the best solution.
However, the choice belongs entirely to the patient, but he or she is helped by the specialized and precious indications of the cardiologist.
How Does Atrial Fibrillation Occur
Atrial fibrillation is due to the development of electrical short circuits inside the top chambers of the heart. Usually these short circuits begin in the top chamber on the left . They are usually triggered by abnormal electrical activity located within the veins that drain blood from the lungs back to the heart .
These rapid short circuits have several consequences:
1. The short circuits drive the pumping chambers rapidly and erratically. This produces palpitations, shortness of breath, and tiredness. In some people it can also cause dizzyness and chest pain. It usually reduces your exercise or physical capacity. It is NOT however a life-threatening rhythm disturbance.
2. The short circuits result in ineffective pumping of the upper chambers. This leads to slow blood flow in both of these upper chambers . This can rarely cause blood clots and possibly stroke. For this reason many patients with atrial fibrillation will require a blood thinner. This may be aspirin, warfarin or one of the newer medications .
Also Check: What Causes Heart Attacks In Women
What Happens In A Heart Ablation
When used for heart rhythm problems such as palpitations, the goal of a heart ablation is to get rid of the tissue that is causing the problem. For example, lets say palpitations are being caused by a small focus of tissue in the upper chamber of the heart. A small tube known as a catheter is passed up to the heart and directed to the area where the palpitation are arising. Electrical energy is then passed through the tube to the end by a wire, essentially burning away the affected area. If successful, this will serve to stop the palpitations.
An alcohol septal ablation for a thick heart is different. In this condition the thick heart obstructs blood that is trying to leave the heart. A catheter is advanced into the coronary arteries that supply the heart with blood. The artery that supplies the thick area is located and alcohol delivered to that area to kill it off so it shrinks. If successful, this will allow blood to flow normally again.
Heart Ablation For Ventricular Tachycardia
VT is a dangerous heart rhythm that can lead to sudden death if not treated. The treatment of VT depends on the underlying cause. There is increasing use of catheter ablation for VT, particularly in those who have not responded to medicines. In a VT ablation, the area of the heart where the dangerous rhythm is starting is identified and then energy applied to that area to prevent it from occurring.
Read Also: How To Slow Down Heart Rate After Adderall
Ablation How Is It Performed
As ablation causes little or no pain, you are usually mildly sedated with local anaesthetic. Long, flexible tubes are inserted through a vein in your groin or at your neck and threaded up to your heart. Once they are in the correct position, high frequency energy is sent through the wire to heat up and destroy an area of tissue that is causing the arrhythmia or irregular heart beat. This procedure usually takes 2 to 4 hours but if more complicated can take longer.
The Potential Risks And Complications Of A Catheter Ablation
Just like any other surgery or medical procedure, deciding to undergo a catheter ablation is not without risks. Despite being a minimally invasive procedure option that most patients recover from quite quickly, it is important to know that you may experience a potential complication if you choose to undergo a catheter ablation for your atrial fibrillation. In most centers, risks for major complications are less than 1%. If you have any questions about the procedure and its risk, you should speak to your doctor before your surgery date to ensure that you make the right choice for your needs.
Some of the most common risks and complications of a catheter ablation include:
-
Bleeding or getting an infection from the catheter insertion site
-
Damaging the lining of the vein or vessel used during the procedure
-
Puncturing the heart tissue, resulting in bleeding around the heart, sometimes requiring emergency drainage.
-
Post-operative blood clots
-
Narrowing or scarring of the vascular vessel used during the procedure
-
Complications from radiation exposure during surgery
-
Allergic reactions to the anesthesia medications
-
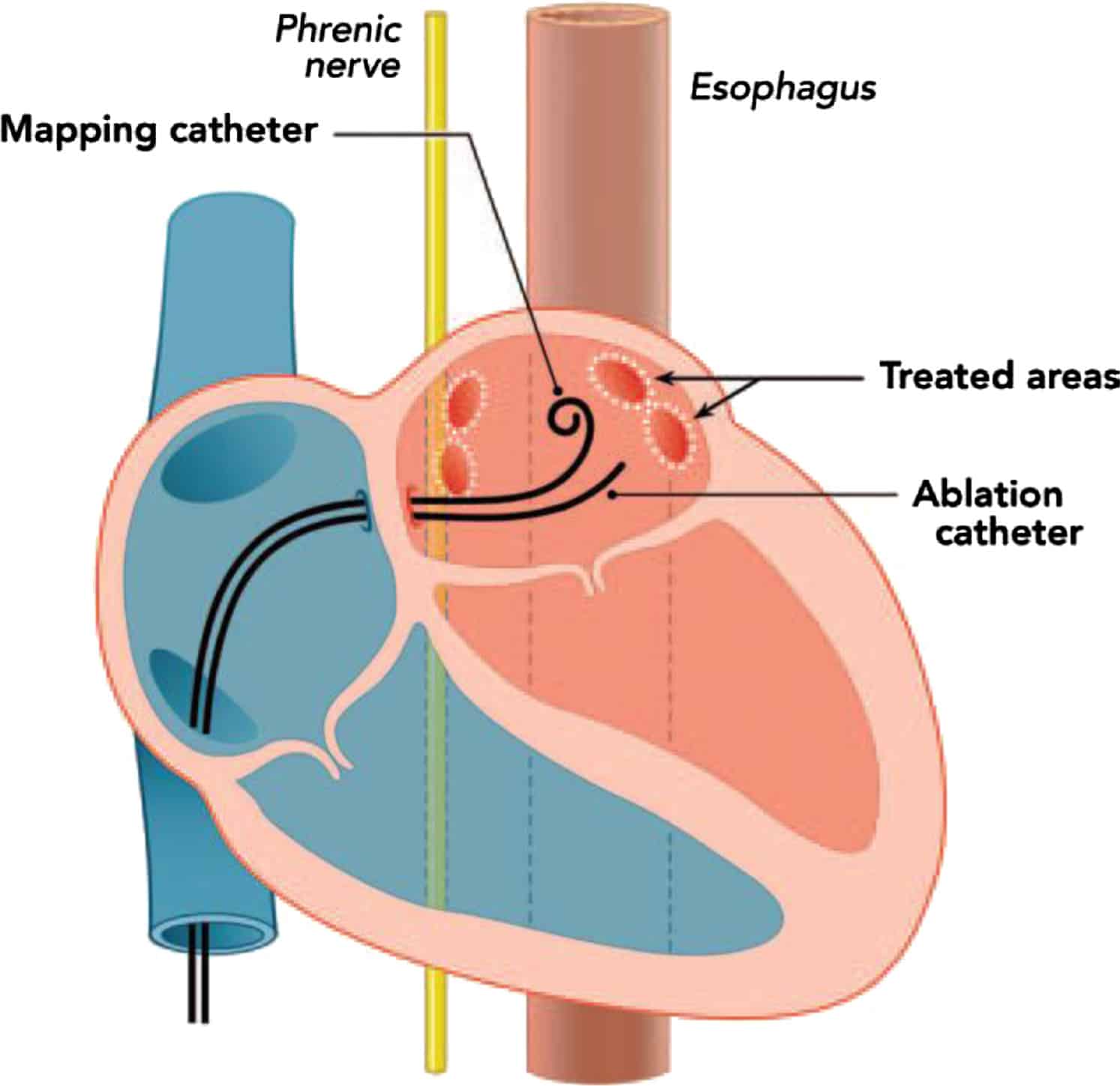
Damage to the esophagus
To minimize the potential risks of choosing this treatment option, be sure to talk to your provider to ensure that you are physically fit for surgery and that the benefits of the procedure outweigh the risks to ensure your safety. Also, ask your doctor what precautions they take to minimize these risks.
Recommended Reading: Why Does My Resting Heart Rate Keep Going Up
A Potential Cure For Afib
Fortunately, people living with AFib have a variety of treatment options available to help control the irregular rhythms, improve heart function and increase quality of life. For many people, AFib can be managed with the use of medications such as blood thinners, heart rate control medications or antiarrhythmic drugs.
However, if medications do not work, cause side effects, or a patient does not want to be dependent on medication, there is a procedure called catheter ablation. This minimally invasive, percutaneous and relatively pain-free procedure can stabilize the heartbeat by electrically isolating the AFib triggers or disrupting the atrial substrate changes, allowing normalization of the heart rhythm.
Ablation is a potentially curative approach for treating atrial fibrillation, says University Hospitals cardiologist and Director of Clinical Electrophysiology Mauricio Arruda, MD. Ablation can completely eliminate or significantly decrease episodes of AFib, decreasing the need for hospitalization, and decreasing the risk of death in the AFib population.
A Failing Electrical System
AFib can present in a variety of ways. While irregular heart rhythms may be persistent or permanent for some patients, others may experience paroxysmal or intermittent AFib, which can occur suddenly, last seconds, minutes or even hours, and may resolve on its own. Paroxysmal AFib is actually no less concerning and can be dizzying and scary for a person unaware of whats happening.
The majority of people with AFib dont even know their heart is malfunctioning this way. They may go to a doctor for a check-up, or for a work-up before a procedure, and an EKG reveals their heart is in AFib. Joe just happened to learn about his AFib during a routine physician office visit. He had no idea the heaviness in his chest and unexplained fatigue was the result of AFib.
Actually, when heart palpitations are not present, the majority of patients symptoms are not attributed to the heart, says Dr. Rushing. They show up at their doctors office for a cholesterol evaluation, or to get ready for a colonoscopy, and AFib is an incidental finding.
Surgical ablation uses either heat or cold energy to electrically isolate the tissue of a small part of the heart to stop its quivering.
This is not an option for patients who have already had heart surgery due to scar tissue, he added. For those patients, open heart surgery is the only option.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Normal Fetal Heart Rate
Impact Of Ablation Techniques
Whereas a consensus has been reached on the suitable approach forablation of patients with paroxysmal AF, no such consensus existsfor patients with persistent and long lasting persistent AF regardingthe optimal technology of treatment.
Numerous clinical trials demonstrated that the main mechanism of AF recurrence after PVI in the paroxysmal population is theresumption of electrical conduction between the veins and left atrialmuscle. This statement is true for either the short or the long termrecurrences . Based upon these observations we shouldassume that at least in PAF, the durability of venous isolation andtherefore permanent electrical disconnection plays a crucial role inmaintaining procedural effectiveness in the long term. Accordingly,any kind of procedural tool or technique which can facilitate the durable isolation of pulmonary veins can be useful.
As mentioned earlier, in patients with persistent and longstandingpersistent AF the data concerning the outcomes are considerably lessfavorable than for PAF. The wide contrast in PVI success rates betweenparoxysmal and persistent AF suggested that the mechanisms can besubstantially different, and probably related to electrophysiologicaland structural remodeling of left atrial substrate. Not surprisingly,current approaches designed to target persistent AF are mainlybased on modification of the atrial substrate, but exhibit remarkabledifferences, and a widely accepted uniform strategy is missing.
Overall Mortality Rates And Survival
In total data on 33 094 interventions were extracted from the NVT national database. The study population is described in Table . The total follow-up time after intervention was 90 386.6 years and the mean follow-up time was 996.9 days. Early mortality rates using the different measures are presented in Fig. . Mortality after discharge from the primary hospital was doubled after 1 year: from 972 deaths to 2052 deaths . In-hospital and 30-day mortalities were nearly identical. However, in Table the difference between these outcome measures is shown. Approximately 20% of all deaths during admission occur after 30 days. The other way around holds true as well: 20% of all deaths within 30 days occur at home or at another care facility.
KaplanMeier survival curve with 95% CI after cardiac surgery. The green line represents the survival rate of the age-matched general population in The Netherlands. The survival rate of the cardiac surgery population equals that of the general population from approximately 120 days after surgery onwards. The hazard after cardiac continues to decline well after 30 days postoperatively. The constant phase of the hazard seems to start after 120 days.
Also Check: Congestive Heart Failure And Kidney Failure
Are There Alternative Remedies I Should Consider For Treating Svt
Alternative treatments are useful in treating arrhythmias, but we must consult a specialist who will recommend the appropriate therapies for the type of arrhythmia we have.
As individuals, we are each different, and unlike traditional medicine, when we talk about an alternative treatment, there is no standard treatment for everyone.
If you want to be successful in using alternative methods, find an excellent integrative heart doctor, discover the cause of your tachycardia and follow the treatment indicated by the specialist. Most of the time, you will not only have to drink tea or take a supplement, but the program will be much more complicated, including changes in lifestyle like diet, sleep and exercise.
