Why Are Heart Attacks So Unpredictable
After youve survived your heart attack, your cardiologist will most likely order a nuclear stress test every year, to determine when you might need a stent, or another stent. But, when you had your heart attack, the stent they put in only keeps open the obstructive lesion right there. That stent cannot prevent another heart attack in a vulnerable plaque somewhere else. Why not?
As time goes on, artery disease slowly and steadily gets worse, as illustrated below, Chest pain occurs when the blood flow is cut off. Notice the two red arrows below, showing the blood flow. The small one on the right is in “obstructive” artery disease where the blockage obstructs the flow of blood, so the blood can’t get through the artery to the heart muscle. This is the type blockage that causes chest pain when someone is exercising. Obstructive blockage is why we do stress tests, to find someone who needs a stent or bypass surgery.
But that’s not where most heart attacks strike.
Stress tests are designed to identify obstructive plaque. But most heart attack patients would have passed the stress test the day before. Vulnerable plaque doesn’t show up on a stress test. Only obstructive plaque does.
This is why heart attacks are so unpredictable. Most heart attacks shut off the blood flow suddenly and without warning.
The arteries weve treated speak for themselves. To see how our program works on the actual arteries, before and after treatment, click this button:
Specialized Treatment And Technology In Zanesville Is Saving Lives
In acute cases like Higgins, excellent, local medical care is vital for survival. In the old days, before Genesis had a heart program doing these procedures, patients were transferred to Columbus 60 miles from here which delayed treatment, recalls Dr. Albirini. Now, our communities have access to outstanding care close to home it makes a big difference in outcomes.
In fact, Genesis Hospital provides superior heart and vascular care compared to the majority of the heart centers around the nation, according to national quality indicators collected by the American College of Cardiology. We are successful because we have the expertise, the technology, and we work so well together. The ED team, the cardiologists, the technicians and nurses everyone knows his or her role and treats the patient promptly, Dr. Albirini says.
What To Do If You Recognize A Heart Attack
If you think theres any chance you or someone else may be having a heart attack, you need to get medical help as quickly as possible. Even if it turns out to be something else, it is better to act quickly than risk putting your life on the line.
If you recognize the signs of a heart attack, call 9-1-1 immediately. The sooner that treatment begins, the greater likelihood that you can minimize damage to the heart.
The person having the symptoms should not drive. Always have someone else drive you to the hospital if you are not being transported by ambulance.
If the person goes unconscious, you can start cardiopulmonary resuscitation while you wait for emergency medical services . If you are in a public place, ask if there is an AED on site. An AED is a portable device that can check someone’s heart rhythm and, if necessary, deliver an electric shock to help someone who is in cardiac arrest.
Find trainings in CPR and AED use through the American Red Cross, so you are prepared if you are ever in an emergency situation.
Also Check: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Heart Attack Before 50 Ups Early Death Risk
But healthy living can improve those odds, experts say
HealthDay Reporter
TUESDAY, Aug. 30, 2016 — The risk of early death after a heart attack has lessened over the past 30 years among those younger than 50. But it’s still nearly twice as high as the general public, Danish researchers report.
This higher risk is driven mainly by conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes and obesity, which are more common among people who’ve had a heart attack, said lead researcher Dr. Morten Schmidt.
“Patients with a heart attack in young age should be advised that an excess risk of fatal events persists, warranting compliance to their prescribed medicine and efforts to reduce modifiable lifestyle-related risk factors, particularly smoking,” said Schmidt, a researcher at Aarhus University Hospital in Denmark.
Schmidt’s team looked at long-term survival of nearly 22,000 Danes who’d had a heart attack before age 50. The patients were followed for roughly 11 years, and compared with almost 217,000 people in the general population.
The researchers found some good news. Between 1980-1989 and 2000-2009, premature deaths within the first 30 days after a heart attack dropped from 13 percent to 3 percent. Deaths from 31 days to one year fell from about 5 percent to 1.6 percent, while deaths from one to 10 years after a heart attack declined from 24 percent to 9 percent.
The reason for this gender difference is not known, Schmidt said.
Show Sources
Circulation
Strong Family History Genetic Factors Increase Heart Disease Risk
Family history
Having a strong family history of heart disease is partly due to genetics and partly due to other factors. Approximately 10% to 15% of the U.S. population has a strong family history of heart disease. The risks in this group can include family traditions such as preferring sedentary instead of active family time or eating meals that typically include more unhealthy than healthy options.
Additionally, certain conditions that affect heart disease risk, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, tend to run in families. In others, the risk factor levels are OK and individuals are leading a healthy lifestyle, but there still are premature heart attacks in a family. These are the most challenging situations that can benefit from evaluation by a specialist. In fact, if both of your parents had a heart attack before they turned 50, you are seven times more likely to have one yourself.
Our health is strongly tied to our environment if we have been taught or cornered into a certain way of life, it can become “the norm.” Breaking that cycle can be a tough, but it’s absolutely possible with a support network and the guidance of a preventive cardiologist.
Genetic factors
It seems illogical that a healthy person who is active and strong can have a heart attack. But it happens, and when it does, the cause almost always is a genetic condition that runs in the family.
Related reading: 10 truths about statins and high cholesterol
Recommended Reading: What Is Your Max Heart Rate
Heart Attack Statistics By Age
Heart attacks have been the major cause of death across the world. The heart attack statistics available to us from sources in the medical field support this fact clearly. So, in this article, let us go through some statistics to understand the connection between heart attacks and the age of a person.
Heart attacks have been the major cause of death across the world. The heart attack statistics available to us from sources in the medical field support this fact clearly. So, in this article, let us go through some statistics to understand the connection between heart attacks and the age of a person.
A heart attack, or myocardial infarction, is caused due to a blockage in the flow of blood to the heart. The main cause of heart attacks is believed to be fatty deposits on the walls of arteries. Fat deposits leads to the narrowing of the arteries and they get ruptured, leading to clotting of bloodstream. The statistics related heart attacks, by age, reveals that this ailment leads to more deaths as compared to various other serious ailments. Family history, work related stress, lack of proper sleep, smoking, drinking excessively and lack of exercise are the main reasons for heart attacks. Given below are some heart attack statistics which you need to read carefully to get an idea of how heart attacks affect people of different ages.
Heart Failure Life Expectancy Calculator
Prognostic Utility and Clinical Significance of Cardiac Mechanics in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection FractionPredicting survival in heart failure: a risk score based on 39 372 patients from 30 studiesACC/AHA Guidelines for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Heart Failure in the Adult: Executive Summary A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines
The heart failure life expectancy calculator is a simple, yet effective, tool for predicting the 1-year and 3-year survival odds of someone with congestive heart failure.
In the article below, we will focus on congestive heart failure/CHF prognosis, the estimates on how long can you live with congestive heart failure, and the average CHF life expectancy for a given stage of the disease.
Recommended Reading: How To Take Your Heart Rate
Copy The Linklink Copiedmortality From Circulatory Diseases
Circulatory diseases notably heart attack and stroke remain the main cause of mortality in most OECD countries, accounting for almost one in three deaths across the OECD. While mortality rates have declined in most OECD countries over time, population ageing, rising obesity and diabetes rates may hamper further reductions . Indeed, slowing improvements in heart disease and stroke are one of the principal causes of a slowdown in life expectancy gains in many countries .
Heart attacks and other ischaemic heart diseases accounted for 11% of all deaths in OECD countries in 2017. IHDs are caused by the accumulation of fatty deposits lining the inner wall of a coronary artery, restricting blood flow to the heart. Mortality rates are 80% higher for men than women across OECD countries, primarily because of a greater prevalence of risk factors among men, such as smoking, hypertension and high cholesterol.
Among OECD countries, central and eastern European countries have the highest IHD mortality rates, particularly in Lithuania where there are 383 deaths per 100 000 people . Rates are also very high in the Russian Federation. Japan, Korea and France have the lowest rates among OECD countries, at about one quarter of the OECD average and less than a tenth of rates in Lithuania and the Russian Federation .
Deaths from ischaemic heart disease are classified to ICD-10 codes I20-I25, and cerebrovascular disease to I60-I69.
Outdoor Temperature Can Affect Your Chances Of Having A Heart Attack
Large day-to-day swings in temperature were associated with significantly more heart attacks in a study presented at the American College of Cardiologys 67th Annual Scientific Session.
Given that some climate models link extreme weather events with global warming, the new findings suggest climate change could, in turn, lead to an uptick in the occurrence of heart attacks.
Adults who report puffing e-cigarettes, or vaping, are significantly more likely to have a heart attack compared with those who dont use them.
E-cigarettes are battery-operated devices that mimic the experience of smoking a cigarette.
A recent study found that compared with nonusers, e-cigarette users were 56 percent more likely to have a heart attack and 30 percent more likely to have a stroke.
Don’t Miss: What Heart Rate Is Dangerous
High Blood Pressure Causes 47% Of Coronary Heart Diseases
As its other name, silent killer, indicates, high blood pressure rarely shows any symptoms. However, if not controlled, it can be harmful and even accelerate the heart attack frequency. Measuring it is the only way to know whether you have it. One should also aim to make some lifestyle changes or take some medicine to lower hypertension and reduce the risk of a heart attack.
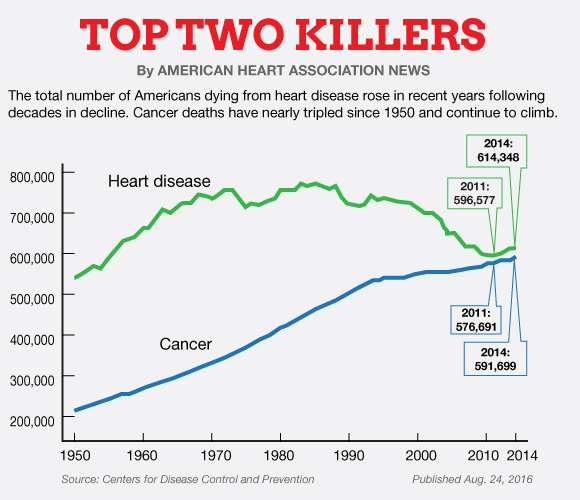
The Top Cause Of Death In 2020 In The Us Was Heart Disease
Heart attack deaths in 2020 were just as great in their number. Since February 2020, coronavirus has taken its toll. Actually, it ranked up to the top three causes of death in the US. Nevertheless, heart disease remains the leading cause of death in the country. It is then followed by cancer and COVID-19.
Also Check: Is 116 Heart Rate High
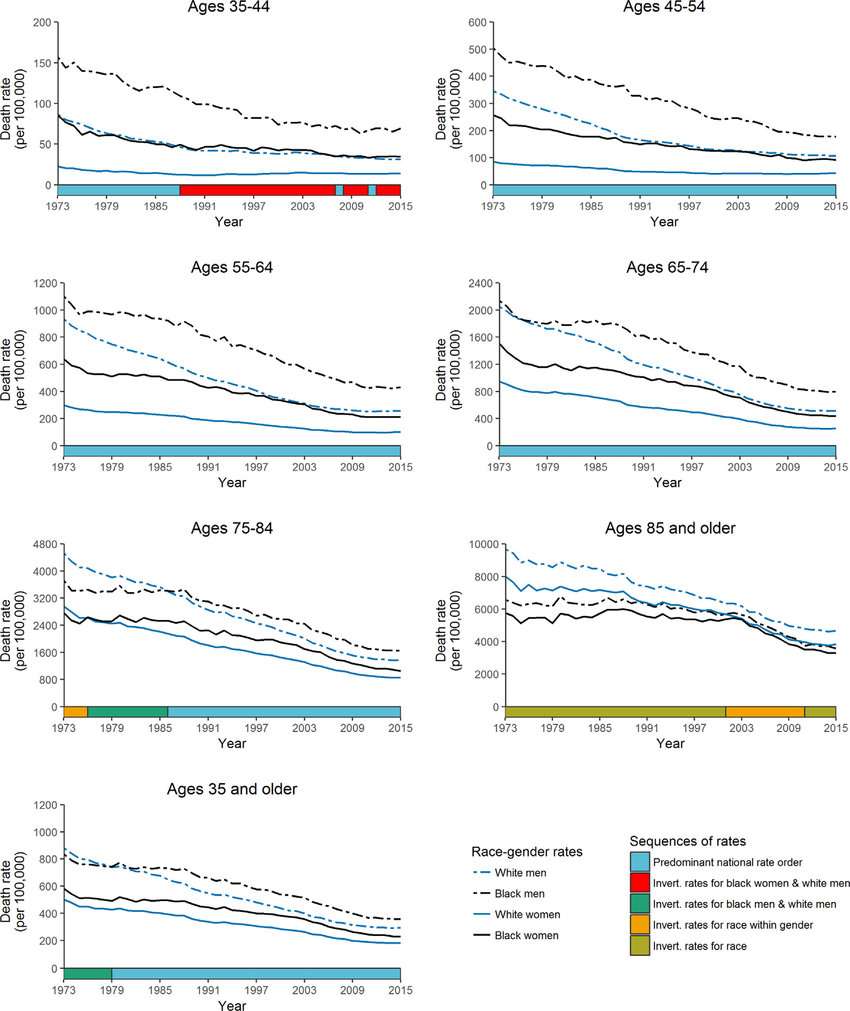
Heart Disease Statistics By Race And Ethnicity
- 47% of black adults in the U.S. have some type of cardiovascular disease, along with 30% of Hispanic U.S. adults.
- Non-Hispanic black adults have the highest CVD death rate , followed by white adults , American Indian/Alaska Native adults , Hispanic adults , and Asian/Pacific Islander adults .
- High blood pressure prevalence is 41.2% for black adults, 28% for white adults, 25.9% for Hispanic adults, and 24.9% for Asian adults.
Not Being Vaccinated Against Flu
Another surprising potential trigger for heart attacks seems to be the failure to get a flu vaccine.
This vaccine is readily available in pharmacies, especially as it gets closer to flu season. The primary purpose of the vaccine is to help equip the body with improved defenses against the viruses that cause flu.
Scientists have discovered that this particular vaccination might actually have some positive effects on the heart as well with an observed 50% reduction in heart attack events among those who do get vaccinated.
This particular benefit seems to be especially important for individuals who have been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, according to one study.
Recommended Reading: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
You May Like: How To Lower Heart Rate Instantly
The Most Important Question A Heart Attack Survivor Can Ask:
What can I do right now to make sure I never have another one?
Find a health care provider who can answer the question Why did I have a heart attack?
There are over 20 modify-able risk factors that cause heart disease. Cholesterol is just one.
Track down every single risk factor responsible. If you dont do the tests to look for it, you will not find it.
Until you know the answer to the question What caused my heart attack? you can never answer the next question What to do about it?
Heart Disease Statistics By Sex
- Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women in the U.S.
- In 2017, heart disease killed 347,879 men and 299,578 women .
- The average age that men will have a heart attack is 65, while for women, its 72.
- Women age 45-65 who have a heart attack are more likely than their male counterparts to die within a year. Women older than 65 who experience a heart attack are more likely than men of the same age to die within a few weeks.
Also Check: What Is A Mini Heart Attack
So Who Is Most At Risk
In general, the probability of you having a heart attack depends on three categories of risk factors, per the American Heart Association: major, modifiable, and contributing. Although all risk factors are crucial, major risk factors carry the most concern, as they cannot be changed and indicate an increased risk for heart disease and attacks.
Those in older populations have a higher heart attack risk. Heart attacks are more likely to occur in men than in women, and men may also have heart attacks at an earlier age.
The American Heart Association also said that heredity can play a role in the likelihood of heart attacks as well. Both family history and racial descent can increase your chances of having a heart attack.
There are medical conditions that can put you at risk for a heart attack as well. These conditions include diseases and disorders such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure, obesity, and diabetes. A June 2021 article published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Innovations, Quality & Outcomes indicated that these same conditions could also be responsible for premature myocardial infarction.
Finally, heart attack risk is higher for individuals who smoke or drink, are physically inactive, experience increased stress, or have an unhealthy diet.
% Of The Hospital Visits Related To Snow Shoveling Are Due To Heart Problems Including Heart Attacks
In the US, around 100 men die during snow shoveling or after it. According to Cleveland Clinic, every year, over 11,000 people visit the hospital with injuries due to snow shoveling. To be more specific, shoveling snow heart attack statistics report that 7% of those people experience cardiac problems, and a substantial part of thema heart attack.
You May Like: When To Measure Resting Heart Rate
Diabetes Makes Adults Twice More Prone To A Heart Attack
Heart attack statistics prove that adults with diabetes are twice more prone to a heart attack. Whats more, people with diabetes are more likely to develop heart disease at a younger age. Diabetes is quite dangerous since high blood glucose can damage the nerves that control your blood vessels and heart muscles.
What Are The Survival Rates For Heart Failure
Survival rates are based on studies of large groups of people with certain diagnoses and generally presented as a 5-year survival rate, which is the percentage of people who lived for at least 5 years after diagnosis.
You can find online calculators that ask you to submit information to get a life expectancy prediction. However, these calculators are not always accurate since they are based on studies of certain population groups over a period of time .
Table: Survival rates for patients with heart failure
| Survival | |
|---|---|
| 10 | About 24.5% on average |
For example, the 5-year survival rate for patients with heart failure is about 76%. This means that about 76 out of 100 people who were diagnosed with heart failure could live for at least 5 years.
Generally, young patients with heart failure have a better prognosis than older patients. Early diagnosis and treatment help increase life expectancy as well.
Recommended Reading: Under Resting Conditions, Heart Rate Is Primarily Under The Control Of What Control System
