Stages And Classes Defined
Heart failure is generally classified by the severity of a patients symptoms. The most common classification system is the New York Heart Association Functional Classification. There are four levels of clinical classification used to stratify both the presence of symptoms and limitations experienced during physical activity. The severity of symptoms is made by comparison to normal breathing, shortness of breath, and/or angina .1
The symptoms of heart failure associated with function during physical activity are an important indicator of disease progression and prognosis.1-2
- Class I: No limitation of physical activity. Ordinary physical activity does not cause symptoms of HF.
- Class II: Slight limitation of physical activity. Comfortable at rest, but ordinary physical activity results in symptoms of HF.
- Class III: Marked limitation of physical activity. Comfortable at rest, but less than ordinary activity causes symptoms of HF.
- Class IV: Symptoms occur even at rest discomfort with any physical activity. Unable to carry on any physical activity without symptoms of HF.
Class I and II are typically categorized as mild heart failure, while class III and IV are considered more severe or advanced heart failure. A person can move back and forth between these classes based on their symptoms. When a patient has a heart failure exacerbation, they will have more symptoms and likely be a higher class, but when their symptoms are better controlled, they will fall into a lower class.1-4
What Is The Outlook With Heart Failure
With the right care, congestive heart failure wont stop you from doing the things you enjoy. Your prognosis, or outlook for the future, will depend on:
- How well your heart muscle is working.
- Your symptoms.
- How well you respond to your treatment plan.
- How well you follow your treatment plan.
One study says that people with heart failure have a life span 10 years shorter than those who dont have heart failure. Another study showed that the survival rates of people with chronic heart failure were 80% to 90% for one year, but that dropped to 50% to 60% for year five and down to 30% for 10 years.
A different study found that people who had heart failure and were discharged from the hospital had expected life spans ranging from three to 20 years, depending on various factors like age and gender. Its important to look at your specific situation when considering your prognosis.
How Can You Prevent Heart Failure
Some lifestyle measures can help treat heart failure and prevent the condition from developing. Maintaining a moderate weight and exercising regularly can significantly decrease your risk of heart failure. Reducing the amount of salt in your diet can also lower your risk.
Other habits that may prevent heart failure include:
- limiting alcohol intake
Recommended Reading: Does Heart Rate Increase After Eating
Heart Failure Treatment Is A Team Effort
Heart failure management is a team effort, and you are the key player on the team. Your heart doctor will prescribe your medications and manage other medical problems. Other team members — including nurses, dietitians, pharmacists, exercise specialists, and social workers — will help you achieve success. But it is up to YOU to take your medications, make dietary changes, live a healthy lifestyle, keep your follow-up appointments, and be an active member of the team.
If you notice anything unusual, don’t wait until your next appointment to discuss it with your doctor. Call them right away if you have:
- Unexplained weight gain
- Swelling in your ankles, feet, legs, or belly that gets worse
- Shortness of breath that gets worse or happens more often, especially if you wake up feeling that way
- Bloating with a loss of appetite or nausea
- Extreme fatigue or more trouble finishing your daily activities
- A lung infection or a cough that gets worse
- Fast heart rate
- New irregular heartbeat
What Is The Outlook For People With Heart Failure
With the right care, heart failure may not stop you from doing the things you enjoy. Your prognosis or outlook for the future will depend on how well your heart muscle is functioning, your symptoms, and how well you respond to and follow your treatment plan.
Everyone with a long-term illness, such as heart failure, should discuss their desires for extended medical care with their doctor and family. An “advance directive” or “living will” is one way to let everyone know your wishes. A living will expresses your desires about the use of medical treatments to prolong your life. This document is prepared while you are fully competent in case you are unable to make these decisions at a later time.
Show Sources
Don’t Miss: What Is The Icd 10 Code For Congestive Heart Failure
What About Congestive Heart Failure
You may hear some health professionals use the term congestive heart failure, or CHF. CHF is actually not a separate kind of heart failure, but it is a descriptive term that can be used with any of the three types of heart failure discussed earlier. When the chief symptoms of heart failure of any type are caused by excessive fluid accumulation, leading to symptoms of lung congestion and edema, the doctor is likely to refer to it as congestive heart failure.
Heart failure is different from cardiac arrest, a term used to describe when the heart stops beating.
Classification Based On Pumping Ability
Nowadays, heart failure is increasingly being classified based on the pumping ability of the heart. This is because the pumping ability plays an important role when choosing the most suitable medication. There are two types of heart failure here:
- Heart failure with reduced pumping ability: The heart muscle has become weaker, and no longer pumps enough blood around the body when it contracts . As a result, the organs in the body dont get enough oxygen. The medical term for this is heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
- Heart failure with preserved pumping ability: Although the heart muscle is still strong, it can no longer relax and widen enough after it has squeezed blood out, so it doesnt fill up with blood properly. Despite pumping strongly enough, not enough blood is pumped out into the body as a result, especially during physically strenuous activities. Doctors call this heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
Heart failure with reduced pumping ability is sometimes referred to as systolic heart failure, and heart failure with preserved pumping ability is also known as diastolic heart failure. The systolic phase of the cardiac cycle is the phase when the heart contracts , and the diastolic phase is when the heart relaxes and widens.
You May Like: How Do You Calculate Max Heart Rate
Cardiac Mortality In Placebo Controlled Heart Failure Trials
| Trial | |
| 33 | 1.2 |
EF ejection fraction. SOLVD-P, SOLVD-T=studies of left ventricular dysfunction prevention arm and treatment arm .
H-ISDN=hydralazine and isosorbide dinitrate.
*Treatment with H-ISDN.
Treatment with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors prevents or delays the onset of symptomatic heart failure in patients with asymptomatic, or minimally symptomatic, left ventricular systolic dysfunction. The increase in mortality with the development of symptoms suggests that the optimal time for intervention with these agents is well before the onset of substantial left ventricular dysfunction, even in the absence of overt clinical symptoms of heart failure. This benefit has been confirmed in several large, well conducted, postmyocardial infarction studies.
What Is The Importance Of Ejection Fraction
Your ejection fraction is one way to measure the severity of your condition. If its below normal, it can mean that you have heart failure. Your ejection fraction tells your healthcare provider how good of a job your left or right ventricle is doing at pumping blood. Usually, your EF number is talking about how much blood your left ventricle is pumping out because its your heart’s main pumping chamber.
Several non-invasive tests can measure your EF. With this information, your healthcare provider can decide how to treat you or find out if a treatment is working as it should.
A normal left ventricular ejection fraction is 53% to 70%. An LVEF of 65%, for example, means that 65% of the total amount of blood in your left ventricle is pumped out with each heartbeat. Your EF can go up and down, based on your heart condition and how well your treatment works.
Read Also: How To Stop Heart Palpitations From Anxiety
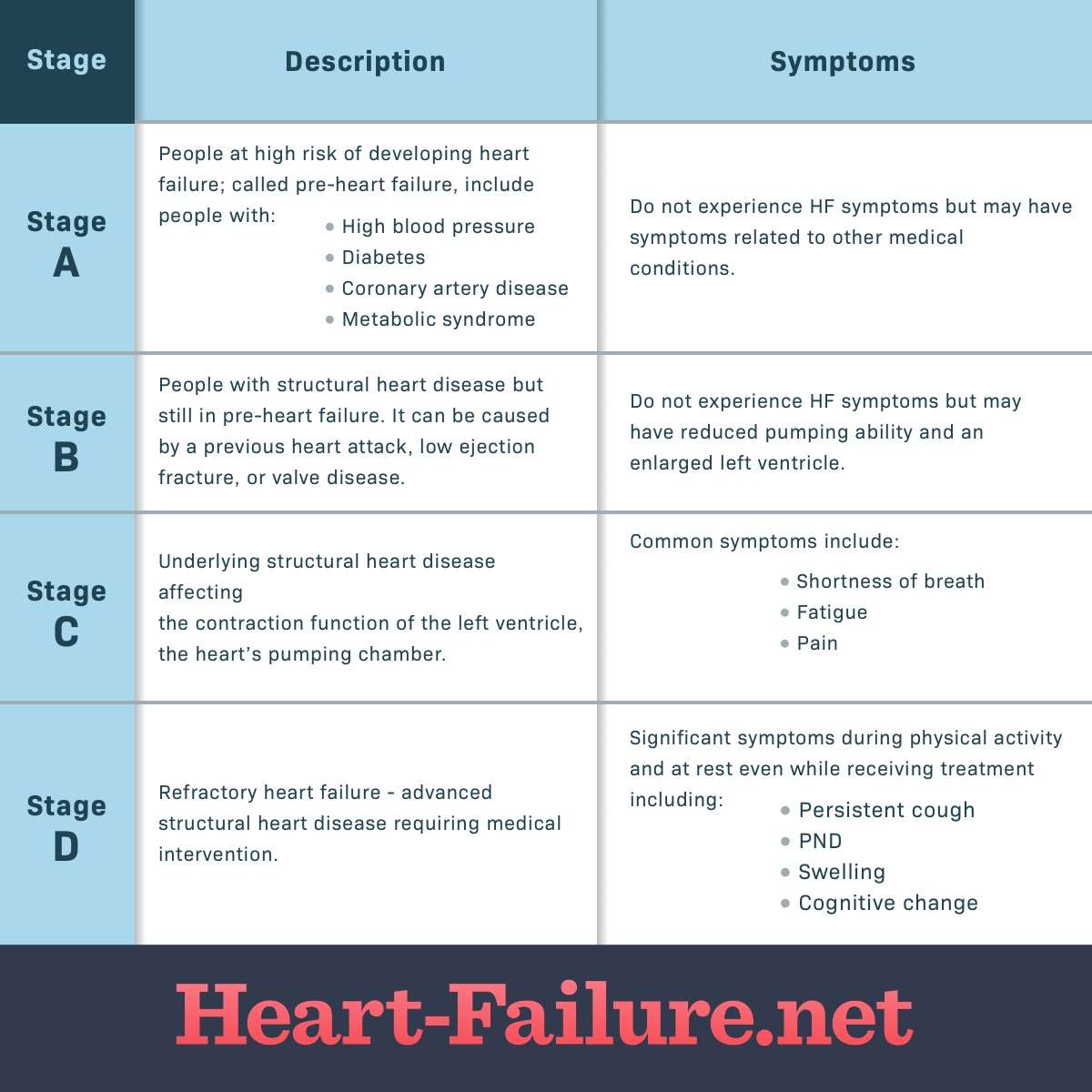
What Are The Stages Of Heart Failure
- print page
- Bookmark for later
Heart failure can be a misunderstood diagnosis. It describes a heart that is not pumping blood as well as it should, but it doesnt mean the heart has “failed” or stopped working.1 There are different types of heart failure and different classifications used by healthcare providers to assess the stage and functional status of a person with HF.
Common Causes Of Lower Limb Oedema
- Gravitational disorderfor example, immobility
- Congestive heart failure
- Venous thrombosis or obstruction, varicose veins
- Hypoproteinaemiafor example, nephrotic syndrome, liver disease
- Lymphatic obstruction
Fatigue and lethargy
Fatigue and lethargy in chronic heart failure are, in part, related to abnormalities in skeletal muscle, with premature muscle lactate release, impaired muscle blood flow, deficient endothelial function, and abnormalities in skeletal muscle structure and function. Reduced cerebral blood flow, when accompanied by abnormal sleep patterns, may occasionally lead to somnolence and confusion in severe chronic heart failure.
You May Like: Does Anxiety Increase Heart Rate
You Don’t Have To Face Hf Alone
The term heart failure makes it sound like the heart is no longer working at all and theres nothing that can be done. Actually, heart failure means that the heart isnt pumping as well as it should be. Congestive heart failure is a type of heart failure that requires seeking timely medical attention, although sometimes the two terms are used interchangeably.
Your body depends on the hearts pumping action to deliver oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood to the bodys cells. When the cells are nourished properly, the body can function normally.With heart failure, the weakened heart cant supply the cells with enough blood. This results in fatigue and shortness of breath and some people have coughing. Everyday activities such as walking, climbing stairs or carrying groceries can become very difficult.
Heart failure is a term used to describe a heart that cannot keep up with its workload. The body may not get the oxygen it needs.
Heart failure is a serious condition, and usually theres no cure. But many people with heart failure lead a full, enjoyable life when the condition is managed with heart failure medications and healthy lifestyle changes. Its also helpful to have the support of family and friends who understand your condition.
Precipitating Causes Of Heart Failure

- Arrhythmias, especially atrial fibrillation
- Angina pectoris or recurrent myocardial ischaemia
- Anaemia
- Iatrogenic causefor example, postoperative fluid replacement or administration of steroids or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Poor drug compliance, especially in antihypertensive treatment
- Thyroid disordersfor example, thyrotoxicosis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pregnancy
In a patient with appropriate symptoms and a number of physical signs, including a displaced apex beat, elevated venous pressure, oedema, and a third heart sound, the clinical diagnosis of heart failure may be made with some confidence. However, the clinical suspicion of heart failure should also be confirmed with objective investigations and the demonstration of cardiac dysfunction at rest. It is important to note that, in some patients, exercise-induced myocardial ischaemia may lead to a rise in ventricular filling pressures and a fall in cardiac output, leading to symptoms of heart failure during exertion.
Read Also: How Much Does Open Heart Surgery Cost
Nyha Classification For Chronic Heart Failure
New York Heart Association classification is used to grade the severity of functional limitations in a patient with heart failure :
- class I no limitation of physical activity
- ordinary physical activity does not cause fatigue, breathlessness or palpitation
According to a study conducted, the following criteria were used by cardiologists to determine the NYHA class of a patient :
- self reported walking distance – 70%
- difficulty in climbing stairs – 60%
- ability to walk to local landmarks – 30%
- breathlessness interferes with daily activities – 23%
- breathless when walking around the house – 23%
- no specific questions – 13%
This study has also pointed out that NYHA classification system is subjective and poorly reproducible since there are no clear standard criteria for assigning an NYHA class .
Note:
Reference:
Sensitivity Specificity And Predictive Value Of Symptoms Signs And Chest X Ray Findings For Presence Of Heart Failure In 1306 Patients With Coronary Artery Disease Undergoing Cardiac Catheterisation
| Clinical features |
| 32 |
Oedema
Swelling of ankles and feet is another common presenting feature, although there are numerous non-cardiac causes of this symptom. Right heart failure may manifest as oedema, right hypochondrial pain , abdominal swelling , loss of appetite, and, rarely, malabsorption . An increase in weight may be associated with fluid retention, although cardiac cachexia and weight loss are important markers of disease severity in some patients.
Recommended Reading: Does Ativan Lower Heart Rate
What Are The Types Of Heart Failure
Systolic dysfunction happens when the heart muscle doesn’t contract with enough force, so there is less oxygen-rich blood pumped throughout the body.
Diastolic dysfunction happens when the heart contracts normally, but the ventricles donât relax properly or are stiff, and less blood enters the heart during normal filling.
A calculation done during an echocardiogram, called the ejection fraction , is used to measure how well your heart pumps with each beat to help determine if systolic or diastolic dysfunction is present. Your doctor can discuss which condition you have.
New York Heart Association Classification System
The NYHA Classification system is a simple and widely used tool that classifies patients with heart failure into one of four classes according to their degree of symptoms at rest and with activity. In the early stages of heart failure, the heart may function adequately both at rest and with activity. With progression of the disease, the heart will first not be able to meet the demands of the body with activity, and patients will begin to demonstrate clinical signs and symptoms with activity. With further progression of the disease, patients will demonstrate signs and symptoms of heart failure even at rest. The NYHA Classification system is the system most commonly used by physicians to prognosticate and monitor the effectiveness of treatment interventions in heart failure.34 The classes used in this system, I to IV with I indicating less severity and higher numbers indicating greater severity, are described in Table 25-5. Classification is based on the patient’s self-report of signs and symptoms. Patients can move between classes, either up or down, depending on the severity of their disease at the time.
The NYHA Classification system has been examined for its ability to predict mortality. With optimal treatment, there is a 1-year mortality of 10% to 15% for stable patients classified in NYHA class I and II, 15% to 20% for patients classified in class III, and 20% to 50% for patients classified in class IV.35
Maithri Siriwardena, Eddy Fan, in, 2018
Also Check: How To Measure Your Resting Heart Rate
New York Heart Association Classification
Doctors usually classify patients’ heart failure according to the severity of their self-reported symptoms. The classification system used most often is the New York Heart Association Functional Classification. Four levels of clinical classification are used to classify people according to symptoms and limitations experienced during physical activity. Symptom severity is compared to normal breathing, shortness of breath, and/or angina .1 Classification of heart failure based on function during physical activity, often called exertion, is often an important indicator of prognosis.1,2
- Class I: No limitation of physical activity. Ordinary physical activity does not cause symptoms of HF.
- Class II: Slight limitation of physical activity. Comfortable at rest, but ordinary physical activity results in symptoms of HF.
- Class III: Marked limitation of physical activity. Comfortable at rest, but less than ordinary activity causes symptoms of HF.
- Class IV: Symptoms occur even at rest discomfort with any physical activity. Unable to carry on any physical activity without symptoms of HF.
Class I and II are typically considered mild heart failure, while class III and IV are considered more severe or advanced heart failure. A person can move back and forth between these classes as they are based on symptoms. When a patient has a heart failure exacerbation, they will have more symptoms and likely be a higher class, but when their symptoms are better controlled, they will be a lower class.
Prevalence Of Heart Failure
Population based estimates of the prevalence of heart failure in Australia is limited however, in 2014 it was estimated that there were 480,000 patients over the age of 18 living with heart failure. This represents approximately 2.1% of the adult population1.
It must be noted that in Australias indigenous population, the age standardised prevalence rates of heart failure is approximately 1.7 times higher than non-Indigenous Australians2. This is largely due to the high rates of rheumatic heart disease and cardiovascular disease within these communities. The prevalence estimates of rheumatic heart disease have been steadily increasing to approximately 2% of the Indigenous population in the Northern Territory and 3.2% of Indigenous people aged 35-44 years old3.
In 2015 -2016 data shows that there were approximately 173,000 admissions where cardiomyopathy and heart failure were the main diagnosis, this represents an estimated hospitalisation rate of 1.6% of all hospital admissions4.
Survival rates vary widely in clinical studies depending on the study group having acute or chronic heart failure. Contemporary studies into acute heart failure are generally consistent with approximately 80% survival at one month and 57-80% survival at one year5. Chronic heart failure survival rates may range from 81% one year survival to 63% at 5 years, which may be comparable to some non-haematological malignancies6.
Don’t Miss: What Heart Rate Is Too High
