Understanding The Heart’s Electrical System
To understand arrhythmias, it helps to understand the heart’s internal electrical system. The heart’s electrical system controls the rate and rhythm of the heartbeat.
With each heartbeat, an electrical signal spreads from the top of the heart to the bottom. As the signal travels, it causes the heart to contract and pump blood. The process repeats with each new heartbeat.
Each electrical signal begins in a group of cells called the sinus node or sinoatrial node. The SA node is located in the right atrium , which is the upper right chamber of the heart. In a healthy adult heart at rest, the SA node fires off an electrical signal to begin a new heartbeat 60 to 100 times a minute.
From the SA node, the electrical signal travels through special pathways in the right and left atria. This causes the atria to contract and pump blood into the heart’s two lower chambers, the ventricles .
The electrical signal then moves down to a group of cells called the atrioventricular node, located between the atria and the ventricles. Here, the signal slows down just a little, allowing the ventricles time to finish filling with blood.
The electrical signal then leaves the AV node and travels along a pathway called the bundle of His. This pathway divides into a right bundle branch and a left bundle branch. The signal goes down these branches to the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump blood out to the lungs and the rest of the body.
What Complications May Occur After Surgery
Sometimes, complications can occur after surgery. These are the most common complications.
Complications may include:
-
Shock. Shock is a severe drop in blood pressure that causes a dangerous reduction of blood flow throughout the body. Shock may be caused by blood loss, infection, brain injury, or metabolic problems. Treatment may include any or all of the following:
-
Stopping any blood loss
-
Helping with breathing
-
Reducing heat loss
-
Giving intravenous fluids or blood
-
Providing oxygen
-
Prescribing medicines, for example, to raise blood pressure
Hemorrhage. Hemorrhage means bleeding. Rapid blood loss from the site of surgery, for example, can lead to shock. Treatment of rapid blood loss may include:
IV fluids or blood plasma
Blood transfusion
More surgery to control the bleeding
Wound infection. When bacteria enter the site of surgery, an infection can result. Infections can delay healing. Wound infections can spread to nearby organs or tissue, or to distant areas through the blood stream. Treatment of wound infections may include:
Surgery or procedure to clean or drain the infected area
Anticoagulant medicines
Thrombolytic medicines
Surgery or other procedures
Lung complications. Sometimes, pulmonary complications arise due to lack of deep breathing and coughing exercises within 48 hours of surgery. They may also result from pneumonia or from inhaling food, water, or blood, into the airways. Symptoms may include wheezing, chest pain, fever, and cough .
What Can Be Done To Prevent It
As you prepare to have heart surgery, you may be looking for ways to reduce the chances of complications. Managing your overall risk factors for AFib is the best way to reduce your risk for post-operative atrial fibrillation as well. Although some risk factors are impossible to eliminate, keeping your body as healthy as possible before surgery will reduce the likelihood of post-operative AFib and other complications from surgery.
- Manage your chronic conditions. Thyroid problems, anemia, diabetes, and high blood pressure are among the risk factors for AFib. If you have any of these or other chronic conditions, treating them prior to surgery may reduce your risk for complications. This includes taking any prescribed medications and following your doctors advice on managing these conditions.
- Eat healthy foods and exercise. The healthier you are going into surgery, the healthier you are coming out of surgery. Eat a heart healthy diet and make exercise part of your daily routine. Aim for 30 minutes a day of moderate exercise at least five days a week.
- Limit stress. Stress can be a trigger for atrial fibrillation, and we know that having surgery can be a stressful event. Managing stress includes physical stress on your body as well as mental or emotional stress in your life. After surgery, managing your pain reduces stress on your body, and having the right support systems in place can help manage mental and emotional stress.
Don’t Miss: Which Of The Following May Be Classified As A Risk Factor For Coronary Heart Disease
Can Surgery Cause Heart Rhythm Issues
If you are preparing for heart surgery or have recently had heart surgery, you may be thinking about potential complications and wondering what to expect for your recovery period. Did you know that many patients experience a heart rhythm issue following heart surgery?
The most common type of heart rhythm issue after surgery is atrial fibrillation. Up to 40% of patients who have heart surgery experience post-operative AFib. Inflammation in the chest after surgery is the suspected cause of the arrhythmia, and many times the heartbeat returns to normal as healing occurs.
Reasons Your Heart Rate Is High
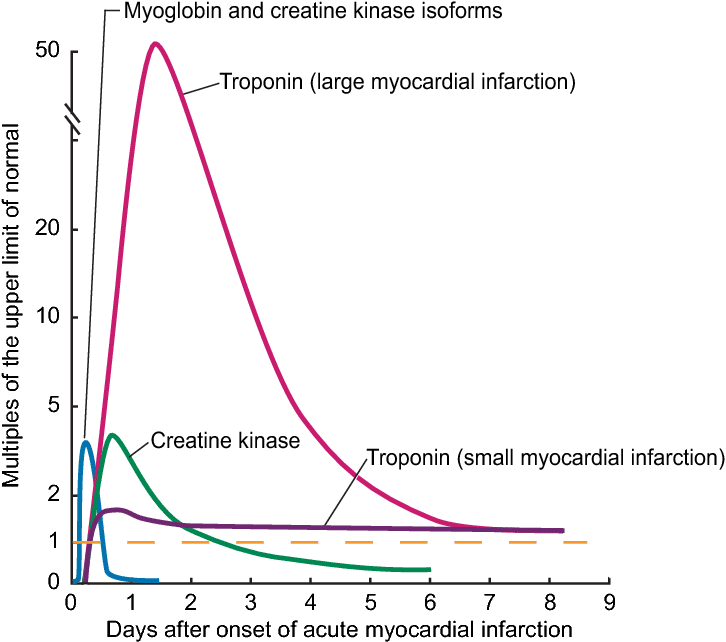
Youve probably noticed that your heart rate rises when you exercise and that it drops when youre lying in bed. But does your heart rate ever feel elevated for no apparent reason?
Having an increased heart rate isnt a health condition in and of itself rather, its a symptom caused by any number of circumstances. It may be a reaction to something thats happening in your life, or it may be caused by a health condition.
When you feel your heart pounding in your chest unexpectedly, dont jump to conclusions that theres something wrong with your heart, but if the problem continues without an explainable and simple cause, see a doctor to discuss your concerns, says interventional cardiologist, Ali Moosvi, M.D.
Also Check: What Should Sleeping Heart Rate Be
When Changes In Heart Rhythms Warrant A Physicians Attention
Though most fluctuations in heart rhythms will likely be harmless, there are times your first response should be to seek medical advice.
- Your symptoms are sudden and abnormal. If theres a clear first time that you notice a rhythm change in your heart, its a good idea to alert your doctor, Anderson says. You should also call your doctor when a change in heart rhythms corresponds to chest pain, losing consciousness or a prolonged sense that you might pass out. Likewise, contact a medical professional if a rhythmic abnormality persists.
- Your history involves other heart issues. If you were born with a malformation if youve had heart surgery if youve had a heart attack or long-standing, untreated high blood pressure or if there is something otherwise abnormal with your heart and you notice abnormal heart rhythms, you should see your doctor.
- Your family history puts you at increased risk. Your doctor may ask you to attend more closely to changes in your heart rhythms if your family has a history of heart disease or sudden death.
How To Reduce Your Risk For Atrial Fibrillation After Surgery
Because overall heart health plays a role in developing atrial fibrillation after surgery, Doshi wants his patients to be as healthy as possible before surgery. A significant amount of atrial fibrillation treatment is prevention, he says. We may be able to adjust their medications and get them in the best shape prior to surgery.
Work with your doctor to plan a healthier diet and improve your physical conditioning with exercise, the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons suggests.
Heres what else you can do to reduce your risk for atrial fibrillation:
- Ask your doctor about post-op pain relief. Research suggests that pain may trigger a response that contributes to post-op irregular heartbeats, according to a study published in 2011 in the journal ISRN Cardiology.
- Ask your doctor about your pre-op blood test results. The same study found that anemia , an electrolyte imbalance, and elevated blood sugar levels could be risk factors for post-op atrial fibrillation.
Recommended Reading: What Is Good Heart Rate
Atrial Or Supraventricular Tachycardia
Atrial or supraventricular tachycardia is an accelerated heart rhythm that starts in the upper chambers of the heart.
It is the most common heart rhythm problem in children and young people. Many people first experience it between the ages of 25 and 40 years.
An episode may last from a few minutes to several hours. It is not usually serious, but, in extreme cases, it unconsciousness and cardiac arrest.
Cardiac Effects Of Common Anesthetic Agents
The table below gives examples of some common individual anesthetic agents and their heart effects. Keep in mind that for each effect, there is likely a study or two that disputes the findings. The data here are consistent with the current edition of the authoritative text,Miller’s Anesthesia . The conflicting conclusions show how complex these interactions are, and how the education and experience of the anesthesia provider help keep us safe during anesthetics.
- Propofol, etomidate and pentothal are “induction” agents used to get patients to sleep.
- Ketamine is a unique drug that may be used for sedation, as well as induction and maintenance of anesthesia.
- Fentanyl and morphine are pain medicines used before, during and after surgery.
- Succinylcholine is a muscle relaxant that makes the placement of the breathing tube and surgery easier to achieve.
- Halothane, isoflurane and sevoflurane are anesthesia gases used to keep patients asleep for surgery, delivered through a breathing tube or mask.
This is NOT a comprehensive list of anesthetic agents these are examples only. Likewise, the effects may vary depending on a large number of factors and interactions. No clinical practice advice is implied, nor should this chart be used for such.
- The specific medications used during anesthesia
- Medications taken by the patient
- Other coexisting diseases
Don’t Miss: What Is A Normal Resting Heart Rate For Women
Preoperative Left Ventricular Stroke Volume And Perioperative Autonomic Function
We further examined cardiac and autonomic function in a separate cohort of patients. One hundred and eighty-one patients with mean age 68 yr who underwent major surgery in the OPTIMISE and POM-O trials had complete beat-by-beat cardiac output monitor data available for analysis . From both trials, patients with preoperative HR > 87 beats min1 had lower mean preoperative stroke volume . Preoperative HR > 87 beats min1 was associated with impaired preoperative stroke volume < 59ml , taking into account patients with an established preoperative diagnosis of heart failure . We also performed a detailed analysis of autonomic data captured in the POM-O cohort to delineate the components of preoperative tachycardia. Heart rate was higher throughout the intraoperative period in patients with preoperative HR > 87 beats min1 . Preoperative HR > 87 beats min1 was chiefly associated with measures indicative of lower parasympathetic activity . This was accompanied by similar sympathetic activity between groups , but higher low-frequency/high-frequency ratio , reflecting dominant sympathetic autonomic modulation of HR in patients with HR > 87 beats min1 attributable to loss of cardiac vagal tone. Spontaneous baroreflex sensitivity was also lower in patients with preoperative HR > 87 beats min1. Higher lactate was observed at the end of surgery in patients with preoperative HR > 87 beats min1 .
High Pulse Rate Symptoms
When the hearts rate is very much rapid, it might not effectively pump blood to the rest parts of the body, depriving the organs and also the tissues of much needed oxygen. This can lead to these tachycardia-related signs and symptoms:
- Heart palpitations an irregular heartbeat or a sensation of flopping in chest
Some individuals who experience tachycardia indicate no symptoms, and the condition is discovered with a heart-monitoring test known as the electrocardiogram
Several conditions can lead to a high pulse rate and also the tachycardia symptoms. Its vital to get a prompt diagnosis and an appropriate care. See the doctor if the child is having any tachycardia symptoms.
Read Also: How Risky Is Open Heart Surgery
A Elevated Pulse Rate Is Known As Tachycardia Which May Be A Normal Response To Some Stimuli Or Part Of Some Medical Conditions
The heart of a healthy adult beats within the range of 60-100 times per minute at rest. This rate is controlled by electrical signals within the heart. An abnormally high pulse rate above 100 beats per minute is also called tachycardia, and it occurs when the heart tissues produce electrical signals rapidly, affecting the upper or lower chamber of the heart, or both.
Tachycardia, or rapid heart rate, may produce either a regular or an irregular rhythm in the heart. At extremely rapid rates, the heart may not be able to pump oxygen-rich blood efficiently to the rest of the body, and may cause symptoms as well as complications.
Effects Of High Heart Rate
The research team found out the factors that are likely to impact the results and found out that:
- a resting heart rate of about 80 beats per minute is linked to about 40% elevated number of risks of death
- a resting heart rate of about 90 beats per minute much doubled the risk, as compared with the ones with the lowest rate
- resting heart rates that is over 90 beats per minute usually triples the risk
Read Also: Dogs With Congestive Heart Failure Stages
High Pulse Rate High Blood Pressure
A rising heart rate does not lead to the blood pressure to increase at the same given rate. Even though the heart is beating much more times, healthy blood vessels usually dilate so as to allow more blood to flow through easily.
When a person exercise, the heart speeds up so that more blood is able to reach the muscles. It might be possible for the high pulse rate to double much more safely, while the blood pressure can respond by increasing a modest amount
Can You Prevent Afib
There is no way to prevent afib or even predict whether you are more likely to have it after surgery. But there are a few things you can do that reduce your risk.
1. Get into shape before surgery. Being in good shape prior to surgery is a good idea. If your surgery isnt urgent, talk with your doctor to create a heart-healthy plan that helps get you ready for surgery. This generally includes eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise.
The healthier your heart is going in to surgery, the less your chances of having afib afterward.
2. Get other conditions under control. Studies show that a few problems you may have before surgery can increase your risk of afib. These include:
- An electrolyte imbalance
- High blood sugar
Your doctor may perform tests before surgery to check for these issues. We also can provide guidance on ways to treat the problems, including changing diet or taking medication or vitamins.
3. Limit stress. Another reason surgery can produce afib is because stress sometimes triggers it. For that reason, ensuring that you have sufficient pain medication after surgery is important.
You May Like: Normal Heart Rate Sleeping
How To Take Your Pulse
Count your pulse: _____ beats in 10 seconds x 6 = _____ beats/minute
Is It Normal To Have A High Heart Rate After Surgery
Postoperative tachycardia is a common and largely unexamined occurrence in patients undergoing orthopedic hip and knee surgery. Postoperative sinus tachycardia is often attributed to catecholamine release in response to surgical stress or anemia, and it is theorized that most patients recover without sequelae.
Also Check: How To Improve Resting Heart Rate
Is Tachycardia Normal After General Anesthesia
Postoperative tachycardia is a common and largely unexamined occurrence in patients undergoing orthopedic hip and knee surgery. Postoperative sinus tachycardia is often attributed to catecholamine release in response to surgical stress or anemia, and it is theorized that most patients recover without sequelae.
Postoperative Tachycardia: Consequence Of Orthopedic Surgery?
What Causes High Pulse Rate At Rest
The resting heart rate, is the number of times that the heart beats in a minute. When youre seated or even lying down and much relaxed, then a normal heart rate is normally between 70 and 100 beats a minute, according to the cardiologists.
Several studies have indicated that higher resting heart rate is related to increased risk of the cardiovascular events and also the death in men and women.
But, whether higher heart rate is an indicator of the poor physical fitness or even the heart disease isnt very much clear. An important question is whether the higher heart rate is a modifiable risk factor for a premature death.
A very fast resting heart rate is able to affect the body in several ways that can be bad for the heart
Don’t Miss: How To Check Heart Rate On Apple Watch
Elevated Heart Rate After Hysterectomy
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
What Are The Dangers Of Afib

It is important to identify afib after heart surgery and treat it if necessary. Because the blood isnt pumped efficiently during afib, it increases your risk of blood clots, which can cause a stroke. If it continues over time, it can weaken your heart, potentially causing heart failure.
Talk to your physician before and after surgery about your potential risks of afib and what you may do to .
Read Also: Can Too Much Vitamin D Cause Heart Palpitations
