Degradation Of Atp And Oxidative Stress
Hypoxia and reperfusion can cause degradation of a significant quantity of ATP. Hypoxanthine, xanthine, and uric acid are ATP degradation products. Hypoxanthine needs xanthine oxidase to be catalyzed into xanthine. XO is also needed to convert xanthine into uric acid. In the process, it produces ROS, hydrogen peroxide , and superoxide anion . XO is converted from xanthine oxidoreductase. Another transformation product of xanthine oxidoreductase is xanthine dehydrogenase , which can be converted to XO by various enzymes. Under hypoxia or reperfusion, a large amount of ATP is degraded and hypoxanthine is produced. The aggregated hypoxanthine increases the substrate for XO, which activates the metabolic pathway to convert xanthine dehydrogenase into XO. Some studies have shown that blood vessel endothelia and cardiac muscle can produce XO locally . The effect of XO on hypoxanthine increases the generation of oxidative radicals and then causes myocardial injury and ventricular remodeling.
A Management Of Acute Diastolic Heart Failure
The initial management of patients with acute diastolic heart failure is identical to that of patients with systolic heart failure and aims at relieving pulmonary and systemic vascular congestion.
Intravenous diuretics are the mainstay therapy in addition to antihypertensive therapy and the use of nitroglycerin and morphine to relieve pulmonary congestion. Suspicion of myocardial ischemia should prompt antiplatelet therapy and evaluation for acute coronary syndrome. Daily weight, strict intake/output monitoring and fluid restriction complement diuretic therapy.
Unlike systolic heart failure, evidence of benefit of neurohormonal antagonism in long-term management of diastolic heart failure is scarce despite its rising burden.
According to guidance from the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association , the mainstay treatment of patients with diastolic heart failure relies on managing the underlying cause:
-
Aggressive blood pressure control
-
Coronary revascularization in patients with coronary artery disease
-
Control of ventricular rate
Systolic Heart Failure Treatment
A persons medical care team may treat systolic heart failure with various medications, including:
- diuretics, which help reduce fluid buildup in the body
- angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, which help lower blood pressure and reduce strain on the heart
- beta-blockers, to reduce the heart rate and blood pressure
- mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists , to lower blood pressure
- angiotensin receptor blockers , which doctors can prescribe if a person cannot tolerate ACE inhibitors
- angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors , a combination medication that doctors use to lower blood pressure and reduce fluid buildup
- SGLT2 inhibitors, which are a treatment for diabetes but also improve outcomes in people with heart failure
- ivabradine , to reduce the heart rate
- digoxin , which lowers the heart rate and strengthens heart contractions
- vasodilators, to lower blood pressure
Systolic heart failure may require a person to take a combination of medications.
Research from 2016 found that taking a combination of ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers can reduce a persons risk of death due to heart failure by up to 35% .
The same research also found that taking a combination of medications could reduce the risk of hospitalization for a person with HFrEF by 64%.
Don’t Miss: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Faqs Related To Diastolic Heart Failure
What happens when there is diastolic heart failure?
If you have diastolic heart failure, your left ventricle has become tighter than normal. Because of this, your heart may not rest the way it should. When it pumps, it cannot fill with blood as it is supposed to. Because there is less blood in the ventricles, less blood is pumped into your body.
What is the life expectancy with diastolic heart failure?
Diastolic heart failure , as defined by the symptoms and indications of HF, preserved ejection fraction, and abnormal diastolic function is approximated to occur in half of all patients presenting with HF. Patients with preserved ejection fraction are older and more often female. The underlying etiology of HF varies, hypertension is more often usual in the patients with preserved ejection fraction, and ischemic heart disease predominates in those with lower ejection fraction.
Diastolic HF is related to a higher mortality rate than that of HF with depressed ejection fraction with a minimum five-year survival rate after the first episode of 43% and a higher mortality rate than the rest general population. Also after significant disease burden, clinical and biological disease-related factors in diastolic HF remains less understood. There is also limited data from well-designed studies considering effective treatment strategies for this group of patients.
Diastolic dysfunction in exercise and its role for exercise capacity?
What are the signs your heart is quietly failing?
Lifestyle Changes That Can Prevent Diastolic Heart Failure
Although you cannot prevent all types of diastolic heart failure, you can take steps to reduce your risk for illnesses or conditions that may exacerbate or complicate the condition.
Try to be active- Moderate exercise helps circulation and decreases stress on your heart muscle.
Regular checkups- If you experience new or changing manifestations or side effects from medications, consult your doctor.
Get a healthy diet to make your heart happy Limit sugar, saturated fat, cholesterol, and salt, and eat a lot of natural products, fruits,; vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy items.
Maintain a solid weight- Losing weight and keeping a sound weight puts less weight and stress on the heart.
In some cases, you may have to stop drinking alcohol altogether. If you can drink, keep your intake low.
Quit smoking- Because Smoking damages blood vessels raises blood pressure, reduces the amount of oxygen in the blood, and makes your heart beat faster.
Take your medications as prescribed- If you have been prescribed medicine for diastolic heart failure or a causative condition, be sure to take it as prescribed.
Also Check: Acid Reflux Heart Fluttering
Definition And Classification Criteria For Diastolic Hf
Table 3 Criteria for diastolic HF according to the European Society of Cardiology .
To date, however, no certain definition of diastolic HF exists and the recognition of its existence is not unanimously accepted . Studies performed by both standard Doppler echocardiography and Tissue Doppler demonstrated how sub-clinic alterations of myocardial systolic function are already overt in diastolic HF. Because of the use of LV EF is a rather insensitive indicator of true LV myocardial contractility, the assessment of LV long-axis function by the simple M-mode of the mitral lateral annulus could help to identify initial LV systolic dysfunction . Finally, it has also to be taken into account how concomitant variables, including obesity, chronic obstructive lung disease and even myocardial ischemia, can be confounding factors leading to “false” diagnosis of diastolic HF, particularly in the elderly population .
How To Diagnose Diastolic Heart Failure
To diagnose heart failure, patients are asked questions about their medical history and undergo a physical exam. There are advanced procedures and technology involved to effectively diagnose the condition, inform treatment, and monitor the heart. Tests can include:
- Blood test: Check the levels of certain fats, cholesterol, sugar, and protein in the blood that could indicate heart problems.
- Chest X-ray: A common imaging test of the lungs, heart, and aorta.
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound exam that uses sound waves to take moving pictures of the hearts chambers and valves.
- Electrocardiogram : Measures the electrical activity of the heart and can help determine if parts are enlarged, overworked, or damaged.
- Electrophysiology study: Records the hearts electrical activities and pathways. It can help find what is causing heart rhythm problems and identify the best treatment.
- Stress testing: Conducted during exercise. If a person cannot exercise, medicine is given to increase their heart rate. Used along with an EKG, the test can show changes in the hearts rate, rhythm, or electrical activity as well as blood pressure. Exercise makes the heart work hard and beat fast while heart tests are conducted.
Don’t Miss: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
How Is Diastolic Heart Failure Diagnosed
Your doctor will give you a physical exam and go over your medical history with you.;Some common tests that are done include and electrocardiogram , a chest x-ray, blood tests, and an echocardiogram. Often times the doctor will order an exercise stress test/treadmill test as well. A heart catheterization is sometimes also done to see if there are any blockages etc within the heart itself.
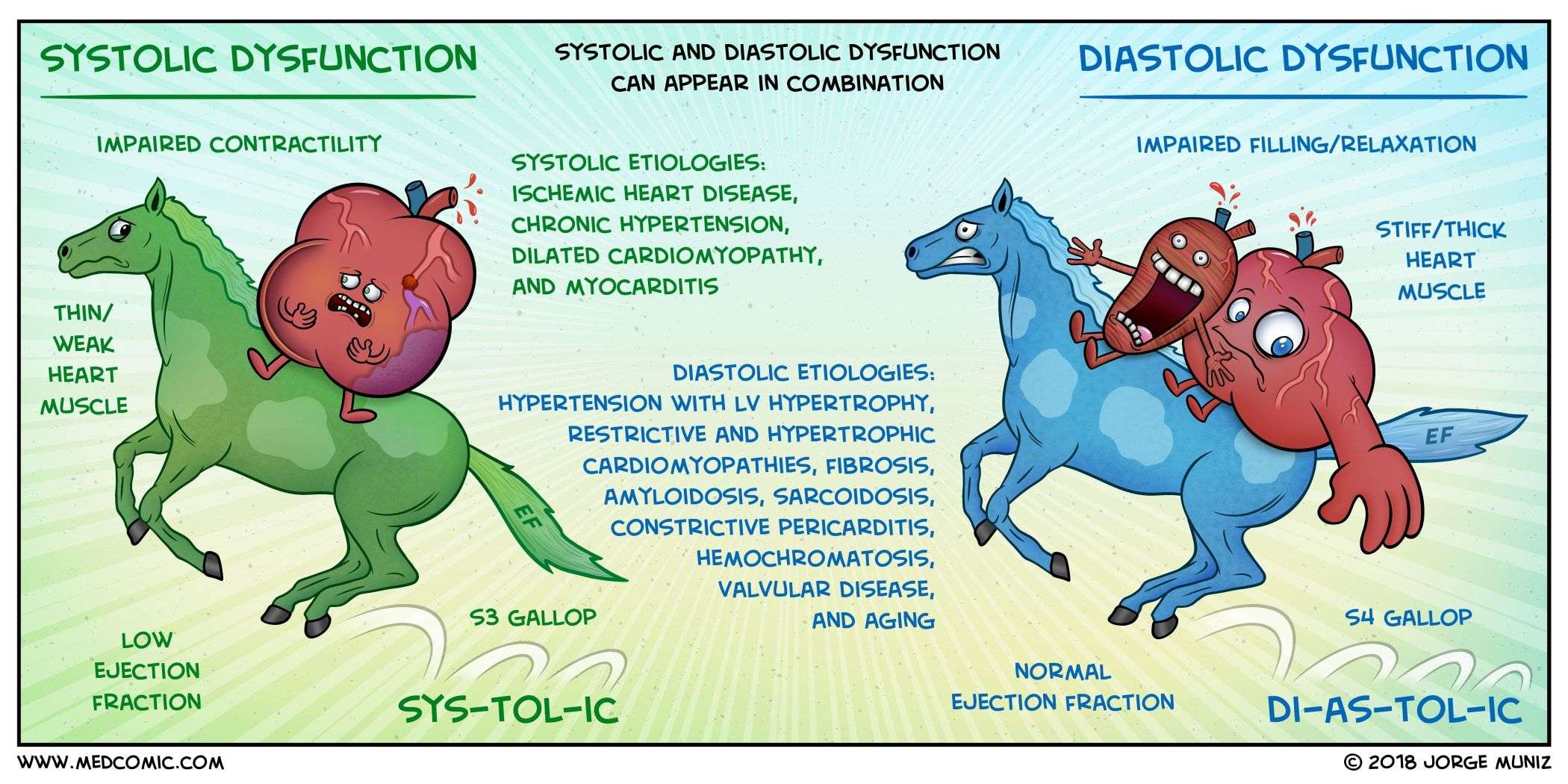
What Is Diastolic Dysfunction And Diastolic Heart Failure
The cardiac cycle is divided into two parts -;systole;and diastole. During systole, the ventricles contract, thus ejecting blood out of the heart and into the arteries. After the ventricles have finished contracting, they relax, and during this relaxation they fill up with blood to prepare for the next systole. This relaxation phase of the cardiac cycle is called;diastole.
Sometimes, as a result of various medical conditions, the ventricles begin to become relatively “stiff.” Stiff ventricles are not able to fully relax during diastole; as a result, the ventricles may not fill completely. As a result of this incomplete filling of the ventricles, the amount of blood pumped with the subsequent heart beat will be slightly reduced. Also, the blood which is returning to the heart can partially “dam up” in the body’s organs, including the lungs. Even more common, however, is swelling in the legs.
The abnormal stiffening of the ventricles and the resulting abnormal ventricular filling during diastole are referred to as;diastolic dysfunction.
Diastolic dysfunction is very mild at first, and usually does not produce symptoms at first. However, diastolic dysfunction tends to progress over time. When the condition becomes is sufficiently advanced to produce pulmonary congestion or swelling in the legs,;diastolic heart failure;is said to be present.
You May Like: How Much Blood Does The Heart Pump
Diastolic Blood Pressure: How Low Is Too Low
- May 17, 2015
Blood pressure consists of two numbers. Systolic pressure, the force exerted on blood vessels when the heart beats, is the upper number. Diastolic pressure, the force exerted when the heart is at rest, is on the bottom ;in more ways than one. Systolic pressure attracts the lions share of attention from physicians and patients, says UAB cardiologist Jason Guichard, M.D., Ph.D.
Physicians are busy people, and like it or not they often focus on a single number, Guichard said. Systolic blood pressure is the focus, and diastolic pressure is almost completely ignored. That is a mistake, he argues. The majority of your arteries feed your organs during systole. But your coronary arteries are different; they are surrounding the aortic valve, so they get blood only when the aortic valve closes and that happens in diastole.
Diastolic pressure has been getting more attention lately, however, thanks in part to an influential paper in Hypertension, written in 2011 by Guichard and Ali Ahmed, M.D., then a professor of medicine in UABs Division of Gerontology, Geriatrics and Palliative Care;and now the associate chief of staff for Health and Aging at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Washington, D.C.
Most people are trying to lower their blood pressure. What would you define as too low, and why is that a problem?
Laboratory Radiographic And Other Tests That Are Likely To Be Useful In Diagnosing The Cause Of This Problem
A routine electrocardiogram may show evidence of myocardial ischemia, signs of ventricular hypertrophy or bundle branch blocks.
Serial cardiac enzymes may indicate acute coronary syndrome as an underlying cause of acute heart failure exacerbation. Frequently a mild elevation in troponin-I could indicate myocardial stress rather than ischemic injury.
Brain natriuretic peptide levels are useful in differentiating between pulmonary and cardiac causes of dyspnea. Elevated BNP is an indicator of cardiac stress and suggests a cardiac contribution to the presenting symptoms but does not rule out pulmonary causes. Of note, obese individuals may have low BNP levels due to increased catabolism of BNP in adipose tissue, and heart failure in these patients cannot be ruled out with low BNP levels.
In addition to providing a diagnosis, echocardiography is also necessary to rule out other conditions that may present in a similar manner such as constrictive pericarditis and acute mitral and aortic regurgitation.
Non-invasive evidence of diastolic dysfunction can be obtained with Doppler echocardiography by measuring the mitral inflow velocity in early diastole and during atrial contraction . Changes in the pattern of these velocities and the resulting E/A ratio reflect progressive stages of diastolic dysfunction.
Also Check: How To Calculate Resting Heart Rate
Surgical Options To Treat Underlying Causes Of Heart Failure
- Coronary artery bypass graft or angioplasty to prevent and treat heart failure caused by blocked arteries. During bypass surgery, blood vessels taken from another part of the body usually the leg are used to link the open parts of a blocked artery around the blockage. In angioplasty, a thin flexible tube called a catheter is inserted through a small incision in the groin or neck into a blood vessel. In one procedure, a balloon is introduced through the catheter into the center of a blocked blood vessel. When the balloon is inflated, the blockage material is compressed back against the walls of the artery. A small metal device, called a stent, may be inserted through the catheter to serve as a permanent barrier to keep the plaque compressed. In another type of procedure, instruments are introduced through the catheter to remove the plaque.
- Implantation of pacemakers and other devices such as artificial heart valves
- Repairing congenital heart defects
Who Is Most Likely To Have Heart Failure
Heart failure is most common among older adults.
The American Heart Association writes that heart failure affects:
- 7.8% of males and 4.5% of females aged 6079
- 8.6% of males and 11.5% of females aged 80 and older
Aging can lead to diastolic heart failure because the heart muscles naturally stiffen over time, since age decreases muscle elasticity.
Also Check: Can Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Systolic Heart Failure Diagnosis
Doctors also refer to systolic heart failure as heart failure with reduced ejection fraction .
Ejection fraction is a measurement of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out each time it contracts.
The American Heart Association note that in general, the normal ejection fraction of a heart falls between 50% and 70%, while an ejection fraction of 4150% is borderline reduced. A person who has HFrEF may have an ejection fraction of less than 40%.
When diagnosing HFrEF, a doctor may use an echocardiogram to check a persons ejection fraction percentage.
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to form a picture of the heart.
Types Of Cardiomyopathy & Heart Failure
NYU Langone heart specialists are familiar with all types of cardiomyopathy, which means sickness of the heart muscle. This condition changes the shape and function of the heart. It reduces the hearts ability to pump blood and can cause heart arrhythmias, in which the heart beats too slowly or quickly.
Heart failure occurs when conditions such as cardiomyopathy, heart valve disease, or congenital heart disease damage the heart, reducing its ability to pump blood to the body.
Despite its name, heart failure isnt a complete loss of heart function, as occurs in sudden cardiac arrest, when the heart suddenly stops beating. Heart failure means the organ isnt pumping blood to the rest of the body as well as it should. This is a serious and progressive conditionyet manageable.
Doctors use a test called an echocardiogram to determine the percentage of blood the heart pumps with each contraction. This is called ejection fraction. A normal hearts ejection fraction is typically between 55 percent and 70 percent. The ejection fraction number is used to describe different types of heart failure or cardiomyopathy.
Don’t Miss: Vitamin D3 And Heart Palpitations
Can You Prevent Dd
Although all types of heart failure arent preventable, there are still steps you can take to lower your risk of conditions that can lead to DD. If you show symptoms of DD, your doctor will grade it as mild, moderate or severe.;
According to research done on DD and heart disease risk, asymptomatic DD is common in the general population, even in patients without heart failure. It increases with age and is prevalent among older women with systemic hypertension and ventricular hypertrophy. Diastolic dysfunction is linked to excessive weight, diabetes, age and limited physical activity or a sedentary lifestyle.
The heart becomes less efficient at relaxing as we get older, explains Dr. Jaber. When patients come in to get an ultrasound of the heart after experiencing symptoms such as shortness of breath, they should ask about both pumping and relaxation.
Quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, dietary changes, weight loss and aggressively controlling hypertension, high cholesterol and coronary artery disease are effective measures you can take to preventDD.;
Frequent exercise and managing diabetes should be considered as well, says Dr. Jaber.
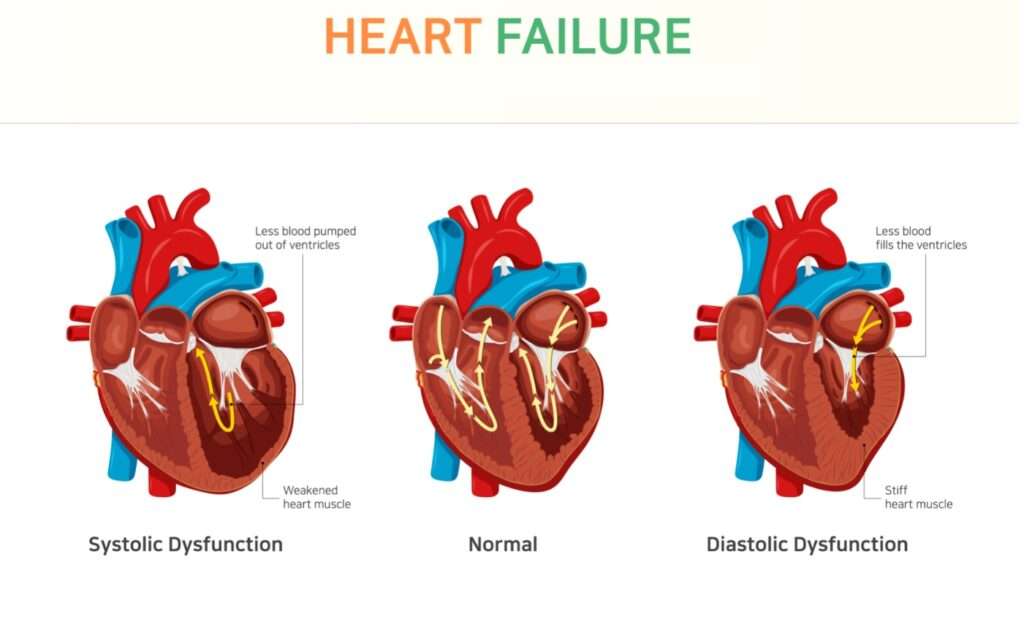
Systolic Versus Diastolic Heart Failure
The key difference between systolic and diastolic heart failure is in how well the left ventricle is pumping blood. As blood circulates though the heart, its final trip before going out to the rest of the body is the left ventricle. If it isnt performing well, the body doesnt get enough oxygen-rich blood, and fluids can back up affecting the lungs, kidneys and other organs.
Diastolic heart failure means the left ventricle pumping out as it should, but when it relaxes to refill with blood between beats it isnt taking in as much as it needs to. In cases of systolic heart failure, the left ventricle is filling with blood, but cant pump it out effectively.
Diagnosing systolic versus diastolic heart failure can be difficult and requires experience, skill and access to leading-edge tools possessed by the specialists at the Advanced Heart Failure and Recovery Program.
Precise diagnosis is crucial, because the treatments for systolic or diastolic heart failure can be quite different, especially when mechanical assist devices may be needed.
You May Like: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Diastolic Heart Failure Prevention
As with many health conditions, preventative action is vital to avoiding diastolic heart failure. According to studies, nitric oxide is shown to reduce blood pressure and prevent artery blockage and stroke. By boosting the nitric oxide levels in the body with food, preventing heart failure may be possible. The following foods are able to increase nitric oxide levels in the body:
- Dark chocolate: Raw cacao beans are full of antioxidants and increase the nitric oxide levels in the body. They help lower blood pressure and reduce inflammation. That being said, it is high in sugar and should only be consumed on occasion.
- Beets: Several studies have shown that beetroot is able to lower blood pressure, is high in antioxidants and betalains, and reduces inflammation.
- Cayenne: The warming impact of this spice can help dilate blood vessels. Using excessive amounts is not recommended, but including a sprinkling in meals can be helpful.
Here are some preventative measures you can take:
- Lower your sodium intake
- Get active with moderate exercise to boost circulation and reduce stress
- Eat a healthy diet and limit sugar, saturated fat, and cholesterol
- Get regular checkups
