Clinical Contributors To This Story
Sarah L. Timmapuri, M.D. contributes to topics such as Cardiac / Heart Health, Exercise / Fitness.
If your heart is racing as youre sitting reading this article, its possible your body is trying to tell you something. A high resting heart rate, or a heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute, means your heart is working extra hard to pump blood through your body. And, that extra effort could result in a wide range of negative effects on your overall health, including feelings of dizziness and fatigue and most seriously blood clots, heart failure and, in rare cases, sudden death.
Normal resting heart rate is anywhere between 60 and 100 beats per minute, and its simple to check how fast yours is beating. While idle, hold your pointer and middle finger between your bone and tendon on the thumb side on your wrist until you feel your pulse, and count the number of beats for a minute that is your resting heart rate.
Certain aspects of someones resting heart rate are directly connected to uncontrollable factors, such as age and genetics, however there are certain actions that be taken to help decrease heart rate and improve overall wellbeing for those whose resting heart rate is above normal.
Here are six proven ways to lower your resting heart rate:
Recommended Reading: Fitbit Charge 2 Heart Rate Accuracy
So Your Resting Heart Rate Is Normal
Congrats! A normal RHR reading is definitely a good thing, but if you’re monitoring it for fitness or wellness-related reasons, it’s not the only thing to pay attention to. That’s because “normal” doesn’t necessarily equal “healthy.”
In fact, in a recent study, middle-aged men who had a RHR of 75 bpm or higher at the start of the study were twice as likely to die over the next 11 years, compared to men with a RHR of 55 or below.
“Ideally, you want your resting heart rate to be somewhere between 50 and 70 bpm,” says Haythe. “But I don’t think that people need to be obsessively checking.” Once a month is totally fine.
“Something also very important is how quickly your heart rate comes down after you exercise,” Haythe said. “We want to see that your heart rate is slow at rest, that it increases appropriately with exercise, and that it comes down quickly after aerobic activity — within a few minutes.”
Regardless of which method you use, when trying to gauge how healthy you are, one thing is certain: Any results should be considered alongside other metrics, like blood pressure and cholesterol, in consultation with your doctor, especially if you notice changes over time.
Read more:Heart rate variability: The most important health metric you aren’t tracking
Normal Pulse Rate For Older Women
Your resting pulse rate is one of three vital signs, along with your blood pressure and respiratory rate, that provide a snapshot of your overall health. Your pulse rate is lower when youre resting calmly and goes up when you exercise and your heart works harder to provide oxygen-rich blood to vital organs. Older women have the same normal resting pulse range as their younger counterparts, according to Medline Plus.
Read Also: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
Don’t Miss: Top Part Of Heart Not Working
What Is A Normal Or Resting Heart Rate
There are three general ways to classify heart rate, 1) normal, 2) fast and 3) slow.
- A resting heart rate is normal between 60-100 beats per minute.
- A resting heart rate is fast at greater than 100 beats per minute.
- A resting heart rate is slow at less than 60 beats per minute.
A resting heart rate predicts longevity and cardiovascular disease, and current evidence suggests that it is also an important marker of outcome in cardiovascular disease, including heart failure. A normal heart rate is generally stated to be between 60-100 beats per minute at rest . However, recent studies have suggested that an ideal resting heart rate is between 50-70 beats per minute. It is well-known that the average resting heart rate for well-trained athletes is between 40-60 beats per minute! A heart rate can change dramatically while sleeping or with daily activity and exercise. Usually, a heart rate will be slower during sleep, faster during daily activities or with exercise, and recover quickly back to a resting rate after exercise. This means your heart has appropriate heart rate variability and recovery, which is associated with good heart health. Your resting heart rate can also be used to estimate how much energy your body uses, or your basal metabolic rate.
Your Maximum Heart Rate
The rate at which your heart is beating when it is working its hardest to meet your body’s oxygen needs is your maximum heart rate. Your maximum heart rate plays a major role in setting your aerobic capacitythe amount of oxygen you are able to consume. Several large observational studies have indicated that a high aerobic capacity is associated with a lower risk of heart attack and death. And a small controlled trial demonstrated that men and women with mild cognitive impairment who raised their aerobic capacity also improved their performance on tests of memory and reasoning.
Also Check: What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
Correlation With Cardiovascular Mortality Risk
| This section needs more medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. Please review the contents of the section and add the appropriate references if you can. Unsourced or poorly sourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: “Heart rate” news ·newspapers ·books ·scholar ·JSTOR |
A number of investigations indicate that faster resting heart rate has emerged as a new risk factor for mortality in homeothermic mammals, particularly cardiovascular mortality in human beings. Faster heart rate may accompany increased production of inflammation molecules and increased production of reactive oxygen species in cardiovascular system, in addition to increased mechanical stress to the heart. There is a correlation between increased resting rate and cardiovascular risk. This is not seen to be “using an allotment of heart beats” but rather an increased risk to the system from the increased rate.
Given these data, heart rate should be considered in the assessment of cardiovascular risk, even in apparently healthy individuals. Heart rate has many advantages as a clinical parameter: It is inexpensive and quick to measure and is easily understandable. Although the accepted limits of heart rate are between 60 and 100 beats per minute, this was based for convenience on the scale of the squares on electrocardiogram paper a better definition of normal sinus heart rate may be between 50 and 90 beats per minute.
Exercise And Heart Rate
Like any other muscle, your heart needs exercise to keep it fit and healthy. Regular exercise can help reduce your risk of heart disease and other health conditions, such as diabetes.
To keep your heart healthy, you should aim to do 150 minutes of low to moderate intensity exercise a week. If you have a heart condition, talk to your doctor about what exercise and target heart rates are safe for you.
One way to measure the intensity of your exercise is by using your heart rate. To exercise at a low to moderate intensity your heart rate should be at 50 to 70% of your approximate maximum heart rate.
The easiest way to get an approximate maximum heart rate is to calculate 220 your age. You then need to calculate 50 to 70% of your MHR.
For example, if you’re 40-years-old:
- your approximate maximum heart rate is: 220 40 = 180 beats per minute
- 50% of your MHR is 180 X 0.5 = 90 bpm
- 70% of your MHF is 180 X 0.7 = 126 bpm.
Alternatively, you can use our heart rate chart below to get a rough idea.
Remember if you’re on medications to slow your heart rate down, you may not be able to meet these upper heart rates and the aim should be to exercise at a rate that makes you lightly puff.
Don’t Miss: Ibs And Palpitations
Can Resting Heart Rate Be Too High
Can resting heart rate be too high?
As mentioned, normal heart rate can range between 60 to 100 beats per minute. So, if your resting heart rate is consistently higher than 100, do you need to be worried?
“The more beats your heart has to take on a regular basis, the more strain it places on your heart over time. A resting heart rate regularly above 100 beats per minute is called tachycardia, which can place you at an increased risk of heart disease, and even death if your heart rate climbs high enough,” warns Dr. Chebrolu.
This means that it’s incredibly important to talk to your doctor if you’re resting heart rate is consistently high. He or she can run the tests and bloodwork needed to assess your overall heart health.
Your doctor can also recommend lifestyle changes that may help lower your resting heart rate, including:
- Getting regular exercise
- Regularly practicing relaxation techniques, such as yoga and meditation
- Losing excess weight
- Maintaining healthy choices and modifying your cardiovascular risk factors
- Avoiding certain prescription and over-the-counter medications that can affect your heart rate
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol use
“In particular, starting an exercise program can help you decrease your resting heart rate up to one beat per minute for every week or so that you train with reductions in resting heart rate, over time, ranging from 10 to 12 beats per minute,” adds Dr. Chebrolu.
What Is A Good Heart Rate For My Age
A good heart rate differs from individual to individual, and it depends upon your age and the kind of physical work you do.
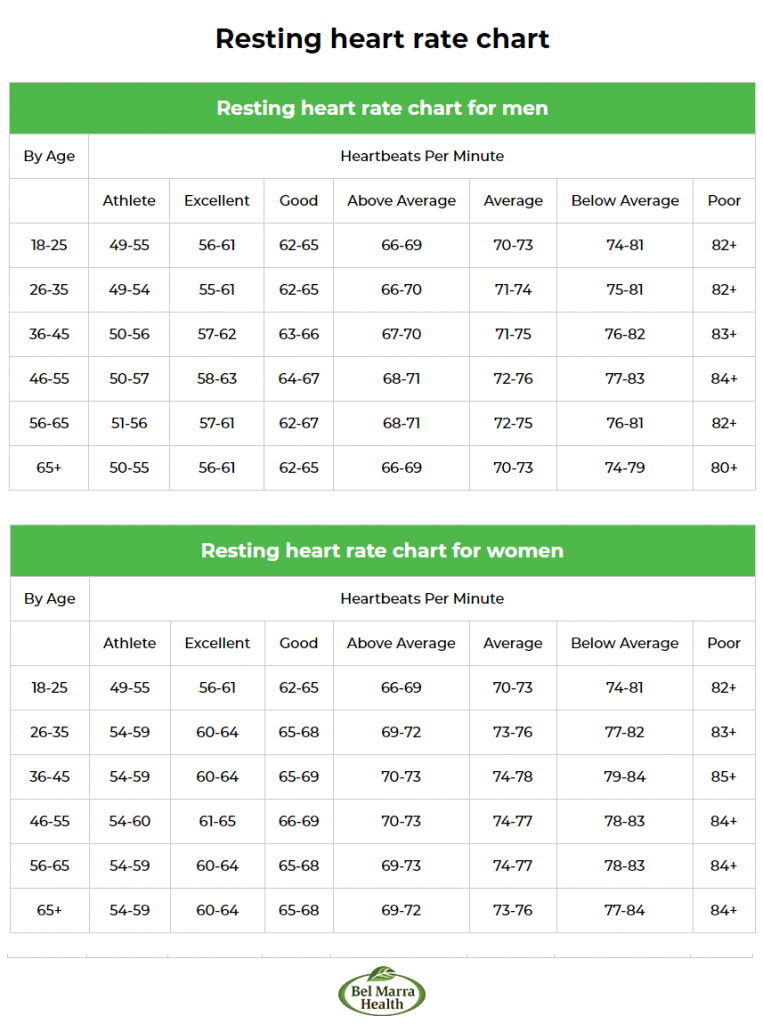
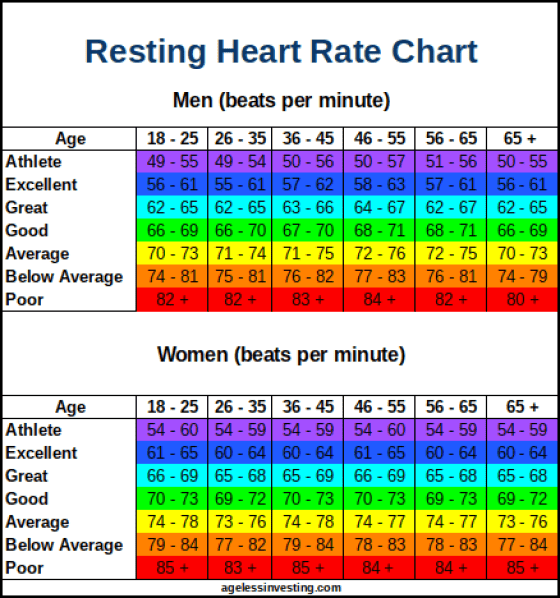
Given below is the chart showing normal heart rates by age.
Heart Rate by Age Range
| Approximate Age Range | |
| 15 years or older | 60-100 |
However, a heart rate that is lower than 60 per minute does not necessarily mean that it is abnormal. If you are an athlete or someone who is engaged in moderate to vigorous physical activity, you may have your heart rate between 40 and 60 per minute.
Read Also: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Recommended Reading: What Are The Early Signs Of Congestive Heart Failure
Heart Rate Tips To Keep In Mind
- Start at your beginning. Before getting overly concerned about your heart rate, Martin says, its best to simply get moving. If you havent exercised much before, start where youre comfortable and gradually exert yourself more over time.
- Listen to your body. Your body provides other indicators of how hard its working that you need to consider along with heart rate. Pay attention to how hard youre breathing or sweating, and stop if you feel very uncomfortable, Martin says. Devices recording your heart rate have been known to malfunction, for exampleanother reason listening to your body is important.
- Remember that target heart rate is just a guide. Dont get overly fixated on numbers, Martin says. Ideally, they just push you to work a little harder.
How To Take Your Resting Heart Rate
The best time to check your resting pulse is when you’re relaxed, so do it before you perform any sort of strenuous activity or wait for at least two hours afterward. First thing in the morning before you’ve had caffeine is typically a good time in that regard. So is right before you go to sleep, says Dr. Razavi, who recommends taking your resting heart rate once a day, so you can compare readings for the most accurate number.
Most fitness trackers or wearables can provide accurate heart rate figures, as do blood pressure cuffs, says Dr. Razavi. If you don’t have a heart rate monitor, follow these steps to check your pulse:
Read Also: Typical Resting Heart Rate For A Healthy Individual
Lowering A Rapid Heart Rate
Pulse rates can spike due to nervousness, stress, dehydration and overexertion. Sitting down and taking slow, deep breaths can generally lower your heart rate. Exercising and getting fitter will usually lower heart rate, too.
Cooling down after a workout is important, according to the AHA. Because your heart is beating faster, your body temperature is higher and your blood vessels are dilated, stopping too fast could make you feel sick or even pass out.
The AHA recommends stretching and walking. Stretching helps reduce the buildup of lactic acid, which cause cramps and stiff muscles. Follow these tips:
- Walk for about 5 minutes, or until your heart rate gets below 120 beats per minute.
- Stretch, and hold each stretch 10 to 30 seconds. If you feel you need more, stretch the other side and return for another set of stretching.
- The stretch should be strong, but not painful.
- Do not bounce.
- Breathe while youre stretching. Exhale as you stretch, inhale while holding the stretch.
How Do You Check Your Pulse
You can measure your heart rate manually by checking your pulse. Follow these three steps.
- Find your pulse in your wrist .
- Count each beat for a total time of 30 seconds.
- Double the number of beats you counted. This is your heart rate or pulse, measured in beats per minute.
Also make a note of whether your heart beats at an even or uneven rhythm. A normal heart beats at a steady rhythm like a clock, tick tock tick tock.
Some people like to use a heart rate monitor to measure their heart rate. These monitors are often included in fitness trackers, which are now widely available in sports stores and other retail outlets. However, their accuracy depends on the quality of the device.
Also Check: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Can Resting Heart Rate Be Too Low
While less common, some people may have a resting heart rate that falls lower than 60 beats per minute.
“When a person’s heart muscle is in excellent condition, it doesn’t have to work as hard to keep a steady beat. Therefore, people who exercise frequently and are very physically fit can have a resting heart rate that falls below 60 beats per minute. In fact, a trained athlete’s resting heart rate can be as low as 40 beats per minute,” explains Dr. Chebrolu.
Additionally, medications, specifically beta blockers, can also slow your heart rate.
“The time to worry about a low heart rate is if you’re not very active and you’re not taking medications but your resting heart rate frequently falls below 60 beats per minute, especially if you’re also experiencing dizziness, shortness of breath or fainting,” warns Dr. Chebrolu. “This can be a sign of bradycardia a slower than normal heart rate that can lead to poor oxygen flow to your vital organs.”
Next Steps:
What Are Heart Palpitations
A heart palpitation is when you suddenly become aware of your heart beating, usually in an irregular way. Sometimes you can feel it in your ears or your chest when youre lying down. Your heart beat may feel:
- too fast or slow
- like its fluttering
- like its thudding, or pounding.
It is not unusual to feel heart palpitations occasionally and mostly they are harmless. However if youre experiencing them on a regular basis, see your doctor.
Read Also: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
What Is A Healthy Heart Rate What Is Optimal
An optimal heart rate about one beat per second at rest, or . Consequently, for every 10 beats per minute increase, theres a 10 to 20% increased risk of premature death.
Theres strong evidence showing that everyone with a high heart rate is at risk , even otherwise healthy individuals. But there are ways that you can slow your heart rate naturally.
First, check your resting heart rate before you make any changes using the method in section 2. This reading will be your baseline number to track your progress and test which programs work for you. Secondly, record your heart rate after any changes you make.
Why Does Resting Heart Rate Matter
Resting heart rate is an indicator of overall health. Changes in resting heart rate can be among the first signs of an underlying issue. Having a lower resting heart rate doesnt necessarily indicate a cause for concern. Elite athletes and people who have a high fitness level tend to have lower resting heart rates. Medications and sleeping patterns can also lead to lower resting heart rates.
In some cases, low heart rates or significant decreases from your normal baseline can be a sign of an underlying problem such as heart disease. Additionally, heart attack, underactive thyroid, and some infections can also cause low resting heart rate.
Your heart rate varies when youre under stress during strenuous exercise and when youre just lounging. Its normal for your heart rate to be higher when you exercise because your heart has to pump oxygenated blood to your organs faster when youre exerting a lot of energy. Exercise and mood changes can cause an increase in resting heart rate. Think about the last time you were really excited or nervous. The feeling of your heart pounding in your chest is a reflection of an increased heart rate.
When your heart rate is consistently too high, you may have a health problem. Asthma and other breathing conditions can cause an increased resting heart rate. Anemia, heart problems, and medications can also raise heart rate numbers.
Read Also: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
What Your Heart Rate Can And Cant Tell You About Your Health
Before the rise in popularity of fitness trackers and smartwatches, cardiologist Sadiya Khan said patients rarely came in with questions about why their heart rates seemed high or low. But the growing interest in wearable devices, which some early research suggests can even detect coronavirus symptoms, means many people have a trove of real-time health information at their fingertips.
I see a lot more people asking about heart rate because you can track it, you can monitor it, you can make pretty graphs on your Apple Watch, said Khan, an assistant professor of medicine at Northwestern Universitys Feinberg School of Medicine.
But while your heart rate can be a key indicator of your health, Khan and other experts emphasized that it is just one piece of the puzzle.
Its a place to start, said Seth Martin, a cardiologist and associate professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins. If thats your entry into thinking about ones health, then thats great. But your heart rate cant tell you everything you need to know about your health, he added, and it is important not to fixate on that one measure.
