Valves Maintain Direction Of Blood Flow
As the heart pumps blood, a series of valves open and close tightly. These valves ensure that blood flows in only one direction, preventing backflow.
- The tricuspid valve is situated between the right atrium and right ventricle.
- The pulmonary valve is between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery.
- The mitral valve is between the left atrium and left ventricle.
- The aortic valve is between the left ventricle and the aorta.
Each heart valve, except for the mitral valve, has three flaps that open and close like gates on a fence. The mitral valve has two valve leaflets.
Introduction To The Heart
The heart is a muscular organ behind the sternum , slightly to the left of the center of the chest. A normal adult heart is about the size of a fist. The function of the heart is to pump blood through blood vessels of the cardiovascular system. The continuous flow of blood through the system is necessary to provide all the cells of the body with oxygen and nutrients, and to remove their metabolic wastes.
How Your Heart Works
Your heart
The human heart is one of the hardest-working organs in the body.
On average, it beats around 75 times a minute. As the heart beats, it provides pressure so blood can flow to deliver oxygen and important nutrients to tissue all over your body through an extensive network of arteries, and it has return blood flow through a network of veins.
In fact, the heart steadily pumps an average of 2,000 gallons of blood through the body each day.
Your heart is located underneath your sternum and ribcage, and between your two lungs.
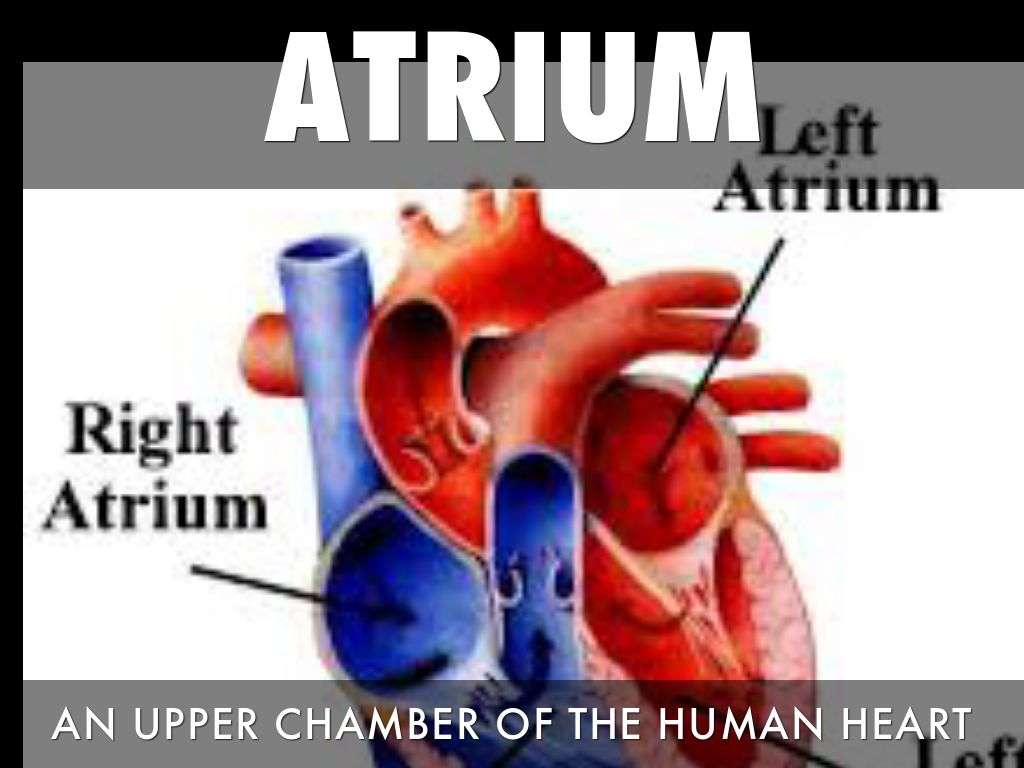
The hearts four chambers function as a double-sided pump, with an upper and continuous lower chamber on each side of the heart.
The hearts four chambers are:
- Right atrium. This chamber receives venous oxygen-depleted blood that has already circulated around through the body, not including the lungs, and pumps it into the right ventricle.
- Right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps blood from the right atrium to the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery sends the deoxygenated blood to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen in exchange for carbon dioxide.
- Left atrium. This chamber receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins of the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle.
- Left ventricle. With the thickest muscle mass of all the chambers, the left ventricle is the hardest pumping part of the heart, as it pumps blood that flows to the heart and rest of the body other than the lungs.
Read Also: Can Prednisone Cause Heart Palpitations
When Should I Talk To A Doctor
You should call your healthcare provider if you experience:
- Bluish lips or skin color.
- Swollen ankles, feet or abdomen.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Your pulmonary arteries play an important role getting carbon dioxide out of your blood and oxygen back into it. Many conditions that affect the pulmonary arteries and pulmonary blood circulation are congenital or present at birth. But coronary artery disease and other heart disease can damage the pulmonary arteries. Depending on the heart problem, you may need surgery or other treatments to improve blood flow and oxygenation. Your healthcare provider can offer suggestions on ways to improve your heart health.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/10/2021.
References
- Adult Congenital Heart Association. . Accessed 3/10/2021.Pulmonary Hypertension
- American Heart Association. Problem: . Accessed 3/10/2021.Pulmonary Valve Regurgitation
- Castaner E, Gallardo X, Rimola J, et al. Radiologic overview. RadioGraphics. Accessed 3/10/2021.Congenital and acquired pulmonary artery anomalies in the adult:
- Kreibich M, Siepe M, Kroll J, et al. Circulation. 2015 131:310-16. Accessed 3/10/2021.Aneurysms of the pulmonary artery.
- Tucker WB, Weber C, Burns B. . StatPearls . 2020. Accessed 3/10/2021.Anatomy, thorax, heart pulmonary arteries
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services.Policy
How Can I Protect My Heart And Pulmonary Arteries
Many of the conditions that affect the pulmonary arteries are present at birth. While you cant prevent these problems, these actions can promote better heart health:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet with plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Get at least 150 minutes of cardiovascular physical activity every week.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
Don’t Miss: Typical Resting Heart Rate For A Healthy Individual
The Left Side Of The Heart
Oxygen-rich blood from the lungs passes through the pulmonary veins . It enters the left atrium and is pumped into the left ventricle. From the left ventricle, the blood is pumped to the rest of the body through the aorta.
Like all of the organs, the heart needs blood rich with oxygen. This oxygen is supplied through the coronary arteries as its pumped out of the hearts left ventricle.
The coronary arteries are located on the hearts surface at the beginning of the aorta. The coronary arteries carry oxygen-rich blood to all parts of the heart.
How The Heart Works
The heart is an organ, about the size of a fist. It is made of muscle and pumps blood through the body. Blood is carried through the body in blood vessels, or tubes, called arteries and veins. The process of moving blood through the body is called circulation. Together, the heart and vessels make up the cardiovascular system.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Dangerously High Heart Rate
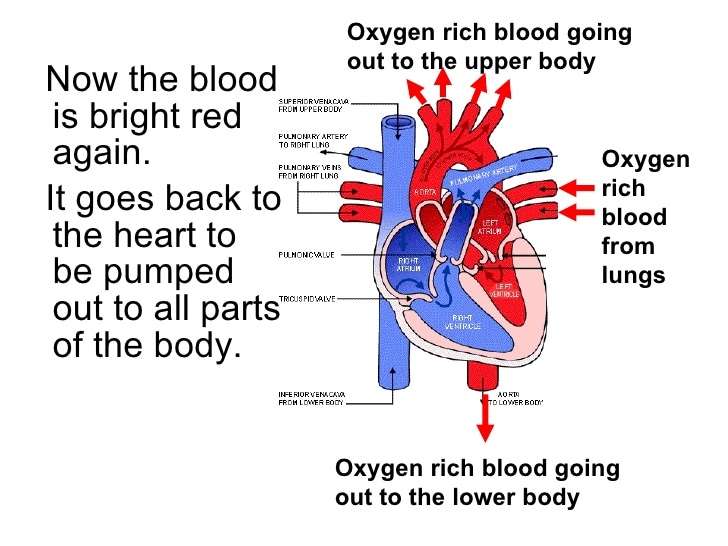
Blood Flow Through The Heart
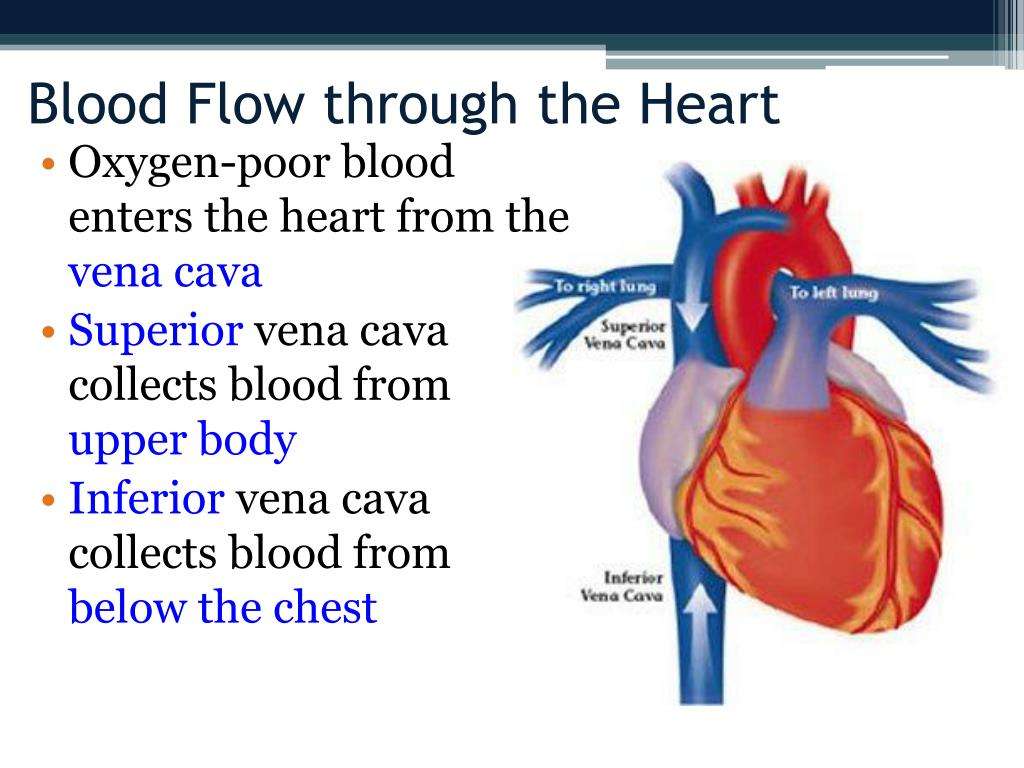
When working properly, deoxygenated blood coming back from organs, other than the lungs, enters the heart through two major veins known as the vena cavae, and the heart returns its venous blood back to itself through the coronary sinus.
From these venous structures, the blood enters the right atrium and passes through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. The blood then flows through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery trunk, and next travels through the right and left pulmonary arteries to the lungs, where the blood receives oxygen during air exchange.
On its way back from the lungs, the oxygenated blood travels through the right and left pulmonary veins into the left atrium of the heart. The blood then flows through the mitral valve into the left ventricle, the hearts powerhouse chamber.
The blood travels out the left ventricle through the aortic valve, and into the aorta, extending upward from the heart. From there, the blood moves through a maze of arteries to get to every cell in the body other than the lungs.
Blood Vessels Of The Heart
The blood vessels of the heart include:
- venae cavae deoxygenated blood is delivered to the right atrium by these two veins. One carries blood from the head and upper torso, while the other carries blood from the lower body
- pulmonary arteries deoxygenated blood is pumped by the right ventricle into the pulmonary arteries that link to the lungs
- pulmonary veins the pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart
- aorta this is the largest artery of the body, and it runs the length of the trunk. Oxygenated blood is pumped into the aorta from the left ventricle. The aorta subdivides into various branches that deliver blood to the upper body, trunk and lower body
- coronary arteries like any other organ or tissue, the heart needs oxygen. The coronary arteries that supply the heart are connected directly to the aorta, which carries a rich supply of oxygenated blood
- coronary veins deoxygenated blood from heart muscle is ‘dumped’ by coronary veins directly into the right atrium.
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
How Do Congenital Heart Defects Develop
As a fetuss heart develops from a simple tube to a four-chambered heart with associated veins and arteries, defects may develop. Part of the heart may develop partially or not at all, a hole in the wall of the heart may form, or the heart arteries and veins may form abnormal connections with the heart. Congenital heart defects are often thought to be genetic, but they can also be caused by illness or behavioral factors in the mother such as viral infections like German measles, certain prescription drugs and over-the-counter medicines, alcohol, or illegal drugs. Some conditions like Down syndrome and Turner syndrome are associated with CHDs.
How Does Blood Flow Through Your Lungs
Once blood travels through the pulmonic valve, it enters your lungs. This is called the pulmonary circulation. From your pulmonic valve, blood travels to the pulmonary arteries and eventually to tiny capillary vessels in the lungs.
Here, oxygen travels from the tiny air sacs in the lungs, through the walls of the capillaries, into the blood. At the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, passes from the blood into the air sacs. Carbon dioxide leaves the body when you exhale. Once the blood is oxygenated, it travels back to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
Don’t Miss: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Feature: Human Biology In The News
When a patients heart is too diseased or damaged to sustain life, a heart transplant is likely to be the only long-term solution. The first successful heart transplant was undertaken in South Africa in 1967. There are over 2,200 Canadians walking around today because of life-saving heart transplant surgery. Approximately 180 heart transplant surgeries are performed each year, but there are still so many Canadians on the transplant list that some die while waiting for a heart. The problem is that far too few hearts are available for transplant there is more demand than supply . Sometimes, recipient hopefuls will receive a device called a Total Artificial Heart , which can buy them some time until a donor heart becomes available.
Figure 14.3.10 A Total Artificial Heart, shown here, can be used for short periods of time in order to maintain a patient until a donor heart becomes available.
Watch the video below Total artificial heart option from Stanford Health Care to see how it works:
Total artificial heart option at Stanford , Stanford Health Care, 2014.
Functions Of The Heart/lung
The heart is a strong and muscular, cone-shaped organ that is about the size of a fist. It pumps blood throughout the body and is located behind the breastbone between the lungs. Deoxygenated blood flows from the heart to the lungs where it gives up wastes and is freshly oxygenated. From there, the blood returns to the heart and is pumped to the rest of the body. Heart failure is the inability of the heart to pump enough blood to maintain normal body requirements. Birth defects or any condition that damages or overloads the heart muscle can cause it. Treatment depends on the cause of heart failure and the age and condition of the patient.
Lungs are a pair of highly elastic and spongy organs in the chest. They are the main organs involved in breathing. They take in air from the atmosphere and provide a place for oxygen to enter the blood and for carbon dioxide to leave the blood. The lungs are divided into lobes, with three on the right and two on the left.
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
How Do Doctors Treat Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
Without treatment, hypoplastic left heart syndrome is almost always immediately fatal within the first few days of birth. Treating the defect is an involved process. Prostaglandin E1 will help keep the patent ductus open as doctors try to balance blood flow to the lungs and body with other drugs to allow the baby to survive. Although heart transplantation is an option for children with this disorder, the most popular option is called staged reconstruction. Staged reconstruction shows promising results and involves a series of three surgeries that are designed to make the patients heart as efficient as possible. These surgeries, particularly the first, are dangerous and difficult, but the outlook for patients with this defect is improving.
What Are The Coronary Arteries
Like all organs, your heart is made of tissue that requires a supply of oxygen and nutrients. Although its chambers are full of blood, the heart receives no nourishment from this blood. The heart receives its own supply of blood from a network of arteries, called the coronary arteries.
Two major coronary arteries branch off from the aorta near the point where the aorta and the left ventricle meet:
- Right coronary artery supplies the right atrium and right ventricle with blood. It branches into the posterior descending artery, which supplies the bottom portion of the left ventricle and back of the septum with blood.
- Left main coronary artery branches into the circumflex artery and the left anterior descending artery. The circumflex artery supplies blood to the left atrium, as well as the side and back of the left ventricle. The left anterior descending artery supplies the front and bottom of the left ventricle and the front of the septum with blood.
These arteries and their branches supply all parts of the heart muscle with blood.
When the coronary arteries narrow to the point that blood flow to the heart muscle is limited , a network of tiny blood vessels in the heart that aren’t usually open may enlarge and become active. This allows blood to flow around the blocked artery to the heart muscle, protecting the heart tissue from injury.
Read Also: Ibs And Heart Palpitations
What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
The left ventricle is the major muscular pump
What heart chamber pumps blood through the aortic semilunar valve?
From there, blood is forced through the mitral valve into the left ventricle. This is the muscular pump that sends blood out to the rest of the body. When the left ventricle contracts, it forces blood through the aortic semilunar valve and into the aorta.
What is the chamber that pushes blood through the aortic valve? The right ventricle pumps the oxygen-poor blood to the lungs through the pulmonary valve. The left atrium receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle through the mitral valve. The left ventricle pumps the oxygen-rich blood through the aortic valve out to the rest of the body.
What Chamber is the aortic semilunar valve?
The valve between the left ventricle and the aorta is the aortic semilunar valve. When the ventricles contract, atrioventricular valves close to prevent blood from flowing back into the atria.
Which Type Of Blood Vessel Has Thicker Walls
Arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins return blood to the heart. Veins are generally larger in diameter, carry more blood volume and have thinner walls in proportion to their lumen. Arteries are smaller, have thicker walls in proportion to their lumen and carry blood under higher pressure than veins.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Say Heart Attack In Spanish
What Conditions And Disorders Affect The Pulmonary Arteries
The most common problems with the pulmonary arteries are congenital heart defects, meaning the issue is present at birth. To understand these defects you have to understand a little about the development of the heart and the circulation before you are born. Normal development of the heart and pulmonary arteries requires that the two sides of the heart shares the work equally and the way that happens is that there are two communications between the pulmonary and the systemic circulation, one atrial and one between the pulmonary artery and the aorta . Disturbed balance result in problems. These communications normally close soon after birth.
Any of these conditions can be associated with arrhythmias and cause heart failure.
Caring for Your Heart and Pulmonary Arteries
Preparing For An Appointment
After a patent foramen ovale has been diagnosed, you’ll likely have a lot of questions for your doctor. Some questions you may want to ask include:
- What caused this to happen?
- How dangerous is this condition?
- What treatments are available, and which do you recommend?
- What are the risks of a procedure to close the patent foramen ovale?
- I have other health conditions. How can I best manage these conditions together?
- Should activity be restricted in any way?
- Could I have passed this condition on to my child?
- Are there any brochures or other printed material that I can take home with me? What websites do you recommend visiting?
©1998-2021 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research . All rights reserved. Terms of Use
Recommended Reading: How Does Heart Disease Affect The Skeletal System
What Are The Types Of Congenital Heart Defects
Congenital heart defects vary widely in structure and severity. CHDs usually involve one of the following: abnormal passages in the heart or between blood vessels, problems with the valves that control the emptying and filling of the heart chambers, mismatched or abnormally located or developed blood vessels near the heart, or structural or developmental malformations in the heart itself.
How Is Tricuspid Atresia Diagnosed
- Tricuspid atresia may be seen on fetal ultrasound before a child is born. This test uses sound waves to form a picture of the babys heart. This test can be done as early as when the mother is 12 weeks pregnant.
- If it isnt found before birth, signs of a heart problem may be noted during a physical exam shortly after birth.
- If a heart problem is suspected, your child will be referred to a pediatric cardiologist. This is a doctor who diagnoses and treats heart problems in children. To confirm tricuspid atresia, several tests may be done. These include:
- Chest X-ray. X-rays are used to take a picture of the heart and lungs.
- Electrocardiography . The electrical activity of the heart is recorded.
- Echocardiography . Sound waves are used to create a picture of the heart and look for structural problems and other problems.
You May Like: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Why Blood Pressure In Pulmonary Artery Is More Than That In Pulmonary Vein
The blood in the pulmonary arteries is pumped by the right ventricle of the heart. Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart and enter the left atrium. Since the blood in the pulmonary arteries is pumped by the heart, it flows under greater pressure than the blood in the pulmonary veins.
