Types Of Heart Failure
In heart failure, the heart can no longer pump enough blood around the body. The heart muscle is either too weak or not elastic enough. Different parts of the heart may be affected too. The type of medication people use for the treatment of heart failure will depend on the type of heart failure they have.
Heart failure often only affects the left or right side of the heart, but can affect both. Doctors differentiate between three types of heart failure, accordingly:
- Left-sided heart failure: The left ventricle of the heart no longer pumps enough blood around the body. As a result, blood builds up in the pulmonary veins . This causes shortness of breath, trouble breathing or coughing especially during physical activity. Left-sided heart failure is the most common type.
- Right-sided heart failure: Here the right ventricle of the heart is too weak to pump enough blood to the lungs. This causes blood to build up in the veins . The increased pressure inside the veins can push fluid out of the veins into surrounding tissue. This leads to a build-up of fluid in the legs, or less commonly in the genital area, organs or the abdomen .
- Biventricular heart failure: In biventricular heart failure, both sides of the heart are affected. This can cause the same symptoms as both left-sided and right-sided heart failure, such as shortness of breath and a build-up of fluid.
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The symptoms of heart failure depend on which side of your heart is affected and how serious your condition has become. Most symptoms are caused by reduced blood flow to your organs and fluid buildup in your body.
Fluid buildup happens because the flow of blood through your heart is too slow. As a result, blood backs up in the vessels that return the blood to your heart. Fluid may leak from the blood vessels and collect in the tissues of your body, causing swelling and other problems.
Symptoms of heart failure may include:
- Feeling short of breath when you do things like climbing stairs. This may be one of the first symptoms you notice.
- Fatigue or weakness even after rest.
What Can I Do To Manage Swelling From Extra Fluid
- Elevate your legs above the level of your heart. This will help with fluid that builds up in your legs or ankles. Elevate your legs as often as possible during the day. Prop your legs on pillows or blankets to keep them elevated comfortably. Try not to stand for long periods of time during the day. Move around to keep your blood circulating.
- Limit sodium . Ask how much sodium you can have each day. Your healthcare provider may give you a limit, such as 2,300 milligrams a day. Your provider or a dietitian can teach you how to read food labels for the number of mg in a food. He or she can also help you find ways to have less salt. For example, if you add salt to food as you cook, do not add more at the table.
- Drink liquids as directed. You may need to limit the amount of liquid you drink within 24 hours. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much liquid to have and which liquids are best for you. He or she may tell you to limit liquid to 1.5 to 2 liters in a day. He or she will also tell you how often to drink liquid throughout the day.
- Weigh yourself every morning. Use the same scale, in the same spot. Do this after you use the bathroom, but before you eat or drink. Wear the same type of clothing each time. Write down your weight and call your healthcare provider if you have a sudden weight gain. Swelling and weight gain are signs of fluid buildup.
Recommended Reading: Icd 10 For Heart Failure
What Causes Heart Failure
Heart failure can start suddenly after a medical condition or injury damages your heart muscle. But in most cases, heart failure develops slowly from long-term medical conditions.
Conditions that can cause heart failure include:
Systolic And Diastolic Failure
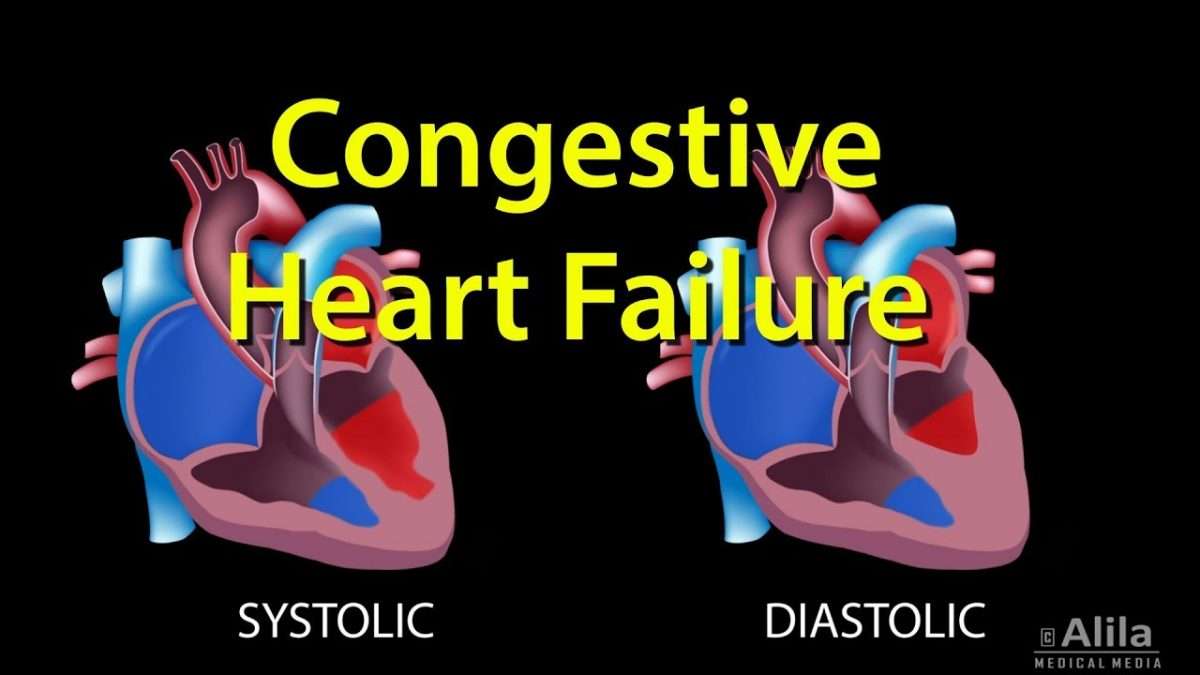
Systolic and diastolic heart failure each result in a decrease in stroke volume. This leads to activation of peripheral and central baroreflexes and chemoreflexes that are capable of eliciting marked increases in sympathetic nerve traffic.
Although there are commonalities in the neurohormonal responses to decreased stroke volume, the neurohormone-mediated events that follow have been most clearly elucidated for individuals with systolic heart failure. The ensuing elevation in plasma norepinephrine directly correlates with the degree of cardiac dysfunction and has significant prognostic implications. Norepinephrine, while directly toxic to cardiac myocytes, is also responsible for a variety of signal-transduction abnormalities, such as downregulation of beta1-adrenergic receptors, uncoupling of beta2-adrenergic receptors, and increased activity of inhibitory G-protein. Changes in beta1-adrenergic receptors result in overexpression and promote myocardial hypertrophy.
Dont Miss: What Is Target Heart Rate Definition
Also Check: What Is The Heart Rate
How Common Is Heart Failure
In the United States alone, more than six million adults have been diagnosed with heart failure.
Heart failure is usually divided into two categories based on which side of the heart it mainly affects. The right side of the heart collects oxygen-depleted blood from the body and brings it to the lungs to be filled with fresh oxygen. The left side of the heart receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and sends it out to the rest of the body.
While the end result is the same, symptoms can vary based on whether the right or left side of the heart is affected.
Verywell / Jessica Olah
How Is Heart Failure Treated
Your healthcare providers will help you manage any other health conditions that may be causing your heart failure. The goals of treatment are to manage, slow, or reverse heart damage. Treatment may include the following:
- Medicines may be given to help regulate your heart rhythm and lower your blood pressure. You may also need medicines to help decrease extra fluid. Medicines, such as NSAIDs, may be stopped if they are making your heart failure worse. Do not stop any of your medicines on your own.
- Cardiac rehab is a program run by specialists who will help you safely strengthen your heart. In the program you will learn about exercise, relaxation, stress management, and heart-healthy nutrition. Cardiac rehab may be recommended if your heart failure is not severe.
- Oxygen may help you breathe easier if your oxygen level is lower than normal. A CPAP machine may be used to keep your airway open while you sleep.
- Surgery can be done to implant a pacemaker or another device in your chest to regulate your heart rhythm. Other types of surgery can open blocked heart vessels, replace a damaged heart valve, or remove scar tissue.
Also Check: Why Would My Heart Rate Be High
Classification Based On Pumping Ability
Nowadays, heart failure is increasingly being classified based on the pumping ability of the heart. This is because the pumping ability plays an important role when choosing the most suitable medication. There are two types of heart failure here:
- Heart failure with reduced pumping ability: The heart muscle has become weaker, and no longer pumps enough blood around the body when it contracts . As a result, the organs in the body dont get enough oxygen. The medical term for this is heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
- Heart failure with preserved pumping ability: Although the heart muscle is still strong, it can no longer relax and widen enough after it has squeezed blood out, so it doesnt fill up with blood properly. Despite pumping strongly enough, not enough blood is pumped out into the body as a result, especially during physically strenuous activities. Doctors call this heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
Heart failure with reduced pumping ability is sometimes referred to as systolic heart failure, and heart failure with preserved pumping ability is also known as diastolic heart failure. The systolic phase of the cardiac cycle is the phase when the heart contracts , and the diastolic phase is when the heart relaxes and widens.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The signs and symptoms depend on how severe your heart failure is. The signs and symptoms you have may be due to the backup of fluid and blood in your tissues. It may also be due to decreased oxygen in your blood. You may have any of the following:
- Trouble breathing with activity that worsens to trouble breathing at rest
- Shortness of breath while lying flat
- Severe shortness of breath and coughing at night that usually wakes you
- Feeling lightheaded when you stand up
- Purple color around your mouth and nails
- Confusion or anxiety
- Periods of no breathing, then breathing fast
- Lack of energy , or trouble sleeping
- Swelling in your ankles, legs, or abdomen
- Heartbeat that is fast or not regular
- Fingers and toes feel cool to the touch
Don’t Miss: How To Avoid Heart Attack
The Flow Of Blood Through Your Heart
To understand the different types of heart failure, it helps to know how your heart pumps blood:
Heart Failure: Left Sided Vs Right Sided
Heart failure is a clinical condition characterized by inability of the heart to pump blood efficiently enough to maintain tissue perfusion.
Left Sided Heart failure
most common causes
- Aortic or Mitral valve disease
- Myocardial disease
Left sided Failure leads to low perfusion of organs
- The left side of heart supply body organs including brain. Lower perfusion to brain leads to hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy.
- In kidneys low perfusion leads to Prerenal Azotemia.
- Reduced supply to muscle leads to fatigue and tiredness.
Left sided Failure leads to Pulmonary Venous Congestion
Left atria receives venous return from lungs, as the left ventricle fails to pump blood in systemic circulation there is increase in end diastolic volume and left atrium is unable to maintain the venous reception from the lungs, hence there is Pulmonary venous congestion. This increased pressure in pulmonary vein causes pulmonary edema . Edema fluid accumulates in alveolar space which makes gaseous exchange difficult and leads to dyspnea. Patient also complains of orthopnea and PND .
Heart failure cells there is leakage of hemosiderin and other iron containing particles which are phagocytosed by macrophages. These macrophages are called siderophages or heart failure cells.
left sided heart failure infographics
Right sided Heart Failure
Left sided failure is the most common cause of right sided failure. Isolated right-side failure is seen in cor pulmonale .
Increased Jugular venous pressure .
Don’t Miss: What To Wear After Heart Surgery
Precipitating Causes Of Heart Failure
A previously stable, compensated patient may develop heart failure that is clinically apparent for the first time when the intrinsic process has advanced to a critical point, such as with further narrowing of a stenotic aortic valve or mitral valve. Alternatively, decompensation may occur as a result of the failure or exhaustion of the compensatory mechanisms but without any change in the load on the heart in patients with persistent, severe pressure or volume overload. In particular, consider whether the patient has underlying coronary artery disease or valvular heart disease.
The most common cause of decompensation in a previously compensated patient with heart failure is inappropriate reduction in the intensity of treatment, such as dietary sodium restriction, physical activity reduction, or drug regimen reduction. Uncontrolled hypertension is the second most common cause of decompensation, followed closely by cardiac arrhythmias . Arrhythmias, particularly ventricular arrhythmias, can be life threatening. Also, patients with one form of underlying heart disease that may be well compensated can develop heart failure when a second form of heart disease ensues. For example, a patient with chronic hypertension and asymptomatic LV hypertrophy may be asymptomatic until an MI develops and precipitates heart failure.
- Profound anemia
You May Like: Who Performed The First Open Heart Surgery Successful
What Are The Symptoms Of Right
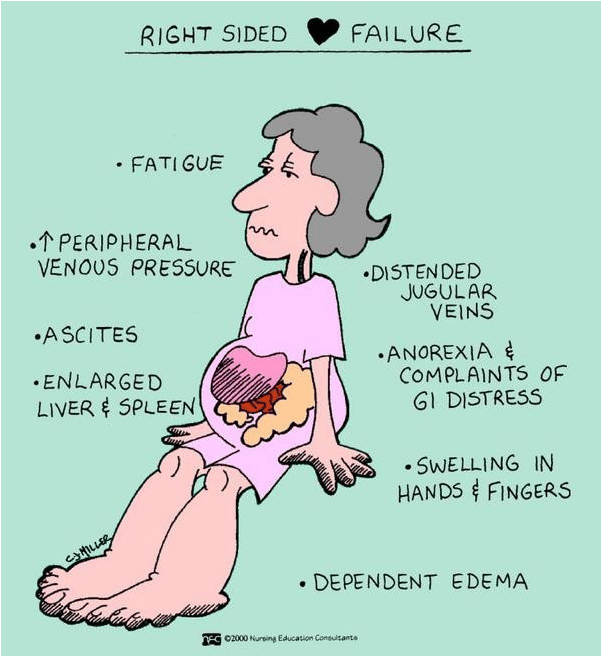
The main sign of right-sided heart failure is fluid buildup. This buildup leads to swelling in your:
- Feet, ankles and legs.
- Gastrointestinal tract and liver .
Other signs include:
Where you accumulate fluid depends on how much extra fluid and your position. If youre standing, fluid typically builds up in your legs and feet. If youre lying down, it may build up in your lower back. And if you have a lot of excess fluid, it may even build up in your belly.
Fluid build up in your liver or stomach may cause:
Once right-sided heart failure becomes advanced, you can also lose weight and muscle mass. Healthcare providers call these effects cardiac cachexia.
Read Also: How Blood Pumps Through The Heart
Clinical Manifestations Of Heart Failure
The clinical manifestation of heart failure is largely influenced by the primary side of dysfunction as left sided, right sided or biventricular. Left ventricular dysfunction increases pulmonary pressure and consequently pulmonary congestion occurs leading to dyspnoea and tachypnoea . As the peripheral circulation is reduced , renal dysfunction, peripheral malperfusion and malabsorption of nutrition with the signs of cardiac cachexia develop. In a chronic state, the permanent activation of neurohumoral systems lead to further volume overload , peripheral vasoconstriction , increased heart rate at rest and during exercise, and to a further deterioration of the cardio-renal system. Anemia , increased pulmonary pressure and muscle fatigue deteriorate the symptoms of dyspnoea as well. Overload of the heart leads to enlargement of the heart itself and as a measure the cardiothoracic index increases with leftward shift of the palpable cardiac pulsation. Mostly in volume overload situations filling volume of the ventricle increases periodically and a typical 3rd or 4th heart sound as protodiastolic gallop occurs . In consequence, heart failure influences almost all organ systems and thus heart failure is a systemic disease or a syndrome with a broad clinical spectrum.
Heart Failure: Pumping And Filling Problems
|
Normally, the heart stretches as it fills with blood , then contracts to pump out the blood . The main pumping chambers in the heart are the ventricles. Heart failure due to systolic dysfunction usually develops because the heart cannot contract normally. It may fill with blood, but the heart cannot pump out as much of the blood it contains because the muscle is weaker or because a heart valve malfunctions. As a result, the amount of blood pumped to the body and to the lungs is reduced, and the ventricle usually enlarges. Heart failure due to diastolic dysfunction develops because the heart muscle stiffens and may thicken so that the heart cannot fill normally with blood. Consequently, blood backs up in the left atrium and lung blood vessels and causes congestion. Nonetheless, the heart may be able to pump out a normal percentage of the blood it receives . The heart chambers always contain some blood, but different amounts of blood may enter or leave the chambers with each heartbeat as indicated by the thickness of the arrows. |
You May Like: What Is A Good Heart Rate For Exercise
What Is Congestive Heart Failure Right
Right-sided Congestive Heart Failure occurs when the right ventricle of the heart has difficulty pumping blood into your lungs. As a result, blood backs up in your blood vessels, that triggers fluid retention in the lower abdomen, extremities, and other vital organs. Right sided congestive heart failure can occur on its own, for example when triggered due to lung disease or heart valve disease. In severe cases, hepatomegaly can happen resulting in altering liver function, coagulopathy and jaundice.
Recommended Reading: What If My Heart Rate Is Over 100
What Is An Ejection Fraction
An ejection fraction is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. An ejection fraction of 60% means that 60% of the total amount of blood in the left ventricle is pushed out with each heartbeat. A normal ejection fraction is between 50% and 70%.
Organs like the kidneys require a certain amount of pressure as blood flows through them to work properly. A weak pump can reduce this pressure and in turn decrease the ability of other organs, like the kidneys, to do their jobs. This is how heart failure can lead to multiple organ failure and even death.
Don’t Miss: How To Take Heart Rate Manually
Complications Of Left Heart Failure
Because left heart failure leads to a backup of blood in the lungs, other organs do not receive enough oxygen-rich blood. Symptoms of decreased blood flow to the brain, such as trouble with memory and concentration, affect people with advanced left heart failure. The kidneys are also vulnerable to poor blood flow in left heart failure. When the kidneys fail to receive enough blood and oxygen, kidney damage eventually occurs. Without treatment, most causes of left heart failure also lead to an enlarged heart. If the heart becomes dilated and enlarged, it is more prone to dangerous, abnormal heart rhythms another complication of left heart failure.
Right Sided Vs Left Sided Heart Failure
When the heart fails to pump blood adequately to the body tissues owing to the decrease in the pumping capacity of the right heart chambers, this condition is identified as the right heart failure. When the heart failure is due to the faltering of the pumping capacity of the left heart chambers, this is known as left sided heart failure. Pumping Capacity In right sided heart failure, pumping capacity of the right heart chambers is decreased. It is the pumping capacity of the left heart chambers that is decreased in the left sided heart failure. Causes
· Aortic and mitral valve diseases
· Other myocardial diseases such as myocarditis
Read Also: Can Low Vitamin D Cause Heart Palpitations
