What You Can Do
Some risk factors of heart failure, like age, cant be modified. Still, people with CHF can take steps to improve the long-term prognosis. The first thing to do is to be familiar with any family history of heart disease. You’ll also want to learn about all the possible symptoms. Don’t ignore any symptom that you think is cause for concern. Tell your healthcare provider about them right away.
Regular exercise, along with managing any other health issues you may have, can also help to keep CHF under control.
Why Legs Swell Causes
One of the most common and dangerous causes of edema of the lower extremities is cardiological pathologies. In the presence of cardiovascular diseases, swelling of the legs is more pronounced than with renal failure or other pathologies.
Cardiac edema of the lower extremities has increased density, the skin is cool, and resorption occurs extremely slowly .It is also possible the appearance of a specific cyanotic hue. The main cardiological causes of edema of the lower extremities include :
- Amyloidosis of the heart is formed against the background of the development of rheumatic diseases, Crohns disease, lung damage, lymphogranulomatosis and other diseases with a similar etiology. May be hereditary
- Cardiomyopathies develop against the background of hard-borne or chronic parasitic, viral diseases, disorders of the endocrine system, metabolism, lack of vitamins, etc.etc .
- Cardiosclerosis irreversible changes in the structure of the muscle tissue of the heart against the background of myocardial infarction, myocarditis or long-term development of angina pectoris.
In some cases, the cause of the development of cardiac edema of the legs can be arterial hypertension of various etiologies.
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Failure
You may not have any symptoms of heart failure, or the symptoms may be mild to severe. Symptoms can be constant or can come and go. The symptoms can include:
- Congested lungs. Fluid backup in the lungs can cause shortness of breath with exercise or difficulty breathing at rest or when lying flat in bed. Lung congestion can also cause a dry, hacking cough or wheezing.
- Fluid and water retention. Less blood to your kidneys causes fluid and water retention, resulting in swollen ankles, legs, abdomen , and weight gain. Symptoms may cause an increased need to urinate during the night. Bloating in your stomach may cause a loss of appetite or nausea.
- Dizziness, fatigue, and weakness. Less blood to your major organs and muscles makes you feel tired and weak. Less blood to the brain can cause dizziness or confusion.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats. The heart beats faster to pump enough blood to the body. This can cause a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
If you have heart failure, you may have one or all of these symptoms or you may have none of them. They may or may not indicate a weakened heart.
Don’t Miss: How Is A Heart Attack Treated
If I Have Obesity How Do I Reduce My Risk Of Heart Disease
Losing 5% to 10% of your weight can lower your risk factors for heart disease. Small lifestyle changes can help improve metabolic syndrome, which lessens your heart disease risk. These changes include:
- Aerobic exercise: 150 minutes a week of aerobic exercise can help reduce abdominal fat and overall obesity. That works out to 30 minutes of activity, five days a week. Choosing activities that you enjoy, such as brisk walking, dancing or swimming, can help you stay motivated.
- Dietary changes: Eating fewer calories can help reduce abdominal fat. Changing your diet can also help you lose weight and improve overall obesity. There are studies that support recommending the Mediterranean diet to help reduce your risk of heart attack and death related to heart problems. This diet includes eating mostly plant-based foods such as root and green vegetables, fresh fruits, legumes, nuts and whole grains. plus moderate servings of dairy, eggs, fish, lean poultry and seafood.
What other steps can I take to reduce my risk of heart disease?
Besides lifestyle changes, other options to help reduce your risk of heart disease include:
See your healthcare provider to come up with a plan for your weight loss that makes the most sense for you.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Division Of Cardiology Oregon Health Sciences University Portland Usa
Barry H. Greenberg
-
Book Title: Congestive Heart Failure
-
Book Subtitle: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Comprehensive Approach to Management
-
Editors: Jeffrey D. Hosenpud, Barry H. Greenberg
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-8315-4
-
Copyright Information: Springer-Verlag New York, Inc. 1994
-
Softcover ISBN: 978-1-4613-8317-8
Recommended Reading: How Soon Can I Fly After Heart Bypass Surgery
Precipitating Causes Of Heart Failure
A previously stable, compensated patient may develop heart failure that is clinically apparent for the first time when the intrinsic process has advanced to a critical point, such as with further narrowing of a stenotic aortic valve or mitral valve. Alternatively, decompensation may occur as a result of the failure or exhaustion of the compensatory mechanisms but without any change in the load on the heart in patients with persistent, severe pressure or volume overload. In particular, consider whether the patient has underlying coronary artery disease or valvular heart disease.
The most common cause of decompensation in a previously compensated patient with heart failure is inappropriate reduction in the intensity of treatment, such as dietary sodium restriction, physical activity reduction, or drug regimen reduction. Uncontrolled hypertension is the second most common cause of decompensation, followed closely by cardiac arrhythmias . Arrhythmias, particularly ventricular arrhythmias, can be life threatening. Also, patients with one form of underlying heart disease that may be well compensated can develop heart failure when a second form of heart disease ensues. For example, a patient with chronic hypertension and asymptomatic LV hypertrophy may be asymptomatic until an MI develops and precipitates heart failure.
- Profound anemia
- Pregnancy
- Nutritional deficiencies
How To Help Prevent Kidney Disease When You Have Diabetes
Kidney Disease Edema can occur because the disease leads to extra fluid and sodium in the circulatory system, which then builds up pressure in the blood vessels and leads to swelling. Kidney disease can cause edema in multiple areas.
Kidney Damage Nephrotic syndrome which occurs when the small filtering blood vessels in the kidneys dont work properly and allow protein to be lost in the urine can result. This causes a declining level of protein in the blood, which can lead to fluid accumulation and edema.
Liver Cirrhosis A scarring of the liver tissue, it can lead to abdominal edema. This happens because cirrhosis causes a lack of proteins in the liver, which can lead to increased pressure in the blood vessels and fluid seeping into the abdomen.
Severe Lung Conditions Conditions such as emphysema can lead to edema if pressure in the lungs and heart gets too high.
Also Check: What Is The Recovery Time For Open Heart Surgery
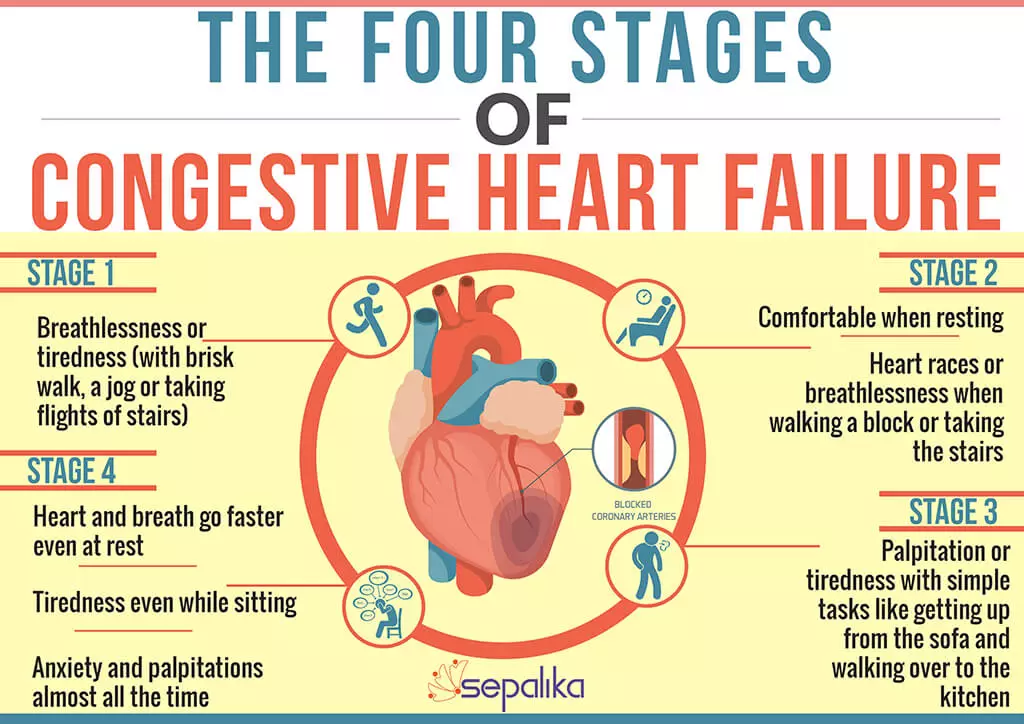
Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The main symptoms of heart failure are:
- breathlessness after activity or at rest
- feeling tired most of the time and finding exercise exhausting
- feeling lightheaded or fainting
- swollen ankles and legs
Some people also experience other symptoms, such as a persistent cough, a fast heart rate and dizziness.
Symptoms can develop quickly or gradually over weeks or months .
How Is Heart Failure Treated
Your treatment will depend on the type of heart failure you have and, in part, what caused it. Medications and lifestyle behaviors are part of every treatment plan. Your healthcare provider will talk to you about the best treatment plan for you. Treatment is the same, regardless of gender.
As heart failure gets worse, your heart muscle pumps less blood to your organs, and you move toward the next stage of heart failure. Since you cant move backward through the heart failure stages, the goal of treatment is to keep you from moving forward through the stages or to slow down the progression of your heart failure.
Stage A treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage A heart failure includes:
- Regular exercise, being active, walking every day.
- Stopping the use of tobacco products.
- Treatment for high blood pressure .
- Treatment for high cholesterol.
- Not drinking alcohol or using recreational drugs.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or an angiotensin II receptor blocker if you have coronary artery disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, or other vascular or cardiac conditions.
- Beta-blocker if you have high blood pressure.
Stage B treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage B heart failure includes:
Stage C treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage C HF-rEF includes:
If the treatment causes your symptoms to get better or stop, you still need to continue treatment to slow the progression to Stage D.
Stage D treatment
You May Like: Can Alcohol Cause Heart Palpitations
Factors That Can Worsen Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The symptoms of heart failure can be worsened by a number of factors, including:
- anaemia
- too much salt, fluid, or alcohol in the diet
- pregnancy
- some viral and bacterial infections
- kidney diseases
Treatment for heart failure may include:
- medicines, such as
- diuretics to remove excess fluid and improve symptoms of heart failure
- mineralcortiocoid receptor antagonists are also recommended and used in most patients with heart failure to reduce mortality and hospitalisation
- ACE inhibitors to open up blood vessels, reduce blood pressure and reduce sodium retention and water retention
- certain beta-blockers to slow the heart rate and reduce its work
- aldosterone blockers to reduce blood pressure and reduce the effects of damage to the heart muscle
- ACE inhibitors, beta blockers and aldosterone blockers can increase survival and reduce the likelihood of hospitalisation.
Heart Edema An Overview
5.11 Cardiac Edema
Cardiac edema appears in cardiac failure. There are a few special semiological features of cardiac edema. It is very important to know these because we can recognize clinically cardiac edema in a patient with cardiac failure. Semiological features of cardiac edema are as follows:
- 1.
-
At first, the edema is intermittent because it is vesperal and disappears in the morning.
It is significant that cardiac edema appears in the evening after the effort during the day and disappears in the morning after the patient rests during the night and in dorsal position, which allows the redistribution of the edema, increases the blood supply of the kidney, and allows nocturnal urination . In this way, the edema disappears in the morning. The phenomenon is illustrated in the next schema.
Vesperal and Disappears in the Morning
It is intermittent.
It appears in the evening and disappears in the morning.
This phenomenon appears in the evening, and during the night the lying down position of the body allows the circulation of blood flow in the renal arteries to be ameliorated, and because the outflow of blood inside the renal arteries increases, there appears urination in the nightnocturiaand in this way the interstitial fluid accumulated in the legs is eliminated and in the morning has disappeared.
In chronic cardiac failure, the edema appears in the night and persists in the morning.
Cyanotic
Lower limbs cyanotic and swollen
Cold
Recommended Reading: Right Sided Heart Failure Causes
Stage A Treatment Options
Treatment options in stage A mainly focus on promoting your overall health and disease prevention. If you meet the stage A criteria, your doctor will recommend lifestyle changes to slow or stop disease progression.
Heart Failure Doctor Discussion Guide
What Is The Recovery Time
Heart transplant surgery is a complicated, extensive surgery procedure and recovery times are typically longer than most heart surgeries. The expected hospital stay is at least seven to 10 days, and usually up to three weeks. The time you spend in the hospital depends on your specific situation, health and how the surgery went. Overall, recovery from this procedure usually takes several months.
You May Like: How Do You Measure Heart Rate
What Happens After This Procedure
After your heart transplant, the following will need to happen.
Immune system suppression
After the procedure, providers will start you on medications that will suppress your immune system. They do that because your immune systems normal reaction to a foreign object is to treat it like an infection or other harmful invader and attack it. That suppression protects the new heart from attack by your own immune system.
Providers will continue to monitor your condition and vital signs closely. They do that to watch for any signs that your body is rejecting the new heart . Youll also need to take those medications for the rest of your life.
Nervous system reconnection
Providers will also monitor the new heart’s electrical function. That’s necessary because the donor’s heart doesn’t connect to your nervous system. Fortunately, your heart can still manage how fast it beats in other ways. Your resting heart rate will usually stay at the high end of normal or slightly higher .
In many people, the heart recipient’s nervous system can form new connections with the donor’s heart. The sympathetic nervous system connections, which control your fight-or-flight response and speed up your heart, form after about six months. The parasympathetic nervous system connections, which help your heart slow down and relax, form after about 18 months to two years. In some cases, this reconnection doesnt happen, but this isnt usually the case.
Follow-up care
What Causes Heart Failure
Although the risk of heart failure doesnt change as you get older, youre more likely to have heart failure when youre older.
Many medical conditions that damage the heart muscle can cause heart failure. Common conditions include:
- Tobacco and recreational drug use.
- Medications. Some drugs used to fight cancer can lead to heart failure.
Recommended Reading: How To Regulate Heart Rate
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide And B
ANP and BNP are endogenously generated peptides activated in response to atrial and ventricular volume/pressure expansion. ANP and BNP are released from the atria and ventricles, respectively, and both promote vasodilation and natriuresis. Their hemodynamic effects are mediated by decreases in ventricular filling pressures, owing to reductions in cardiac preload and afterload. BNP, in particular, produces selective afferent arteriolar vasodilation and inhibits sodium reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule. It also inhibits renin and aldosterone release and, therefore, adrenergic activation. ANP and BNP are elevated in chronic heart failure. BNP especially has potentially important diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications.
For more information, see the Medscape Drugs & Diseases article Natriuretic Peptides in Congestive Heart Failure.
What Are The Symptoms Of Pediatric Congenital Heart Disease
Often, there are no symptoms associated with these defects. The defects are usually found during routine physical examinations. In cases where there are symptoms, they may include:
- Trouble breathing.
- Bluish tones to the skin .
- Poor eating habits.
- Swelling in the abdomen or around the eyes.
- Rapid heartbeat.
Also Check: Explain How Hypertension, Heart Disease, And Stroke Are Related.
How Does A Healthy Heart Work
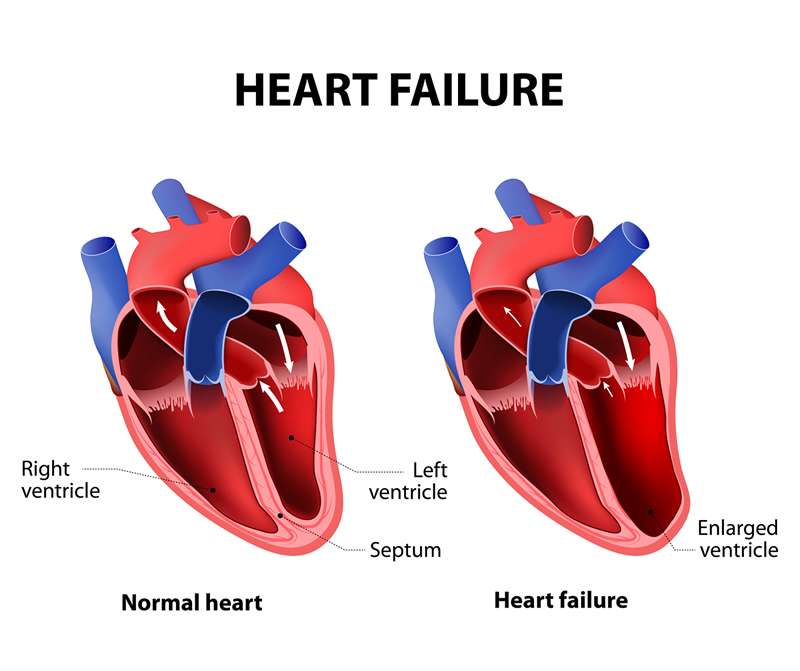
The heart is part of the circulatory system, which carries blood throughout the body. The heart is made of muscle and works like a pump to keep the blood moving through the blood vessels .
The heart has 4 chambers the right atrium and the left atrium on top and the right and left ventricles on the bottom. The heart is divided by a solid wall called the septum into 2 sides: the right side sends blood to the lungs to get oxygen, while the left side of the heart moves oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body through the aorta .
Blood enters the heart through the right atrium and moves to the right ventricle, where it then moves through the pulmonary artery to the lungs to pick up oxygen. The newly oxygenated blood then enters the heart through the left atrium and moves to the left ventricle, where it is sent through the aorta to the rest of the body.
There are also 4 valves in the heart, which open and close to allow blood to move through the chambers:
- The aortic valve, located on the left side of the heart, between the aorta and the left ventricle.
- The mitral valve, located between the left ventricle and the left atrium.
- The pulmonary valve, located on the right side of the heart between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery .
- The tricuspid valve, located on the right side of the heart between the right ventricle and the right atrium.
The exterior of the heart.
Blood vesselsarteries, veins, and capillaries–are also involved in helping blood flow:
Causes Of Swelling In Legs And Ankles Incongestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure can cause both peripheral edema and abdominal edema . This is because the heart is too weak to pump blood around the body properly, so the blood gathers in front of the heart. Because of this, and due to the increased blood pressure in the veins, fluid seeps out into the surrounding tissue.
This may cause swelling in the legs or a build-up of fluid in the abdomen. If the person spends a lot of time lying down, the edema might show up on his or her back .
Congestive heart failure can also cause edema in the lungs . This is not common, but the condition is life-threatening. It means the lungs are filling with fluid because the left side of the heart is not strong enough to pump the blood returning from the lungs.
The blood gathers in the blood vessels of the lung, and fluid seeps out into the lung tissue. The signs are shortness of breath and rapid, shallow breathing or coughing.
Don’t Miss: How To Tell Your Heart Rate
