Diagnostic Tests And Procedures
To diagnose coronary heart disease, your doctor may order some of the following tests.
If you have coronary heart disease risk factors, your doctor may recommend diagnostic tests even if you do not have symptoms.
Nonobstructive coronary artery disease and coronary microvascular disease can be missed because patients or doctors may not recognize the warning signs. Diagnosing these types often requires more invasive tests or specialized tests, such as cardiac PET scans, that are not widely available.
Heart With Muscle Damage And A Blocked Artery
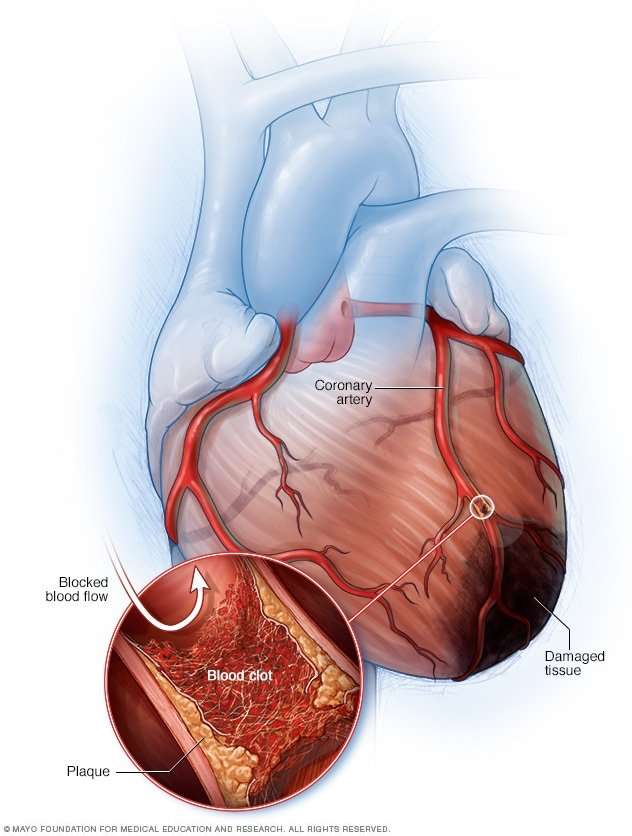
A less common cause of heart attack is a severe spasm of a coronary artery. The spasm cuts off blood flow through the artery. Spasms can occur in coronary arteries that aren’t affected by atherosclerosis.
Heart attacks can be associated with or lead to severe health problems, such as heart failure and life-threatening arrhythmias.
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart can’t pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. Arrhythmias are irregular heartbeats. Ventricular fibrillation is a life-threatening arrhythmia that can cause death if not treated right away.
Will I Recover From My Heart Attack
The answer is most likely yes.
The heart muscle begins to heal soon after a heart attack. It usually takes about eight weeks to heal.
Scar tissue may form in the damaged area, and that scar tissue does not contract or pump as well as healthy muscle tissue. As a consequence, the extent of damage to the heart muscle can impact how well the heart pumps blood throughout the body.
How much pumping function is lost depends on the size and location of the scar tissue. Most heart attack survivors have some degree of coronary artery disease and will have to make important lifestyle changes and possibly take medication to prevent a future heart attack. Taking these steps can help you lead a full, productive life.
Learn more about recovering from heart attack.
Also Check: Can Ibs Cause Heart Palpitations
The Role Of Inflammation In Heart Attack And Stroke
“Exactly how inflammation plays a role in heart attack and stroke remains a topic of ongoing research,” added Deepak Bhatt, M.D. “It appears that the inciting event in many heart attacks and some forms of stroke is buildup of fatty, cholesterol-rich plaque in blood vessels.”
Bhatt is chief of cardiology for the VA Boston Healthcare System, director of the Integrated Interventional Cardiovascular Program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital & VA Boston Healthcare System, and associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School.
“The body perceives this plaque as abnormal and foreign it does not belong in a healthy blood vessel,” he said. “In response, the body tries to wall off the plaque from the flowing blood. However, under the wrong set of circumstances, that plaque may rupture, and its walled-off contents can come into contact with blood and trigger a blood clot formation.”
Bhatt added, “This combination of plaque and blood clots causes the majority of heart attacks and certain types of stroke, if the blood clot obstructs blood flow to the heart or brain.”
An artery to the heart thats blocked causes a heart attack. A blocked artery in or leading to the brain causes an ischemic stroke.
Is My Heart Permanently Damaged
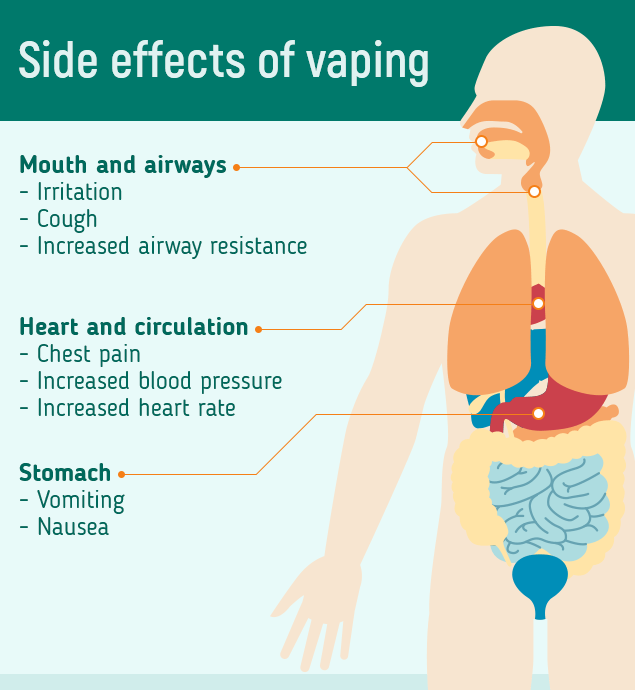
When a heart attack occurs, the heart muscle that has lost blood supply begins to suffer injury. The amount of damage to the heart muscle depends on the size of the area supplied by the blocked artery and the time between injury and treatment.
Heart muscle damaged by a heart attack heals by forming scar tissue. It usually takes several weeks for your heart muscle to heal. The length of time depends on the extent of your injury and your own rate of healing.
The heart is a very tough organ. Even though a part of it may have been severely injured, the rest of the heart keeps working. But, because of the damage, your heart may be weakened, and unable to pump as much blood as usual.
With proper treatment and lifestyle changes after a heart attack, further damage can be limited or prevented.
Learn more about heart damage detection.
Don’t Miss: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Family History And Genetics
A family history of early heart disease is a risk factor for coronary heart disease. This is especially true if your father or brother was diagnosed before age 55, or if your mother or sister was diagnosed before age 65. Research shows that some genes are linked with a higher risk for coronary heart disease.
How Heart Defects Affect Your Body
They donât usually cause pain, but without regular blood flow, your body doesnât get the oxygen it needs. That may lead to bluish skin, shortness of breath, and feeling tired. Defects often make your heart work harder, which can cause heart failure — when your heartâs too weak to pump blood the way it should. That can cause problems like arrhythmia, trouble breathing, and fluid in your lungs.
You May Like: Does Higher Heart Rate Burn More Calories
Family History And Cardiovascular Disease Risk
A personâs family history of disease can increase their tendency to develop:
- Diabetes.
- A particular body shape.
Although having a family history of CVD is a risk factor you canât change, it does not mean that you will develop it. However, if you do have a family history of CVD, it is important to reduce or remove other risk factors. For example, adopting healthy eating patterns, do not smoke, and lead an active, healthy lifestyle.
What Is A Heart Attack
A heart attack is a frightening experience. If you have experienced a heart attack, or are close with someone who has, you should know this: You are not alone. In fact, tens of thousands of people survive heart attacks and go on to lead productive, enjoyable lives.
As you work toward recovery, the frequently asked questions below can help you better understand what has happened, and how your heart can heal. Knowledge is power. Arming yourself with this information can help you can live a healthier, longer life.
Don’t Miss: How Much Can Marijuana Increase A Person’s Heart Rate
How Your Heart Changes With Age
People age 65 and older are much more likely than younger people to suffer a heart attack, to have a stroke, or to develop coronary heart disease and heart failure. Heart disease is also a major cause of disability, limiting the activity and eroding the quality of life of millions of older people.
Aging can cause changes in the heart and blood vessels. For example, as you get older, your heart can’t beat as fast during physical activity or times of stress as it did when you were younger. However, the number of heartbeats per minute at rest does not change significantly with normal aging.
Changes that happen with age may increase a person’s risk of heart disease. A major cause of heart disease is the buildup of fatty deposits in the walls of arteries over many years. The good news is there are things you can do to delay, lower, or possibly avoid or reverse your risk.
Returning To Normal Activities
After a heart attack, most people who don’t have chest pain or discomfort or other problems can safely return to most of their normal activities within a few weeks. Most can begin walking right away.
Sexual activity also can begin within a few weeks for most patients. Talk with your doctor about a safe schedule for returning to your normal routine.
If allowed by state law, driving usually can begin within a week for most patients who don’t have chest pain or discomfort or other disabling problems. Each state has rules about driving a motor vehicle following a serious illness. People who have complications shouldn’t drive until their symptoms have been stable for a few weeks.
Read Also: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Are Heart Attack Symptoms In Women Different
Although most women and men report symptoms of chest pain with a heart attack, women are slightly more likely than men to report unusual symptoms. More vague or less typical “heart” symptoms reported in women include:
- Upper back or shoulder pain.
- Jaw pain or pain spreading to the jaw.
- Pressure or pain in the center of the chest.
- Light headedness.
- Pain that spreads to the arm.
- Unusual fatigue for several days.
If you experience any of these symptoms of a heart attack, call for emergency assistance . Don’t wait for your symptoms to “go away.” Early recognition and treatment of a heart attack can reduce the risk of heart damage. Even if you’re not sure your symptoms are a heart attack, get it checked.
The best time to treat a heart attack is within one hour of the onset of the first symptoms. Waiting just a couple hours for medical help may change your treatment options, increase the amount of damage to your heart muscle and reduce your chance of survival.
How Is A Heart Attack Treated
Heart attack treatment begins immediately. The goal of treatment is to treat you quickly and limit heart muscle damage.
Medications
The goals of medication therapy are to break up or prevent blood clots, prevent platelets from gathering and sticking to the plaque, stabilize the plaque, and prevent further ischemia. These medications must be given as soon as possible to decrease the amount of damage to the heart muscle. The longer the delay in starting these drugs, the more damage that occurs and the less benefit they can provide.
Thrombolytic medications are used to break up clots blocking the artery
Medications given right after the start of a heart attack may include:
- Other antiplatelet drugs
- Any combination of the above
Other drugs, given during or after a heart attack lessen your heart’s work, improve the functioning of the heart, widen or dilate your blood vessels, decrease your pain, and guard against any life-threatening heart rhythms. Your doctor will prescribe the appropriate medications for you.
Interventional Procedures
During or shortly after a heart attack, you may go to the cardiac catheterization laboratory to directly evaluate the status of your heart, arteries and the amount of heart damage. In some cases, procedures are used to open up your narrowed or blocked arteries. These procedures may be combined with thrombolytic therapy to open up the narrowed arteries, as well as to break up any clots that are blocking them.
Coronary artery bypass surgery
Also Check: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Blood Pressure And Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Blood pressure is the pressure of the blood in your arteries as it is pumped around your body by your heart. Blood pressure depends on two main things: the amount of blood pumped by your heart and how easily the blood can flow through your arteries.
Your blood pressure will go up and down throughout the day, depending on the time of day and what you are doing. However, high blood pressure is a condition where your blood pressure is consistently high.
Your family history, eating patterns, alcohol intake, weight and level of physical activity have a strong influence on blood pressure. In some people, medicines, including the oral contraceptive pill, contraceptive âdepotâ injections, steroids and arthritis medicines, can also raise blood pressure.
High blood pressure can overload your heart and arteries and speed up the artery-clogging process. This can lead to problems such as heart attack and stroke.
High blood pressure can also affect arteries to other parts of your body, such as the eyes, kidneys and legs.
If high blood pressure is not treated, your heart may weaken because of the constant extra demand. This may cause âheart failureâ, a serious condition with symptoms such as tiredness, shortness of breath and swelling of the feet and ankles.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
Ask your doctor questions to learn more about your risk for heart disease and what to do about it. Learn what you can do if you are at increased risk or already have a heart problem.
To learn more about making heart-healthy lifestyle changes, visit the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
You May Like: What Is A Dangerously High Heart Rate
Heart Attack Symptoms: Women Vs Men
Women may experience classic symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath as many men do, but they also tend to experience stomach pain, back pain, and other non-classic symptoms.
Because of the subtlety in those symptoms, many women brush off these warning signs and already have heart damage by the time they get to the Emergency Department.
And many women put their families before their own health. But you cant take care of your loved ones if your own health is not where it needs to be.
Are There Other Causes Of Heart Attack Besides Blockage
Sometimes a coronary artery temporarily contracts or goes into spasm. When this happens the artery narrows, and blood flow to part of the heart muscle decreases or stops.
The causes of spasms are unclear. A spasm can occur in normal-appearing blood vessels as well as in vessels partly blocked by atherosclerosis. A severe spasm can cause a heart attack.
Another rare cause of heart attack is spontaneous coronary artery dissection, which is a spontaneous tearing of the coronary artery wall.
You May Like: How To Find Thrz
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Disease
Sometimes heart disease may be silent and not diagnosed until a person experiences signs or symptoms of a heart attack, heart failure, or an arrhythmia. When these events happen, symptoms may include1
- Heart attack: Chest pain or discomfort, upper back or neck pain, indigestion, heartburn, nausea or vomiting, extreme fatigue, upper body discomfort, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
- Arrhythmia: Fluttering feelings in the chest .
- Heart failure: Shortness of breath, fatigue, or swelling of the feet, ankles, legs, abdomen, or neck veins.
Learn the Facts About Heart Disease
- About 659,000 people in the United States die from heart disease each yearthats 1 in every 4 deaths.1,2
Why Didnt I Have Any Warning
The process of atherosclerosis has no symptoms. When a coronary artery narrows and constricts blood flow, other nearby blood vessels that serve the heart sometimes expand to compensate, which may explain why there are no warning signs.
Such a network of expanded nearby blood vessels is called collateral circulation, and it helps protect some people from heart attacks by delivering needed blood to the heart. Collateral circulation can also develop after a heart attack to help the heart muscle recover.
Also Check: Flonase Heart Rate
What Is Heart Failure
Heart failure can occur due to a number of reasons:
- The ventricles in your heart, which are the chambers in charge of pumping blood throughout your body, can either become damaged, too stiff, or too weak to function properly. When this happens, your body does not receive all the blood it needs.
- To try to correct these problems, the chambers in your heart will expand and thicken in an effort to allow the heart to pump stronger. The heart also pumps at a faster rate to increase the amount of blood flow pumped through the body. This is a temporary solution, however, and eventually your heart failure will progress.
- As heart failure progresses, you may experience symptoms in other parts of your body that indicate your heart is no longer able to function properly.
What Happens In The First Few Days After A Heart Attack
You will be closely monitored in the first few days after your heart attack
Depending on the severity of your heart attack, the treatmentyou have received and your home situation, you will usuallybe in hospital for 3 to 5 days.
- The first 24-48 hours after a heart attack is when your condition will be most unstable.
- This period is often spent in a coronary care unit , a specialised intensive care unit for heart patients, or in an acute medical ward where your heart function can be monitored closely.
- Your blood sugar level will also be closely monitored. After a heart attack, some people have an increase in their blood sugar level. If this happens you might need treatment with insulin to reduce your blood sugar levels.
- As a result of your heart attack, other conditions can develop. For example, your heart may not be able to pump blood around your body as well as it did before, or there may be damage to the control of the electrical activity of your heart.
- It is normal to feel very tired after a heart attack. Initially try to limit any visiting to your immediate family and keep visits brief. Meals are intentionally light as a heavy meal will increase demand on your heart. Eating smaller meals more often means that your heart will not have to work so hard.
You May Like: 10 Second Trick To Prevent Heart Attack
Coping With Life’s Pressures
Heart disease has many other mind-body connections that you should consider. Prolonged stress due to the pressures at home, on the job, or from other sources can contribute to abnormally high blood pressure and circulation problems. As with many other diseases, the effects vary from person to person. Some people use stress as a motivator while others may “snap” at the slightest issue.
How you handle stress also influences how your cardiovascular system responds. Studies have shown that if stress makes you angry or irritable, you’re more likely to have heart disease or a heart attack. In fact, the way you respond to stress may be a greater risk factor for heart problems than smoking, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
Heart Attacks Affect More Than Just The Heart
While this is not a bad way to go about treating health issues, according to a new study, aliments such as an acute heart attack affect the body as a whole and should not be viewed in isolation.
The researchers of this study believe that, especially in cases of a heart attack, the body is affected in a systemic way, having an impact on other organs such as the liver and spleen.
We have demonstrated the need to rethink our tunnel vision that focuses solely on the heart in the event of a heart attack. A myocardial infarction is not an isolated event the rest of the body responds as well,said Matthias Zimmermann, a Ph.D. student at the Medical University of Vienna.Medical science today separates the various disciplines into easier and more manageable parts. While it is a more efficient way to get a better grasp of complex topics, it may inadvertently lead to a segregation of medical issues that are actually related.
Don’t Miss: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
