De Novo Acute Heart Failure
Acute heart failure is broadly defined as a rapid onset of new or worsening signs and symptoms of HF . It is often a potentially life-threatening condition, requiring hospitalisation, and emergency treatment is aimed predominantly at managing fluid overload and haemodynamic compromise. This umbrella term includes patients presenting for the first time with typical symptoms and signs of heart failure and also those with worsening of their pre-existing cardiomyopathy .
De novo AHF occurs when there is a sudden increase in intracardiac filling pressures and/or acute myocardial dysfunction which can lead to decreased peripheral perfusion and pulmonary oedema. The most common aetiology is cardiac ischaemia where -total coronary occlusion leads to decreased contractility in myocardium subtended by the affected coronary artery. In this case, management is focussed not only on haemodynamic compromise but also on reperfusion with the aim of restoring myocardial contractile function.
In addition to myocardial dysfunction, AHF can be precipitated by acute valvular incompetence. This most commonly occurs in an ischaemic context leading to acute mitral regurgitation but can also occur without ischaemia per se as is the case with infective and non-bacterial thrombotic endocarditis. Extra-cardiac pathologies may also precipitate AHF as is the case with pulmonary embolism or pericardial effusion causing tamponade, both of which reduce LV output and therefore reduce peripheral perfusion
Systolic Heart Failure Prognosis
Prognosis for systolic heart failure, and left-sided heart failure in general, varies depending on the cause of the condition, severity of symptoms and presence of co-existing medical problems. Some may improve with medication and lifestyle changes. For others, severe symptoms can be life-threatening and require an implanted device, surgical heart repair or a heart transplant.
Etiology Congestive Heart Failure
There are numerous causes for systolic heart failure, but the most common is related to coronary artery disease and prior myocardial infarctions. This entity is termed an ischemic cardiomyopathy and accounts for nearly half of systolic heart failure cases in the United States.
Dilated cardiomyopathy is the second leading cause of systolic HF. This can be idiopathic , a viral cardiomyopathy, peripartum and hypertensive heart disease . These include doxorubicin therapy, stress-induced , alcohol-related, selenium or thiamine deficiency, tachycardia-mediated, giant cell arteritis, hyperthyroidism, cocaine use, obstructive sleep apnea and familial cardiomyopathies.
The third leading cause of systolic HF is valvular heart disease. This includes aortic valve stenosis, aortic valve regurgitation, mitral valve stenosis and mitral regurgitation. In many developing nations, the most common cause of systolic HF is Chagas disease, which is related to Trypanosoma cruzi and transmitted by triatomine bugs.
Recall that right heart failure and diastolic heart failure are different entities from the left-sided systolic heart failure reviewed here. The most common cause of right HF is pressure overload related to left HF. Diastolic HF is most commonly caused by hypertension as a part of hypertensive heart disease. Aging of the heart contributes to diastolic HF as well.
Read Also: What Is Right Sided Heart Failure
Causes Of Heart Failure
Heart failure is often the result of a number of problems affecting the heart at the same time.
Conditions that can lead to heart failure include:
- coronary heart disease where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become clogged up with fatty substances , which may cause angina or a heart attack
- high blood pressure this can put extra strain on the heart, which over time can lead to heart failure
- conditions affecting the heart muscle
- heart rhythm problems , such as atrial fibrillation
- damage or other problems with the heart valves
- congenital heart disease birth defects that affect the normal workings of the heart
Sometimes obesity, anaemia, drinking too much alcohol, an overactive thyroid or high pressure in the lungs can also lead to heart failure.
Coping With Heart Failure
Dealing with heart failure symptoms can be difficult, particularly when it impacts daily life. Exercise ability may be significantly limited, with some people having shortness of breath with minimal activity or even while at rest. In addition, leg swelling can become painful, and it can be hard to find shoes that fit.
Staying organized is very important. Consider investing in a pill sorter to keep track of all of the medications you are prescribed. Each morning, write down your weight, blood pressure, and any symptoms on a calendar and bring this to your healthcare provider visits.
For some, cutting back on salt can be a big help. Using other spices can help keep flavor in meals without the added salt.
As with any chronic condition, support from loved ones can help you cope. Many hospitals also offer support groups for people with heart failure.
You May Like: What Foods Cause Heart Palpitations
Congestion And Organ Dysfunction
In the heart, elevated ventricular filling pressures lead to increased ventricular wall tension, myocardial stretch and remodelling, contributing to a progressive worsening in cardiac contractility, valvular regurgitation and systemic congestion. In response to the increased wall tension, circulating natriuretic peptides are physiologically released by atrial and ventricular cardiomyocytes as a compensatory mechanism, and often high-sensitivity cardiac troponins are detectable in a large proportion of patients with AHF, revealing nonischaemic myocyte injury or necrosis. Increases in left atrial pressure and mitral valve regurgitation will increase the hydrostatic pressure in the pulmonary capillaries, thereby increasing fluid filtration rate from the capillaries to the pulmonary interstitium, causing lung stiffness and dyspnoea. Notably, the relationship between hydrostatic pressure and interstitial fluid content is rather complex, as other mechanisms are involved in fluid homeostasis. For example, the lymphangiogenic factor VEGF-D has been found to regulate and mitigate pulmonary and systemic congestion in patients with HF or renal failure,,. Indeed, in the early stage of lung congestion, the lymphatic system can cope with the large volume of interstitial fluid, but eventually, the drainage capacity is exceeded. Hence, fluid moves to pleural and intra-alveolar spaces causing pleural effusion and pulmonary oedema.
Tests For Acute Heart Failure
Your doctor will assess your medical history and perform a physical exam. Theyll listen to your heart and lungs with a stethoscope to detect any congestion or abnormal heart rhythms. Your doctor may also check for fluid buildup in your abdomen, legs, and the veins in your neck.
In addition, your doctor might request tests such as:
- Blood tests. These could include a BNP test, which measures a hormone related to heart failure.
- Electrocardiogram . During this test, your doctor will attach electrodes to your skin and record your hearts electrical activity.
- Stress test. This test measures your heart activity during physical exercise. Its not typically recommended if you already have signs and symptoms of heart failure.
Imaging tests that a doctor can use to help diagnose heart failure include:
- Chest X-ray. This test allows your doctor to better examine your heart and lungs.
- Echocardiogram. This test uses sound waves to form a live, moving image of your heart so your doctor can see which areas of your heart are affected.
- Angiogram. If your doctor thinks you may have a blocked artery, they will insert a thin tube into your groin or arm and into your coronary arteries. After injecting dye through a catheter, your doctor can see an image of your arteries.
When needed, other imaging tests can be used to look for underlying causes of heart failure:
Together, your physical exam and test results can help your doctor learn about the health of your heart.
Also Check: What Is An Abnormal Heart Rate
What Does Systolic Reading Indicate
The first or top number is your systolic blood pressure. This is the amount of pressure in your arteries during the contraction of your heart muscle. The second or bottom number is your diastolic blood pressure. This is the lowest level your blood pressure reaches as your heart relaxes between beats.
Anemia And Iron Deficiency
Anemia is common among patients with chronic heart failure and is frequently multifactorial. Anemia is associated with worse symptoms and outcomes in HF and so reversible causes should be sought and treated. Iron deficiency Iron Deficiency Anemia Iron deficiency is the most common cause of anemia and usually results from blood loss malabsorption, such as with celiac disease, is a much less common cause. Symptoms are usually nonspecific… read more is among the most common causes of anemia in HF, and iron replacement therapy should be considered once treatable causes such as blood loss have been excluded. Oral iron replacement is often less effective due to poor absorption and other reasons, thus intravenous iron replacement is preferred.
Read Also: How Do Video Games Affect Your Heart Rate
Usmle Step 2 Style Questions Usmle
A previously healthy one-month-old infant is admitted to the hospital because of respiratory distress. He was born at term following an uncomplicated pregnancy and delivery. He had been well until 2 days ago when he developed fever and malaise. His is 162/min, respirations are 54/min, and is 64/48 mm Hg. Examination shows evidence of . A viral infection is suspected as the etiology of his acute heart failure. Which of the following is the most likely virus?
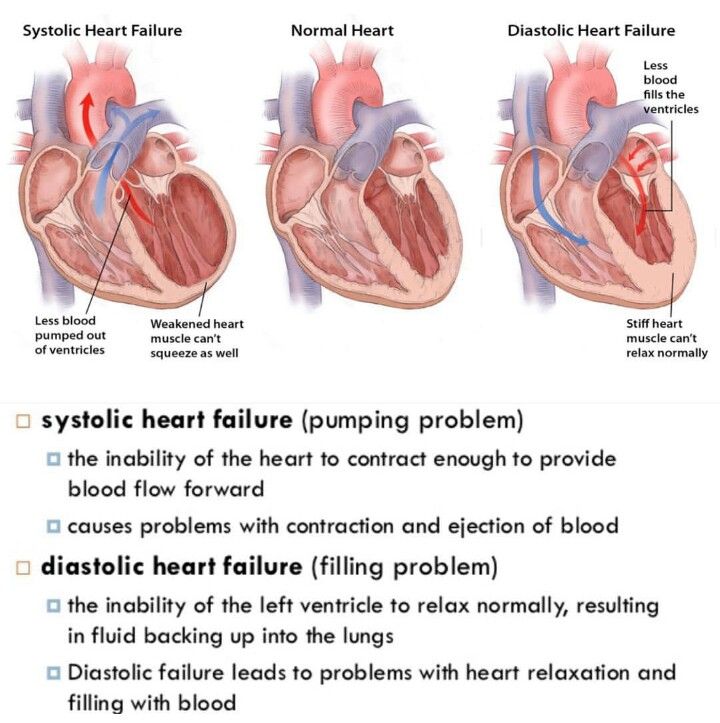
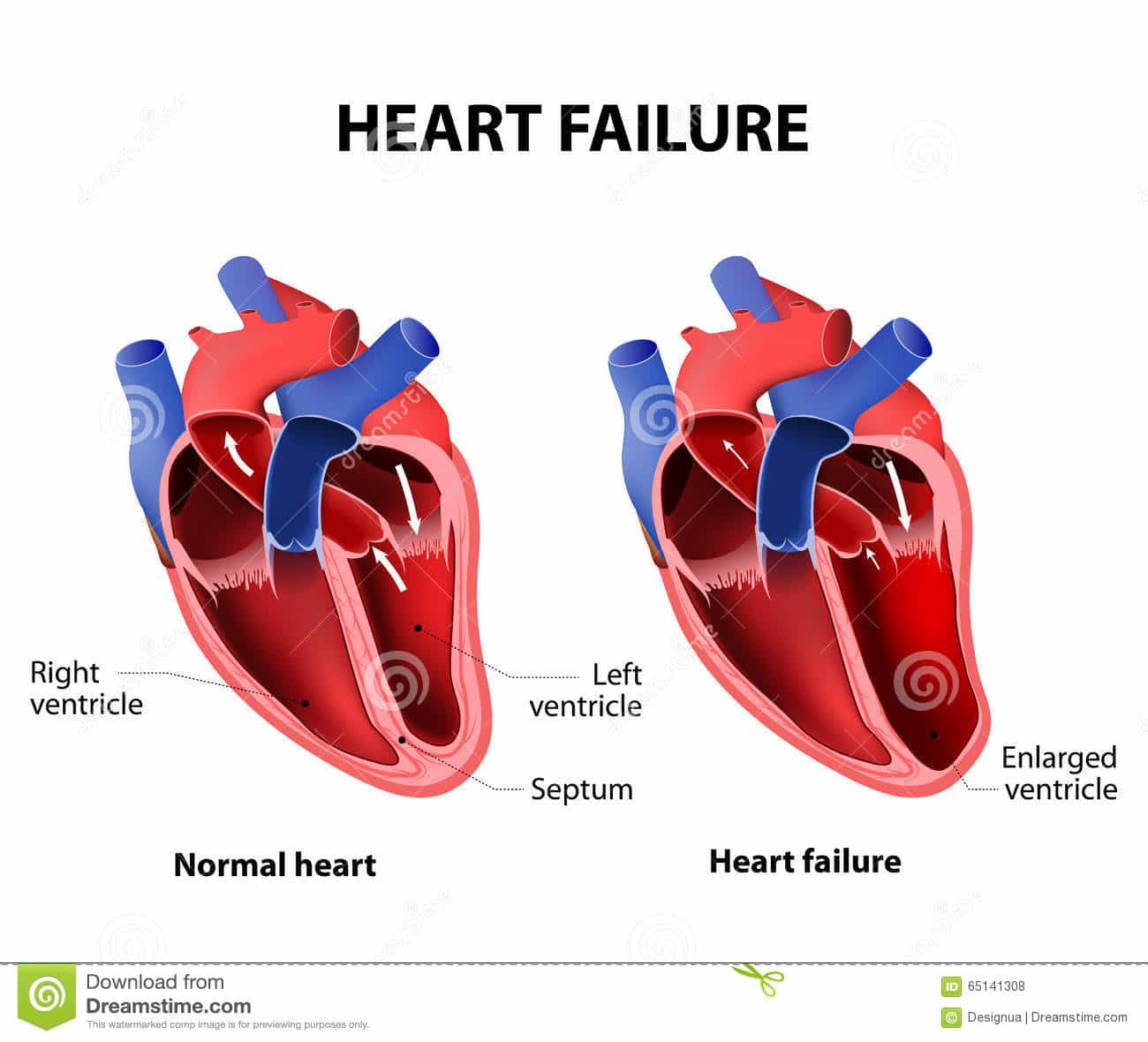
s used to describe a point at which the heart cant supply enough blood to meet the s demands.
This can happen in two ways, either the hearts ventricles cant pump blood hard enough during systole, called , or not enough blood fills into the ventricles during diastole, called .
In both cases, blood backs up into the lungs, causing congestion or fluid buildup, which is why its also often known as , or just CHF.
Congestive heart failure affects millions of people around the world and since it means that the s needs are not being met, it can ultimately lead to death.
Part of the reason why so many people are affected by heart failure, is that there are a wide variety of like and valvular disease that can impair the hearts ability to pump out blood andover timecan ultimately cause the heart to fail.
The heart rate is pretty intuitive, but the stroke volumes a little tricky.
So notice that not all the blood was pumped out right?
And the stroke volume is only a fraction of the total volume.
Palliative And Hospice Care
Someone living with a serious condition like heart failure can access palliative care at any stage of their condition. Palliative care is intended to support overall wellness and quality of life and can happen alongside other treatments.
With very severe heart failure, people may choose to access hospice care to receive supportive care at the end of life.
Also Check: Swollen Ankles Heart Failure
Outlook For Heart Failure
Heart failure is a serious long-term condition that will usually continue to get slowly worse over time.
It can severely limit the activities you’re able to do and is often eventually fatal.
But it’s very difficult to tell how the condition will progress on an individual basis.
It’s very unpredictable. Lots of people remain stable for many years, while in some cases it may get worse quickly.
Symptoms Congestive Heart Failure
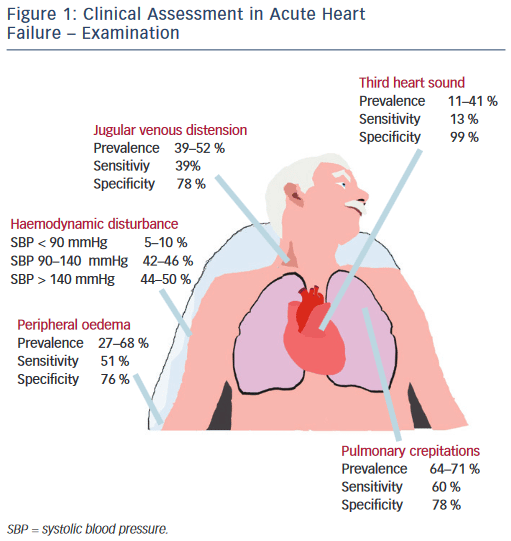
The general symptoms of congestive heart failure are the same regardless of the etiology and attributed to either fluid retention related to the activated RAAS or low cardiac output. They can also be categorized as from left heart failure vs. right heart failure.
Left HF will result in low cardiac output symptoms and transmission of the increased left-sided cardiac pressures into the lungs, causing pulmonary edema and a sense of dyspnea. With physical exertion, the heart demands increased cardiac output that is unable to be satisfied in states of HF, significantly increasing left heart pressures and causing this transient pulmonary edema.
As those increased pressures from the left heart affect the right ventricle, right heart failure can ensue. The most common cause of right HF is left HF.
Right heart failure symptoms include lower extremity dependent edema. When the legs are elevated at night, the fluid redistributes centrally, causing pulmonary edema that results in orthopnea or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, or PND. Hepatic congestion can occur, causing right upper quadrant abdominal pain.
Symptoms related to low cardiac output include fatigue, weakness and, in extreme cases, cardiac cachexia.
The New York Heart Association functional classification system helps to categorize patients based on their symptoms of heart failure.
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Congestive Heart Failure
Chronic Systolic Heart Failure
Chronic systolic heart failure occurs over a period of time, typically caused by other heart conditions such as high blood pressure, a damaged heart, or coronary artery disease.
Baptist Health is known for advanced, superior care for patients with heart disease and the diagnosis, management and treatment of systolic heart failure. You will appreciate timely appointments and a professional, friendly atmosphere where we take time to listen to your concerns. At Baptist Health, you have access to the regions most comprehensive, multidisciplinary team of specialists and innovative therapies, including many available only through specialized clinical trials. In every way, we work to demonstrate the utmost in excellent care to those who trust us with their health.
What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Systolic Heart Failure
Although there have been recent improvements in congestive heart failure treatment, researchers say the prognosis for people with the disease is still bleak, with about 50% having an average life expectancy of less than five years. For those with advanced forms of heart failure, nearly 90% die within one year.
Read Also: Replacement Valve Heart Surgery
Surgery And Percutaneous Procedures
Surgery may be appropriate when certain underlying disorders are present. Surgery in patients with advanced HF should be done in a specialized center.
Surgical closure of congenital or acquired intracardiac shunts can be curative.
If HF is primarily due to a valvular disorder Overview of Cardiac Valvular Disorders Any heart valve can become stenotic or insufficient , causing hemodynamic changes long before symptoms. Most often, valvular stenosis or insufficiency… read more , valve repair or replacement should be considered. Patients with primary mitral regurgitation are more likely to benefit than patients with mitral regurgitation secondary to LV dilation, in whom poor myocardial function is likely to continue postoperatively. Surgery is preferably done before myocardial dilation and damage become irreversible. More recently, percutaneous mitral valve repair procedure, in which a clip is applied to approximate the anterior and posterior mitral leaflets, has been shown to reduce death and HF hospitalization in carefully selected patients with symptomatic HF despite optimal medical management and moderate to severe or severe mitral regurgitation with preserved LV size is a syndrome of ventricular dysfunction. Left ventricular failure causes shortness of breath and fatigue, and right ventricular failure causes peripheral and abdominal fluid… read more ).
Prognosis Of Systolic Heart Failure
In general, a diagnosis of heart failure is serious, since it can cause life-threatening arrhythmias and organ failure.
Taking medications as prescribed, monitoring fluid status, and close follow-up with a healthcare provider can help people with heart failure stay out of the hospital and improve quality of life.
Advanced treatments and heart transplant are also options for those with very severe heart failure.
You May Like: Does High Heart Rate Mean High Blood Pressure
Unspecified Systolic Heart Failure
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
I50.21 Acute systolic heart failure
Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes.
Diagnosis Congestive Heart Failure
The diagnosis of congestive heart failure is predominantly by history and physical, though echocardiography and cardiac catheterization can be beneficial.
Physical examination during systolic congestive HF will reveal a S3 heart sound if significant left ventricular dilation is present. A S4 heart sound can be present in diastolic HF. The point of maximal impulse, or PMI, will be laterally displaced and, at times, the S3 can even be palpable. Cardiac murmurs will be present if valvular heart disease is present, contributing to the HF such as aortic stenosis or mitral regurgitation.
Physical examination in states of right heart failure may reveal elevated jugular venous pressure including hepatojugular reflux, lower extremity pitting edema and ascites. Pleural effusions may be present and more prominent on the right compared to the left.
Echocardiography is indicated in all patients with a new diagnosis of congestive HF to help determine the etiology. The LV systolic function can be measured, including ejection fraction. Diastolic function assessment can help determine the left heart pressures. The cardiac valves can be interrogated for significant regurgitant or stenotic lesions.
Recommended Reading: What Does A Heart Attack Look Like On An Ecg
Medications For Systolic Heart Failure
Depending on the severity of systolic heart failure and its underlying cause, your doctor may prescribe medications. Some of the drug options for treating systolic heart failure include:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers relax the blood vessels to lower blood pressure.
- Beta blockers make the heart beat more slowly and with less force.
- Aldosterone blockers help the body release sodium and water.
- Angiotensin receptorneprilysin inhibitors reduce excess fluid in the body and relax blood vessels, making it easier for your heart to pump blood.
Treatments For Heart Failure
Treatment for heart failure usually aims to control the symptoms for as long as possible and slow down the progression of the condition.
How you’re treated will depend on what is causing your heart failure.
Common treatments include:
- lifestyle changes including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and stopping smoking
- medicine a range of medicines can help many people need to take 2 or 3 different types
- devices implanted in your chest these can help control your heart rhythm
- surgery such as a or a heart transplant
Treatment will usually be needed for life.
A cure may be possible when heart failure has a treatable cause. For example, if your heart valves are damaged, replacing or repairing them may cure the condition.
You May Like: Training Zones Heart Rate
