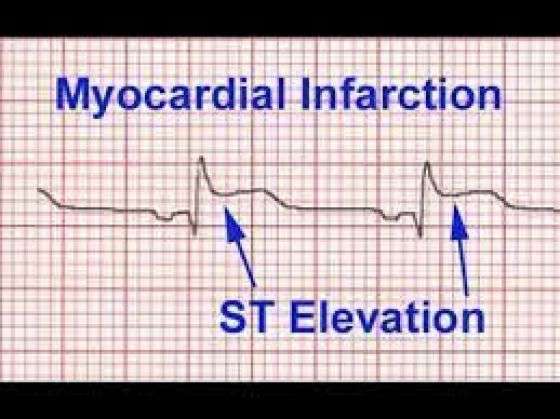
Type #: Posterior St Segment Elevation Mi
This one is tricky when isolated, but it is very important not to miss. We treat it just like any other ST segment elevation MI, which is of course time sensitive.
The posterior wall is supplied by the posterior descending artery. The PDA branches from the right coronary artery in 80% of people therefore, occlusion of RCA can result in both an inferior STEMI and a posterior MI as well. Sometimes, it is obvious on the ECG when a posterior MI accompanies an inferior STEMI, but it can also occur all by itself.
The ECG criteria to diagnose a posterior MI treated like a STEMI, even though no real ST segment elevation is apparent include:
- ST segment depression in V1 to V4. Think of things backwards. These are the septal and anterior ECG leads. The MI is posterior , so there is ST depression instead of elevation. Turn the ECG upside down, and it would look like a STEMI.
- The ratio of the R wave to the S wave in leads V1 or V2 is greater than 1. This represents an upside-down Q wave .
- ST segment elevation in the posterior leads of a posterior ECG . A posterior ECG is done by simply adding three extra precordial leads wrapping around the left chest wall toward the back.
Below are some examples including isolated posterior MIs, inferior STEMIs with posterior involvement and a posterior ECG.
Below are two examples of ECG tracings with both inferior STEMI and posterior involvement. Remember, the more you look at the better!
Inferior-Posterior STEMI Example #1
Looking For Ischaemia / Angina On An Ecg
Obviously the thing to remember here is that a good history and examination is vital here – the ECG is useful but can be completely normal in someone with terrible real angina. So bear this in mind before you read on…If possible try and get an ECG done previously when the patient isnt having chest pain so you can see any differences which can be more useful than one ECG by itself.The main area to look for is the ST segment, which is just the flat area between the QRS and the T wave. The ST segment should be at the same level as the rest of the flat sections of the ECG trace or the baseline. In ischaemia the ST segment sinks lower than the baseline, otherwise known as ST depression. The other thing you can see on the angina ECG above is that the T wave is upside down. T wave inversion or even flattening is another sign of angina, but it is not a good one. It could also signify an old or current heart attack . But clues like this are useful when you become more experienced and you are trying to interpret more difficult ECGs.There are some things you should bear in mind before you can say if the patient really has angina or not.
How Silent Heart Attacks Are Discovered
Some patients whose heart attacks go unrecognized learn about them weeks or months later when they visit the doctor, often for a yearly physical.
We can tell the size of the heart attack by how much heart muscle has been damaged, often on an electrocardiogram , or even more precisely on a cardiac ultrasound, or echocardiogram, says Dr. Rimmerman.
Other patients visit their doctors soon after a silent heart attack because they experience persistent symptoms, such as fatigue and shortness of breath.
Sometimes these symptoms are caused by a leaky mitral valve, caused by scarring of the heart muscle and associated valve dysfunction after a heart attack. Serious complications can follow, including decompensated heart failure, heart rhythm disorders and loss of consciousness.
Read Also: Can Ibs Cause Palpitations
How Far Back Can An Ekg Show A Heart Attack
An EKG can potentially reveal that you had a heart attack years ago without knowing it. Abnormal electrical patterns during the test suggest that part of your heart may have been damaged from lack of oxygen.
Not all heart attacks produce noticeable symptoms. If youve had a silent heart attack, you may not know it occurred until you have an imaging test like an EKG, MRI, CT scan, or ultrasound.
An EKG is one tool that doctors use to find evidence of previous heart attacks, but its best used when combined with other diagnostic techniques like blood tests and imaging. Its relatively common for EKG results to give a false positive.
One study measured the accuracy of an EKG for diagnosing a previous heart attack compared to a cardiac MRI. The researchers found that EKGs had:
- Poor sensitivity. The EKG only correctly identified a previous heart attack 48.4 percent of the time compared to an MRI.
- Good specificity. The EKG correctly identified that no previous heart attack had occurred 83.5 percent of the time compared to MRI.
- Positive predictive accuracy. People with EKG results that suggested they had a heart attack had a 72 percent chance of actually having had a heart attack.
- Negative predictive accuracy. People with EKG results that suggested they didnt have a heart attack had a 64.2 percent probability of not actually having had a heart attack.
An EKG can potentially predict a future risk of heart attack by uncovering abnormalities in the electrical activity of your heart.
Interpreting The Ecg Results
The electrical signals generated from the electrodes are processed to obtain the hearts electrical activity from 12 different angles, each of which shows a separate tracing. By examining any abnormalities on the ECG and which leads they are stemming from, your healthcare provider can get important clues about the status of the heart. Learning to read an ECG and recognize these patterns takes months of training and practice.
Recommended Reading: Ibs And Heart Palpitations
What Are The Possible Presentations Of Heart Failure On Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography may suggest an acute tachyarrhythmia or bradyarrhythmia as the cause of heart failure. It may also aid in the diagnosis of acute myocardial ischemia or infarction as the cause of heart failure, or it may suggest the likelihood of a prior myocardial infarction or the presence of coronary artery disease as the cause of heart failure.
Heart failure can have multiple and diverse presentations on ECGs .
References
Ho KK, Pinsky JL, Kannel WB, Levy D. The epidemiology of heart failure: the Framingham Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993 Oct. 22 :6A-13A. . .
American Heart Association. Classes of heart failure. Available at . Updated: May 8, 2017 Accessed: June 18, 2017.
Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al, American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013 Oct 15. 128:e240-327. . .
Lindenfeld J, Albert NM, Boehmer JP, et al, for the Heart Failure Society of America. HFSA 2010 comprehensive heart failure practice guideline. J Card Fail. 2010 Jun. 16:e1-194. . .
Braunwald E. The pathogenesis of congestive heart failure: then and now. Medicine. 1991 Jan. 70:68-79. .
Can Silent Heart Attacks Be Prevented Or Avoided
A healthy lifestyle can help prevent any kind of heart attack. This includes:
- Quitting smoking if you smoke and avoiding secondhand smoke.
- Keeping a healthy diet that is low in fat and low in cholesterol.
- Exercising regularly.
- Managing your blood sugar level if you have diabetes.
- Seeing your doctor regularly for check-ups.
Don’t Miss: Can Ibs Cause Heart Palpitations
What An Abnormal Ekg Indicates
Because an EKG measures so many different aspects of the hearts function, abnormal results can signify several issues. These include:
Defects or abnormalities in the hearts shape and size: An abnormal EKG can signal that one or more aspects of the hearts walls are larger than another. This can signal that the heart is working harder than normal to pump blood.
Electrolyte imbalances:Electrolytes are electricity-conducting particles in the body that help keep the heart muscle beating in rhythm. Potassium, calcium, and magnesium are electrolytes. If your electrolytes are imbalanced, you may have an abnormal EKG reading.
Heart attack or ischemia: During a heart attack, blood flow in the heart is affected and heart tissue can begin to lose oxygen and die. This tissue will not conduct electricity as well, which can cause an abnormal EKG. Ischemia, or lack of blood flow, may also cause an abnormal EKG.
Heart rate abnormalities: A typical human heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats per minute . An EKG can determine if the heart is beating too fast or too slow.
Heart rhythmabnormalities: A heart typically beats in a steady rhythm. An EKG can reveal if the heart is beating out of rhythm or sequence.
How Can You Tell The Difference Between A Heart Attack And Angina
Angina is the specific type of pain you experience when the heart is in trouble. Heart attacks, on the other hand, occur when the narrowing is severe or causes a blockage, leading to actual damage to the heart muscle. In other words, a heart attack is an actual medical condition and angina is a symptom.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Bleeding Around The Heart
Have An Apple Watch You Can Help
Its early days for wearables in healthcare, but there is a lot of potential. For example, recent research suggests that if you can monitor people with a cryptogenic stroke for three weeks rather than the standard 48 hours, you can detect 5x as much atrial fibrillation .
What would happen if we could extend that monitoring interval to a year? Your whole life?
If you have an Apple Watchregardless of whether you have a heart conditionyou can help us find out. Were running the mRhythm Study with the UCSF Health eHeart Study, using Cardiogram to train a deep learning algorithm to detect atrial fibrillation. You can contribute regardless of whether you have a heart condition.
If you have an Apple Watch, please do sign up at mRhythmStudy.org.
Notes
In more detail: every normal heart beat has four phases, starting with an electrical impulse generated by the SA node , which causes an atrial contraction , passes through the AV node , and finally causes a ventricular contraction . The ventricals then repolarize .
More specifically, AVNRT, or AV-Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia, in which a harmful loop develops in the hearts electrical circuit. Think of it as recursion without a base case.
Recovering From A Heart Attack
You’ll usually stay in hospital for about two to five days after having a heart attack. This depends on what treatment you’ve had and how well you’re recovering.
Many people make a full recovery after a heart attack, but you might not be able to do everything you used to. Going to cardiac rehabilitation can help you get back to normal as quickly as possible.
A heart attack can be a frightening experience and it can take time to come to terms with what’s happened. Its natural to be worried about your recovery, feel scared, frustrated and isolated.
For support and advice, visit our emotional support page.Practical matters like driving, going back to work or finances might be a worry after a heart attack. You can get support and advice on these topics and more on our practical support page.
- Hear from Mark who was 39 when he had a heart attack.
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
How Are Silent Heart Attacks Diagnosed
Many times, silent heart attacks are found during a routine check-up. If your doctor thinks you may have had one, he or she may order imaging tests. These could include an electrocardiogram , which is a special ultrasound, or a CT scan or MRI of your heart.
These tests can show if your heart muscle has been damaged, signaling that youve had a heart attack. If youve gone to the emergency room with silent heart attack symptoms, the doctor may order blood tests.
What Are These Unusual Symptoms
Non-classic symptoms of heart attack may include the following:
- Unexplained fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Discomfort in the throat, neck, jaw or a single extremity
Some patients may only experience what they believe is heartburn and simply take antacid medication to relieve it instead of recognizing that the pain could be heart-related.
Dr. Rimmerman notes that most people think heart attacks cause a sharp pain on the left side of the chest. Yet heart attacks most often cause discomfort in the center of the chest, along with a sensation of unremitting squeezing, fullness or tightness, he says.
Given the way TV and movies portray heart attacks as obvious events, its not surprising that less common heart attack symptoms pass unnoticed.
You May Like: Is Tylenol Bad For Your Heart
What Is The Difference Between An Electrocardiogram And An Echocardiogram
An electrocardiogram is a test performed by placing electrodes on the chest, arms, and legs to record the activity of the heart. This test is used to detect an irregular heartbeat and damage to the heart muscle or tissue. An echocardiogram uses high-frequency sound waves to take a picture of the heart and is used to see how well the heart pumps blood and blood clots, among other things,
What Tests Are Used To Diagnose Heart Failure
Tests your doctor might order to diagnose heart failure include:
Blood tests to check for anemia, thyroid problems, and high cholesterol, conditions that can be related to heart failure. There is also a blood test for B-type natriuretic peptide , which can indicate active heart failure.
Electrocardiogram to assess the heart rate and rhythm. This test can often detect heart disease, heart attack, an enlarged heart, or abnormal heart rhythms that may cause heart failure.
Chest X-ray to see if the heart is enlarged and if the lungs are congested with fluid.
Echocardiogram, an ultrasound test, to evaluate heart muscle function, to see how well the heart is pumping, and to detect problems with the heart valves that may cause heart failure. Ejection fraction also can be measured. EF is a measure of how much blood is pumped out of the heart with each beat, and how much blood pumps through the heart with each beat. A normal EF is generally greater than 50%, which means that over half of the blood volume in the heart’s main pumping chamber is pumped out with each beat.
Radionuclide ventriculography to show the pumping function of the left and right ventricles during heart contractions. This test can also measure EF. Rarely performed by itself, this test may be part of an exercise stress test.
You May Like: Can Antihistamines Cause Heart Palpitations
Should I Still Call 999 Or Go To Hospital If I’m Worried About My Health
Whether or not you have coronavirus symptoms, it’s essential to dial 999 if you have symptoms that could be a heart attack, or if your heart symptoms get worse.
We are hearing that fewer people are being seen in hospital with heart attacks in recent weeks, which suggests that people are not seeking help when they should do. If you have any of the symptoms described above, you should call 999.
Don’t delay because you think hospitals are too busy – the NHS still has systems in place to treat people for heart attacks. If you delay, you are more likely to suffer serious heart damage and more likely to need intensive care and to spend longer in hospital.
Atrial Fibrillation: An Irregularly Irregular Arrhythmia
Atrial fibrillation is the most common abnormal heart rhythm, responsible for about a quarter of all strokes. In atrial fibrillation, electrical activity within the atria becomes chaotic, which causes the ventricles to contract at seemingly-random intervals. Whats worse, if youre in atrial fibrillation, you may not feel it, potentially leading to cryptogenic stroke.
The good news is an optical heart rate sensor can detect atrial fibrillation. In the graph above, you can see high absolute variability , a higher fraction missing measurements , and a lack of periodicity in heart rate variability.
Note that although atrial fibrillation is often paired with a higher heart rate , thats not always the case. In the example above, the persons heart rate is actually lower than average . And note that since were working with an optical heart rate sensor, we dont get information on P waves or the width of the QRS complex. If we suspected asymptomatic atrial fibrillation based on Apple Watch data, wed usually want to confirm with an ECG.
Don’t Miss: Can This 10 Second Trick Prevent Your Heart Attack
How Do I Know If I Have Heart Failure
Doctors diagnose heart failure by taking a medical history and conducting a physical exam and tests.
During the medical history your doctor will want to know if:
- You have any other health problems such as diabetes, kidney disease, angina , high blood pressure, or other heart problems
- You smoke
- You drink alcohol, and if so, how much
- You are taking medications.
During the physical, the doctor will check your blood pressure, use a stethoscope to hear sounds associated with heart failure in the heart and lungs, and look for swollen neck veins, an enlarged liver, and swollen feet.
Cost And Health Insurance
Generally, an ECG is covered by most health insurance plans, but there are always exceptions. If you are insured and concerned that your plan may not cover the test, or if you have a plan with minimal coverage, you might want to check your benefits in advance. As with many procedures, your plan may also require you to pay a copay, and you should be able to find out by calling the number on your insurance card.
Don’t Miss: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
