What Are Normal And High Bnp Levels
BNP tests, also called a B-type natriuretic peptide test, measure BNP by picograms per milliliter or nanograms per liter. The range includes:
- Normal: Less than 100 pg/mL
- High: More than 400 pg/mL
- Between 100 to 400 pg/mL requires a doctors evaluation
Another test that measures BNP, called the NT-proBNP, has these ranges that vary by age:
BNP Levels by Ages Chart
| Condition | |
|---|---|
| Over the age of 75 | More than 1,800 |
Tests results can also vary by sex, body mass index, health history, and other factors. Levels tend to get higher as you age. BNP is also usually higher in women than men. People who are obese tend to have lower levels. Ask your doctor what your specific results mean for you.
What Is A B
A B-type natriuretic peptide test is a blood test. It measures the levels of a certain type of hormone in your blood called a B-type natriuretic peptide. This test gives your healthcare provider information about your heart.
Higher-than-normal levels of BNP in your blood can be a sign that your heart isnt working as it should. It can mean that your heart isnt pumping enough blood through your body. Since BNP is cleared by your kidneys, it may also mean that your kidneys are not functioning properly.
Some laboratories offer a similar test called aminoterminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide . Both the BNP and NT-proBNP tests show similar information, although the absolute values of NT-proBNP are about five to 10 times higher than BNP.
Providers use a BNP or an NT-proBNP test to diagnose heart failure. If you already know you have heart failure, your provider may order this test to check the severity of your condition. They may also use this test to monitor how heart failure treatments are working. In some cases, your provider may also order it if they think you may be at higher risk of developing heart failure.
Natriuretic Peptide Measurement In Heart Failure
Summary
This paper is an up-to-date account of research and current clinical practice guideline recommendations. Chris Higgins summarizes the recommendations of 2 new guidance documents on the use of natriuretic peptides in heart failure. The first document is a systematic review of published research on the role of biomarkers in heart failure conducted by an expert group on behalf of the American Heart Association . The second document is the 2017 update of 2013 American College of Cardiology /AHA Guideline for Management of Heart Failure. The article begins with brief overviews of BNP/NT-proBNP and heart failure.
Measurement of circulating natriuretic peptide concentration has been a routine part of the clinical assessment of patients with suspected heart failure for close to 15 years following discovery that heart failure is associated with increased concentration of both peptides. Voluminous research over this 15-year period has sought to refine and extend the clinical utility of the two tests and allow evidence-based guidelines for their clinical use in heart failure.
The focus of, and impetus for this article is two recently published, potentially influential papers . Together they provide current group expert view of the value of BNP, NT-proBNP testing in heart failure. The first is a systematic review of published research on the role of biomarkers in heart failure conducted by an expert group on behalf of the American Heart Association .
Recommended Reading: Fat Burn Heart Rate Zone Calculator
Influences On Bnp And Nt
The optimal cut-off value of BNP and NT-ProBNP for the diagnosis of diastolic heart failure is unclear. It may relate some factors. The most important factors the cut-off values of BNP and NT-proBNP are method-dependent. Hammerer- Lercher et al pointed out that the performance of BNP for the diagnosis of systolic or diastolic left ventricular dysfunction is not affected by the assay used, whereas the performance of NT-proBNP for the diagnosis of isolated diastolic left ventricular dysfunction is assay dependent . They found that both BNP assays and both NT-proBNP assays performed equally well for the diagnosis of systolic left ventricle dysfunction despite the poor agreement between NT-proBNP assays . In patients with isolated diastolic left ventricular dysfunction, the diagnostic performance of the Triage BNP was significantly better than that of Biomedica NT-proBNP. Furthermore, the performance of the Biomedica NT-proBNP assay was significantly worse than that of the Roche NT-proBNP assay for diagnosis of isolated diastolic left ventricular dysfunction. In other studies the Triage BNP assay when compared to the Shionoria assay gives consistently higher values and the magnitude of difference increases with concentration of peptide . The Biomedica method shows considerably higher values compared to the Elecsys method suggesting that higher cut-off values are needed to be comparable .
Exercise causes a slight increase in BNP levels which are detectable at short-term .
When Is A B

Your provider orders this test to look for higher levels of BNP in your blood to check for cardiovascular disease. You may get a BNP or NT-proBNP test if you have symptoms of heart failure.
Symptoms of heart failure include:
- Cough that seems dry or hacking and gets worse when laying down.
- Nausea and vomiting or loss of appetite.
- Swelling in your abdomen, legs, ankles and feet.
- Urinating more than usual at night .
Heart failure means your heart isnt pumping blood as it should. It doesnt mean that your heart has failed or stopped working entirely. If your provider has already diagnosed you with heart failure, they may order a BNP or NT-proBNP test to monitor how treatments are working.
Get emergency medical help if you have these symptoms. Heart failure is life-threatening and requires immediate treatment.
Read Also: How To Stop A Heart Attack Before It Happens
How Common Is Heart Failure
According to the American Heart Association, more than 6 million people in the United States are living with heart failure and the number is growing. It is estimated that one in five American adults age 40 and older will develop heart failure in their lifetime. You may be at increased risk of developing heart failure if you have conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure, or diabetes, or if you have had a heart attack. Other risk factors include tobacco use, alcohol use, and obesity.
You May Like: Afrin Heart Palpitations
What Are Natriuretic Peptide Tests
Natriuretic peptides are substances made by the heart. Two main types of these substances are brain natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide . Normally, only small levels of BNP and NT-proBNP are found in the bloodstream. High levels can mean your heart isn’t pumping as much blood as your body needs. When this happens, it’s known as heart failure, sometimes called congestive heart failure.
Natriuretic peptide tests measure the levels of BNP or NT-proBNP in your blood. Your health care provider may order a BNP test or an NT-proBNP test, but not both. They are both useful in diagnosing heart failure, but rely on different types of measurements. The choice will depend on the equipment available in your provider’s recommended laboratory.
Other names: brain natriuretic peptide, NT-proB-type natriuretic peptide test, B-type natriuretic peptide
Recommended Reading: What Side Of The Heart Pumps Blood To The Lungs
What Do Abnormal Levels Of Bnp Mean
For people who dont have heart failure, normal BNP levels are less than 100 picograms per milliliter . BNP levels over 100 pg/mL may be a sign of heart failure.
For NT-proBNP, normal levels are less than 125 pg/mL for people under 75 years old and less than 450 pg/mL for people over age 75. NT-proBNP levels over 900 pg/mL may be a sign of heart failure.
Every person has their own range of BNP or NT-proBNP level range. Ask your provider about the specific measurements of your BNP test or NT-proBNP test.
Heart failure medications, including beta blockers, ACE inhibitors and diuretics, can lower BNP or NT-proBNP levels in the blood. If youre taking these drugs to treat heart failure, your BNP or NT-proBNP test results may be lower than if youre not taking them. Your levels can also be lower if you have obesity or kidney failure.
Depending on the results of the BNP test, your provider may order follow-up tests, such as an electrocardiogram . This test monitors your heart rate through sensors attached to your skin. It can help your provider diagnose or evaluate heart failure and other heart problems.
What Are The Implications
The study does not appear to support a change to clinical practice.
BNP monitoring could be effective for younger patients with reduced ventricular ejection fraction. However, the population with heart failure that is difficult to manage is frequently older and often have other illness besides heart failure.
Trials were conducted in specialist clinics, used a variety of BNP monitoring methods, and did not identify a BNP target to treat. This research is promising, but further evaluation of which people with heart failure might benefit is probably required before this becomes standard practice.
Read Also: How To Test For Heart Failure
Monitoring Patients With Heart Failure
BNP measurement is a potential tool for monitoring treatment response in patients with heart failure because of the tests ability to diagnose heart failure, predict prognosis, and correlate with more invasive clinical measures .36 Prognostic studies have shown that BNP levels measured after treatment took effect were more predictive of the risk of death or further cardiovascular events than those initiated at first presentation.37,38
Ideally, randomized trials would offer definitive evidence however, only two small trials have evaluated BNP-guided treatment.39,40 The first trial showed a nearly twofold decrease in cardiovascular events,39 and the second trial showed a decrease in BNP levels with BNP-guided treatment.40 However, according to the ACC/AHA guideline on the management of heart failure, the value of serial BNP measurements in guiding therapy for patients with heart failure is not well established.32 Larger randomized controlled trials are needed before routine BNP monitoring of heart failure can be recommended.
Read the full article.
- Get immediate access, anytime, anywhere.
- Choose a single article, issue, or full-access subscription.
- Earn up to 6 CME credits per issue.
You May Like: Typical Resting Heart Rate For A Healthy Individual
Does Blood Work Show Congestive Heart Failure
For the diagnosis of heart failure, tests for two types of natriuretic peptides are now available: BNP and pro-BNP . In individuals with congestive heart failure, blood levels of both of these chemicals rise. It is believed that measuring these levels may help diagnose heart failure in people who do not have symptoms such as shortness of breath.
Blood tests can also reveal other problems related to the heart. For example, increased levels of troponin I or T indicate damage to the cardiac muscle. The level of creatine kinase , a protein found in muscles, rises when there is damage to muscle tissue. The concentration of sodium in the blood, which is called serum sodium, decreases when the body loses water due to diarrhea or vomiting. Reduced levels of potassium in the blood indicate that the body is losing potassium through its urine. A low concentration of magnesium in the blood may be a sign of heart disease or diabetes mellitus.
Congestive heart failure is a condition in which the heart fails to pump enough blood into the blood vessels, causing them to become enlarged and requiring medication to maintain normal blood pressure. As many as 500,000 Americans are diagnosed with CHF each year. The number of cases is expected to increase as the population ages.
The main symptom of CHF is fatigue.
You May Like: How Do Heart Attacks Feel
Rv Dysfunction And Pulmonary Disease
Danish researchers extrapolated the relationship between BNP and LV dysfunction and the relationship between BNP and right ventricular dysfunction. In 50 patients with normal LV function and normal coronary arteries who were referred for lung transplantation, NT-proBNP levels were determined before they underwent right heart catheterization. Patients with primary pulmonary hypertension had NT-proBNP concentrations 40 times higher than those of patients with terminal parenchymal lung disease.
Levels of NT-proBNP have also been useful in predicting uncomplicated clinical courses of patients with a diagnosis of acute pulmonary embolism . In a study 73 patients with confirmed PE, Swiss investigators measured their NT-proBNP levels within 4 hours of diagnosis. Twenty patients had adverse outcomes, which was defined as death or the need for any of cardiopulmonary resuscitation, thrombolysis, embolectomy, vasoactive medications, or mechanical ventilation. An NT-proBNP level less than 500 pg/mL had a negative predictive value of 97% for complications due to PE. The NT-proBNP level remained an independent predictor for adverse outcome even after the analysis was adjusted for age, sex, history of CHF, and severity of PE.
Definition Of Diastolic Heart Failure
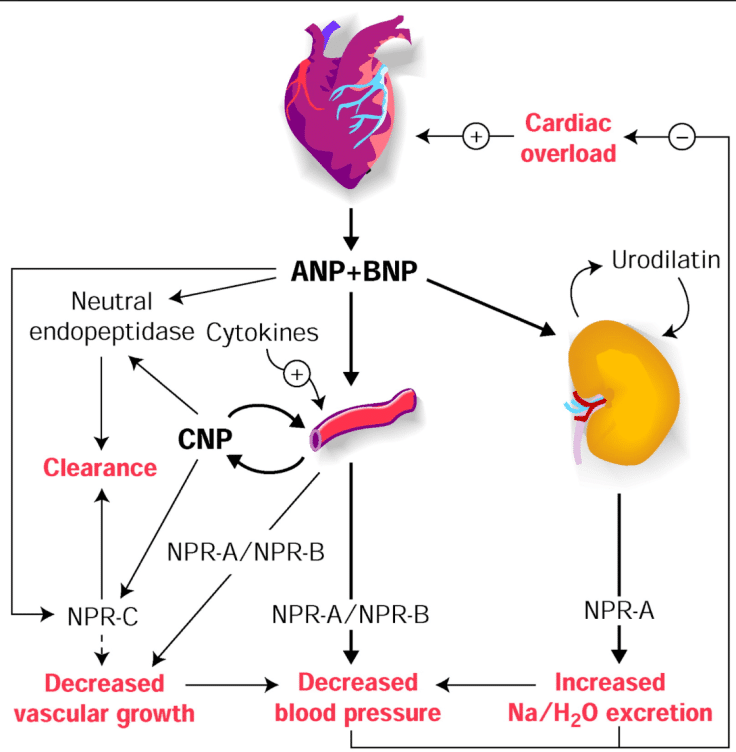
According to the 2005 Heart Failure Guideline from European Society of Cardiology , a diagnosis of primary diastolic HF requires three conditions to be simultaneously satisfied: presence of signs or symptoms of heart failure, evidence of abnormal left ventricular relaxation, diastolic distensibility, or diastolic stiffness and preserved left ventricular systolic function.
Also Check: What Is Treatment For Heart Attack
What Causes The Bnp To Be High
BNP levels may rise due to intrinsic cardiac dysfunction or as a result of other factors such as pulmonary or renal illness . BNP levels are linked to various indicators of heart health, such as the New York Heart Association classification. As people get older, their hearts become more efficient at pumping blood, so they require a higher percentage of their maximum activity to pump the same amount of blood. This is why patients over 40 years old with cardiovascular disease often have higher BNP levels than those without significant blockages in their arteries.
To calculate your risk of having a heart attack or stroke, use the Framingham Risk Score. It’s based on things like age, gender, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, systolic blood pressure, diabetes status, and smoking history. Your risk will change over time depending on what you do. If you maintain an active lifestyle and keep blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels within recommended limits, then you should reduce your risk of having a heart attack or stroke.
Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood into the circulatory system to meet the body’s needs. Heart failure can be chronic or acute. With chronic heart failure there is damage to the heart muscle that prevents it from working efficiently. With acute heart failure there is some reversible cause for the malfunction – usually an infection or severe stress on the heart.
About Article Author
Bnp And Ntprobnp In Monitoring Of Patients With Heart Failure
Plasma BNP concentrations are known to fall rapidly on treatment of patients with heart failure.In the clinic setting, patients whose functional status improved between visits showed a statistically significant reduction in plasma BNP concentration of about 50% other variables such as NT-proANP and ANP or ejection fraction showed no statistically significant change.Pilot data have suggested that vasodilator treatment can be titrated to reduce BNP concentrations towards the normal range in patients with mild to moderate heart failure.
However, the monitoring of therapy by measuring plasma BNP concentration is complicated by the wide variation of plasma BNP levels reported in patients with symptomatic heart failure, which may make titration to a target dose of BNP difficult. Furthermore, recentdata show a progressive rise in a variety of natriuretic peptides as patients renal function deteriorates.As yet it is unclear what reduction in creatinine clearance is necessary for this effect appear it may be relatively modest but nevertheless has implications for targeting of therapy. Reducing the plasma BNP concentration in the clinical setting by stepping up the diuretic dose may result in the patient developing worsening renal function, which may offset the expected reduction in BNP. Therefore, to titrate drugs against BNP is therefore not as simple an idea as it first appears.
4.4.1 Practical application
| Study |
|---|
You May Like: Alternative To Open Heart Surgery
Screening For Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction
After an acute myocardial infarction, plasma BNP concentration rises in proportion to the size of the infarct.It has been suggested that BNP measurement may have a role in screening for left ventricular systolic dysfunction in patients after myocardial infarction, and also in the general population.
Among post-MI patients, plasma BNP concentrations are inversely associated with ejection fraction.One study compared plasma BNP concentrations with quantitative and qualitative echocardiography, clinical evaluation and a clinical scoring system in 75 patients who had survived the first two days after an acute myocardial infarction.A cut-off value of 15pmol/l gave a sensitivity of 84% and a specificity of 62% for detecting a left ventricular ejection fraction < 40% on echocardiography. However, other studies have been less convincing.
Similarly, there are inconclusive data for the role of screening for asymptomatic left ventricular systolic dysfunction in the general population.
However, other studies have suggested BNP has a limited diagnostic utility in identifying left ventricular systolic dysfunction in the community.In part this may be because plasma BNP concentrations are not specific for left ventricular systolic dysfunction and the degree of elevation of plasma concentration may be much less marked in those who are asymptomatic.
4.2.1 Practical application
More work is needed with regard to screening before a recommendation to change current practice can be made.
What Is Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure is a dangerous condition in which the heart fails to adequately pump blood throughout the body. As a result, the bodys tissues and organs do not get enough nutrients and oxygen.
CHF is failure of the heart muscle and inability to perform properly. Heart failure can be either acute, happens quickly, or chronic, develops slowly over a long period of time.
Heart failure does not mean that the heart has stopped beating, it simply means the heart is not functioning properly. It can affect one or both sides of the heart. Specifically, congestive heart failure is a type of heart failure however, the terms are often used interchangeably.
Congestive heart failure is specifically when blood returning to the heart backs up and causes congestion in the body resulting in edema. The fluid can also back up into the lungs causing pulmonary edema. CHF affects the body’s inability to function properly including the kidneys’ ability to dispose of sodium and water.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 6.2 million adults in the United States have heart failure.
Medical conditions that can increase risk associated with CHF include but are not limited to:
- Coronary artery disease
- Valvular heart disease
Recommended Reading: Scars From Heart Surgery
