Is Pleural Effusion Serious
The seriousness of the condition depends on the primary cause of pleural effusion, whether breathing is affected, and whether it can be treated effectively. Causes of pleural effusion that can be effectively treated or controlled include an infection due to a virus, pneumonia or heart failure. Two factors that must be considered are treatment for associated mechanical problems as well as treatment of the underlying cause of the pleural effusion.
Fluid Retention After Surgery
The term edema refers to the visible swelling that is caused by accumulation of excess fluid in the body tissues. There have been instances of edema in individuals who have undergone a surgery. This write-up will throw some light on the possible causes of fluid retention after surgery.
The term edema refers to the visible swelling that is caused by accumulation of excess fluid in the body tissues. There have been instances of edema in individuals who have undergone a surgery. This write-up will throw some light on the possible causes of fluid retention after surgery.
Accumulation of fluid in the interstitial spaces of bodys organs could be caused due to a wide range of reasons. It could be a symptom of serious medical conditions such as heart failure, kidney problems, thyroid problems, diabetes, metabolic disorders or chronic venous insufficiency. Lymphatic obstruction, which is a medical condition that is characterized by the inability of the lymphatic vessels to drain lymph fluid from the body tissues due to a blockage in lymphatic vessels, could also cause lymphedema. Lymphedema could be caused due to injuries or infections. It could even develop as a post-surgery complication owing to the damage caused to lymphatic vessels during surgery.
How Often Does Heart Surgery Cause A Pleural Effusion
Three recent medical studies shed light on this question. A study in the European Respiratory Journal analyzed patients who developed a pleural effusion after a heart surgery. About 40% of the patients developed a pleural effusion, and on average, by day seven post-op. A greater proportion of pleural effusions occurred following a coronary artery bypass graft surgery compared to heart valve replacement operations.
A similar study the American College of Chest Physicians analyzed how often patients got a pleural effusion after undergoing CABG, valve replacement, or both. Among the patients in the study, only 6.6% experienced a clinically significant pleural effusion within 30 days following the operation.
Pleural effusions were more frequent in patients with other associated cardiac conditions. Another study in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine aimed to determine how often a pleural effusion developed related to the type of heart surgery. Pleural effusions in the patients undergoing only CABG surgery, or CABG plus valve surgery was higher than patients undergoing valve surgery only.
In that study, 40% of patients who had a CABG surgery developed a PE in the immediate post-op period. Most of the effusions were small, and they tended to gradually resolve themselves. Occasionally, however, the pleural effusion persisted or a new effusion developed within the first few months after surgery.
Don’t Miss: Dog Congestive Heart Failure When To Put Down
What Are The Pleura
The pleura are two large, thin layers of tissue, or membranes. One lines the inside of the chest cavity and the other wraps around the outside of the lungs . According to the Cleveland Clinic, the pleura act to lubricate and facilitate breathing. Between these two layers is a small gap called the pleural space that’s usually filled with about 3 to 4 teaspoons of fluid.
The Mayo Clinic describes the pleura as acting like two pieces of smooth satin gliding past each other, with the pleural fluid serving as a lubricant to allow your lungs to expand and contract when you breathe.
If the pleura becomes inflamed, the layers of the pleural membrane rub against each other like pieces of sandpaper, producing pain when you breathe. The pain only lessens or stops when you hold your breath.
Fluid Around Heart And Lungs: Causes Symptoms And Treatment
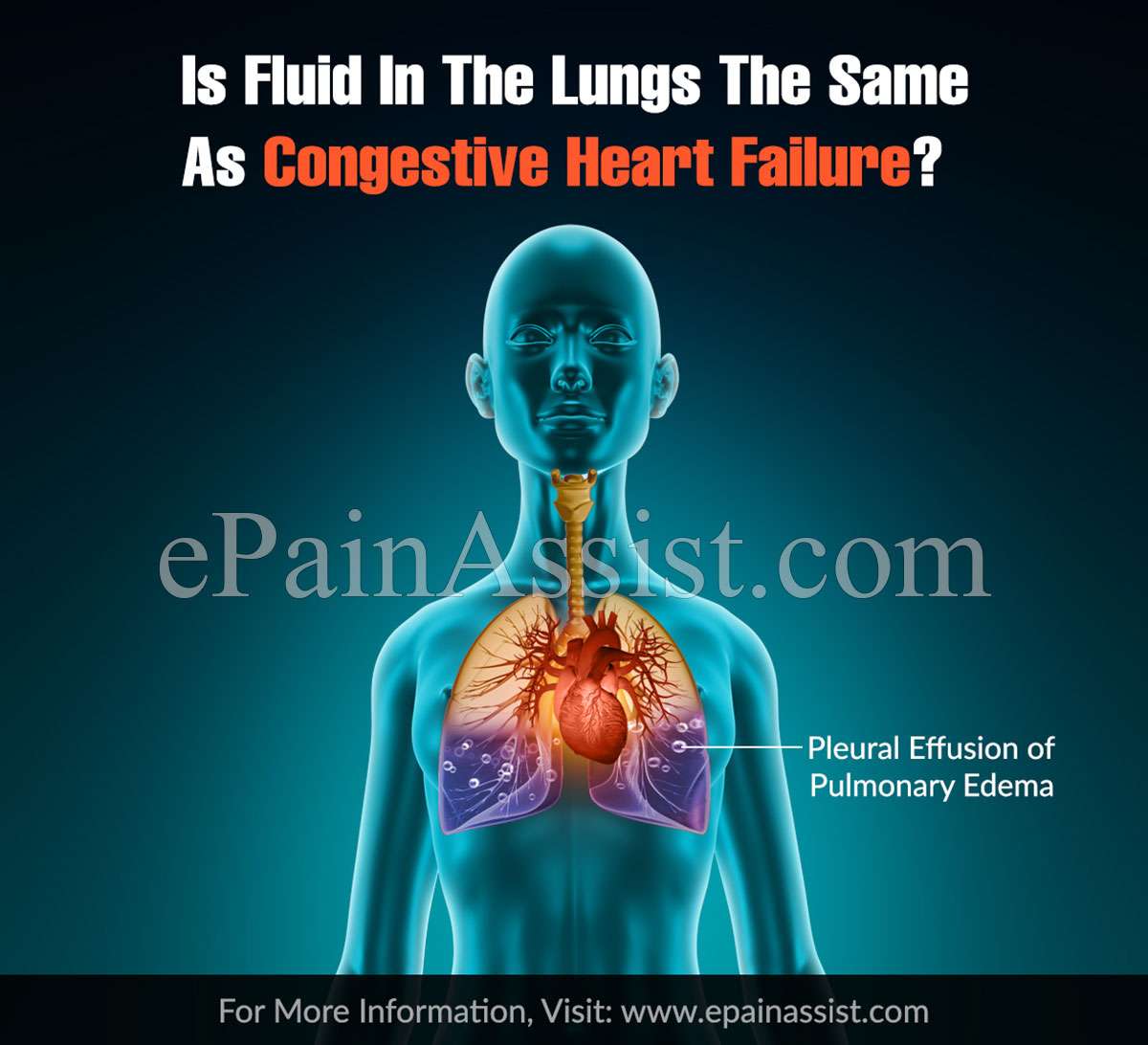
Human heart and lungs are vital organs present in the rib cage. Both these organs are surrounded by thin membrane. The membrane is lined in two layers. One layer covers the organ and other layer is adherent to the inside of chest wall. Membrane surrounding the heart is called pericardium and membrane surrounding the lung is called pleura.
Some amount of fluid is present in between the two layers. It functions as a cushion for heart and lung during traumatic injury and from friction. However, abnormal accumulation of fluid around the heart and lungs can cause problem, the condition is called pericardial effusion and pleural effusion.
Pain in chest and difficulty in breathing are two common symptoms with large accumulation of fluid. Pleural effusion and pericardial effusion is caused by infection or if the body is not able to handle the fluid properly. Treatment of the condition will depend on the underlying cause. Often excess of fluid reduces on its own or may need to be drained with the help of a needle.
Don’t Miss: Why Is My Resting Heart Rate So Low
What Customers Are Saying:
I feel so much better today, and upon further investigation believe that there is a chance that the responses I got saved me from a serious, even life threatening situation. I am very grateful to the experts who answered me.
Susan O.USA
I can go as far as to say it could have resulted in saving my sons life and our entire family now knows what bipolar is and how to assist and understand my most wonderful son, brother and friend to all who loves him dearly.Thank you very much
Corrie MollPretoria, South Africa
I thank-you so much! It really helped to have this information andconfirmation. We will watch her carefully and get her in for theexamination and US right away if things do not improve. God bless you aswell!
ClaudiaAlbuquerque, NM
Outstanding response time less than 6 minutes. Answered the question professionally and with a great deal of compassion.
KevinBeaverton, OR
Suggested diagnosis was what I hoped and will take this info to my doctor’s appointment next week.I feel better already! Thank you.
ElanorTracy, CA
Thank you to the Physician who answered my question today. The answer was far more informative than what I got from the Physicians I saw in person for my problem.
JulieLockesburg, AR
You have been more help than you know. I seriously don’t know what my sisters situation would be today if you had not gone above and beyond just answering my questions.
John and StefanieTucson, AZ
Pleural Effusion Following Bypass Surgery Pleural Effusion And Cardiac Surgery
Since my dad died of complications and hospital acquired infections, after a triple bypass, I am well aware of the things that can occur, following surgery. He developed very serious pneumonia, that he could never recover from, in spite of the continual use of antibiotics.
Pleural effusion occurs when excess fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity. While there is normally some fluid present in the pleural cavity, a healthy person will have less than 15 ml of fluid in each space. Lymphatics will usually absorb this fluid, but when they cannot, because of an overabundance, a pleural effusion occurs. The excess fluid can be thin or very thick. This is quite common after cardiac surgery, and occurs in up to 90% of bypass patients. Pleural effusion may occur during the first 30 days after surgery, or it can also occur later.
The pleural spaces are small spaces between the lungs and the rib cage, and they are covered by a thin membrane called the pleura. When pleural effusion occurs, the lungs cannot fully expand.
There are 2 types of pleural effusion, , and depending on the type, the causes can include bacterial pneumonia , cancers such as lung, breast, and lymphoma, viral infections, pulmonary embolism, cirrhosis, tuberculosis, lupus, bleeding, trauma to the chest, rupture of the esophagus, asbestos exposure, abdominal abscesses, and rheumatoid arthritis, as well as other causes.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Normal Resting Heart Rate For A Woman
What Causes Fluid In The Lungs After Surgery
Pulmonary edema or plural effusion However, in pleural effusion, water fluid collects in the layers of the pleura that are ouside the lungs. It can result from heart failure, cirrhosis, or a pulmonary embolism. It can also occur after heart surgery.
Is fluid in the lungs normal after surgery?
The air then fills the space outside of the lung, between the lung and chest wall. Atelectasis is common after surgery or in people who are or were in the hospital. Risk factors for developing atelectasis include: Anesthesia.
What causes respiratory complications after surgery?
Recent findings: General anesthesia and surgery are the main causes of postoperative respiratory complications. Atelectasis, a common respiratory complication, may contribute to pneumonia and acute respiratory failure.
Pulmonary Edema Vs Pneumonia
Pneumonia is another serious condition of the lungs. Unlike edema, pneumonia is caused by either a viral, fungal, or bacterial infection. As your lungs become infected, fluid builds up in the air sacs .
While both pulmonary edema and pneumonia cause a form of buildup in the lungs, the former is primarily caused by CHF. Pneumonia, on the other hand, is caused by an infection. A weakened immune system can increase your chances of getting pneumonia from a common cold or flu.
Symptoms of pneumonia may include:
- high fever with chills
Dont Miss: Who Performed The First Open Heart Surgery Successful
You May Like: Heart Attacks Signs And Symptoms
Breathing And Coughing Exercises After Heart Surgery
3 Minute Read
After your heart surgery, your doctor and recovery team will give you a number of exercises to do on a regular basis that will help you get back to feeling like your old self again. Here you will find information about breathing and coughing exercises that will help to speed your recovery.
Treatment For Fluid Around The Heart And Lungs
Many cases of fluid buildup around the heart and lungs resolve without any specific treatment. In few other cases treating the underlying cause will improve the condition.
For example if the accumulation is caused due to tuberculosis, anti tuberculosis treatment with medications will gradually reduce excess collection of fluid.
If accumulation is in excess and the symptoms worsen, the fluid may need to be drained with a large bore needle. The procedure is performed by a trained doctor with the help of sonogram in sterile environment.
Recommended Reading: Heart Failure Congestion
Atelectasis And Gas Exchange After Cardiac Surgery
Senior Registrar, Department of Cardiothoracic Anesthesia.
Associate Professor, Department of Cardiothoracic Anesthesia.
Associate Professor, Department of Diagnostic Radiology.
Professor and Chair, Department of Clinical Physiology.
Anesthesiology
Arne Tenling, Thomas Hachenberg, Hans Tyden, Goran Wegenius, Goran Hedenstierna Atelectasis and Gas Exchange after Cardiac Surgery. Anesthesiology 1998 89:371378 doi:
Sometimes a high intrapulmonary shunt occurs after cardiac surgery, and impairment of lung function and oxygenation can persist for 1 week after operation. Animal studies have shown that postoperative shunt can be explained by atelectasis. In this study the authors tried to determine if atelectasis can explain shunt in patients who have had cardiac surgery.
Nine patients having coronary artery bypass graft surgery and nine patients having mitral valve surgery were examined using the multiple inert gas elimination technique before and after operation. On the first postoperative day, computed tomography scans were made at three levels of the thorax.
Large atelectasis in the dorsal part of the lungs was found on the first postoperative day after cardiac surgery. However, there was no clear correlation between atelectasis and measured shunt fraction.
Read Also: Target Heart Rate When Working Out
What Is The Most Common Postoperative Pulmonary Complication
Atelectasis is one of the most common postoperative pulmonary complications, particularly following abdominal and thoracoabdominal procedures .
What can happen to your lungs after surgery?
Sometimes lung problems happen because you dont do deep breathing and coughing exercises within 48 hours of surgery. They may also happen from pneumonia or from inhaling food, water, or blood into the airways. Symptoms may include wheezing, chest pain, shortness of breath, fever, and cough.
What are the risk factors for pleural effusion?
Common risk factors in the development of pleural effusion include pre-existing lung damage or disease, chronic smokers, neoplasia , alcohol abuse, use of certain medications .
Don’t Miss: Best Watch For Heart Rate Monitoring
What Are The Symptoms Of Pleural Effusions
According to the Cleveland Clinic, symptoms of pleural effusions include:
- Dry, nonproductive cough
- Shortness of breath, or difficult, labored breathing
- Orthopnea, which is the inability to breathe easily unless you are sitting up straight or standing
The Cleveland Clinic also notes that some patients with pleural effusion have no symptoms, and only learn of the condition because of a chest x-ray that is performed for another reason.
To Help You Balance Your Fluids After Heart Surgery Your Doctor May Ask You To:
- Avoid adding salt when cooking.
- Avoid processed foods.
- Take a medication to remove excess fluid if needed.
Other symptoms of increased fluid include decrease in energy level and dizziness.
It is important to notify your doctor or nurse as soon as possible to prevent any problems related to excess fluid.
For more information: See your Guide to Cardiac Surgery binder. If you have any questions or concerns, please call the Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute Post Discharge Phone Line at the number you were provided or your doctors office.
This information is about care at Cleveland Clinic and may include instructions specific to Cleveland Clinic Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute patients only. Please consult your physician for information pertaining to your care.
Don’t Miss: End Stage Congestive Heart Failure Weight Loss
What Causes Fluid Around The Heart And Lungs
Build up of excess fluid in pericardium and pleura can result from number of causes.
Causes of fluid buildup around heart:
- Viral or bacterial infection.
- Accumulation of fluid after heart surgery or after heart attack.
- Rheumatoid arthritis or other autoimmune disease.
- Kidney and liver failure.
- Trauma or puncture wound which infiltrates the pericardium.
- Radiation therapy involving radiation of the lung tissue.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Metastatic infiltration in lung and breast cancer.
- Certain chemotherapy drugs.
- Prescription drugs such as hydralazine, isoniazide, phenytoin etc.
Causes of fluid buildup around lungs:
Abnormal fluid accumulation can occur between the layers of pleura due to several reasons.
- Infection such as tuberculosis of lungs.
- Viral infection such as dengue fever.
- Organ failure which includes liver and kidney failure.
- Cancer of lungs.
- Metastasis occurring from breast cancer, ovarian cancer or prostate cancer.
- Autoimmune diseases such as lupus, rheumatic arthritis.
- After open heart surgery.
- Congestive cardiac failure.
What Causes Lung Fluid Retention After Heart Valve Surgery
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
You May Like: What Is The Treatment For Heart Attack
What Is Fluid Accumulation In The Lungs After Surgery
Accumulation of fluid in the lungs also called pulmonary edema is a complication after a surgery that may or may not be fatal, depending on the type of surgical procedure and the severity of the fluid accumulation.
What are the symptoms of fluid retention after cardiac surgery?
Retention of fluid after cardiac surgery is not uncommon. These patients experience swelling in the legs. Fluid retention in lungs is usually a post surgical complication. Breathing difficulty, cough etc. are some of its symptoms. If not treated the condition can become fatal. Use of certain drugs after surgery.
What causes fluid around the lungs in lung cancer?
Fluid Around the Lungs or Malignant Pleural Effusion. This area is called the pleural space. About half of people with cancer develop a pleural effusion. When cancer grows in the pleural space, it causes a malignant pleural effusion. This condition is a sign that the cancer has spread, or metastasized, to other areas of the body.
What Is Pleural Effusion
Pleural effusion, also called water on the lung, happens when fluid builds up in the space between your lungs and chest cavity.
Thin membranes, called pleura, cover the outside of the lungs and the inside of the chest cavity. Theres always a small amount of liquid within this lining to help lubricate the lungs as they expand within the chest during breathing. However, if too much fluid builds up, for example, because of a medical condition, problems can arise. Doctors call this pleural effusion.
Various conditions can lead to pleural effusion, but congestive heart failure is the
The doctor may drain the fluid or carry out pleurodesis if youre likely to need repeated drainage. This involves insering a shunt that redirects the fluid away from the chest.
They may prescribe antibiotics if you have or are susceptible to infection. Steroids or other anti-inflammatory medications may reduce pain and inflammation. They will also discuss other treatment options for cancer.
People who are undergoing treatment for cancer may also have compromised immune systems, making them more prone to infections or other complications.
The treatment and outcome will depend on the cause of the pleural effusion.
Read Also: Hole In Heart Surgery Risks
Pleural Effusion Post Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery: Associations And Complications
John D. L. Brookes1^, Michael Williams1,2^, Manish Mathew1, Tristan Yan1,2,3,4,5^, Paul Bannon1,2,5,6
1Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, 3Professor of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery, Macquarie University 4Clinical Professor of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, The University of Sydney 6Bosch Professor of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, The University of Sydney , Australia
Contributions: Conception and design: All authors Administrative support: None Provision of study materials or patients: None Collection and assembly of data: JDL Brookes, M Williams Data analysis and interpretation: JDL Brookes, M Williams Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
^ORCID: John D. L. Brookes, 0000-0002-8568-6130 Michael Williams, 0000-0002-7002-9728 Tristan Yan, 0000-0002-7473-1522.
Correspondence to:
Background: One of the most frequent complications of coronary artery bypass grafting is pleural effusion. Limited previous studies have found post-CABG pleural effusion to be associated with increased length-of-stay and greater morbidity post-CABG. Despite this the associations of this common complication are poorly described. This study sought to identify modifiable risk factors for effusion post-CABG.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study of prospectively collected data assessed patients who underwent CABG over two-years. Data was collected for risk factors and sequelae related to pleural effusion requiring drainage.
doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-2082
