Tips For Heart Attack Prevention
The goal after your heart attack is to keep your heart healthy and lower your risk of having another heart attack. Take your medications as directed, make healthy lifestyle changes, see your doctor for regular heart checkups, and consider a cardiac rehabilitation program.
Why do I need to take drugs after a heart attack?
You might take certain drugs after a heart attack to:
- Prevent blood clots
- Prevent plaques by lowering cholesterol
You might take medications that treat an uneven heartbeat, lower your blood pressure, control chest pain, and treat heart failure.
Know the names of your medications, what theyâre used for, and when you need to take them. Go over your medications with your doctor or nurse. Keep a list of all your medications, and take it to each of your doctor visits. If you have questions about them, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
It sounds like a no-brainer, but don’t skip your medications. Many people don’t take their medications the way their doctor told them to. Figure out what keeps you from taking your medicine — it could be side effects, cost, or forgetfulness — and ask your doctor for help.
What lifestyle changes are needed after a heart attack?
To keep heart disease from getting worse and to head off another heart attack, follow your doctor’s advice. You might need to change your lifestyle. Here are some changes you can make that can cut your risk and put you on the path to a healthier life:
Why should I take part in cardiac rehabilitation?
Medicines To Break Down Blood Clots
Medicines used to break down blood clots, known as thrombolytics or fibrinolytics, are usually given by injection.
Thrombolytics, or fibrinolytics, target and destroy a substance called fibrin. Fibrin is a tough protein that makes up blood clots by acting like a sort of fibre mesh that hardens around the blood.
You may also be given a medicine called a glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor if you have an increased risk of experiencing another heart attack in the future.
Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors do not break up blood clots, but they prevent blood clots from getting bigger. They’re an effective method of stopping your symptoms getting worse.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
- How concerned should I be about having another heart attack?
- How successful are the treatments for a heart attack?
- Whats the most important thing I can do to prevent a silent heart attack?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
You may not even know youve had a silent heart attack until weeks or months after it happens. Its best to know whats normal for your body and get help when something doesnt feel right. Knowing the subtle signs of a silent heart attack can help you identify one. Be sure to get regular checkups with your healthcare provider. You can also help yourself by treating medical problems that can lead to a heart attack. Switching to a healthier diet and adding exercise can help as well.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/28/2021.
References
Don’t Miss: How To Get Your Heart Rate
How Is A Heart Attack Treated
Quick treatment to get the blood flowing to your heart muscle again is important. This can reduce the amount of permanent damage to your heart and save your life.
Many people need to have emergency treatment to restore the blood flow:
- Coronary angioplasty re-opens the blocked coronary artery by inserting one or more stents. This helps keep the narrowed artery open.
- Thrombolysis involves giving you clot-busting medicine to dissolve the blood clot that’s blocking the coronary artery.
- Coronary bypass surgery helps to restore normal blood flow by using a blood vessel from your leg, arm or chest in your heart to bypass the blocked artery.
You might not have these treatments if your doctor decides it’s not safe or necessary.
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft

A coronary angioplasty may not be technically possible if the anatomy of your arteries is different from normal. This may be the case if there are too many narrow sections in your arteries or if there are lots of branches coming off your arteries that are also blocked.
In such circumstances, an alternative operation, known as a coronary artery bypass graft , may be considered.
A CABG involves taking a blood vessel from another part of your body and attaching it to your coronary artery above and below the narrowed area or blockage. This new blood vessel is known as a graft.
The graft diverts blood around narrowed or clogged parts of your major arteries to improve blood flow and oxygen supply to your heart.
You May Like: How To Measure Your Resting Heart Rate
Heart Attack Early Diagnosis And Treatment Can Save Your Life
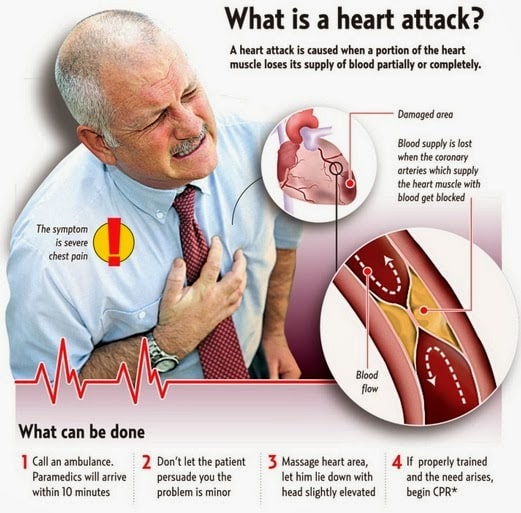
Chest pain might be a warning sign of a heart attack. Not all heart problems come with clear warning signs.
Chest pain might happen during daily activities or exercise. Some people may feel tightness, pain, or aching sensation in their chest that may spread to their neck, jaw, or shoulder. Sweating and irregular heart beat might also be signs of a heart attack. If you have any of these symptoms, you should call an ambulance right away.
Dr. Rapin Kukreja, an interventional cardiologist at Bangkok Heart Hospital, explained to us about the cause of a heart attack or myocardial infarction. A heart attack occurs when one or more of your coronary arteries become blocked. Buildup plaque narrows the arteries and reduces blood flow to the heart muscle. The plaques can rupture and a blood clot forms at the site of the rupture. The clot can completely block the flow of the blood through the coronary artery causing a heart attack.
If the damaging area of the heart muscle is large, it might cause a sudden death
Nowadays, there is an increase in the number of heart attack patients. The ages of the patients are also lower. However, declines have been observed in mortality rate from acute myocardial infarction.
3-4 hours after a heart attack is the best window period. A cardiologist will try to open the narrowed artery within 90 minutes in order to preserve the heart muscles. Within this period, there is 60%-70% chance of good functional recovery.
Q How Is Smoking Related To A Heart Attack
- Lack of oxygen supply to the heart
- Increased blood pressure and heart rate.
- Clotting of blood.
- Damage to cells that line coronary arteries and other blood vessels.
You May Like: What Are Signs Of Heart Attack
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, another class of blood vessel dilators,often are given orally after a large heart attack to improve the healing ofheart muscle. Examples of ACE inhibitors include captopril , enalapril, lisinopril , and ramipril . Thesemedications lower the blood pressure and reduce the workload of the heart,thereby helping the damaged heart muscle to recover. They are especially helpfulin patients who have recovered from heart attacks but have high blood pressure,heart failure, major damage to the left ventricle, and diabetes mellitus. For additional information, please see the ACE Inhibitors article.
Q If I Am On Medication To Treat Heart Disease Does That Mean I Am No Longer At Risk Of A Heart Attack
Recommended Reading: Risk Factors For Heart Attack
Who Is Most At Risk For A Heart Attack
Several key factors affect your risk of having a heart attack. Unfortunately, some of these risk factors aren’t things you can control.
- If you have certain health conditions or diseases.
Age and sex
Your risk of heart attack increases as you get older, and your sex also influences when your risk of a heart attack starts to increase:
- Men: The risk of heart attack increases greatly at age 45.
- Women: The risk of heart attack increases greatly at age 50 or after menopause.
Family history
If you have a parent or sibling with a history of heart disease or heart attack especially at a younger age your risk is even greater. That risk increases with the following:
- Your father or a brother who was diagnosed with heart disease at age 55 or younger.
- Your mother or a sister who was diagnosed with heart disease at age 65 or younger.
Lifestyle
The lifestyle choices you make can also affect your risk of having a heart attack. The following lifestyle factors increase your risk of heart attack:
- Lack of physical activity.
- Eating disorders .
How A Heart Attack Is Treated
Treatment of an acute heart attack must be early and aggressive. Medical therapy is used to stabilize the cardiovascular system and prevent or at least mitigate long-term complications. This may include angioplasty and the use of thrombolytics or other priority medications for a heart attack.
Heart attacks need to be urgently treated because the blockage of one of the coronary arteries that supplies blood to the heart causes an area of muscle to begin to dieand the longer blood flow is hindered, the more damage that occurs.
You May Like: Heart Valve Repair Without Surgery
What Happens During Coronary Angioplasty
A tiny tube known as a balloon catheter will be put into a large artery in your groin or arm. The catheter passes through your blood vessels and up to your heart. This is done over a fine guide-wire, using x-rays to guide it. It is then moved into the narrowed section of your coronary artery.
Once in position, the balloon is inflated inside the narrowed part of the coronary artery to open it wide. A stent is usually inserted into the artery to help keep it open afterwards.
Q What Is Cardiac Arrest
Recommended Reading: Does Clonidine Lower Heart Rate
Common Heart Attack Types And Treatments
The type of heart attack you experienced determines the treatments that your medical team will recommend. A heart attack occurs when a blockage in one or more coronary arteries reduces or stops blood flow to the heart, which starves part of the heart muscle of oxygen.
The blockage might be complete or partial:
- A complete blockage of a coronary artery means you suffered a STEMI heart attack or ST-elevation myocardial infarction.
- A partial blockage is an NSTEMI heart attack or a non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction
Treatments differ for a STEMI versus NSTEMI heart attack, although there can be some overlap.
Hospitals commonly use techniques to restore blood flow to part of the heart muscle damaged during a heart attack:
- You might receive clot-dissolving drugs , balloon angioplasty , surgery or a combination of treatments.
- About 36 percent of hospitals in the U.S. are equipped to use a procedure called percutaneous coronary intervention , a mechanical means of treating heart attack.
At a hospital equipped to administer PCI, you would likely be sent to a department that specializes in cardiac catheterization, sometimes called a cath lab. There, a diagnostic angiogram can examine blood flow to your heart and reveal how well your heart is pumping. Depending on the results of that procedure, you may be routed to one of three treatments: medical therapy only, PCI or coronary artery bypass grafting .
Precaution Tips After A Mild Heart Attack
If you have suffered a mild heart attack, your doctor may recommend some lifestyle and health changes in order to reduce your risk of experiencing a secondary cardiac event. These tips include:
Stop smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease, as it damages the walls of the blood vessels and may prevent blood and oxygen from reaching the heart and organs. Smoking tobacco also encourages the formation of blood clots that can cause heart attacks, while the nicotine found in cigarettes can raise your blood pressure.
Control your blood pressure: Managing your blood pressure can prevent excess stress from being placed on your heart and blood vessels. Talk to your doctor about ways to naturally lower and manage your blood pressure, as well as the medicinal options that are available to you.
Control your cholesterol: An excess of LDL or bad cholesterol can increase your risk of heart disease, and if your levels are high, your doctor may recommend a prescription to control it as well as encourage you to eat healthier and exercise regularly.
Check for diabetes: Be sure to get screened for diabetes, as both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can increase your risk of suffering a heart attack or stroke.
Exercise: Exercising regularlyespecially cardio activitiescan help make your heart stronger and lower your cholesterol and blood pressure. Jogging, running, walking, bicycling, and swimming are all good examples of cardio exercises to help get your heart pumping.
Also Check: How To Find Maximum Heart Rate
What Happens After A Mild Heart Attack
After experiencing a mild heart attack, other symptoms may make themselves known and affect your physical and mental state. You might feel fatigued, as the episode will have weakened your heart muscle and made it more difficult for the heart to pump blood throughout the rest of the body. You may also experience some discomfort in your chest, as damage to the heart impairs blood flow and can result in chest pain.
Depression is another side effect of experiencing a mild heart attack, as after such a traumatic event, you may feel a fear of death or mortality as well as a loss of control over your life. Finally, heart arrhythmias may develop after a mild heart attack, as part of the muscle that conducts the impulse to beat may be damaged and cause the heart to beat irregularly.
Whats The Bottom Line
The best way to know if you can benefit from aspirin therapy is to ask your health care provider. You should not start aspirin on your own.
Written by American Heart Association editorial staff and reviewed by science and medicine advisers. See our editorial policies and staff.
Last Reviewed: Mar 20, 2019
You May Like: What Should My Heart Rate Be For Cardio
Antiplatelet Agents And Dual Antiplatelet Therapy
Commonly prescribed include:
Keeps blood clots from forming by preventing blood platelets from sticking together.
Reason for Medication
- Helps prevent clotting in patients who have had a heart attack, unstable angina, ischemic strokes, TIA and other forms of cardiovascular disease.
- Can also be prescribed preventively when plaque buildup is evident but there is not yet a major blockage in the artery.
- Certain patients will be prescribed aspirin combined with another antiplatelet drug also known as dual antiplatelet therapy .
Dual Antiplatelet Therapy
Some patients who have heart attacks, that have stents placed in their coronary arteries, or undergo coronary artery bypass graft surgery are treated with two types of antiplatelet agents at the same time to prevent blood clotting. This is called dual antiplatelet therapy .
One antiplatelet agent is aspirin. Almost everyone with coronary artery disease, including those who have had a heart attack, stent, or CABG are treated with aspirin for the rest of their lives. A second type of antiplatelet agent, called a P2Y12 inhibitor, is usually prescribed for months or years in addition to the aspirin therapy.
The type of medication and the duration of your treatment will vary based on your condition and other risk factors. The risks and benefits of DAPT should be discussed with your health care provider.
- Cholesterol absorption inhibitor: Ezetimibe
- Combination statin and cholesterol absorption inhibitors: Ezetimibe/Simvastatin
How Do I Take Care Of Myself Long
After a heart attack, you may need to make some changes in your life, such as:
- Eating a diet thats good for your heart.
- Quitting tobacco use.
- Staying at a healthy weight.
You should also follow your providers instructions and keep taking medicines they ordered for you. And its important to have regular checkups with your healthcare provider. In some cases, your provider may want to do another electrocardiogram.
You May Like: End Stage Heart Failure Life Expectancy
Are The Symptoms Of Heart Attack Different For Women
The most common heart attack symptom for women is pain or discomfort in the chest. However, women are more likely to have a heart attack without having any chest pain. Therefore, women should pay close attention to other symptoms of heart attack. These include shortness of breath, sweating, fatigue, and dizziness.
Living With A Heart Attack
After youve had a heart attack, you are at higher risk of having another one. Your doctor will likely recommend heart-healthy lifestyle changes to help reduce your risk. They include:
- Maintaining a heart-healthy diet
- Being physically active
- Quitting smoking
Symptoms during a second heart attack may be different than the first one. If you have any new symptoms of heart attack or are in any doubt, call 911. Early treatment is the key to surviving a heart attack.
You May Like: Does Menopause Cause Heart Palpitations
