What Are The Different Medical Terms For A Heart Attack
Acute coronary syndrome : An umbrella term for situations where the blood supplied to the heart muscle is suddenly blocked. Learn more about ACS.
STEMI: A common name for ST-elevation myocardial infarction, a type of heart attack caused by a complete blockage in a coronary artery.
NSTEMI: A non-ST-elevated myocardial infarction, a type of heart attack in which an artery is partially blocked and severely reduces blood flow.
Myocardial infarction : The damaging or death of an area of the heart muscle resulting from a blocked blood supply to that area. Its also the medical term for a heart attack.
Coronary thrombosis: Formation of a clot in one of the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. Also called coronary occlusion.
Coronary occlusion: An obstruction of a coronary artery that hinders blood flow to some part of the heart muscle. Coronary occlusion is a cause of heart attack.
How Heart Attack Symptoms Vary Between Men And Women
We use women and men in this article to reflect the terms that have been historically used to gender people. But your gender identity may not align with how your body experiences symptoms of a heart attack. Your doctor can better help you understand how your specific circumstances will translate into symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
Many people experience a mix of heart attack symptoms regardless of sex or gender. However, there are sex-specific differences in the presentation, biology, and outcomes of heart attacks.
A women , the pain is often described as tightness, squeezing, or pressure in the chest, while men tend to describe it as a heavy weight on the chest.
According to the American Heart Association , women are somewhat more likely than men to experience the following heart attack symptoms:
- shortness of breath
- pain in the upper back or jaw
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- extreme fatigue
Higher levels of estrogen can reduce the risk of a heart attack. As a result, women have a greater risk of a heart attack after menopause than before menopause.
However, women who have a heart attack are more at risk of underdiagnosis and undertreatment.
For example, a 2018 Swiss study found that women tend to wait longer to contact emergency services after experiencing typical heart attack symptoms. Researchers also found that women tend to experience greater delays in receiving treatment in emergency settings.
When Do Most Heart Attacks Occur
From the outside, a heart attack can seem very sudden. But from the inside like inside an artery its actually pretty predictable.
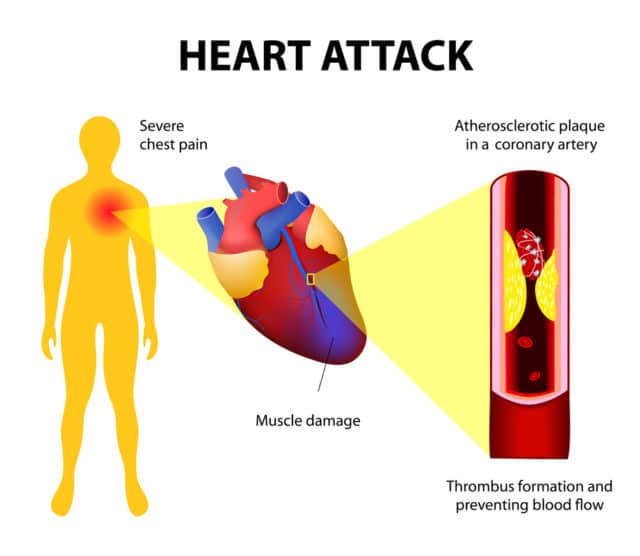
Clogged arteries, also called coronary artery disease , are the primary cause of heart attacks . Arteries get clogged by something called plaque, a fatty substance that builds up on artery walls. Plaque often builds up when theres too much fat and cholesterol in the diet and too much cholesterol in the blood. Essentially, stuff starts sticking to the artery walls of the heart as blood passes through, and eventually a blood clot can form. If its big enough, that clot can block the artery entirely.
In a heart attack, oxygen supply to the heart has been cut off, resulting in damage to or death of heart muscle. The heart stops pumping if the blood flow isnt immediately restored. When it stops pumping, thats a heart attack. In the United States, about 1.1 million people suffer heart attacks every year, and about half of those heart attacks result in death .
Heart attacks seldom happen without some kind of warning. They can often be explained by medical history, including high cholesterol or high blood pressure, or by a family history of heart disease. But can they also be explained by external circumstances, like time of year or time of day? Are there certain occasions that pose greater risk for people with heart disease?
You May Like: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Don’t Miss: Last Days Congestive Heart Failure
How To Reduce Heart Attack Risk
An important step in reducing your heart attack risk is to get on top of your heart health and speak to your doctor about having an annual heart health check. This may involve discussing your family history then measuring your blood pressure, blood sugar and total cholesterol levels. Unhealthy levels of these can increase your risk of heart disease and heart attack, but they may not show any visible symptoms.
Making positive lifestyle changes to decrease your risk factors is another key step in reducing the risk of heart attack. Even small changes can have a positive impact on your risk. These can include maintaining a healthy weight through a heart-healthy diet and lowering alcohol intake, exercising regularly, quitting smoking and taking steps to manage blood pressure levels as well as to lower cholesterol levels. Speak to your doctor about what changes you can make.
Reduce your risk of heart attack and cardiovascular disease by making positive lifestyle changes like being more active and eating a healthier diet. Images: Pexels
How Is Hri Fighting Heart Attack
HRI is conducting innovative research to develop new therapies for detecting, preventing and treating heart attacks.
Our Arterial Inflammation and Redox Biology Group is investigating unstable atherosclerotic plaque, which can cause blockages leading to heart attack, and how to detect and prevent the formation of this high-risk plaque.
Our Coronary Diseases Group is investigating whether the anti-inflammatory drug colchicine, which has already proved safe and effective for treating conditions like arthritis and gout, can be repurposed to protect against repeat heart attacks. A collaboration between the Coronary Disease Group and our Clinical Research Group has also discovered that the heart releases certain substances during a heart attack that can be detected in the laboratory.
Our Cardiovascular Medical Devices Group is using cutting-edge bioengineering improvements to develop a new generation of medical devices to reduce the chances of thrombosis during surgical medical interventions.
Our Thrombosis Group is undertaking research to understand how blood clot formation occurs in healthy individuals. This research is crucial for developing safer and more effective therapies for heart attacks, amongst other cardiovascular diseases.
Also Check: Triple Bypass Heart Surgery Procedure
Anatomy Of Your Heart
Your heart is in the center of your chest, near your lungs. It has four hollow heart chambers surrounded by muscle and other heart tissue. The chambers are separated by heart valves, which make sure that the blood keeps flowing in the right direction. Read more about heart valves in Blood Flow.
Anatomy of the interior of the heart. This image shows the four chambers of the heart and the direction that blood flows through the heart. Oxygen-poor blood, shown in blue-purple, flows into the heart and is pumped out to the lungs. Then oxygen-rich blood, shown in red, is pumped out to the rest of the body, with the help of the heart valves.
Dont Miss: Ibs Heart Palpitations
Why Choose The Hospitals Of Providence For Your Early Heart Attack Care
The Hospitals of Providence has EHAC teams who genuinely care about you and your loved ones. Our hospitals are located across El Paso to provide accessible care to the communities in this city and nearby areas. At the same time, we have received multiple recognitions for the compassionate care and patient-centered cardiovascular services we offer.
Some of the accreditations and recognitions we received in recent years are as follows:
For Sierra Campus
- Chest Pain Reaccreditation by the Society of Cardiovascular Care
- ACC HeartCARE Center Designation by the American College of Cardiology
- Grade A rating for patient safety in the Leapfrog Groups Fall 2019 Safety Score
Read Also: What Is Maximum Heart Rate By Age
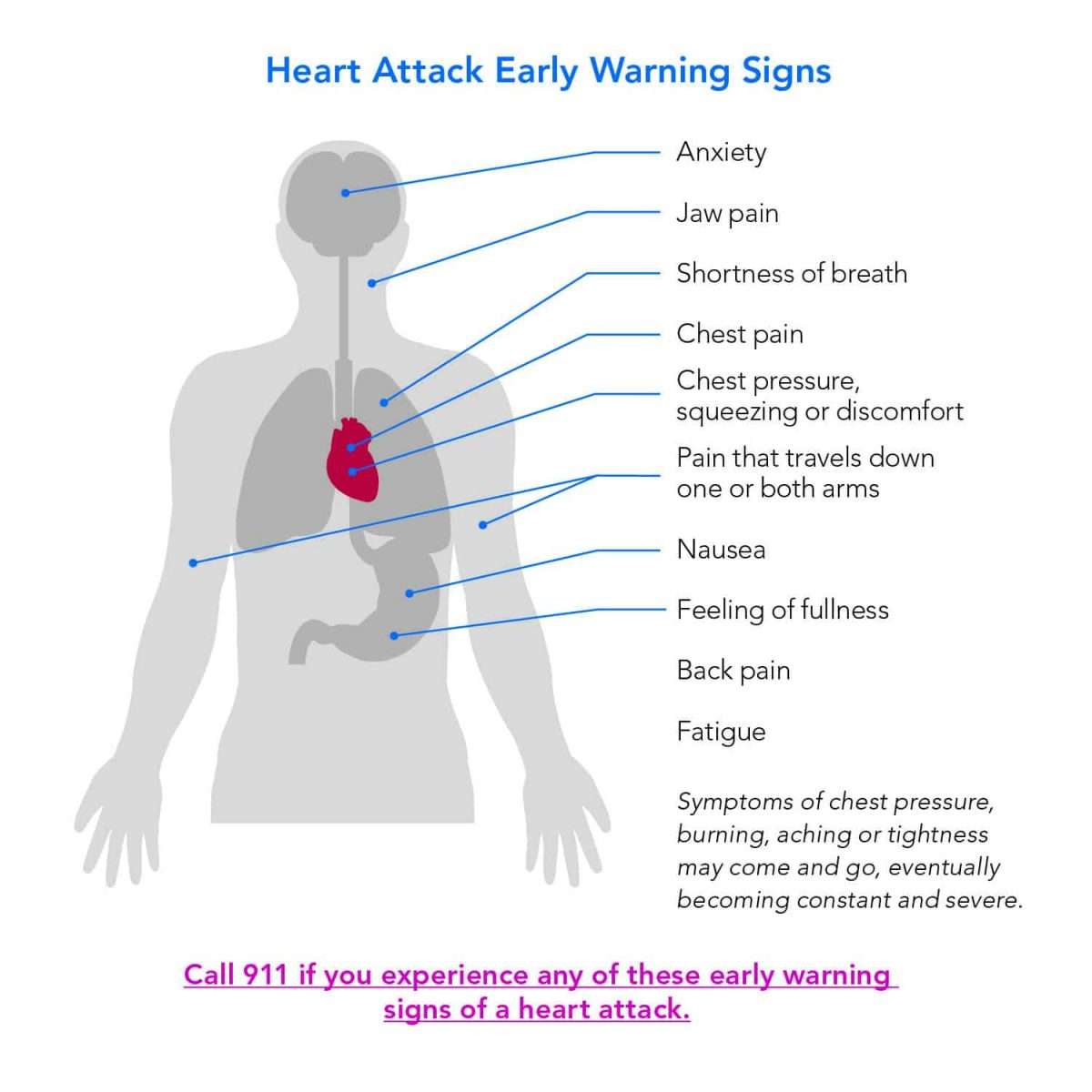
Symptoms Of A Heart Attack
The following are the most common symptoms of a heart attack. But each person may have slightly different symptoms.
- Severe pressure, fullness, squeezing, pain, or discomfort in the center of the chest that lasts for more than a few minutes
- Pain or discomfort that spreads to the shoulders, neck, arms, or jaw
- Chest pain that gets worse
- Chest pain that doesn’t get better with rest or by taking nitroglycerin
- Chest pain that happens along with any of these symptoms:
- Sweating, cool, clammy skin, or paleness
- Shortness of breath
- Unexplained weakness or fatigue
- Rapid or irregular pulse
Although chest pain is the key warning sign of a heart attack, it may be confused with other conditions. These include indigestion, pleurisy, pneumonia, tenderness of the cartilage that attaches the front of the ribs to the breastbone, and heartburn. Always see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Causes Of Heart Attack
A heart attack, as previously described, occurs when the blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked. However, other conditions, traits or habits may also raise your risk for this condition. These are known as risk factors and include:
Non-modifiable risk factors: These factors are irreversible and cannot be changed. The more of these risk factors you have, the greater your chance of a heart attack.
- Occur at any age however, if youre over 40 or have multiple risk factors work closely with your doctor.
- Family history/Genetics
- Little to no physical activity
- Obesity or having a body mass index BMI of 30 or greater
- Long history of cigarette smoking and/or drug abuse
- Diabetes: when your blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high
- Extreme emotional stress
You May Like: How Long Does The End-stage Of Congestive Heart Failure Last
Chest Pain Pressure And Discomfort
Most people with heart attacks experience some sort of chest pain or discomfort. But its important to understand that chest pains dont occur in every heart attack.
Chest pain is a common sign of a heart attack. People have described this sensation as feeling like an elephant is standing on their chest.
Some people dont describe chest pain as pain at all. Instead, they may say they felt chest tightness or squeezing. Sometimes this discomfort can seem bad for a few minutes and then go away. Sometimes the discomfort comes back hours or even a day later. These could all be signs your heart muscle isnt getting enough oxygen.
If you experience chest pains or tightness, you or someone around you should call 911 immediately.
Pain and tightness can also radiate in other areas of the body. Most people associate a heart attack with pain working its way down the left arm. That can happen, but pain can also appear in other locations, including:
American Heart Association , some women may even think their heart attack symptoms are flu-like symptoms.
A heart attack can cause exhaustion due to the extra stress on your heart to try to pump while an area of blood flow is blocked. If you often feel tired or exhausted for no reason, it could be a sign that something is wrong.
Fatigue and shortness of breath are more common in women than men and may begin months before a heart attack. Thats why its important to see a doctor as early as possible when you experience early signs of fatigue.
Heart Attack Vs Cardiac Arrest: Whats The Difference
A heart attack, which is often referred to as a myocardial infarction, happens when blood that normally flows to the heart is blocked or cut off. Without enough oxygen-rich blood flowing to the heart, it can cause damage to one of the most important organs in the body, and the heart muscle can begin to die.
A cardiac arrest, on the other hand, is known as sudden cardiac death. The word arrest means to stop or bring to a halt. In the case of cardiac arrest, the heart stops beating, which is an extremely serious health issue. Cardiac arrest can cause near-immediate death or disability.
A heart attack and cardiac arrest are both life threatening medical emergencies. Its helpful to know the symptoms of each.
Don’t Miss: Can Panic Attacks Cause Heart Attack
Diagnosing A Heart Attack
Doctors diagnose a heart attack by performing a physical exam and ordering an electrocardiogram to check your hearts electrical activity.
A doctor may order an echocardiogram or a cardiac catheterization to determine the strength and vitality of your heart. Its also common to have a sample of your blood taken to check for signs of heart muscle damage.
When Can I Resume My Usual Activities
Recovery from a heart attack after youre released from the hospital depends on the severity of the heart attack, how soon treatment began, methods used and the health conditions you had if any before your heart attack. Your healthcare provider can explain the next steps for your recovery and what you can expect. In general, most people can return to work or resume their usual activities anywhere between two weeks to three months after their heart attack.
Recommended Reading: Recovery From Open Heart Surgery
Should I Still Call 999 Or Go To Hospital If I’m Worried About My Health
Whether or not you have coronavirus symptoms, it’s essential to dial 999 if you have symptoms that could be a heart attack, or if your heart symptoms get worse.
We are hearing that fewer people are being seen in hospital with heart attacks in recent weeks, which suggests that people are not seeking help when they should do. If you have any of the symptoms described above, you should call 999.
Don’t delay because you think hospitals are too busy – the NHS still has systems in place to treat people for heart attacks. If you delay, you are more likely to suffer serious heart damage and more likely to need intensive care and to spend longer in hospital.
Reduces High Blood Pressure
Exercise is the perfect alternative to medicines in controlling high blood pressure. Hypertension or high blood pressure increases with age. It becomes important to indulge in some form of physical activity to control it.
Not only exercising but regular exercising is the key to reducing high BP. If you have moderate blood pressure, exercise can keep it that way. But you have high blood pressure, physical fitness can lower it for heart attack prevention.
Read Also: Does Heart Rate Increase After Eating
Catriona Found A Listening Ear
Mum of two Catriona had a heart attack just as lockdown was beginning, and she felt anxious and on edge because the usual support wasnt available.
I was given booklets about diet and exercise when I was discharged home and I was told someone would be in touch, but I didnt know when. I did feel quite isolated and I wasnt confident about what to do next, so thats why I phoned Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland.
Catriona began talking to Wendy from our Advice Line and got the invaluable practical and emotional support she really needed.
I feel like I can ask Wendy anything even if its a daft question. And I know I could call her at any time if I feel worried. It is so reassuring to know she is there for me.
Waiting For The Ambulance
It is important to rest while you wait for an ambulance, to avoid unnecessary strain on your heart.
If you know that you are not allergic to aspirin and you have aspirin available, chew an adult size tablet while you are waiting for the ambulance to arrive.
The aspirin will help to thin your blood and restore the blood flow to your heart.
Also Check: Open-heart Surgery Survival Rate 2020
Q What Is The Link Between Cardiac Arrest And Heart Attack
What Does Depression Have To Do With A Heart Attack
Depression is common after a heart attack. As many as 1 out of every 3 people who have had a heart attack report feelings of depression. People with a higher risk of depression after a heart attack include:
- People who have had depression before.
- People who feel alone and without social or emotional support.
Many people who have depression dont recognize it. They dont seek help or get treatment. Being depressed can make it harder for you to recover physically. Depression can be treated.
Some people have anxiety after a heart attack, fearing it will happen again. Talk to your doctor about your feelings so that you can manage or reduce your anxiety.
Not all heart attacks are alike
Did you know that you can have a heart attack without feeling any chest pain? Heart failure and heart disease dont show the same signs for everyone, especially women.
The heart is a muscle that contracts to pump blood throughout the body. A heart attack occurs when the heart muscle doesnt get enough blood. Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle. When there isnt enough blood flowing to your heart muscle, the affected part can get damaged or die. This is dangerous and sometimes deadly.
Less commonly, something like stress, physical exertion, or cold weather causes the blood vessel to contract or spasm, which decreases the amount of blood that can get to your heart muscle.
There are many risk factors that contribute to having a heart attack, including:
Recommended Reading: Rapid Heart Rate While Sleeping
Q Can Stress Cause Heart Attack
