High Resting Heart Rate: Should You Worry
In general, a slower resting heart rate is a sign of good health. Some athletes and people who are very active even have heart rates that dip below 60 when theyre at rest.
A high resting heart rate, on the other hand, can be an indicator of problems such as:
- Poor physical condition.
- Infections.
- Thyroid problems.
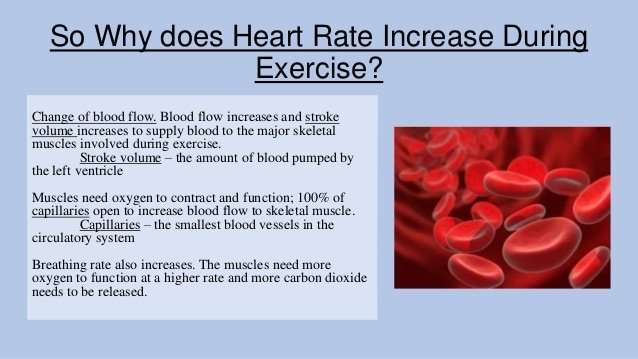
Often, a high resting heart rate is a sign that your heart is working harder than it needs to. Like any muscle, the heart doesnt work as well when its out of shape. In people who arent very active, the heart isnt as efficient. It has to work harder to pump blood through your body, Dr. Singh says.
Normal Heart Rate Fluctuations
The amount your heart rate fluctuates after meals varies based on the size of the meal. It might increase 10 to 30 beats per minute . In most people, a boost in heart rate after meals isn’t problematic, says Berkley Wellness. The American Heart Association says average heart rates for adults are 60 to 100 beats per minute . But, Dr. Howard LeWine, M.D. with Harvard Health Publications, says resting heart rates above 90 beats per minute are considered high, so avoid exceeding this level even after meals. Check your pulse to determine heart rate before and after eating. If you’re feeling dizzy or are experiencing heart palpitations after meals, your heart rate might be too high.
Your Diet May Be The Culprit
If youre not an overeater, what you eat or dont eatrather than the amount of food you consumecould cause a pounding heart. Youve likely heard about limiting processed sugars and high-carbohydrate foods. In addition to causing weight gain and other health issues, these two can cause heart palpitations in people who deal with low blood sugar, hypoglycemia. Foods that are high in sodium may also cause heart pounding. If you enjoy a lot of processed and canned foods, they could be the cause of your heart palpitations. In addition, eating rich or spicy foods may cause heartburn. A pounding heart often accompanies heartburn.
Read Also: How To Find Thrz
Types Of Fast Heart Rate
Fast heart rates can occur in different parts of your heart. Doctors identify different types of fast heart rate, related to the location in which they occur. These include:
- , often referred to as afib: a rapid, caused by irregular electrical impulses in the atria, which are the upper chambers of your heart. Afib is the most common type of tachycardia.
- Atrial flutter: A rapid, regular heartbeat, sometimes experienced by people who also suffer from atrial fibrillation
- Sinus tachycardia: This occurs when your body responds to stimuli such as exercise or emotional distress with a normal increase in heart rate.
- Supraventricular tachycardia : A fast heartbeat that starts above the lower chambers of the heart
- Ventricular tachycardia : A rapid rate caused by abnormal electrical signals in the lower chambers of the heart, called ventricles. Episodes of VT that last longer than a few seconds can be life-threatening.
- Ventricular fibrillation: A fast rate that occurs when rapid, irregular electrical impulses cause the lower chambers of your heart to quiver instead of pumping blood to your body. This type can be deadly and may require your heart to be restored to normal rhythm via electric shock to the heart.
Potential severe complications of fast heart rate depend on which type of tachycardia you have, how fast your heart is beating , how long your rapid heart rate lasts, and whether you have other . Some of the more serious consequences are:
-
Sudden death
Causes Of Fast Heartbeat After Eating
1. Natural Reaction
Your heartbeat goes up because your heart starts pumping blood harder so that there is enough blood in the stomach and intestine to complete the digestion process. Without enough blood in the abdominal area after you eat your food, your body will fail to assimilate food effectively.
2. Eating Too Much
Consuming large meals may well be the reason why you are experiencing fast heartbeat. Your body increases the flow of blood to the digestive tract to help digestion when you consume too much food. As a result, your heart has to beat harder and faster to provide enough blood. This increased blood flow is at its highest about 25-40 minutes of having a large meal and may last up to a couple of hours.
3. Eating Specific Foods
Specific food triggers may also cause fast heartbeat following a meal. The most common triggers are alcohol and caffeine. You may also have other food sensitivities that you can track only when you keep a food diary for a few weeks. Moreover, some food additives are also responsible for causing fast heartbeat. High sodium meals, Monosodium glutamate consumption, and nitrates can also cause and aggravate heart palpitations. You may also notice fast heartbeat if you are sensitive to gluten, a protein found in wheat.
4. High-Sugar Meals
5. Certain Medications
6. Meal Experience
7. Allergies
You May Like: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
Some Symptoms For The Same Are
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Chest pain
That said, many patients who come in with complaints of heart palpitations often tend to blame the problem on the food they eat. However, does food cause heart palipitations? They certainly do.
Palpitations after eating food is a common occurrence, and its a result of your bodys response to specific food or drinks, that results in jolting the hearts electrical system and thus castigate sensations like skipped beats or a fast heart rate. Caffeine is one of the most common causes of this feeling.
The Toll It Takes On Your Health
Whether your favorite treat is a burger and fries or chocolate cake, its okay to indulge once in a while in moderation. Moderation can be difficult to determine, though, as portion sizes in America continue to grow. Over the last five decades, the average size of food servings, whether from fast food, sit-down restaurants or grocery stores, has grown by as much as 138 percent. This, along with unhealthy relationships with food, can result in overeating.
Overeating occurs when you eat beyond the point of feeling full. When you overeat, your body works overtime in order to support the digestive system. The amount of blood sent to your gut causes your heart rate to go up. Your stomach has to expand in order to make room for the food. It releases hydrochloric acid to help break down food, which can result in heartburn.
The Link Between a Heavy Meal and Heart Attacks
Fatty meals are particularly taxing on the heart. In addition to contributing to higher cholesterol levels, unusually heavy meals may increase your risk of heart attack, possibly due to changes in blood flow and increases in heart rate and blood pressure after eating. If you have heart disease, limit foods that are high in fat and carbohydrates, particularly at a big meal, a celebration with lots of food, or when dining out at your favorite restaurant.
The Link Between Obesity and Heart Disease
Recommended Reading: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Eating And The Pounding Heart
Its not unusual to feel like your hearts pounding after exercise. Well even agree that a little romance can make the heart pound. But eating? For some patients who visit a cardiology clinic in Suffolk County, NY, meals seem to trigger heart palpitations. Eating does cause changes in blood flow, which can result in an increased heart rate. Eating can also cause an increase in blood pressure. If you overeat, you force your heart to work harder than normal. You need more blood going to your digestive system, which causes your heart rate to go up.
When To Seek Help
Heart rate fluctuations are normal, and an increased heart rate is expected after meals. However, avoid eating very large meals when possible, which may generate large boosts in heart rate. Instead, opt for smaller more frequent meals, keep resting heart rate within a recommended range, and talk with your doctor if you experience heart palpitations or dizziness after meals.
Don’t Miss: What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
Treatment For Heart Palpitations
Treatment depends on the diagnosis.
Your doctor may conclude that your heart palpitations arent a serious threat to your health. In this case, youll likely benefit from lifestyle changes.
Avoiding common cold medications with pseudoephedrine and stimulants in food and drinks can limit your palpitations. Quitting smoking can also help.
If your palpitations are a serious issue, your doctor will likely prescribe a beta-blocker or calcium channel blocker. These are antiarrhythmic drugs. They keep your heart rate even and regular by improving blood flow throughout your body.
These medications often treat your conditions within a few hours. However, they usually take several months to several years to correct conditions related to arrhythmia.
If your palpitations are life threatening, your doctor may use a defibrillator or a pacemaker to help get your heart back into a normal rhythm. These treatments will give you immediate results.
Your doctor may monitor you over a few days or even a few years to continue treating your heart palpitations.
How And Why This Occurs
The reason your heart rate goes up after eating has to do with increases in metabolism and blood flow to the digestive tract. This occurrence is also known as postprandial hyperemia. The National Center for Biotechnology Information says gastrointestinal blood flow increases and is characterized by a boost in aortic pressure, cardiac output, and heart rate.
You May Like: Can Lexapro Cause Heart Palpitations
When I Eat Carbs And Sugar My Heart Rate Increases Why Is That
Ive been on a very low carb diet for the past four months. When I eat carbs and sugar, my heart rate increases and I can feel it even when Im not doing anything. Why is that? Can I stop it?
A person is diagnosed with tachycardia when the heart rate is more than 100 beats per minute . The normal resting heart rate for adults is about 60 to 100 BPM and for infants, it is about 110 BPM.
Tachycardia after eating is an uncommon disorder and for the people who experience it, it can create anxiety and stress. Experiencing slightly higher heart rate after having snacks or meals is quite normal, because increased flow of blood is required to digest the food. But, if your heart starts beating rigorously after meals, then it could be a symptom of tachycardia. There is no need to panic as people who experience it can lead a normal life.
The episodes of rapid heartbeat usually begin within 30 to 60 minutes after a meal. The heart rate may go up to 120 beats per minute or even more. Sometimes, it lasts up to 6 hours. An adrenaline rush may be experienced by the person. There can be difficulty in resting, sleeping, or breathing. The person may suffer from bloating and indigestion. If your heart starts beating irregularly or very rapidly after eating, you could have cardiac arrhythmia.
Causes of High Heart Rate after Meals
> > Processed food or food high in oil or food rich in MSG, nitrates and sodium can make your heart beat faster.
Whats A Normal Heart Rate
A heart rate is a measurement of the number of times the heart muscle beats per minute. Healthy kids and adults will have hearts that beat at different speeds because of their age and body size. If the heart is beating too fast or too slow, this could mean you have an underlying health problem. Your resting heart rate will also allow you to gauge your current heart health.
In general, a lower resting heart rate means the heart is beating less per minute, which likely means its more efficient. Your resting heart rate tells you how fast your heart is beating when youre in a relaxed state, like sitting or laying down. If your resting heart rate is too high, this might mean you have lower physical fitness, or that youre at risk of developing a heart condition.
Knowing what your target heart rate should be for your age can help you recognize if and when your heart rate is abnormal, which may be an indication that its time to go to the doctor.
| Normal heart rate by age | |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| 18 and older | 60-100 bpm |
As we get older, the range of whats considered to be a healthy normal resting heart rate will change.
The average healthy adult will have a resting heart rate of 60 bpm or higher. Although in clinical practice, the resting heart rate between 60 and 100 bpm is considered to be normal, people with a resting heart rate higher than 80 bpm could have an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
RELATED: Heart disease statistics
Recommended Reading: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Signs You Need Emergency Fast Heart Rate Treatment
Brief episodes of fast heart rate, such as palpitations that last only a second or two, generally arent a reason to worry, unless you also have a history of heart problems or disorders such as afib. You should still discuss them with your doctor, but you likely do not need to rush to the ER.
However, if you have tachycardia symptoms that include the following, seek emergency help :
- Chest that lasts more than a few minutes
- Difficulty breathing
- Irregular heartbeat
The treatment you receive will depend on your symptoms and the type of heart disorder you have. If you have ventricular tachycardia along with other symptoms that your body is in distress, such as trouble breathing and , your emergency treatment can involve:
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
How To Deal With Fast Heartbeat After Eating
In most cases, an elevated pulse rate is your body’s natural response following a meal. Still, it can make you feel concerned. Here are some suggestions.
1. Identify the Cause of Fast Heartbeat
You do not need to worry too much about the racing heart after eating, but it is still a good idea to talk to your doctor to pinpoint the real cause of fast heartbeat. You may require medical treatment in case your condition is the outcome of digestive or endocrine problems. Your doctor will conduct a physical exam and ask you about any other symptoms you may be experiencing. They may also order several diagnostic tests, including urine tests, blood tests, a stress test, an electrocardiogram, an echocardiogram, and a Holter monitor test to help make a diagnosis properly.
2. Tips for Treating Fast Heartbeat After Eating
Here are some tips you can try to resolve the issue and normalize your heartbeat again:
Read Also: Ibs Heart Palpitations
Heart Palpitations After Eating
Some people experience heart palpitations after eating. These palpitations will typically start soon after the meal and may last for minutes or hours depending on the severity of the palpitations and the underlying cause.
In most cases, the heart palpitations themselves are not dangerous. However, if you are experiencing heart palpitations for the first time you should discuss these symptoms with your doctor. If you experience symptoms similar to a heart attack including pain in your arm, a feeling of pain or pressure in your chest, dizziness or trouble breathing, seek immediate medical treatment.
Heart palpitations can be caused by eating too much
Heart palpitations after eating can be caused by consuming large meals. Following the consumption of food, the body directs blood flow to the digestive tract in order to assist with digestion. The amount of blood flow to the abdomen increases based on the size of the meal consumed. This increased blood flow reaches its peak approximately 25 to 40 minutes after eating and can last for 1 to 2 hours following a meal. In order to compensate for this change in blood flow, the heart must work harder. This can lead to a faster heart rate and heart palpitations.
If you notice that your heart palpitations tend to happen after large meals, try eating smaller meals throughout the day. As a bonus, this may also help with other digestive complaints.
Specific foods act as palpitation triggers
The stomach and the vagus nerve
Heart Rates And Eating Disorders
One area that is a constant concern with those with eating disorders has to do with heart rate, in particular, low heart rate. This issue is generally observed at low body weight but can happen anytime there has been a significant amount of weight loss. In general, as one loses weight one loses muscle mass. With the loss of muscle mass there may be loss of heart mass as the heart is a muscle.
The body, being generally wise, will try to preserve the heart as long as it can, but under the stress of continued weight loss or malnutrition wasting of the heart muscle can occur. Initially the heart may beat more quickly to compensate for being a smaller size, but this is quite exhausting for the heart and ultimately can lead to further damage. To conserve heart muscle and thus keep the entire body functioning as well as possible there will be a slowing of heart rate, called bradycardia. Bradycardia can be very dangerous and is one of the leading causes of illness, hospitalization, and death for those with eating disorders. Heart rates in the 40s or lower are particularly dangerous. As heart rate goes down the risk of arrhythmia, or abnormal rhythm of the heart, becomes more likely. A heart rate in the 40s will often fall into the 30s while asleep, thus increasing these risks. This is why clients with heart rate in their 40s will be hospitalized, both for safety in the moment and for overnight monitoring.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Also Check: Flonase And Heart Palpitations
