What Is The Prognosis For Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome
The prognosis for POTS is generally good, although it can severely disrupt daily living. POTS symptoms may come and go for years. In approximately 80% of cases, the condition improves, but many people have residual symptoms.
The biggest risk to people with POTS is getting hurt if they faint and fall.
Whats The Difference Between Blood Pressure And Pulse
Blood pressure and pulse are two measurements that a doctor may use to monitor your heart and overall health. While theyre similar, they can each say very different things about whats happening in your body.
Pulse, also called heart rate, refers to the number of times your heart beats in one minute. Typical pulse measurements range from 60 to 100 beats per minute.
Blood pressure is an estimate of the force your blood is exerting on your blood vessels. A typical value for blood pressure is 120/80. Doctors consider blood pressure to be elevated when its between 130 and 139 systolic over 80 to 89 diastolic .
If you have high blood pressure with a low pulse, it means your blood is putting increased pressure on your blood vessels, but your hearts beating fewer than 60 times per minute. Read on to learn more about what this combination means for your health.
Recommended Reading: Typical Resting Heart Rate For A Healthy Individual
Does Dehydration Cause A Low Heart Rate
If youre dehydrated, even slightly, your heart has to work harder to pump blood, which can increase your heart rate and cause an irregular heartbeat or palpitations. Dehydration thickens your blood and makes blood vessel walls constrict which can cause hypertension, or high blood pressure, and strain your heart.
Don’t Miss: Treatments Congestive Heart Failure
Can Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome Be Prevented
Unfortunately, theres nothing you can do to prevent developing POTS. But there are steps you can take to try to prevent flare-ups by knowing what your triggers are.
Some general guidelines for preventing flare-ups include:
- Maintain a consistent temperature: Its important for people with POTS to maintain an even temperature, as extremes, especially heat, can make symptoms worse. Air conditioning, cooling vests, handheld misters, personal fans and wearing layers in case of temperature fluctuations can all help. When showering, try to use lukewarm water, as either hot or cold can trigger POTS symptoms. Using a shower chair can also be helpful.
- Avoid prolonged standing: Standing for a long time makes symptoms worse for most people with POTS. If you must stand for a long time, try flexing and squeezing your feet and muscles or shifting your weight from one foot to the other.
- Avoid alcohol: Alcohol can worsen symptoms because it dehydrates your body.
How Is Bradycardia Diagnosed

When you see your doctor, they will measure your heart rate. Your heart rate might have returned to normal, so its a good idea to keep a record of when you experience bradycardia or related symptoms.
Your doctor will also need to work out the cause of your bradycardia. They will ask about your symptoms and your medical and family health history, and will examine you. Tests, such as an electrocardiogram, or ECG, might be done to check your heart. Depending on what is found, you might need further tests such as a stress test.
You May Like: How Long Can Someone Live With Congestive Heart Failure
How Prednisone Affects Heart Rate
Prednisone is a corticosteroid used to treat a number of inflammatory conditions, including severe allergic reaction, certain forms of arthritis, endocrine disorders, and immune system disorders. It is also used to treat certain types of cancer.
However, prednisone comes with many side effects, one of which is a change in heart rate. This medication can cause irregular potassium, calcium, and phosphate levels, which can cause heartbeat irregularities.
Prednisone is used to treat a wide variety of conditions.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Say Heart Attack In Spanish
Patent Foramen Ovaleand Migraine
According to Kurth, migraine is often seen in people who have a hole between the right and left upper chambers, or atria, of their heart, called patent foramen ovale . According to the American Heart Association , everyone is born with this hole, but in most people, it closes a few months after the person is born. However, it remains open in roughly one-quarter of the population. The condition typically goes undetected, but it may be investigated if a person reports severe migraine, the AHA says.
People who have migraine with aura are more likely to have PFO, and migraine with aura is more prevalent in people who have PFO compared with the general population, according to the American Headache Society.
Theres some evidence that surgically closing a PFO can reduce migraine days in some people, particularly those who have migraine with aura. A double-blind study published in December 2017 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, found that among people with migraine with aura who underwent surgery to close their PFO, 49 percent had fewer migraine days 10 to 12 months later, and for about 15 percent, their migraine attacks stopped entirely.
Read Also: Heart Rate Is 50 Beats Per Minute
What Causes A Low Heart Rate
Many things can bring on a slow heart rate.
A heart malfunction
The most common cause for bradycardia is a malfunction in the hearts natural pacemaker, the sinus node. It controls how quickly the top and bottom heart chambers pump blood through the body.
AV Block
Another cause of bradycardia is atrioventricular block , in which the top and bottom chambers dont communicate well and your heart rate drops as a result.
Its like having virtual electrical cables and wires inside the heart, Dr. Baez-Escudero says. These deteriorate as we age. Common medications used in older populations can also often make bradycardia more significant.
Age
Age is the most common risk factor for developing bradycardia. The condition is most common among men and women over age 65.
Having certain illnesses or conditions
Illness or other conditions may also cause bradycardia. These include:
- Heart attacks due to coronary artery disease.
- A bacterial infection in the blood that attacks your heart.
- Inflammation of your heart muscle.
- Low thyroid function.
- Too much potassium in your blood.
- Certain medications, including beta blockers and antiarrhythmics.
Congenital heart defects, diabetes or long-standing high blood pressure all may make bradycardia more likely, says Dr. Baez-Escudero.
How To Raise Blood Pressure
It is not necessary to raise the blood pressure unless low blood pressure is causing concerning symptoms. Anyone who has concerning symptoms should contact a doctor or healthcare professional.
However, some general tips that may also help keep a persons blood pressure within an optimal range include.:
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day may help prevent dehydration. It may also help counteract the effects of some medications that dry the body out or make it use more water, such as diuretics.
Those who experience headaches from low blood pressure as they stand up may want to pay close attention to their movement. Changing positions slowly and gradually may help prevent symptoms.
Anyone who suspects a medicine is causing the symptoms should talk to a doctor about changing their dosage or prescription.
Do not stop taking a medication without direct guidance from a doctor.
You May Like: Can Zinc Cause Heart Palpitations
Urgent Advice: Call 999 If:
You have sudden chest pain that:
- spreads to your arms, back, neck or jaw
- makes your chest feel tight or heavy
- also started with shortness of breath, sweating and feeling or being sick
- lasts more than 15 minutes
You could be having a heart attack. Call 999 immediately as you need immediate treatment in hospital.
How To Manage Medication Side Effects
If you have been prescribed one of these medicines, and experience any unpleasant side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. You can report side effects to the Yellow Card Scheme which helps the Governments medicines safety agency identify, collate and address trends. If you feel that you want to stop taking any medicine, you should talk to your doctor first.
Don’t Miss: Signs Of Silent Heart Attack
Can A Concussion Cause Heart Rate Increase Or Decrease
Yes. You may notice that your baseline, resting heart rate increases or decreases after a head injury. One common cause of a high heart rate would be overactivation of the sympathetic nervous system. Alternatively, the parasympathetic nervous system could overreact and drive your heart rate down.
A stable increase or decrease, however, is less common than situational heart rate symptoms such as heart palpitations or exercise intolerance.
How Should Your Heart Rate Behave
When healthy, the heart adapts rapidly to biological needs, coordinating with the brain through the autonomic nervous system , pressure receptors, and chemical receptors in the body to increase or decrease beats-per-minute . If you go for a run, your limbs need more oxygen and nutrients from your blood, so the heart beats faster to accommodate that need. When you rest, your heart rate should be slow and steady.
Your heart rate also responds to your emotions. If your coworker taps you on the shoulder and startles you, your heart rate will spike in response . But when you realize theres no danger, your heart should settle into its resting rate quickly.
The autonomic nervous system plays a large role in these reactions. The ANS controls automatic processes in your body like blood pressure, heart rate, breathing , digestion, and more. Two parts of the ANS are the sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system .
The SNS is responsible for your fight or flight response, while the PNS is in charge of rest and digest. The SNS, when activated, will pull your heart rate higher. The PNS, on the other hand, will help it decrease. Together, the ups and downs in your heart rate are part of a healthy, functioning body.
You May Like: Can Ibs Cause Heart Palpitations
The Importance Of Monitoring Your Heart Rate
If you are concerned about a low heart rate, visiting your physician can help determine the causes. Your doctor will first ask about your usual activities and conduct a physical exam.
They may use an electrocardiogram to measure the electrical signals in your heart, in order to see whether theyre firing correctly. Wearing a 24-hour monitor can also help your doctor see how your heart performs over time.
Once your doctor decides you might need treatment, they will try to rule out medications or other pre-existing conditions as causes. Sometimes changing medications or similar strategies can solve the problem.
If not, implanting a pacemaker via minimally invasive surgery is the only option to speed up your heart rate, Dr. Baez-Escudero says.
However, he notes that bradycardia isnt often an emergency, so doctors have time to choose the right treatment.
In general, bradycardia allows time for us to evaluate the condition and rule out if any other condition is responsible, Dr. Baez-Escudero says. Then, we can adjust medications or take other steps if we need to.
What Can You Do Now
If you have persistent symptoms after your head injury, including heart rate changes, its important to get treatment. You can consult our team after filling out some paperwork, so that we understand your medical history.
In the meantime, do your best to eat foods that will support your brain and nervous system, get exercise even if its difficult, and sleep as well as you can. If any of your heart-related symptoms are worrisome to you, see your doctor about short-term solutions until youre able to get treatment for your injury.
About Dr. Jaycie Loewen
Also Check: Can Lisinopril Cause Heart Palpitations
What Can Cause Heart Palpitations And Headaches To Occur Together
Aaron Kandola
Medical News Today
Several things can cause heart palpitations and headaches to occur together, including low blood pressure, dehydration, and diet. Some conditions may require treatment, but the symptoms can pass on their own.
Heart palpitations are heartbeats that are more noticeable. For example, they can cause a pounding or fluttering feeling.
Headaches cause pain in the head, face, or neck.
Heart palpitations and headaches can occur together. This article will discuss several possible causes of this and how to treat them.
Medications
Some medications, including vasodilators and the calcium channel blocker nifedipine, can cause both headaches and heart palpitations as side effects.
Anyone who experiences these side effects from taking medications can talk with their doctor about trying other approaches.
Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when the body does not contain enough fluids or water, which it needs to function well.
Water is essential for bodily cells to function correctly. The body loses water through breathing, sweating, and urinating. When levels drop too low, however, it causes feelings of thirst.
Dehydration can cause a person to experience both heart palpitations and headaches.
Staying dehydrated can also cause other symptoms, including:
- a decrease in the volume of urine
- loss of consciousness
The Effects Of Concussion On Heart Rate
There are many reasons that your heart rate could change after a concussion. One of the biggest is dysautonomia: Dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system. In most patients, dysautonomia presents as overactivation of the sympathetic nervous system . Dysautonomia could cause your heart to receive imbalanced signals, leading to symptoms.
Here is a list of many other possible reasons you may have heart rate changes after a head injury:
- Brain dysfunction in the anterior insula, which interacts closely with the ANS
- Injury to the brain, brain stem, or vagus nerve, which sends signals directly to the heart
- Gastrointestinal symptoms
With all those possible drivers of heart rate changes and interactions between potential causes, its little wonder that patients have heart-related symptoms after concussion. Here are some common ones weve seen.
Don’t Miss: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
What Causes Elevated Heart Rate And Dizziness
Dizziness. A high heart rate can make you feel suddenly dizzy. When your heart beats faster than it should, it will pump more blood. If blood is rushing to your brain, it can make you feel lightheaded and dizzy. Vertigo is another common problem associated with tachycardia , according to MedlinePlus .
Low Blood Pressure And Headaches
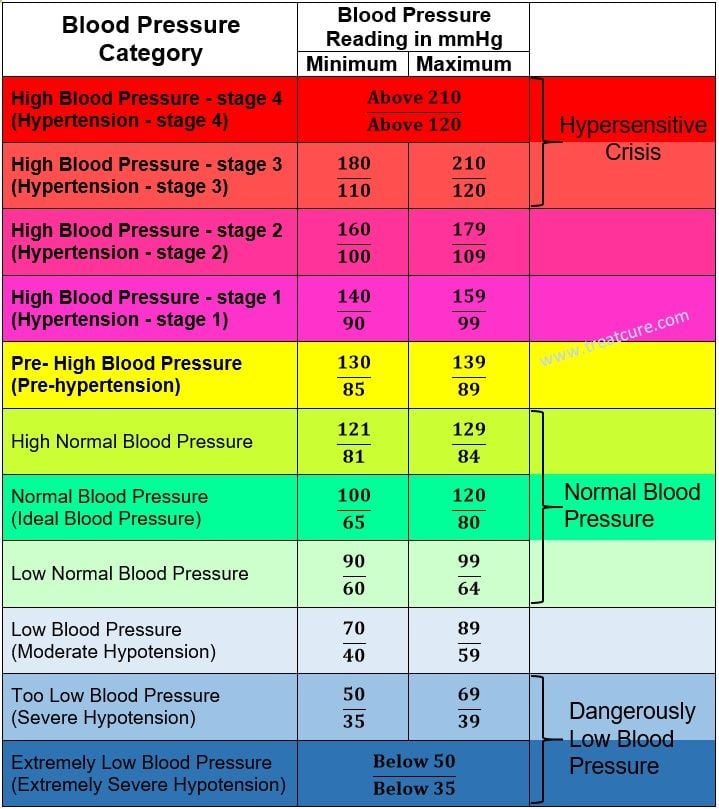
A normal blood pressure is considered less than 120/80 milligrams of mercury . The top number is called the systolic reading and the bottom number is the diastolic reading. They correspond to the different parts of the heart’s beating cycle.
Hypotension occurs when blood pressure is low and causes symptoms. This varies by individual. For example, someone whose resting blood pressure is typically high may experience symptoms of low blood pressure at a higher level than another individual.
While there is no specific cutoff for blood pressure to be called hypotension, a blood pressure below 90/60 mmHg in an otherwise healthy person may be considered low.
Headaches can have a range of causes. Low blood pressure is just one of many possibilities.
You May Like: Female Symptoms Of Heart Attack
Postural Tachycardia Syndrome And Migraine
Some research has shown a link between migraine and conditions that affect a persons heart rate, though cause and effect has not yet been established.
A small study published in April 2018 in the journal Neurology found that nearly all patients who had postural tachycardia syndrome a condition that causes heart rate to speed up when a person stands up, while blood pressure stays the same also experienced headaches. Nearly two-thirds of participants had chronic migraine, and nearly one-third reported episodic migraine. The researchers also found that people who had chronic migraine were more likely to have abnormal blood pressure.
These findings back up earlier research cited in a review published in December 2018 in the journal Autonomic Neuroscience. The findings established a strong link between migraine and POTS, and researchers have reported that between 40 and 96 percent of people who have POTS also have headache or migraine.
But while migraine might cause the heart to race due to the pain and anxiety associated with the migraine attack, say Elgendy, a fast heart rate does not cause migraine.
Diagnosing The Root Of The Symptoms
A doctor will try to narrow down the possible causes headaches and heart palpitations by discussing your symptoms, your family history, and your health history. They will then conduct a physical exam.
They may order tests following your first appointment. If your doctor suspects a condition related to your heart, you may need to get an electrocardiogram , stress test, echocardiogram, arrhythmia monitor, or other test.
If a doctor suspects anemia or hyperthyroidism, they may order a blood test.
Also Check: Congestive Heart Failure Legs
What If You Have A Pre
Some patients have pre-existing heart troubles before their head injury. This could result in a few scenarios:
- The concussion worsens your current health problems.
- The concussion triggers new, additional health issues that need to be managed.
- The concussion changes how you react to your heart medications, resulting in new side effects.
Some people think that once youve tried a medicine and didnt have any side effects, it will always be safe for you. Thats simply not true. A head injury can change the way your body interacts with that medicine.
Perhaps the injury worsens your condition, and you now need a higher dose to manage it. Or, perhaps autonomic dysfunction slows down your GI tract or changes its permeability . With food moving more slowly through your intestines, more of the drug gets absorbed than before your injury, and your body reacts to the increased dose with heart rate changes.
Another example is gaining or losing weight. A different body fat percentage could change how your body responds to a certain medication dose.
If you think any of your symptoms could be side effects of a medication you started taking before or after your injury, talk to your doctor about next steps.
