How Is Heart Failure Treated
Your treatment will depend on the type of heart failure you have and, in part, what caused it. Medications and lifestyle behaviors are part of every treatment plan. Your healthcare provider will talk to you about the best treatment plan for you. Treatment is the same, regardless of gender.
As heart failure gets worse, your heart muscle pumps less blood to your organs, and you move toward the next stage of heart failure. Since you cant move backward through the heart failure stages, the goal of treatment is to keep you from moving forward through the stages or to slow down the progression of your heart failure.
Stage A treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage A heart failure includes:
- Regular exercise, being active, walking every day.
- Stopping the use of tobacco products.
- Treatment for high blood pressure .
- Treatment for high cholesterol.
- Not drinking alcohol or using recreational drugs.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or an angiotensin II receptor blocker if you have coronary artery disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, or other vascular or cardiac conditions.
- Beta-blocker if you have high blood pressure.
Stage B treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage B heart failure includes:
Stage C treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage C HF-rEF includes:
If the treatment causes your symptoms to get better or stop, you still need to continue treatment to slow the progression to Stage D.
Stage D treatment
Treatments For Kidney Failure
The two treatments for kidney failure are kidney transplantation and dialysis. Two different types of dialysis can be done hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
To learn more about each type of treatment, see Choosing a Treatment for Kidney Failure in the A-to-Z Guide.
How Palliative And Hospice Care Can Help With End
Both palliative and hospice care focus on the whole person, including their physical, emotional, social, and spiritual needs. The main difference is that palliative care can be given at any time during a serious illness, and hospice care is given near the end of life typically when a persons prognosis is six months or less.
Palliative and hospice care can also provide help with making difficult treatment decisions, such as whether to be resuscitated if the persons heart stops, or whether to have a tube placed in their throat to help them breathe.
Similarly, people with end-stage heart failure may need to decide when to disable certain medical devices implanted in their body:
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator . Patients can have the shock function turned off, or not replace the battery when the current one runs out. Electrical shocks from ICDs can cause unnecessary distress for patients and loved ones at the end of life.
- Left ventricular assist device . Typically, the patient decides when this heart pump will be shut off before it is implanted. The decision can be discussed again as the end of life nears.
Recommended Reading: Does Diltiazem Lower Heart Rate
Why Its Important To Know Your Ef
If you have a heart condition, it is important for you and your doctor to know your EF. Your EF can help your doctor determine the best course of treatment for you. Measuring your EF also helps your healthcare team check how well our treatment is working.
Ask your doctor how often you should have your EF checked. In general, you should have your EF measured when you are first diagnosed with a heart condition, and as needed when your condition changes.
What Is The Importance Of Ejection Fraction
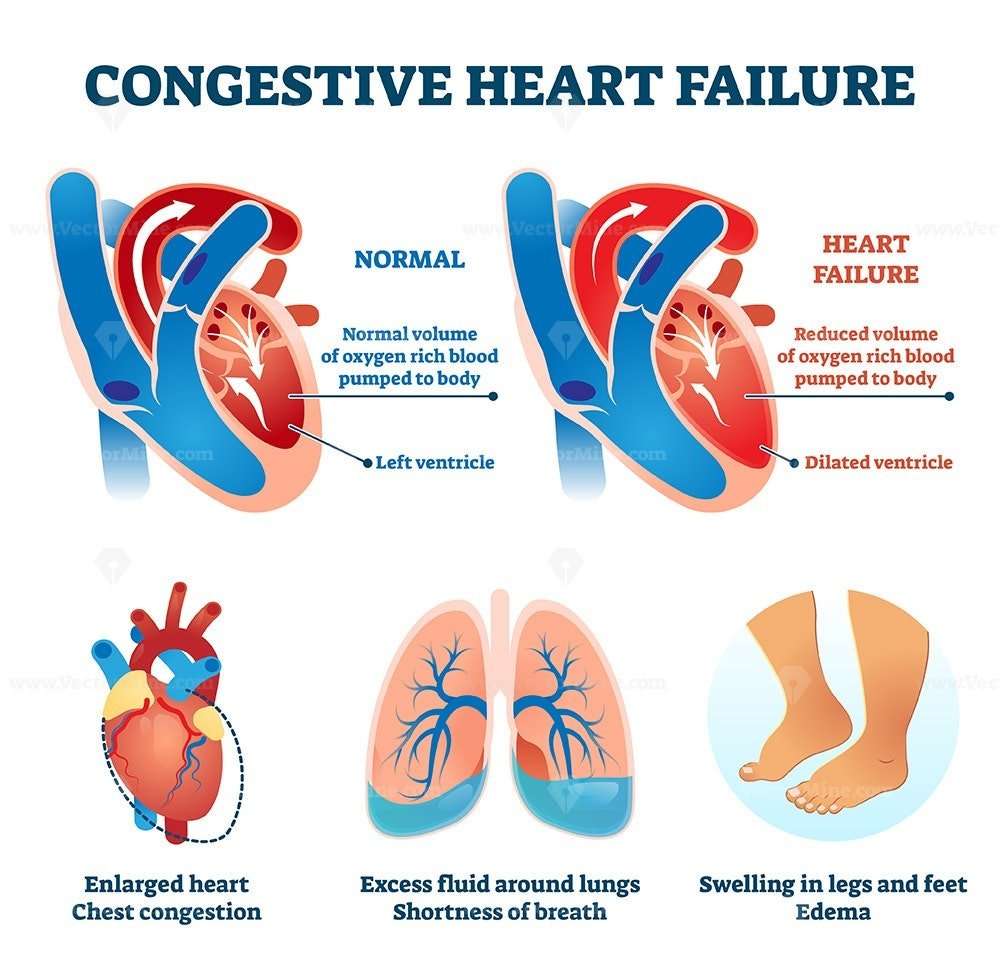
Your ejection fraction is one way to measure the severity of your condition. If its below normal, it can mean that you have heart failure. Your ejection fraction tells your healthcare provider how good of a job your left or right ventricle is doing at pumping blood. Usually, your EF number is talking about how much blood your left ventricle is pumping out because its your heart’s main pumping chamber.
Several non-invasive tests can measure your EF. With this information, your healthcare provider can decide how to treat you or find out if a treatment is working as it should.
A normal left ventricular ejection fraction is 53% to 70%. An LVEF of 65%, for example, means that 65% of the total amount of blood in your left ventricle is pumped out with each heartbeat. Your EF can go up and down, based on your heart condition and how well your treatment works.
Don’t Miss: How To Reverse Heart Failure
Clinical Features Associated With Death
Most of the published reports on the clinical features predicting a poor outcome in patients with heart failure have come from highly selected series of patients. Typically, series are limited to young patients who have been referred for cardiac transplant assessment or for the introduction of vasodilator treatment. Such patients have survived the initial onset of heart failure, but remain severely symptomatic despite pharmacological treatment at their local hospital.,, These patients are unrepresentative of all patients with heart failure. Also, such patients tend to undergo investigations that are not readily available for patients with heart failure in routine clinical practice . The prognostic scoring systems derived from such data are unlikely to be applicable to the generality of patients with heart failure and have little use in clinical practice.
In our present study four factors were found to be independently associated with cardiovascular mortality: age, serum creatinine concentration, systolic blood pressure, and the extent of crackles on auscultation of the lungs.
Mortality increased by 26% for every 10 year increase in age at onset of heart failure, even when allowing for other factors . Although intuitively this might be expected, and other investigators have found it to be so,,, there are reports suggesting the opposite or no association at all.
Symptoms Of Heart Failure
Heart failure interferes with the kidney’s normal function of eliminating excess sodium and waste products from the body. In congestive heart failure, the body retains more fluid, yet not all heart failure patients retain fluid. Here are the symptoms of heart failure:
- Shortness of breath during daily activities.
- Having shortness of breath when lying down or sleeping.
- Weight gain with swelling in the feet, legs, ankles, or stomach.
- Generally feeling tired or weak.
Don’t Miss: What Heart Rate Is Dangerous
Prognosis At Different Ages
Its been a widely accepted clinical opinion for many years that younger people diagnosed with CHF have a better prognosis than older people. There is some evidence to support this theory.
Older people with advanced CHF have a more difficult prognosis. In these cases, its less common to live beyond 1 year post-diagnosis. This could also be because invasive procedures to help the problem arent plausible at a certain age.
This Article Has A Correction Please See:
- Accepted 8 January 2019
Don’t Miss: Home Is Where The Heart Attack Is
Study Population And Identification Of Cases
The study population was that registered with 31 general practices within the southern half of Hillingdon district in west London. The total study population was 151000 as of February 1996 . The general practitioners agreed to refer all suspected cases of new heart failure to a rapid access clinic held at Hillingdon Hospital. Patients who were acutely ill were sent directly to the accident and emergency department of Hillingdon Hospital in the usual way and were identified by daily surveillance of all hospital admissions by a research nurse. From an audit of practice notes, it was estimated that 90% of new heart failure cases had been successfully identified in the study.
A cardiologist took a standardised medical history and examined all the patients except those who died rapidly after hospital admission. In such cases, the clinical findings of the admitting doctors were noted. Whenever possible an ECG, chest radiograph, transthoracic echocardiogram, serum biochemistry, haematology, and thyroid function tests were performed. The echocardiogram was done to a standard protocol and according to accepted guidelines, by either one cardiologist or one of two experienced cardiac technicians. The cross sectional, M mode, Doppler, and colour flow images were recorded on videotape for subsequent analysis. Of the 220 new cases of heart failure identified, 217 had an ECG, 216 a chest radiograph, and 201 an echocardiogram.
An Ejection Fraction Of 20 Percent Is Pretty Bad And If You Know Someone Whose Ef Is This Low Youll Wonder How Much Longer Their Survival Time May Be
Three Year Survival Rate of 20% Ejection Fraction
A report in the International Journal of Cardiology took a look at the survival of congestive heart failure patients with very low left ventricular ejection fraction.
Low LV EF means that the left ventricle does not pump properly, resulting in an inadequate supply of blood for the rest of the body.
The general rule is that a very low EF is a predictor of mortality.
The study by Niebauer et al looked at 99 patients who all had ejection fractions of equal to or less than 20 percent.
74 had ejection fractions of 11 to 20 percent. 25 had EFs of 10 percent or less.
The patients were followed up after three years at which point mortality came in at 74 percent.
However, it was determined that left ventricular ejection fraction was not a predictor of survival rate for these patients.
So what was? Peak VO2 which was measured at the beginning of the study. Peak VO2 turned out to be a strong predictor of mortality.
Read Also: Does High Blood Pressure Make Your Heart Beat Faster
Systolic Vs Diastolic Heart Failure
Diastolic Heart Failure
Diastolic heart failure occurs when your left ventricle can no longer rest between heartbeats because the tissues have hardened. When your heart cannot completely relax, it will not fill with blood again before the next beat.
Systolic vs Diastolic heart failure the difference is simply the Diastolic heart failure type is also called heart failure with preserved ejection fraction . In this type, your doctor can do an imaging test on your heart and determine if your EF looks fine. Your doctor will then should consider if you either have any other heart failure symptoms and if there is evidence that your heart is not functioning properly. If all those criteria are met, you may be diagnosed with diastolic heart failure.
This kind of heart failure often affects older women. It often accompanies other types of heart disease and other non-heart conditions like cancer and lung disease.
Systolic Heart Failure
Systolic vs Diastolic heart failure the difference is simply the Systolic heart failure occurs when the left ventricle of your heart does not completely contract. This means that your heart will not pump sufficiently to move your blood throughout your body in an efficient manner. It is also called heart failure with low ejection fraction .
Ejection Fraction is a measure of how much blood is released each time the heart ventricle is pumped. The more the heart pumps, the healthier it is.
Can You Change Treatments For Kidney Failure
If you start on one type of treatment for kidney failure but feel you would like to try something else, you can speak to your healthcare professional about changing. For most people, it is often possible to change treatments. For example, if you choose hemodialysis, it doesnt mean you cant switch to peritoneal dialysis at a later date. Even if you choose to have a kidney transplant, you may need a period of dialysis until you can be transplanted with a new kidney. It is not uncommon for people who have had kidney failure for many years to have had more than one type of treatment in that time.
Also Check: How Does Your Heart Pump Blood
Why Do I Need Dialysis
If your kidneys are not working properly for example, because you have advanced chronic kidney disease the kidneys may not be able to clean the blood properly.
Waste products and fluid can build up to dangerous levels in your body.
Left untreated, this can cause a number of unpleasant symptoms and eventually be fatal.
Dialysis filters out unwanted substances and fluids from the blood before this happens.
How Do They Remove Fluid From Congestive Heart Failure
The current in-hospital treatment for CHF involves removal of excess fluid with diuretic medication and/or ultrafiltration in which a machine bypasses the kidneys and filters water and salt from the body. However, these treatments can have unwanted side effects such as low blood pressure and worsening kidney function.
Read Also: Heart Failure Fluid Restriction
How Does A Healthy Heart Work
The heart is a muscle about the size of your fist. The hearts job is to pump blood, rich in oxygen and nutrients, to all parts of your body. The left ventricle is the main pumping chamber. In a normal heart, the left ventricle ejects 50% or more of its blood volume out into circulation. This percentage is called the ejection fraction or EF.
- Heart Failure is not a disease.
- Heart Failure is the name used to describe a set of symptoms.
- Heart Failure is caused by diseases that affect the ability of the heart to pump blood.
Stage D And Reduced E
Patients with Stage D HF-rEF have advanced symptoms that do not get better with treatment. This is the final stage of heart failure.
Stage D treatment
The usual treatment plan for patients with Stage D heart failure includes:
- Treatments listed in Stages A, B and C.
- Evaluation for more advanced treatment options, including:
- Heart transplant.
- Research therapies.
Read Also: Do Oxygen Levels Drop During Heart Attack
Can You Get Better After A Diagnosis Of Heart Failure
Heart failure is a chronic, progressive condition, which means it gets worse with time. But even though it doesnt necessarily get better, managing heart failure the right way can help reduce symptoms and slow down the progression of the condition.
I try to get patients to understand that this is not a death sentence, Mountis says.
- Other chronic disease, like diabetes, HIV, or thyroid disease
Depending on the stage and severity of condition, some individuals may need more aggressive treatment, Mountis adds. But it is very possible to live a very good life with a diagnosis of heart failure.
Diagnosing Heart Failure Before It Shows
If you have no symptoms or signs of heart failure, how can you be diagnosed with heart failure? Some people are at a much higher risk of developing heart failure than others. By diagnosing you with stage A heart failure, your doctor will monitor your heart health closely, and suggest treatments that may ward off heart failure signs for as long as possible. A few examples of people who are at risk of developing heart failure include those who have:
-
A family history of heart failure
-
Chronic medical conditions like , , or coronary heart disease
-
A history of alcohol abuse
-
Taken medications, like , that could damage heart tissue
Don’t Miss: What Should My Heart Rate Be When Walking
What Happens If A Screening Yields Normal Results Yet Does Not Explain A Patients Symptoms Such As Chest Pain
There are a small group of patients who come to me with classical symptoms of heart pain and often with abnormal exercise ECG. Yet, they may have normal CT coronary angiogram scans showing widely patent heart vessels.
This group of patients may have Coronary Microvascular Disease . Although the coronary microvascular system is one of the main components of coronary circulation, its relevance has been underestimated for a long time as microvessels are invisible using current imaging techniques, and their function may be assessed only indirectly. Specifically, 50 65% of patients with angina with non-obstructive coronary artery disease are believed to have CMD.
Many of these patients were discharged from follow up as their conventional imaging tests were normal. They are then left frustrated without a firm diagnosis of their symptoms and often end up visiting many doctors across various specialties looking for a diagnosis and treatment. Worse still, many end up being admitted to hospital repeatedly with heart attacks.
Patients with a normal coronary angiogram, and who also have CMD ruled out, can be reassured that they do not require further cardiovascular investigations and therapies. However, those with CMD benefit not just from having a confirmed diagnosis, but can receive tailored treatment to help manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
Article contributed by Dr Paul Ong, cardiologist at Mount Elizabeth Novena Hospital
References
Bangladesh Office
How Is Heart Failure Diagnosed
To make the diagnosis of Heart Failure the following should be done:
- Health History.
- Chest X-Rayto evaluate the size and shape of the heart and detect any fluid in the lungs.
- EKGto determine heart rhythm and search for previous heart damage or thickened heart muscle.
- Blood Test for BNPa hormone made when the heart is overworked.
- Measure Ejection Fraction to gauge effectiveness of the pumping action of the heart. The EF can be determined with an echocardiogram, nuclear scan or angiogram.
Also Check: When Should I Worry About My Heart Rate
