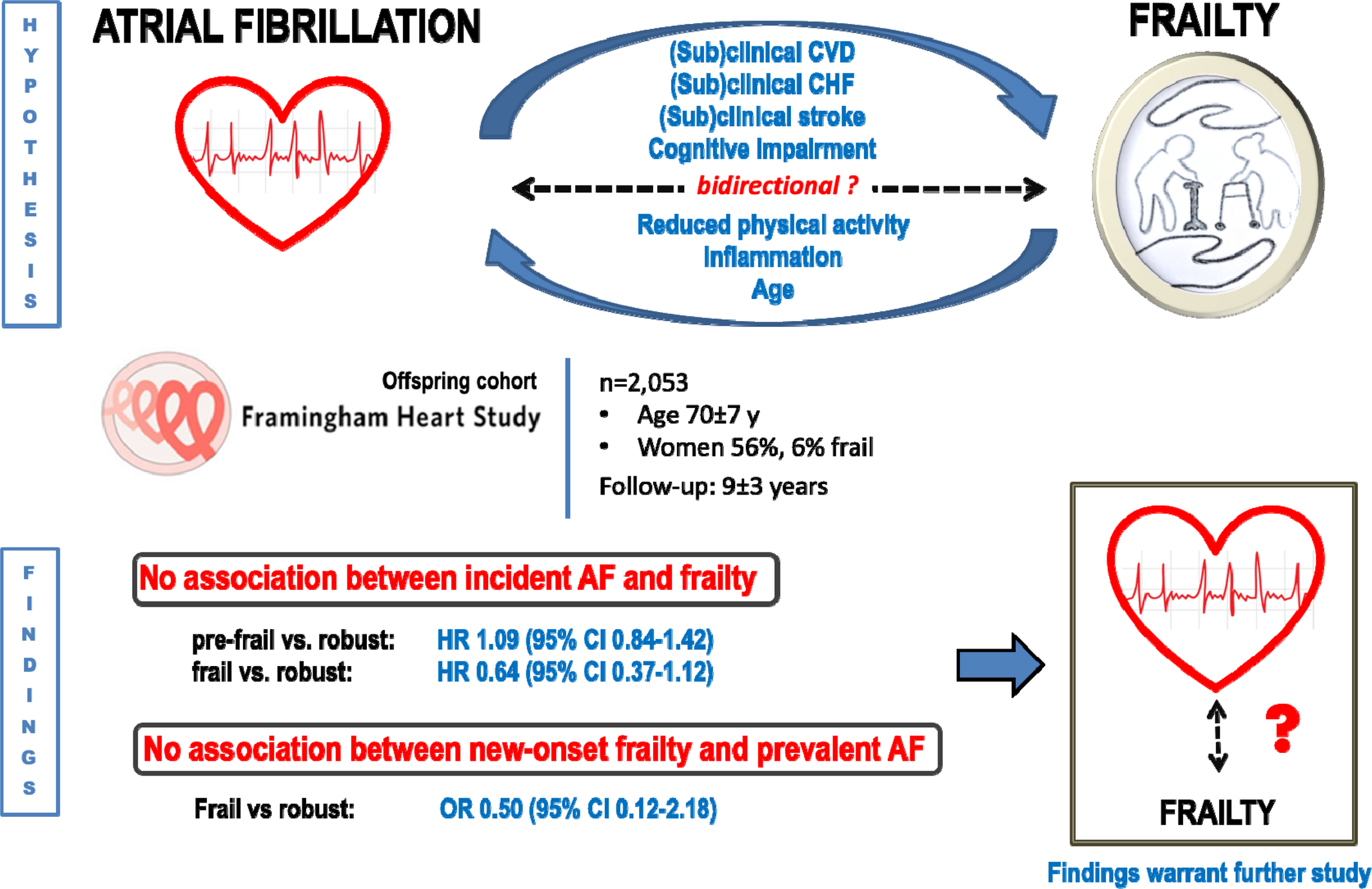
Understanding Heart Failure In The Elderly
When a person has heart failure , it means that their heart is unable to pump enough blood throughout their body. Heart failure usually develops over time. As the heart weakens, it either cannot fill with enough blood, pump with enough force or both. While this cardiovascular condition sounds scary, heart failure does not imply that the heart has stopped working or is about to stop working.
What Causes Atrial Fibrillation To Start
Changes or damage to your hearts tissue and electrical system cause atrial fibrillation. Usually, coronary artery disease or high blood pressure causes those changes. Often a trigger heartbeat causes atrial fibrillation to begin. But sometimes its hard to know the cause of that triggered heartbeat. For some people, there is no identifiable cause. Research is constantly providing new information to help us learn more about the
Afib often runs in families. So, if a close family member has Afib, you have a family history and therefore a higher chance of developing it, too.
Can atrial fibrillation be caused by anxiety?
We dont fully know the connections between atrial fibrillation and anxiety. Research has identified Afib as a cause of anxiety . But few studies have explored anxiety as a cause of Afib. We do know that anxiety can raise your risk of cardiovascular disease and causes a 48% higher risk of cardiac death. However, we need more research to find out if anxiety disorders can cause Afib.
Current Therapeutic Options For Heart Failure In Elderly Patients
F. Guerra
1Cardiology and Arrhythmology Clinic, Department of Biomedical Sciences and Public Health, University Hospital Ospedali Riuniti, Marche Polytechnic University, Ancona, Italy
Academic Editor:
Abstract
Heart failure is a major and growing public health problem with high morbidity and mortality . It affects 1-2% of the general population in developed countries, and the average age at diagnosis is 76 years. Because of a better management of acute phase and comorbidities, HF incidence is increasing in elderly patients, with a prevalence rising to 10% among people aged 65 years or older . Therefore, a substantial number of elderly patients need to be treated. However, because of clinical trial exclusion criteria or coexisting comorbidities, currently recommended therapies are widely based on younger population with a much lower mean age. In this review, we will focus on available pharmacological, electrical, and mechanical therapies, underlining pros, cons, and practical considerations of their use in this specific patient population.
1. Drug Therapy
To date, limited evidence has investigated the effects of the recommended systolic HF therapies in aged patients . However, data from small observational studies and substudies suggest that elderly patients derive similar benefits as younger patients .
2. Anemia and Iron Deficiency
3. Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator
4. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
5. Left Ventricular Assist Device
7. Conclusions
References
Don’t Miss: What Caused Dmx To Have Heart Attack
How Well Do Heart Transplants Work
Transplants are not always the best treatment for older patients, and the demand for donor hearts always outpaces supply. But were doing more heart transplants at UChicago Medicine, and Im happy to see them saving more lives. Were seeing big improvements in survival rates. The average survival rate is now over 11 years. Twenty years ago, the idea that someone could live 20 or 30 years with a transplanted heart was a fantasy. Not anymore.
Ablate And Pace Strategy
There are a few small randomised clinical trials comparing pharmacological rate control and permanent pacing with complete AV node catheter ablation in patients with HF. These trials showed a benefit of an ablate and pace strategy in terms of symptom relief, HF hospitalisations and mortality . AV node ablation solves the problem of rapid ventricular response in AF, which aggravates symptoms and HF.
Catheter ablation of the AV node and permanent pacing should be considered if pharmacological rate control fails . The optimal choice of pacemaker type or pacing mode is still unclear.
Right ventricular or biventricular pacing is the next question which should be answered in the future. There are limited data suggesting an advantage of biventricular pacing versus right ventricular pacing in HF patients.
You May Like: How To Stop Worrying About Heart Attack
What You Need To Know About Heart Failure Treatment For The Elderly
Heart failure is a cardiac condition where the heart does not pump blood as efficiently as it should, resulting in a lack of oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. Though it affects people of all ages, heart failure is the leading cause of hospitalizations in people older than 65. Elderly patients who experience heart failure are likely to already have a chronic cardiovascular condition, but it can also be caused by physical decline due to aging and poor cardiovascular management throughout life. Other risk factors include obesity, a family history of heart failure, hypertension and diabetes.
Early signs of heart failure in the elderly are similar to those found in other age groups, which include worsening or shortness of breath, fatigue, bloating, lack of appetite, persistent cough, lack of appetite and nausea. Other symptoms may include a mental decline or depression.
Can Taking Too Many Medications Impact Older Adults With Heart Failure
Yes. As we age, the body doesnt handle the medicine in the same way. It metabolizes medicines differently, which is why taking too many medications can be a problem for older patients with heart failure. As we age, the liver and kidneys dont work as well, so drugs can sometimes build up in the system. Older people on medicines for their heart might be on five, six or 10 other drugs. So theyre taking a whole cocktail of medicines that might not work well together and could have side effects. Its helpful to re-prioritize medications with your doctor. Over-the-counter pain medications can sometimes be very dangerous in older people because they can raise blood pressure and harm the kidneys. They can also have a sedative effect on people and cause delirium.
You May Like: Can You Fly After Heart Surgery
Atrial Fibrillation And Congestive Heart Failure
DOI: 10.19102/icrm.2011.020404
1Department of Internal Medicine, Charlton Memorial Hospital, Fall River, MA2Cardiac Arrhythmia Service, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA
ABSTRACT.Atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure are common conditions which predispose each other, share risk factors, and are associated with morbidity and mortality. They share common pathophysiology, including structural and electrical remodeling, intracellular calcium dysregulation, and neuroendocrine mechanisms, and also have genetic basis. Despite better survival in patients with sinus rhythm than those with AF, rhythm control has not been found to be superior to rate control. The role of non-antiarrhythimc therapy is also being explored. Catheter ablation and device-based therapy with pacemaker and cardiac resynchronization therapy may also benefit patients with AF and CHF.
KEYWORDS.ablation, antiarrythmic drugs, atrial fibrillation, genetics, heart failure.
The authors report no conflicts of interest for the published content. Manuscript received February 13, 2011, final version accepted March 3, 2011.
Address correspondence to: E. Kevin Heist, MD, PhD, Cardiac Arrhythmia Service, 55 Fruit Street, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. E-mail:
When Should I Call 911
Atrial fibrillation can cause serious medical complications. So, its essential to learn the warning signs and to share them with your family and friends. In many cases, we need someone else to call 911 for us. Immediately call 911 if you have the following symptoms or if you notice them in someone around you:
Signs of bleeding
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded.
These symptoms can happen within an hour before having a cardiac arrest. In some cases, these symptoms might not appear at all, and a person could simply faint. If you or a loved one have Afib, its a good idea to talk with your healthcare provider about how to get help in medical emergencies. For those who live alone or spend lots of time alone, there may be no one home to call for help. Medical alert devices may be a life-saving resource.
You May Like: What Is Normal Blood Pressure And Heart Rate
Control Of Fast Ventricular Rate
Digitalis glycosides are ineffective in converting AF to sinus rhythm . Digoxin is also ineffective in slowing a rapid ventricular rate in AF if there is associated fever, hyperthyroidism, acute blood loss, hypoxia, or any condition involving increased sympathetic tone . However, digoxin should be used to slow a fast ventricular rate in AF unassociated with increased sympathetic tone, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, or the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, especially if there is LV systolic dysfunction.
The usual initial dose of digoxin given to undigitalized patients with AF is 0.5 mg orally. Depending on the clinical response, a second oral dose of 0.25 mg may be administered in 6 to 8 hours, and a third oral dose of 0.25 mg may be given in another 6 to 8 hours to slow a rapid ventricular rate. The usual maintenance oral dose of digoxin administered to patients with AF is 0.25 mg to 0.5 mg daily, with the dose decreased to 0.125 mg to 0.25 mg daily for older patients who are more susceptible to digitalis toxicity .
Amiodarone is the most effective drug for slowing a rapid ventricular rate in AF . However, its adverse effect profile limits its use in the treatment of AF. Oral doses of 200 mg to 400 mg of amiodarone daily may be administered to selected patients with symptomatic life-threatening AF refractory to other drugs.
Implications For Clinicians Policy Makers And Future Research
The mechanism by which atrial fibrillation is associated with an increased risk of a range of different cardiovascular diseases is unclear. In the case of myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation could contribute to demand infarction and the subsequent development of type 2 myocardial infarction.7 It is also possible that the association between atrial fibrillation and non-stroke cardiovascular disease is not causal. Considering our observation that atrial fibrillation is also associated with an increased risk of heart failure, sudden cardiac death, and chronic kidney disease , it seems likely that atrial fibrillation could be acting as a marker for shared underlying risk factors for cardiovascular disease. These include hypertension, which is diagnosed in up to 90% of patients with atrial fibrillation, as well as obesity, diabetes, and obstructive sleep apnoea.125126
Even though the associations we describe cannot indicate causality for the non-stroke outcomes, there is merit in developing clinical risk prediction models for outcomes such as congestive heart failure particularly given our relative and absolute risk estimates. To date, three models have been developed with C statistics ranging from 0.7 to 0.84, but none has been externally validated.127128129 Future models might also benefit from inclusion of non-invasive measures of cardiac function and assessments of novel biomarkers.
What is already known on this topic
What this study adds
Read Also: How Do You Slow Down Your Heart Rate
Aging And Atrial Fibrillation
The relationship between AF and age has been well-described in the literature and epidemiological studies have been instrumental in establishing this link. Indeed, advancing age is the most prominent risk factor for AF. In the Framingham cohort study which followed individuals over a 22 year period, the incidence of AF was noted to increase with advancing age. Age, along with hypertension, congestive heart failure, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, and valvular disease were identified as independent risk factors for the development of AF . This was followed by further studies confirming the link between age and AF, which is now well-established .
Age is also an independent risk factor for stroke . This was signified in the landmark Atrial Fibrillation Investigators schema which identified age as a predictor of stroke in AF patients . The Stroke Prevention in AF study also recognized its pertinence, noting that females over 75 years had a higher rate of thromboembolic events . The age-associated increase in the risk of stroke is not specific to sex and is observed both in males and females . In the Framingham study, stroke risk increased significantly from 1.5 to 23.5% at 5059 years, and 8089 years respectively, and in the latter age group, AF was the sole cardiovascular condition to exert an independent effect on stroke incidence .
Table 1. Stroke risk stratification: CHA2DS2-VASc score.
How Heart Failure Leads To Afib
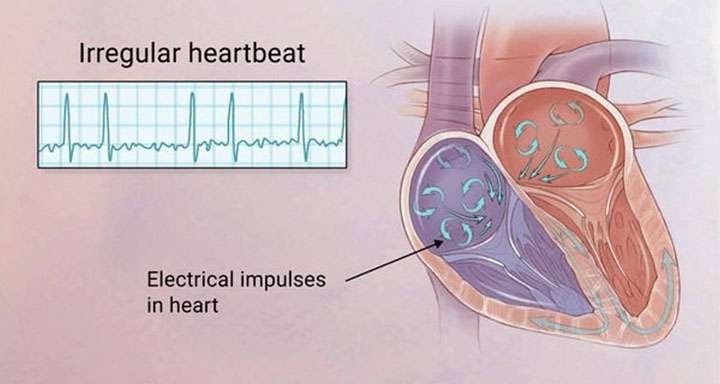
It works in the other direction, too. Your heart’s rhythm is controlled by electrical signals. For those signals to work well, they need healthy heart tissue.
But heart failure can actually stretch your atria and cause tissue in your heart to thicken and scar. Those changes throw off the electrical signals, and that messes up the heart’s rhythm and can cause AFib.
Also Check: What Arm Hurts With Heart Attack
Left Ventricular Systolic Function
-
In patients carefully screened to exclude coronary artery disease and hypertension, there is little change in left ventricular systolic function with increasing age, although cardiac output may decrease in parallel with a reduction in lean body mass.w7 The determinants of cardiac output which may be influenced by age include heart rate, preload and afterload, muscle performance, and neurohormonal regulation.
-
Increases in heart rate in response to exercise or stress caused by non-cardiovascular illnesses, particularly infections, are attenuated with increasing age.w8 Stroke volume increases only by moving up the Frank Starling curve.w9w10 Thus end diastolic volume increases. These age related changes in cardiac response to exercise are mimicked by adrenergic blockade,w11 but adrenergic agonists do not reverse this aging process.w12 The decline in exercise performance with age may additionally relate to peripheral factors, blood flow, and muscle mass rather than being solely the consequence of cardiac performance changes.
How Afib Leads To Heart Failure
When you have AFib, your heart may beat faster than normal, even when you’re just resting. And since the heart’s doing more of a quiver than a strong push, it ends up sending out only some of the blood it normally would. It’s like the difference between a bunch of short, frantic bursts on a bike pump versus long, steady strokes.
AFib can also cause fluid buildup in your lungs. Your lungs fill your blood with oxygen before sending it back to your heart. So now, your heart doesn’t get enough oxygen-rich blood from the lungs, and even if it does, it’s beating too fast to do a good job of pumping it out.
And a rapid heartbeat — or just one that’s never regular — can damage the muscles of your heart.
All of that sets the stage for heart failure. Even though your heart’s working really hard — too hard — your body’s still not getting the oxygen it needs.
You May Like: How To Lower Heart Rate With Exercise
Use Of Antiarrhythmic Drugs To Maintain Sinus Rhythm
The efficacy and safety of antiarrhythmic drugs after cardioversion of AF to maintain sinus rhythm have been questioned. A meta-analysis of six double-blind, placebo-controlled studies of quinidine involving 808 patients who had direct-current cardioversion of chronic AF to sinus rhythm showed that 50% of patients treated with quinidine and 25% of patients treated with placebo remained in sinus rhythm at 1 year of follow-up . However, the mortality was significantly higher in patients treated with quinidine than in patients treated with placebo . In a study of 406 patients with a mean age of 82 years with heart disease and complex ventricular arrhythmias, the incidence of adverse effects causing drug cessation was 48% for quinidine and 55% for procainamide . The incidence of total mortality at the 2-year follow-up was insignificantly higher in patients treated with quinidine or procainamide compared with patients not receiving an antiarrhythmic drug .
In another study, 85 patients were randomized to quinidine and 98 patients to sotalol after DC cardioversion of AF to sinus rhythm . At the 6-month follow-up, 48% of quinidine-treated patients and 52% of sotalol-treated patients remained in sinus rhythm . At 1-year follow-up of 100 patients with AF cardioverted to sinus rhythm, 37% of 50 patients randomized to sotalol and 30% of 50 patients randomized to propafenone remained in sinus rhythm .
How Does Heart Failure Affect The Quality Of Life And Lifestyle
With the right care and treatment plan, many adults still enjoy life even though heart failure limits their activities. How well you feel depends on:
- How well your heart muscle is working.
- Your symptoms.
- How well you respond to your treatment plan.
- How well you follow your treatment plan.
This includes caring for yourself by:
- Taking your medications.
- Tracking and reporting new or worsening symptoms to your provider.
- Keeping regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider.
Because heart failure is a chronic, long-term illness, talk to your doctor and your family about your preferences for medical care. You can complete an advance directive or living will to let everyone involved in your care know what you want. A living will details the treatments you do or dont want to prolong your life. Its a good idea to prepare a living will while you are well in case you arent able to make these decisions at a later time.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you have heart failure, you can take steps to improve your heart health. Take your medications as instructed, follow a low-sodium diet, stay active or become physically active, take notice of sudden changes in your weight, live a healthy lifestyle, keep your follow-up appointments and track your symptoms. Talk to your healthcare provider about questions or concerns you have about your medications, lifestyle changes or any other part of your treatment plan.
References
Read Also: How To Tell The Difference Between Heartburn And Heart Attack
It Can Be The Primary Cause Of Congestive Heart Failure
Sometimes people are first diagnosed with atrial fibrillation, they dont necessarily feel their heart beating fast or irregular, they only notice an increasing shortness of breath. So, when they are finally diagnosed, their heart may have had this rapid heart beat for a few weeks or even months at a time. As a result, heart function becomes weaker than normal.
Once coronary artery disease is ruled out, this condition is referred to as tachycardia-mediated cardiomyopathy. This implies that the rapid heart rate, or tachycardia, from AFib is what has primarily caused CHF. There are a few ways to manage this. One way is ensuring your heart rate is under control. Over time, you can help your heart get stronger again. However, rhythm control, whether it is a procedure or a cardioversion to get a patient out of AFib, tends to help better to improve your heart function and return it to as close to normal as possible.
