Life Expectancy With Congestive Heart Failure
The life expectancy of someone with congestive heart failure depends on the type of heart failure, the cause, the stage of the disease, and how effective treatment is.
When heart failure results from cardiomyopathy or coronary artery disease, a person typically has a less positive outlook than someone with heart failure in its earliest stage.
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Treating Congestive Heart Failure Unique
Yale Medicines team comprises heart failure cardiologists and cardiac surgeons, dedicated advanced-practice, registered nurses and nurse coordinators, dietitians, exercise physiologists, financial counselors, immunologists specializing in transplants, psychologists, and specialists in palliative care.
With a multidisciplinary approach, Yale Medicine physicians include the patients desires as well as input from the family to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that’s right for them.
Factors That Can Worsen Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The symptoms of heart failure can be worsened by a number of factors, including:
- too much salt, fluid, or alcohol in the diet
- some viral and bacterial infections
- kidney diseases
Treatment for heart failure may include:
- medicines, such as
- diuretics to remove excess fluid and improve symptoms of heart failure
- mineralcortiocoid receptor antagonists are also recommended and used in most patients with heart failure to reduce mortality and hospitalisation
- ACE inhibitors to open up blood vessels, reduce blood pressure and reduce sodium retention and water retention
- certain beta-blockers to slow the heart rate and reduce its work
- aldosterone blockers to reduce blood pressure and reduce the effects of damage to the heart muscle
- ACE inhibitors, beta blockers and aldosterone blockers can increase survival and reduce the likelihood of hospitalisation.
You May Like: What Is Acute Heart Failure
Prognosis At Each Stage
The outlook for CHF varies greatly between people, as there are many contributing factors for every individuals situation. However, generally speaking, if CHF is discovered in its earlier stages and properly managed, you can expect a far better outlook than if its discovered much later.
Some people whose CHF is discovered early and treated promptly and effectively can hope to have a nearly standard life expectancy.
Clinical Presentation Of Hf
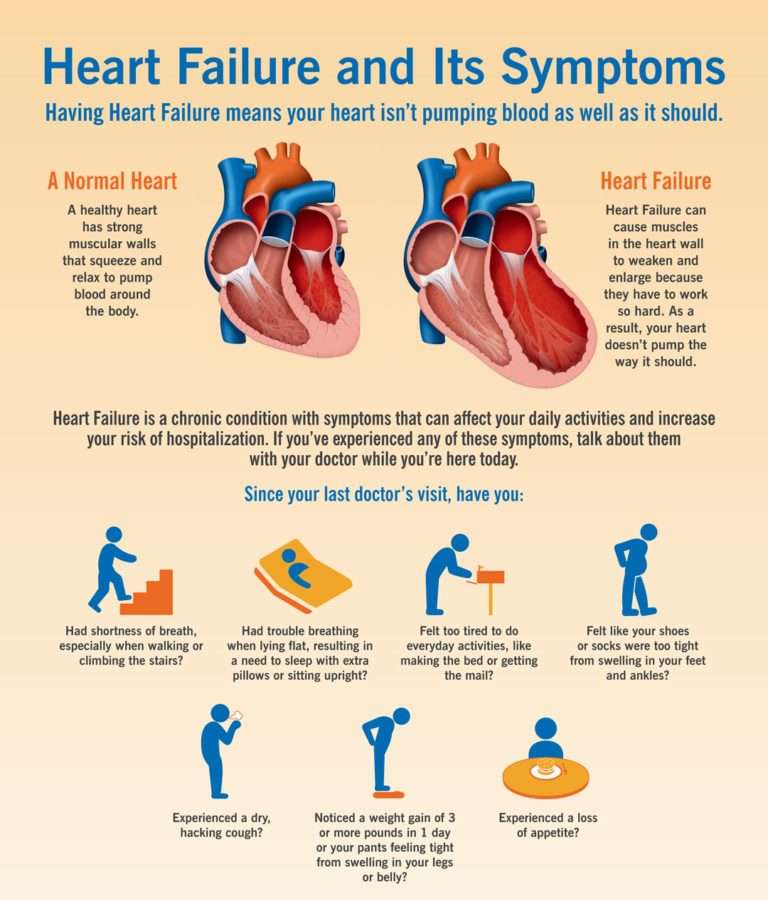
The clinical presentation of HF comprises symptoms of shortness of breath /dyspnea orthopnea/SOB on lying own paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea fatigue/weakness/lethargy edema, abdominal distention and right hypochondrial pain . Due to compensatory mechanisms, early stages of HF lack specific signs however, late stages of HF demonstrate the following signs: tachycardia pedal edema increased jugular venous pressure , abnormal lung sounds S3 gallop . Other signs, such as hepatojugular reflux and ascites, are not found frequently in HF, but have a specificity of 96% and 97%, while a sensitivity of 24% and 1%, respectively . Recent research has uncovered the microvascular dysfunction and subsequent decrease in O2 supply or mismatch with the O2 supply vs. demand in HF patients. Therapeutic strategies to improve muscle microvascular and oxidative function via exercise training, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agents have been proposed to be essential to provide better exercise tolerance and quality of life .
Recommended Reading: Can Heart Attack Symptoms Go On For Days
Point Of Maximal Impulse
The point of maximal impulse of the left ventricle is usually located in the midclavicular line at the fifth intercostal space. With the patient in a sitting position, the physician uses fingertips to identify this point. Cardiomegaly usually displaces the cardiac impulse laterally and downward.
At times, the point of maximal impulse may be difficult to locate and therefore loses sensitivity . Yet the location of this point remains a specific indicator for evaluating the size of the heart.14
Diagnosis Of Congestive Heart Failure
There are several tests to diagnose congestive heart failure starting with a regular physical examination. Your healthcare provider will be able to diagnose any heart failure symptoms by just taking a look at your medical history and current condition.
If your doctor believes you have some symptoms that might be associated with heart failure and you also fall in the high-risk category, then your doctor might suggest you go for an electrocardiogram.
Also Check: What Is A Dangerous Heart Rate For A Child
Stress Ekg Or Echocardiogram
Stress tests are performed to see how the heart performs under physical stress. The heart can be stressed with exercise on a treadmill or in a few instances, a bicycle. If a person cannot exercise on a treadmill or bicycle, medications can be used to cause the heart rate to increase, simulating normal reactions of the heart to exercise.
During the stress test, you will wear EKG leads and wires while exercising so that the electrical signals of your heart can be recorded at the same time. Your blood pressure is monitored throughout the test. The stress test can be performed together with the echocardiogram, described above.
Chf Nursing Care Plan 7
Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Breathing Pattern related to pulmonary congestion secondary to CHF as evidenced by shortness of breath, SpO2 level of 85%, cough, respiratory rate of 25 bpm, and frothy sputum
Desired Outcome: The patient will achieve effective breathing pattern as evidenced by normal respiratory rate, oxygen saturation within target range, and verbalize ease of breathing.
| CHF Nursing Interventions | |
| Assess the patients vital signs and characteristics of respirations at least every 4 hours. | To assist in creating an accurate diagnosis and monitor effectiveness of medical treatment. |
| Administer supplemental oxygen, as prescribed. Discontinue if SpO2 level is above the target range, or as ordered by the physician. | To increase the oxygen level and achieve an SpO2 value within the target range at least 96% |
| Administer the prescribed bronchodilators, steroids, or combination inhalers / nebulizers, as prescribed. | Bronchodilators: To dilate or relax the muscles on the airways. Steroids: To reduce the inflammation in the lungs. Inhalers or nebulizers To facilitate relaxation of the airway. |
| Elevate the head of the bed. Assist the patient to assume semi-Fowlers position. | Head elevation and semi-Fowlers position help improve the expansion of the lungs, enabling the patient to breathe more effectively. |
Recommended Reading: How To Check For Heart Attack
Blood Pressure And Heart Rate
The patient’s blood pressure and heart rate should be recorded. High, normal or low blood pressure may be present. The prognosis is worse for patients who present with a systolic blood pressure of less than 90 to 100 mm Hg when not receiving medication .16 Tachycardia may be a sign of heart failure, especially in the decompensated state. The heart rate increases as one of the compensatory ways of maintaining adequate cardiac output. A decrease in the resting heart rate with medical therapy can be used as a surrogate marker for treatment efficacy. A weak, thready pulse and pulsus alternans are associated with decreased left ventricular function. The patient should also be monitored for evidence of periodic breathing .
Complications Of Congestive Heart Failure
- Rapid Weight Loss Severe heart failure can lead to a rapid loss of weight that can be life-threatening. Heart failure can cause blood to back up into the liver and intestines, causing these organs to swell. This swelling can lead to nausea and loss of appetite, and can prevent the body from absorbing nutrients from food.
- Impaired Kidney Function Congestive heart failure weakens the hearts ability to pump blood, reducing blood flow to the kidneys. This can lead to kidney damage or kidney failure, if left untreated.
- Liver Damage Heart failure can cause fluid to build up in the liver, which can lead to scarring. This makes it more difficult for the liver to carry out its day-to-day functions.
- Arrhythmias Heart failure results in damaged heart muscles, which can lead to the development of an arrhythmia, or abnormal heart beat. Arrhythmias can include the heart beating too quickly, beating too slowly, or beating irregularly.
- Heart Valve Problems If the heart is enlarged due to heart failure, the valves of the heart, which ensure appropriate direction of blood flow through the organ, may not function properly.
- Angina and Heart Attack Heart disease is a major contributing factor in many heart failure cases, and people with congestive heart failure are at continued risk of angina and heart attack.
You May Like: Symptoms Of Heart Attacks And Strokes
Heart Failure Treatment Is A Team Effort
Heart failure management is a team effort, and you are the key player on the team. Your heart doctor will prescribe your medications and manage other medical problems. Other team members — including nurses, dietitians, pharmacists, exercise specialists, and social workers — will help you achieve success. But it is up to YOU to take your medications, make dietary changes, live a healthy lifestyle, keep your follow-up appointments, and be an active member of the team.
If you notice anything unusual, don’t wait until your next appointment to discuss it with your doctor. Call them right away if you have:
- Unexplained weight gain
- Swelling in your ankles, feet, legs, or belly that gets worse
- Shortness of breath that gets worse or happens more often, especially if you wake up feeling that way
- Bloating with a loss of appetite or nausea
- Extreme fatigue or more trouble finishing your daily activities
- A lung infection or a cough that gets worse
- Fast heart rate
- New irregular heartbeat
Is Chf Due Mainly To Heart Valve Disease
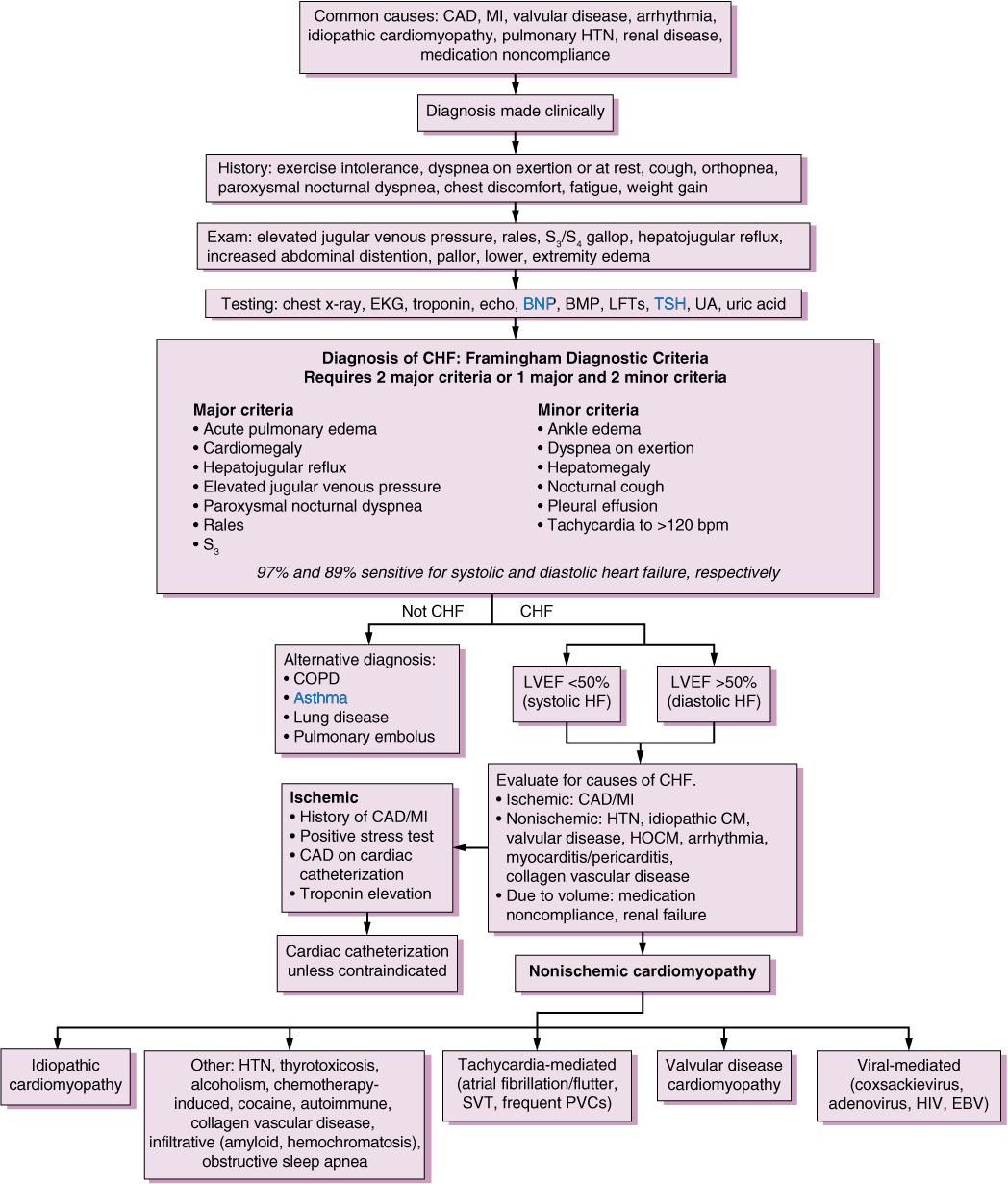
CHF is most commonly caused by valvular insufficiency. It is estimated that 80% of the canine CHF cases are caused by MVI. However, there are many other causes. Disease of the heart muscle , irregularities of rhythm, and narrowing of some of the major blood vessels can also cause CHF. Initially, MVI results in left-sided congestive heart failure. If left untreated, the heart failure may progress to involve both sides of the heart.
Read Also: High Blood Pressure And High Heart Rate
How Is Heart Failure Treated
Your treatment will depend on the type of heart failure you have and, in part, what caused it. Medications and lifestyle behaviors are part of every treatment plan. Your healthcare provider will talk to you about the best treatment plan for you. Treatment is the same, regardless of gender.
As heart failure gets worse, your heart muscle pumps less blood to your organs, and you move toward the next stage of heart failure. Since you cant move backward through the heart failure stages, the goal of treatment is to keep you from moving forward through the stages or to slow down the progression of your heart failure.
Stage A treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage A heart failure includes:
- Regular exercise, being active, walking every day.
- Stopping the use of tobacco products.
- Treatment for high blood pressure .
- Treatment for high cholesterol.
- Not drinking alcohol or using recreational drugs.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or an angiotensin II receptor blocker if you have coronary artery disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, or other vascular or cardiac conditions.
- Beta-blocker if you have high blood pressure.
Stage B treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage B heart failure includes:
Stage C treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage C HF-rEF includes:
If the treatment causes your symptoms to get better or stop, you still need to continue treatment to slow the progression to Stage D.
Stage D treatment
Surgery For Heart Failure
- Coronary bypass surgery treats blocked arteries by removing healthy arteries from other parts of the body and using them to reroute blood around clogged arteries. This improves blood flow to the heart. If severely blocked arteries are a contributing factor to your heart failure, your physician may suggest bypass surgery.
- Heart valve replacement modifies a faulty heart valve to eliminate backward blood flow. A surgeon will either repair the valve, if possible, or replace it with an artificial valve.
- Ventricular assist devices are mechanical pumps implanted in the abdomen or chest and attached to the weakened heart. The devices help pump blood from the lower heart chamber to the rest of your body.
- Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators are implanted beneath the skin in the chest with wires leading through the veins and into the heart. These devices monitor heart rhythm and will shock the heart back into normal rhythm if it develops a life-threatening arrhythmia. They can also act as pacemakers, speeding up the heart if it begins beating too slowly.
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy, also known as biventricular pacing, sends electrical pulses to the hearts lower chambers to help them pump more efficiently.
- Heart transplant is an option in the most serious heart failure cases, when medication or surgery do not help. The procedure involves removing the damaged heart and replacing it with a healthy one from an organ donor.
Don’t Miss: Is 190 Heart Rate Bad
A Management Of Hfref
Stage A
This include patients who are at risk of heart failure but without structural heart disease and it involves patients with risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, history of use of cardiotoxins, and family history of cardiomyopathy.
At this stage, the goal is to reduce risk factorsvia life style modifications including achieving normal body weight, regular exercise, healthy diet, giving up smoking, controlling blood pressure, glucose and cholesterol. This applies to patients with both HFrEF and HFpEF. Controlling hypertension alone in the elderly has been shown to decrease the HF incidence by about 40%.
Stage B
This includes patients with structural heart disease but without any sign or symptoms of heart failure. This can be due to previous myocardial infarction, left ventricular hypertrophy and/or asymptomatic reduced LVEF.
-Given coronary artery disease is the most common cause of heart failure, all patients without an obvious cause should be evaluated for coronary artery disease.
-All patients with HFrEF should be started on an evidence-based b-blocker and ACE-I or ARB as tolerated. ARB is best used in ACE-I intolerant patients. Only 3 ARBs have been studied on HF patients â valsartan, losartan and candesartan.
-If a patient cannot tolerate ACE-I and ARB or are contraindicated, then hydralazine-nitrate combination can be used instead.
Stage C
Patients with prior or current symptomatic heart failure are included in Stage C.
Stage D
When Should I Get Emergency Care
Go to the ER or call 911 if you have:
- New, unexplained, and severe chest pain that comes with shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or weakness
- Fast heart rate , especially if you are short of breath
- Shortness of breath that doesn’t get better if you rest
- Sudden weakness, or you can’t move your arms or legs
- Sudden, severe headache
- Fainting spells
Don’t Miss: Viral Attack On Heart
What Causes Heart Failure
Although the risk of heart failure doesnt change as you get older, youre more likely to have heart failure when youre older.
Many medical conditions that damage the heart muscle can cause heart failure. Common conditions include:
- Tobacco and recreational drug use.
- Medications. Some drugs used to fight cancer can lead to heart failure.
Chf Nursing Care Plan 4
Nursing Diagnosis: Activity intolerance related to imbalance between oxygen supply and demand as evidenced by fatigue, overwhelming lack of energy, verbalization of tiredness, generalized weakness, and shortness of breath upon exertion
Desired Outcome: The patient will demonstration active participation in necessary and desired activities and demonstrate increase in activity levels.
| CHF Nursing Interventions | Rationales |
| Assess the patients activities of daily living, as well as actual and perceived limitations to physical activity. Ask for any form of exercise that he/she used to do or wants to try. | To create a baseline of activity levels and mental status related to fatigue and activity intolerance. |
| Encourage progressive activity through self-care and exercise as tolerated. Explain the need to reduce sedentary activities such as watching television and using social media in long periods. Alternate periods of physical activity with rest and sleep. | To gradually increase the patients tolerance to physical activity. |
| Teach deep breathing exercises and relaxation techniques. Provide adequate ventilation in the room. | To allow the patient to relax while at rest and to facilitate effective stress management. To allow enough oxygenation in the room. |
| Refer the patient to physiotherapy / occupational therapy team as required. | To provide a more specialized care for the patient in terms of helping him/her build confidence in increasing daily physical activity. |
Read Also: Recovering From Open Heart Surgery
How Is Congestive Heart Failure Treated
Doctors will assess the current health status of the patient to establish a baseline, and develop a long-term health plan. This may involve the optimization of medicines and therapies, adding new medication, or possibly enrollment in a clinical trial.
Stabilizing and/or reversing a patients condition often involves long-term, collaborative follow-up with a referring cardiologist or physician.
In serious situations, advanced therapies, which include mechanical solutions, a heart transplant, or hospice, may be offered.
Stage A Treatment Options
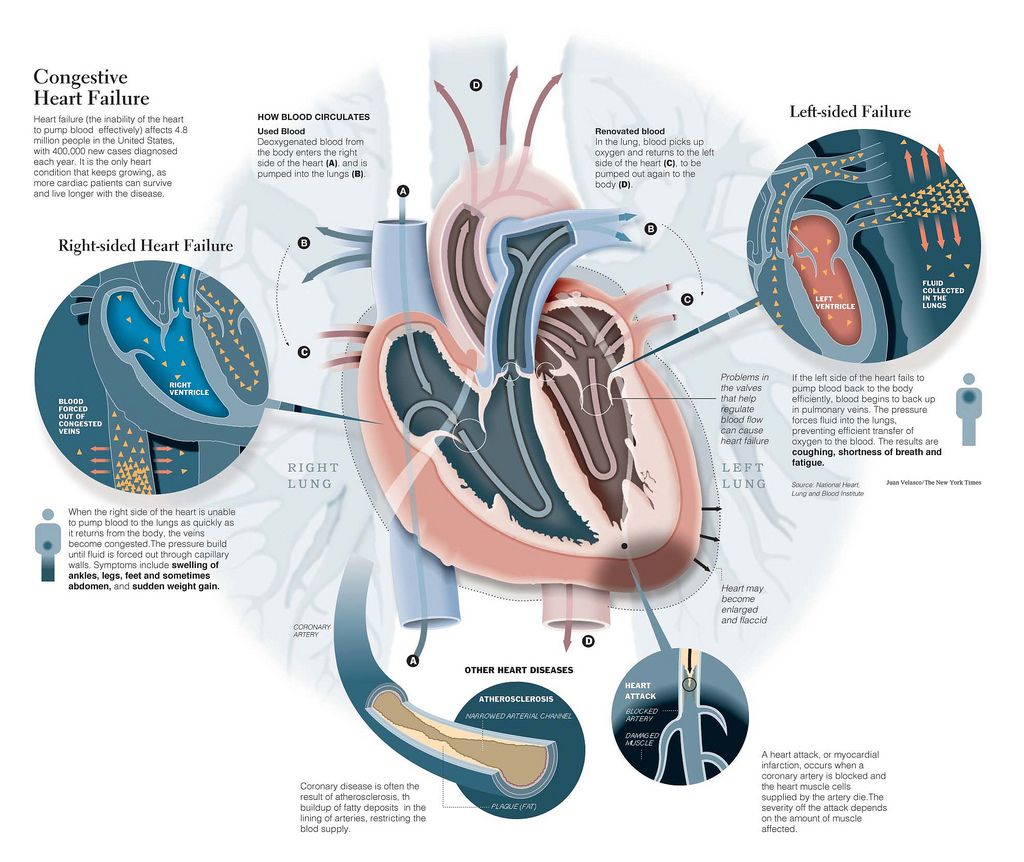
Treatment options in stage A mainly focus on promoting your overall health and disease prevention. If you meet the stage A criteria, your doctor will recommend lifestyle changes to slow or stop disease progression.
Heart Failure Doctor Discussion Guide
Also Check: High Heart Rate When Running
What Is The Outlook For People With Heart Failure
With the right care, heart failure may not stop you from doing the things you enjoy. Your prognosis or outlook for the future will depend on how well your heart muscle is functioning, your symptoms, and how well you respond to and follow your treatment plan.
Everyone with a long-term illness, such as heart failure, should discuss their desires for extended medical care with their doctor and family. An “advance directive” or “living will” is one way to let everyone know your wishes. A living will expresses your desires about the use of medical treatments to prolong your life. This document is prepared while you are fully competent in case you are unable to make these decisions at a later time.
Show Sources
