Smi: Unaware Of Possible Danger
The number of people who suffer an SMI and don’t realize it is alarming. A study in the Nov. 10, 2015, Journal of the American Medical Association looked at almost 2,000 people ages 45 to 84 who were free of cardiovascular disease.
After 10 years, 8% had myocardial scars, which are evidence of a heart attack. Most surprising was that 80% of these people were unaware of their condition. Overall, the prevalence of myocardial scars was five times higher in men than in women.
SMI and regular heart attacks share the same risk factors: smoking, being overweight, lack of exercise, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and diabetes. They can be just as dangerous, too. “SMI often leaves scarring and damage to the heart, which, combined with the fact that many people who have an SMI don’t seek immediate care, can further raise a person’s risk of a second and potentially more harmful heart attack,” says Dr. Plutzky. In fact, people who have an SMI and don’t get treatment have a three times greater risk of dying from coronary artery disease. “A silent heart attack is a loud signal your body sends that you have some kind of underlying health issue that needs attention,” says Dr. Plutzky.
Complications From A Heart Attack
Potential complications from a heart attack can vary widely. They can range from mild to life-threatening.
Some people experience a “minor” heart attack with no associated complications. This is also known as an uncomplicated heart attack.
Other people experience a major heart attack, which has a wide range of potential complications. This may require extensive treatment.
Whats The Difference Between A Cardiac Arrest And A Heart Attack
The phrases cardiac arrest and heart attack are often confused, however are different.If youre having a cardiac arrest you will be unconscious, not breathing or not breathing normally. Your heart has stopped pumping blood around your body and youll need CPR and medical attention immediately. During a heart attack youll be conscious and breathing, but experiencing chest pain or discomfort.A heart attack is a medical emergency and can lead to cardiac arrest so its important to seek medical attention straight away.
Also Check: Can Tylenol Cause Heart Palpitations
Testing: What To Expect
The hours following a heart attack can be scary and confusing. Your medical team may be incredibly busy and focused, and hard-pressed to explain everything thats happening.
You and your caregivers are sure to have questions. You may wonder about the tests and procedures that are being performed.
In the section below, youll find descriptions of the kinds of diagnostic procedures you may encounter as your doctors strive to identify the underlying causes of your heart attack.
Heart Attack Testing: Faq

Q: Why do I have to submit to a bunch of tests?A: Tests help the doctor determine if a heart attack occurred, how much your heart was damaged and what degree of coronary artery disease you might have. The tests screen your heart and help the doctor determine what treatment and lifestyle changes will keep your heart healthy and prevent serious future medical events.
Q: Whats the difference between invasive and non-invasive tests?A: Non-invasive cardiac tests measure your hearts activity through external imaging and electrocardiography. Invasive tests include drawing and testing samples of your blood, and inserting and threading a thin hollow tube called a catheter into a blood vessel to get an inside view.
Q: How can I learn more about the tests that may be performed?A: These diagnostic tests and procedures can reveal if you had a heart attack, how much damage was done and what degree of coronary artery disease you have.
Q: What types of treatment will I get after the hospital diagnoses my heart attack?A: If youve had a heart attack, you may have already had undergone certain procedures to help you survive your heart attack. Those same procedures can help to diagnose your condition. Such procedures include:
Read Also: Tylenol For High Blood Pressure
How Do I Know If Im Having A Heart Attack
Your arteries carry blood, oxygen and nutrients to the heart and to the rest of the body. A heart attack occurs when an artery of the heart is suddenly closed or blocked by a blood clot.
Although the closure happens suddenly, it often results from plaque that has built up in the arteries over time. This process is called atherosclerosis. It is also known as hardening of the arteries. When the artery closes, the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart drops suddenly and sharply. This lack of oxygen causes damage to the heart.
Read Also: How Does Heart Rate Affect Stroke Volume
What Can I Do To Recover After A Heart Attack
Take our quizexternal icon to see how much you know about cardiac rehabilitation.
If youve had a heart attack, your heart may be damaged. This could affect your hearts rhythm and its ability to pump blood to the rest of the body. You may also be at risk for another heart attack or conditions such as stroke, kidney disorders, and peripheral arterial disease .
You can lower your chances of having future health problems following a heart attack with these steps:
- Physical activityTalk with your health care team about the things you do each day in your life and work. Your doctor may want you to limit work, travel, or sexual activity for some time after a heart attack.
- Lifestyle changesEating a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing stressin addition to taking prescribed medicinescan help improve your heart health and quality of life. Ask your health care team about attending a program called cardiac rehabilitation to help you make these lifestyle changes.
- Cardiac rehabilitationCardiac rehabilitation is an important program for anyone recovering from a heart attack, heart failure, or other heart problem that required surgery or medical care. Cardiac rehab is a supervised program that includes
- Physical activity
- Education about healthy living, including healthy eating, taking medicine as prescribed, and ways to help you quit smoking
- Counseling to find ways to relieve stress and improve mental health
Also Check: Is Tylenol Bad For Your Heart
Things You Can Do During A Heart Blockage:
Can Oximeter Detect Heart Attack
If you dont have any idea about what Oximeter is, its function, benefits or unique features, then you have actually made it to the ideal place. Here you are going to find all the info you will need to know about Oximeter and why it is so crucial. Learn everything about Oximeters. Find at the end of the article, our best 3 choises for Oximeters.
Read Also: Apple Watch Heart Rate Monitor Accuracy
Q How Long Do I Need To Rest After A Cardiac Arrest
What Causes Silent Heart Attacks
Silent heart attacks are caused by the same things that cause traditional heart attacks. This happens when part of the heart muscle is damaged or dies because it hasnt received enough oxygen. This is often due to a blocked artery in the heart. Risk factors for silent heart attacks are also the same. They include:
- Smoking.
- Diabetes.
- Age risk increases for men older than 45 and for women older than 55 .
- High cholesterol.
- Family history of heart attack.
- Race African Americans, Mexican Americans, Native Americans and native Hawaiians are at greater risk.
- Lack of exercise.
- Gender women have silent heart attacks more often than men.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction
When Is Chest Pain A Heart Attack
Many people delay calling 999 when having chest pain as they often think it isnt serious. You should dial 999 immediately if your chest pain:
- is sudden
Or if:
- you become short of breath or start to feel sick.
If your chest pain doesnt match these characteristics and you arent experiencing any other heart attack symptoms, there may be other explanations for your chest pain. These include angina, indigestion or a strained muscle.If you frequently experience unexplained chest pain, book an appointment with your GP as its possible you may have an undiagnosed heart condition.
Heart Tests Your Doctor Might Order And What They Mean
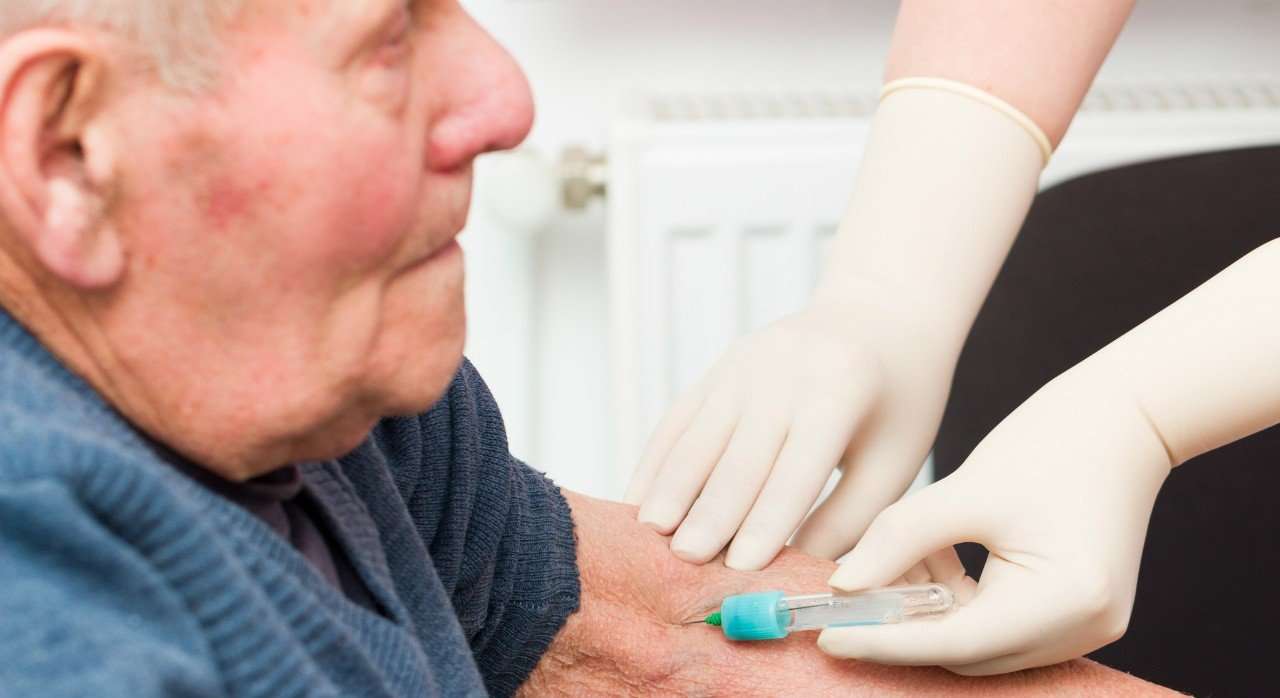
Heart disease patients and those suspected of having heart disease often face a battery of tests. Find out what you should expect if one of these noninvasive heart tests is in your future.
This post is part of a mini blog series dedicated to bringing awareness about your heart health during the American Heart Association’s national #HeartMonth. Miss the other stories? Catch up on 5 Eating Tips for a Healthy Heart, How To Check Your Blood Pressure at Home, How to Know If You’re Having a Heart Attack and Getting Heart Healthy with a Mediterranean Diet.
MRIs. CT scans. ECGs. There are a lot of test names you may hear when you visit your cardiologist, but what are all these tests and why do you need them?
If you have heart issues or are suspected of having a heart condition, your doctor may order an array of tests. But whats their purpose and what should you expect? Michigan Medicine cardiologist Venkatesh Murthy, M.D., offers a guide to the various noninvasive tests your doctor may order, including what theyre designed to do.
1. Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to produce images of your heart. This common test allows your physician to see how your heart is beating and how blood is moving through your heart. Images from an echocardiogram are used to identify various abnormalities in the heart muscle and valves. This test can be done while youre at rest or with exercise to elevate your heart rate .
Reasons for the test:
Reasons for the test:
Reasons for the test:
You May Like: Tylenol And High Blood Pressure
What Is A Heart Attack
A heart attack happens when something blocks the blood flow to your heart so it canât get the oxygen it needs.
More than a million Americans have heart attacks each year. Heart attacks are also called myocardial infarctions . “Myo” means muscle, “cardial” refers to the heart, and “infarction” means death of tissue because of a lack of blood supply. This tissue death can cause lasting damage to your heart muscle..
The Chances Of Survival:
Early detection of symptoms is crucial for surviving a heart attack. Half of the heart attacks happen outside of a hospital, which is why you need to be able to recognize the symptoms. According to figures from the recent study on the heart attacks, 92% of patients experienced chest discomfort, but only 27% of them understood that it was of a heart attack symptom and called the ER.
Recommended Reading: Acid Reflux And Tachycardia
Will Your Insurance Pay
Compared with the $760,000 it costs to treat a single heart attack patient, these tests are cheapbut some insurers won’t pay for them. “The system rewards doctors who do bypasses but doesn’t pay for prevention,” says Arthur Agatston, MD. Many companies are coming around: Most will pay for the stress EKG, blood glucose, and advanced cholesterol tests. Some will cover the gene tests and CIMT. Cardiac calcium scoring usually isn’t covered. Call your carrier beforehand to find out what it will pay for and what your co-payment will be.
How Are Heart Attacks Diagnosed
If you think you might be having a heart attack, you need to head to a hospital straight away. There, a doctor will assess your symptoms and check your vital signs blood pressure, pulse and temperature.
There are several tests that help indicate if youve had a heart attack, and whether damage was caused, such as:
- electrocardiogram electrical leads are placed on your chest, arms and legs to record the electrical signals travelling through your heart muscle
- CT scan or MRI scan
Read Also: Tylenol And Heart Rate
How A Heart Attack Affects Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the inside walls of your arteries as it circulates throughout the body. Just as heart rate changes are unpredictable during a heart attack, so too are blood pressure changes.
Because blood flow in the heart is blocked and a portion of heart tissue is denied oxygen-rich blood, your heart may not be able to pump as strongly as it normally does, thus lowering your blood pressure.
A heart attack may also trigger a response from your parasympathetic nervous system, causing your heart and the rest of your body to relax and not fight while your heart struggles to keep blood circulating. This can also cause a dip in blood pressure.
On the other hand, the pain and stress from the heart attack can raise the blood pressure during a heart attack.
Blood pressure-lowering medications, such as diuretics or angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, can keep your blood pressure low during a heart attack, too.
Risk factors for a heart attack include modifiable factors, such as your weight, as well as those beyond your control, such as your age. Some of the most common conditions that raise your risk for a heart attack include:
- advancing age
Checking Your Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the force of the blood against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps it around your body. There are two ways it’s measured:
Systolic blood pressure. This is the pressure in your arteries when your heart squeezes.
Diastolic blood pressure. It’s the pressure in your when your heart is relaxed, between heartbeats.
Normal blood pressure for an adult, when you’re at rest, is less than 120 over less than 80. The 120 is the systolic pressure. The diastolic pressure is 79.
High blood pressure, also called hypertension, is a blood pressure reading of 130/80 or higher.
Years of high blood pressure can stiffen and narrow your artery walls, which blocks the blood flow to your heart. It can lead to heart disease or heart attack.
Your blood pressure may go up or down depending on your age, heart condition, emotions, activity, and the medications you take. One high reading doesn’t mean you have high blood pressure. You need to measure it at different times while you’re resting to find out your typical numbers.
Also Check: Does Tylenol Help With Heart Palpitations
Other Common Signs And Symptoms
Pay attention to these other possible symptoms of a heart attack:
- Breaking out in a cold sweat
- Feeling unusually tired for no reason, sometimes for days
- Nausea and vomiting
- Light-headedness or sudden dizziness
- Any sudden, new symptoms or a change in the pattern of symptoms you already have
Not everyone having a heart attack has typical symptoms. If you’ve already had a heart attack, your symptoms may not be the same for another one. However, some people may have a pattern of symptoms that recur.
The more signs and symptoms you have, the more likely it is that you’re having a heart attack.
Classic Signs Of A Heart Attack

These are the most commonly expected symptoms of heart attack. If you suddenly experience these symptoms, call 911 or get to your nearest emergency room immediately:
- chest pain, pressure or discomfort that lasts for several minutes or disappears, then returns
- pain or discomfort that affects either or both arms
- back, neck or jaw discomfort
- stomach pain or discomfort
- feeling fatigued
- sweating
If you notice any or all of these symptoms, call 911 and seek emergency medical care immediately, even if you arent experiencing chest pain.
You May Like: Does Coffee Increase Heart Rate
You May Like: Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
What Do Troponin Test Results Mean
According to a 2017 diagnostic evaluation, a troponin level that exceeds the 99th percentile of the upper reference level indicates a heart attack. This means that 99% of people have a value of troponin below the upper reference range.
Additionally, an increase or decrease of 20% or more from the norm may also be consistent with a heart attack.
When considering the accuracy of troponin tests, it helps to understand the definitions of sensitivity and specificity.
Sensitivity refers to the likelihood a troponin test yields a positive result when an individual experiences a heart attack. Health experts refer to this as true positive.
Troponin T blood tests have a sensitivity of 79% and a specificity of 93%. Troponin I blood tests have a sensitivity of 83% and a specificity of 95%.
While it is possible for tests to yield false positive or negative results, troponin tests are usually highly accurate.
High-sensitivity troponin can have a false positive with a few conditions that are not heart attacks. This can happen with conditions that can damage the heart muscle.
Some conditions that can elevate troponin levels
They will also ask about an individuals medical history, focusing on heart attack risk factors. These include:
- age
- comorbidity
- lifestyle
An ECG measures the hearts electrical activity and is an essential tool for heart attack diagnosis. Doctors should perform an ECG within 10 minutes of a person presenting with heart attack symptoms.
