Discover Delicious Food Your Dog Deserves
A failing heart will become much larger than normal too, putting physical pressure on the lungs and windpipe as they become squashed inside your dogs chest. This is why most pups suffering from heart failure cough a lot, particularly at night or when they are picked up.
Because the heart isnt able to pump enough blood around the body, there wont be enough oxygen carried around to the other organs and tissues. In some cases, a dogs other internal organs can suffer from damage due to a lack of oxygen.
Diagnosis Of Stage C Heart Failure
At the time of diagnosis of stage C heart failure, the mean age was 10.4±1.9 years. Median body weight was 6.5 kg and median body condition score was 7 . Muscle condition was scored as normal , mild muscle loss , or moderate muscle loss . Thirty dogs did not have muscle condition score noted in the medical record. Pulmonary edema , pericardial effusion , pleural effusion , and ascites were recorded as clinical signs of congestive heart failure, with some dogs having multiple sites of fluid accumulation. Dietary recommendations were made to 33 dogs including use of a lowsodium diet , low sodium treats , and fish oil supplementation . Exercise restriction was recommended for 33 dogs.
Surgery For Heart Disease In Dogs
Sometimes, surgery might be required to correct an injury or fault inside the heart mechanism. For instance, if your dog has a torn valve, then surgery can be carried out to fix it. Some dogs might have a pacemaker fitted to regulate their heartbeat.
However, most cases of heart failure in dogs do not require surgery to treat, and surgical options would be limited and complex. The majority of dogs with heart failure are prescribed the medications listed above and advised on lifestyle changes to help manage their condition. Both a healthy lifestyle and daily medication will prevent further deterioration of your poochs heart and it will improve their quality of life so that they can continue to live a long and happy life.
Read Also: Lab Test For Heart Failure
What Happens In Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure begins when the heart is unable to provide the tissues with adequate oxygen and nutrients. Without adequate oxygen, the body’s cells become distressed and trigger a series of responses. Various hormones are released in an attempt to increase blood oxygen levels and blood circulation. These hormones conserve fluid in an effort to increase blood volume and the output of blood and oxygen by the heart. For several months, these compensatory responses help the situation and the dog has few observable clinical signs.
Eventually the increased fluid retention becomes a detriment as more and more fluid leaks out of capillaries and into the lungs, abdomen, and other body tissues. Fluid in the lungs is called pulmonary edema, fluid below the skin is called peripheral or limb edema, and fluid in the abdomen is called ascites. When these are present, congestive heart failure is present. Left-sided congestive heart failure is generally associated with MVI and most commonly results in pulmonary edema and coughing. However, within a short time, heart failure will continue to progress and bilateral heart failure will follow.
Treatment For Congestive Heart Failure In Dogs
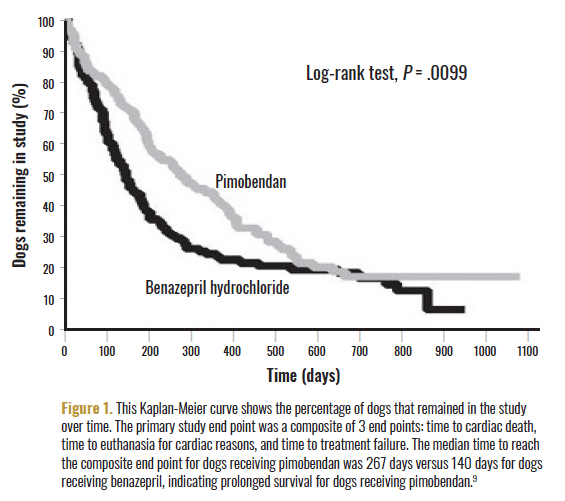
Treatment depends on the underlying heart disease, along with the severity. There is usually no cure for CHF, but there are effective treatments to ensure a good quality of life. If the cause of CHF is a congenital abnormality like a PDA, surgical correction may help to reverse heart failure if performed in a timely fashion. The goal when treating CHF is to reduce fluid buildup and maximize the amount of blood being pumped to the lungs and the rest of the body.
Here are some of the medications, supplements, and diets that may be recommended:
-
ACE inhibitors : Help reduce blood volume and pressure, relieve stress on the heart, and slow the deterioration of the heart muscles.
-
Diuretics: Help stimulate the kidneys to remove excess fluid buildup in the lungs and abdomen.
-
Vasodilators and positive inotropic drugs: Vasodilators help relax blood vessels and decrease pressure on the heart, allowing it to pump blood more easily. Positive inotropes increase the force with which the heart muscle beats, allowing the heart to pump more blood to the lungs and the rest of the body.
-
Nutrition: Limiting the amount of sodium in your dogs diet can decrease fluid buildup in the body. Supplements like vitamin B, taurine, and carnitine, along with antioxidants like coenzyme Q10 and vitamin E, can also help. Finally, a diet that allows your dog to maintain a healthy weight is very important for heart health.
Read Also: What Is Ischaemic Heart Disease
How Does A Pacemaker Work
Once surgically implanted into the body, the pacemaker sends out electrical impulses to the heart muscle helping to synchronize the two lower heart chambers, so they pump blood more efficiently.
Weve found that a CRT pacemaker can improve peoples quality of life, said Dr. Hsing.
CRT pacemakers help a persons heart pump blood better, which can allow them to do activities easier, and can decrease the work of the heart muscle, which can help them live longer.
You May Like: How Long Does Open Heart Surgery Usually Take
Your Veterinarian May Recommend One Or More Of The Following Pharmaceutical Treatments:
- Diuretics are medications help to remove excess fluid buildup from the lungs or abdomen .
- ACE Inhibitors, or inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme, are a group of medications that open up constricted blood vessels and are used primarily in the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure as a way to help the heart pump blood more effectively. .
- Inodilators, are medications that both increase myocardial contractility and open up constricted blood vessels, reducing the workload on your dogs weakened heart .
- Beta-Blockers, in some cases, vets may also prescribe beta-blockers to support efforts to control the heart rate.
These medical interventions effectively treat the symptoms of the disease, vastly improving the quality of the animals remaining life, but do nothing to prevent the progression of the illness.
Its likely that your dog will be put on long-term medication after being diagnosed with compromised heart function, so your visits to the veterinarian may need to be more frequent at first, but once your dogs condition has stabilized with treatment, you can expect to resume a more regular and potentially less frequent visit schedule as your dog shows improvement.
Recommended Reading: Does Hydralazine Lower Heart Rate
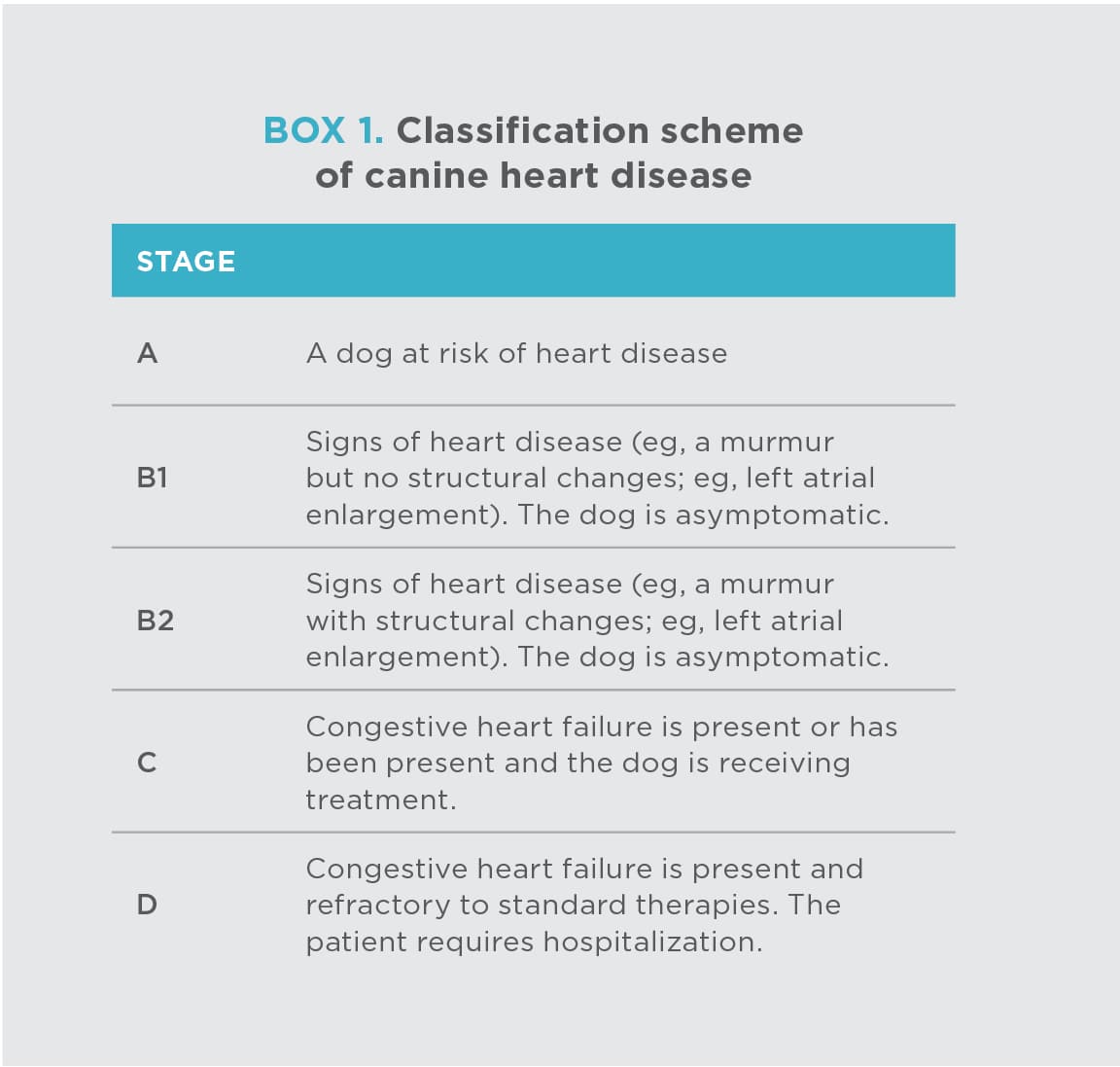
What Are The Stages Of Chf In Dogs
Veterinarians often refer to the condition of a dogâs CHF in four stages, which can be categorized from A to D, Dr. McCullough explains.
A dog with a predisposition or high risk of developing heart failure but has no heart disease or symptoms is in Stage A.
In Stage B, thereâs structural evidence of heart disease, but a dog isnât showing symptoms. Itâs broken into two substages: In B1, your dog doesnât have heart enlargement, while in B2, they do.
In later stages of CHF, symptoms begin to show. Stage C indicates that a dog has symptoms of heart disease, and Stage D is met when your dog has ongoing symptoms that are unresponsive to therapy.
Progressive Symptoms Of Chf In Dogs
In contrast to the long-time lag between Class I and Class II symptoms the illness progresses quickly from Class III to Class IV, so a dog that seemed healthy, active and symptom-free, may suddenly enter a critical phase where the condition requires extensive medical and surgical treatment to manage in order to preserve the life of the dog.
If you notice any of these telltale signs & symptoms of congestive heart failure, make sure to have your pet examined by a veterinarian as soon as possible.
Don’t Miss: Congestive Heart Failure What Is It
Do Dogs Have Heart Attacks
Although it is very rare, the unexpected and sudden death of dogs from heart disease is possible. Some of the main risk factors that increase a dogs chances of having a heart attack include obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, and serious bacterial infections.
If you believe your dog is having a heart attack take them to the nearest emergency care facility as soon as possible. There is a version of CPR that can be performed on dogs, however, it requires special training to do it properly. If done incorrectly, CPR can result in further injuries to your dog and delay getting proper medical attention from a veterinarian.
Causes Of Congestive Heart Failure In Dogs
There are many possible causes of congestive heart failure in dogs but the most common is myxomatous mitral valve disease , also called chronic mitral valve disease, degenerative mitral valve disease, mitral insufficiency, or endocardiosis.
The mitral valve, also known as the bicuspid or left atrioventricular valve, is on the left side of the heart and acts as the doorway between the left atrium and the left ventricle. MMVD occurs when the doorway fails to close, which results in blood leaking through this valve. Over time, it results in left-sided congestive heart failure due to a decreased ability for the left side of the heart to pump oxygen-rich blood to the body. The cause of mitral valve disease is unknown, but there does seem to be a strong genetic component. Many small-breed dogs have a genetic predisposition for mitral valve disease as a cause of congestive heart failure.
In large-breed dogs, the most common inherited form of heart disease is dilated cardiomyopathy , characterized by the heart muscle becoming weak and unable to properly contract. This causes the heart to dilate. Some examples of dogs predisposed to DCM include Doberman Pinschers, Boxers and Great Danes.
Other causes of CHF in dogs include:
-
Heart valve disease
You May Like: Heart Rate For Infants
The Signs Of A Dog Dying Of Heart Failure
If your dog is in the final stages of their heart failure, you may be curious about the typical signs of a dog suffering in their CHF.
To help you make the best decision for your furry friend, lets list some of the signs of a dog dying from their heart failure.
- Frequent coughing
- Coughing up foam, or bloody foam
- Labored breathing
- Weakness, or inability to exercise
- Fainting episodes
- Blue, purple, or muddy gums
- Constant panting
If your dog is experiencing any of the above symptoms, it may be time to discuss quality of life with your veterinarian.
How Veterinarians Diagnose Congestive Heart Failure In Dogs
Diagnosing congestive heart failure will start with listening to the heart and lungs with a stethoscope. Most dogs will have a heart murmur which will be graded in severity from 1 to 6.
-
Grade 1: Very soft murmur, often difficult to hear
-
Grade 2: Soft murmur but readily heard
-
Grade 3: Moderately loud murmur
-
Grade 4: Loud murmur
-
Grade 5: Very loud murmur that can be heard with the stethoscope, barely touching the chest. The vet can feel a vibration through the chest wall over the heart
-
Grade 6: Very loud murmur that can be heard with the stethoscope of the chest . The vet can feel a vibration through the chest wall over the heart
If your veterinarian suspects CHF, he or she will likely want to perform a chest X-ray/radiograph to check for heart enlargement or evidence of fluid on the lungs . Electrocardiogram may also be used to assess the rate and rhythm of the heart.
At this point, your veterinarian may refer you to a veterinary cardiologist for more specialized testing such as an echocardiograph or ultrasound of the heart. An echocardiograph is the most useful tool to identify the source of a murmur, the likely cause of CHF, and a measurement of the hearts ability to pump blood.
You May Like: Heart Attack Sign Women
What Is Heart Failure In Dogs
Heart failure in dogs is simply a shorthand way of saying that your poochs heart is failing to pump blood throughout the body as well as it should. This leads to the dogs circulatory system becoming congested. Many cases are slow-onset, meaning they appear slowly over time and gradually worsen. Heart failure is not a disease in itself, but it is often caused by heart disease.
When a dogs heart is failing, some blood will be leaking back through the different chambers of the heart into the lungs or into the body and backing everything up, a bit like a traffic jam. Because the blood isnt moving correctly, the heart has to work much harder to try and pump it around the body, which means a pups heart rate and blood pressure will become much higher than normal. It will also cause fluid to leak into other areas of the body or into the lungs.
Cbd Oil For Dogs And Heart Murmur Life Expectancy
CBD Oil is for dogs is typically used for dog heart murmurs, but not as a cure all medicine. It is a health supplement that promotes good health and a healthy balance in the body. CBD oil is used to activate the Endocannabinoid receptors inside of your dogs nervous systems which allows them to stay calm, have less anxiety and control inflammation. The most important role CBD oil can play for dogs with heart murmur is its anti-inflammatory properties which reduce swelling and inflammation in the heart.
Dog heart murmur life expectancy varies on the age of your dog and the severity of the condition. If it leads to dog heart failure than the life expectancy will vary. CBD oil will not ensure that your dogs life expectancy will be prolonged, but it will help manage the pain and lower the symptoms making life easier for your dog. It is a supplement that will help with relief during this hard time.
Read Also: What Is The Recovery Time For Open Heart Surgery
How Is Dcm Diagnosed
Before a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy is made, several tests are performed to assess different aspects of heart function.
Auscultation. Listening to the chest with a stethoscope allows your veterinarian to identify murmurs due to the improper closure of heart valves. The murmur’s location and intensity help determine its significance. Heart rhythm is also assessed during auscultation, and if there are concerns, your veterinarian may simultaneously palpate or feel the pulse to determine its strength and rhythm. Auscultation is also used to evaluate the lungs.
Blood and urine tests. Liver and kidney function can be a concern, because these organs are often impaired in heart disease.
ProBNP. This is a blood test that measures a specific protein level in the body that changes with structural changes of the heart and heart disease. It is not as reliable a test as some of the others outlined below to indicate the source or an accurate assessment of the severity of the condition.
Chest radiographs . Chest radiographs allow your veterinarian to examine the lungs and measure the size and shape of the heart. Dilated cardiomyopathy usually causes obvious enlargement of the heart, particularly the left side.
Electrocardiogram . This is an assessment based on the electrical activity of the heart. It allows your veterinarian to accurately determine heart rate and to diagnose any abnormal rhythms.
Summary Of Congestive Heart Failure In Dogs
Congestive Heart Failure in dogs is fairly common, affecting 75% of senior dogs. While there is no cure, medication and lifestyle changes can help manage the condition. As its not always easy to detect in its early stages, prevention is important proper diet, exercise, and weight maintenance are key for canine cardiovascular health. Be aware of the signs and symptoms so you can seek help as soon as you suspect CHF could be an issue, and stay up to date on your annual vet visits.
Don’t Miss: How To Take Your Own Heart Rate
After The Diagnosis Of Advanced Heart Failure
Fortyone of the 54 dogs were reevaluated at our hospital after the diagnosis of AHF. The median number of reevaluations after diagnosis of advanced heart failure was 1 . A median of 2 medication adjustments were made after the diagnosis of advanced heart failure. These included changes in furosemide , and ACEI . Discontinuation of the ACEI was recommended for 2 dogs because of worsening azotemia. Enalapril was the most commonly used ACEI , followed by benazepril , and lisinopril . Other medications added after the diagnosis of AHF included sildenafil , torsemide , digoxin spironolactone , and aldactazide/hydrochlorothiazide . Many dogs were receiving multiple diuretics: 1 , 2 , 3 , or 4 . The number of dogs and the ultimate dosage of medications are shown in Table 2. The total number of medications ranged from 210 . Thirtyeight of the 54 dogs were receiving 5 medications per day.
Types Of Heart Failure In Dogs
There are several types of heart failure in dogs, which are categorised according to the area of the heart thats affected.
The first type is known as left-sided heart failure. This is when the mitral valve fails. Its so named because the mitral valve is on the left-hand side of your poochs heart, separating the atrium and the ventricle. When this valve fails, blood can leak back through it and into your dogs lungs, causing pulmonary oedema. If left untreated, this left-sided heart failure can progress until the whole heart is affected.
The other type is right-sided heart failure. Right-sided heart failure is caused by a failure of the tricuspid valve, which is on the right side of your dogs heart separating the ventricle and the atrium. When the valve fails, blood leaks back through it into the atrium where it can then enter the systemic circulation which is the main circulatory system of your dogs body. As blood enters back into the body and congests circulation, it causes fluid to build up in other areas of the body. This often leads fluid to build up in the abdomen, a condition known as ascites, which causes a swollen belly. Another commonly affected area is your dogs limbs, where fluid can leak from their veins causing their legs to swell in a condition called peripheral oedema.
A third type of heart failure is biventricular failure, which occurs when both the valves in the left and right-hand side of the heart are not working properly.
Recommended Reading: How To Diagnose Heart Failure
