Influences On Bnp Levels
Many medications used to treat heart failure reduce natriuretic peptide concentrations.813 Therefore, many patients with chronic stable heart failure will have BNP levels in the normal diagnostic range . However, digoxin and some beta blockers appear to increase natriuretic peptide concentrations.1416 Exercise causes a short-term increase in BNP levels,17 although only small changes are detectable one hour after exercise.18 No circadian variation has been reported when BNP is measured every three hours for 24 hours,19 and there is less hourly variation with BNP than with ANP.20
Echocardiographic And Natriuretic Peptide Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction Diagnostic Score
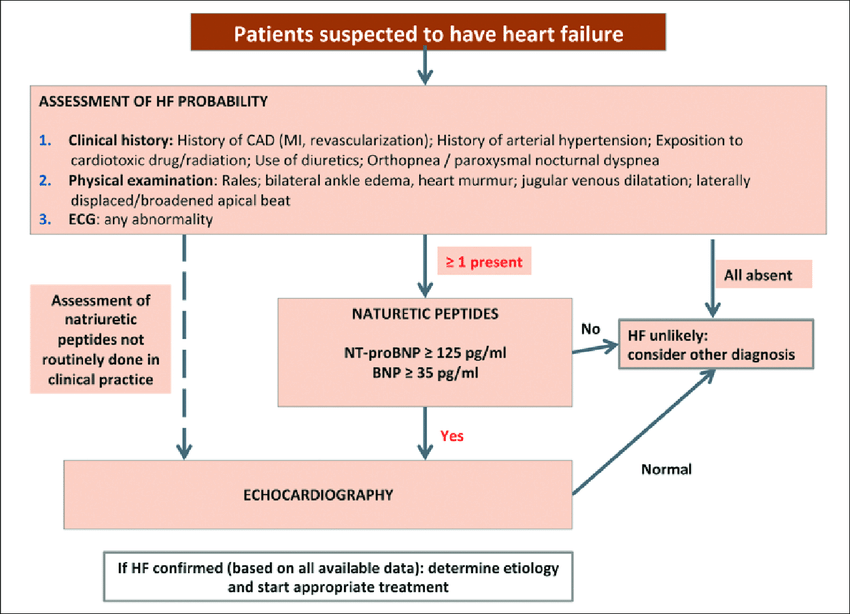
There is no single non-invasive diagnostic criterion for HFpEF so we recommend a combination of echocardiographic measurements of cardiac structure and function, and NP levels. Some may already be available from Step 1.
Many of these measurements are continuously distributed within a population, from normal to possibly abnormal and to overtly abnormal values. Diagnostic cut-points may vary according to age, gender, body weight, renal function, and the presence of atrial fibrillation. To take account of these factors, we recommend the use of major and minor diagnostic criteria according to the severity of an abnormality and the presence of modifiers. Major criteria have been selected for their high specificity, while minor criteria should be more sensitive. Cut-points were derived particularly from studies that compared echocardiographic parameters against invasive haemodynamic data.,,
Echocardiographic measurements of function and morphology
In Step 1 we recommend standard echocardiography, at least to assess LVEF and LV diameter. In Step 2 we recommend more detailed echocardiographic measurements . These could all be obtained during a single study. The echocardiographic criteria in the HFAPEFF score, listed below, mirror consensus recommendations for the diagnosis of LV diastolic function.
Getting A Medical Exam
Also Check: Does Ibs Cause Heart Palpitations
Predictors Of Poor Outcome And High Mortality Rate
In HF patients, exercise intolerance characterized by the reduction in peak VO2/VO2 max capacity has been considered as the primary predictor of mortality and morbidity . In addition, higher age, increased blood urea nitrogen, creatinine and heart rate, lower systolic pressure and serum sodium, presence of dyspnea at rest, lack of long-term treatment with a -blocker, male gender and lower body mass index and hemoglobin levels have been identified as independent predictors of mortality. The following values have been shown to predict the increased mortality in inpatient settings/hospitals .
-
Serum urea > 15 mmol/L
-
Systolic blood pressure < 115 mmHg
-
Serum creatinine > 2.72 mg/dL
-
N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide > 986 pg/mL
-
Left ventricular ejection fraction < 45%
Some of the other predictors of relative poor outcome in chronic heart failure are given below.
-
High NYHA functional class
-
Reduced left ventricular ejection fraction
-
Third heart sound
-
Increased pulmonary artery capillary wedge pressure
-
Reduced cardiac index
-
Raised plasma catecholamine and natriuretic peptide concentrations
Left Ventricular Mass Index And Relative Wall Thickness
Increased LV diastolic wall thickness in a non-dilated heart implies that the patient has LVH. It develops first in the basal segments of the ventricular septum, and a wall thickness 12mm at that site is common in elderly people. Localized septal hypertrophy may be a consequence of abnormal ventriculararterial coupling but it is not sufficient to indicate that there is significant global LV remodelling or hypertrophy.
Left ventricular geometry is often classified using relative wall thickness , calculated as twice the LV posterior wall thickness divided by the LV internal diameter at enddiastole , and using left ventricular mass index normalized to body surface area or height. Four patterns are described: normal , concentric remodelling , concentric hypertrophy , and eccentric hypertrophy .,, In patients with HFpEF, both concentric LVH and concentric remodelling can be observed.
The absence of LVH on echocardiography does not exclude HFpEF. We therefore recommend the finding of concentric hypertrophy as a major criterion, or any one of a lesser degree of LVH, RWT, and LV end-diastolic wall thickness as a minor criterion.,,
Recommended Reading: Reflux And Palpitations
What Causes Heart Failure
Heart failure can be caused by many medical conditions that damage the heart muscle. Common conditions are:
- Coronary artery disease affects the arteries that carry blood and oxygen to the heart . The normal lining inside the arteries breaks down, the walls of the arteries become thick, and deposits of fat and plaque partially block the flow of blood. Over time, the arteries become very narrow or completely blocked, which causes a heart attack. The blockage keeps the heart from being able to pump enough blood to keep your organs and tissues healthy. When arteries are blocked, you may have chest pain and other symptoms of heart disease.
- Heart attack. A heart attack happens when a coronary artery suddenly becomes blocked and blood cannot flow to all areas of the heart muscle. The heart muscle becomes permanently damaged and muscle cells may die. Normal heart muscle cells may work harder. The heart may get bigger or stiff .
- Cardiomyopathy. Cardiomyopathy is a term that describes damage to and enlargement of the heart muscle not caused by problems with the coronary arteries or blood flow. Cardiomyopathy can occur due to many causes, including viruses, alcohol or drug abuse, smoking, genetics and pregnancy .
- Tobacco and illicit drug use.
- Medications. Some drugs used to fight cancer can lead to heart failure.
Calculating And Interpreting The Hfapeff Score
The score has functional, morphological, and biomarker domains. Within each domain, a major criterion scores 2 points or a minor criterion 1 point . Each domain can contribute maximally 2 points, if any major criterion from this domain is positive, or 1 point if no major but any minor criterion is positive. If several major criteria within a single domain are positive, this domain still contributes 2 points and if no major but several minor criteria are positive the contribution still is 1 point. Major and minor criteria are not additive in a single domain. Points are added only when they come from different domains.
Step 2 : Echocardiographic and natriuretic peptide heart failure with preserved ejection fraction workup and scoring system .
For example, 2 major and 1 minor criteria, all in the functional domain, will lead to a total score from that domain of 2 points. The total score would be 5, if at least one minor criterion and one major criterion would be present coming from the morphological and biomarker domains, respectively. It is important to understand that not all parameters from each domain need to be recordable . The HFA-PEFF score can be calculated even if not all parameters are obtained, which adds to the practical utility of the score.
Read Also: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
Living With Heart Failure
Heart failure has no cure. Youll probably have to follow a treatment plan for the rest of your life. This treatment plan can include medicines, lifestyle changes, guides on activity levels, and keeping your appointments. Your restrictions will depend on how severe your heart failure is.
The following tips can help you manage your heart failure at home.
- Follow a diet thats healthy for your heart. You may need to make changes to your diet in order to stay healthy. Many doctors recommend the DASH diet. Avoid eating too much salt or too many salty foods . Salty and high-sodium foods can cause your body to retain water.
- Talk to your doctor before using salt substitutes. They often contain potassium and may not be good for your health. This will depend on your kidney function and what medicines youre taking. Some people need extra potassium, but others dont.
- Keep your blood pressure under control. High blood pressure strains your heart and further weakens it.
- Ask your doctor to recommend an exercise program for you. Try to reduce the stress in your life and get plenty of sleep. If you smoke, quit! If youre overweight, talk to your doctor about how to lose weight safely.
- Talk to your doctor before you take any over-the-counter medicines. Common arthritis medicines such as naproxen and ibuprofen can cause fluid retention.
Diagnosis And Evaluation Of Heart Failure
More recent articles on heart failure and cardiomyopathy are available.
MICHAEL KING, MD, JOE KINGERY, DO, and BARETTA CASEY, MD, MPH
University of Kentucky College of Medicine, Lexington, Kentucky
Am Fam Physician. 2012 Jun 15 85:1161-1168.
Patient information: A handout on this topic is available at .
Heart failure is a common clinical syndrome characterized by dyspnea, fatigue, and signs of volume overload, which may include peripheral edema and pulmonary rales. There is no single diagnostic test for heart failure therefore, it remains a clinical diagnosis requiring a history, physical examination, and laboratory testing. Symptoms of heart failure can be caused by systolic or diastolic dysfunction. Appropriate diagnosis and therapy for heart failure are important given the poor prognosis. Survival is 89.6 percent at one month from diagnosis, 78 percent at one year, and only 57.7 percent at five years.1
Heart failure has an estimated overall prevalence of 2.6 percent.2 It is becoming more common in adults older than 65 years because of increased survival after acute myocardial infarction and improved treatment of coronary artery disease , valvular disease, and hypertension.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Also Check: Heart Palpitations Prednisone
How Is Chf Diagnosed
After reporting your symptoms to your doctor, they may refer you to a heart specialist, or cardiologist.
The cardiologist will perform a physical exam, which will involve listening to your heart with a stethoscope to detect abnormal heart rhythms.
To confirm an initial diagnosis, a cardiologist might order certain diagnostic tests to examine your hearts valves, blood vessels, and chambers.
There are a variety of tests used to diagnose heart conditions. Because these tests measure different things, your doctor may recommend a few to get a full picture of your current condition.
Stage D And Reduced E
Patients with Stage D HF-rEF have advanced symptoms that do not get better with treatment. This is the final stage of heart failure.
Stage D treatment
The usual treatment plan for patients with Stage D heart failure includes:
- Treatments listed in Stages A, B and C.
- Evaluation for more advanced treatment options, including:
- Heart transplant.
- Research therapies.
Don’t Miss: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
Life Expectancy With Congestive Heart Failure
The life expectancy of someone with congestive heart failure depends on the type of heart failure, the cause, the stage of the disease, and how effective treatment is.
When heart failure results from cardiomyopathy or coronary artery disease, a person typically has a less positive outlook than someone with heart failure in its earliest stage.
Undergoing Tests For Heart Failure
You May Like: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Other Causes Of Heart Failure
Pulmonary hypertension and heart failure
Heart failure can be caused by pulmonary hypertension . This condition can damage the right side of your heart, leading to heart failure. In some cases, the pulmonary hypertension itself is caused by an existing heart condition.
- Find out more about pulmonary hypertension on NHS Choices and PHA UK.
Amyloidosis
Amyloidosis happens when abnormal proteins, called amyloid, build up in organs and tissues. This affects how your organs work. If amyloidosis affects the heart it’s called cardiac amyloidosis or stiff heart syndrome and can lead to heart failure.
- Read more about amyloidosis treatment.
Diagnosis Of Heart Failure
To diagnose heart failure, physicians take a complete medical history, conduct a physical exam, and may order a variety of tests, including blood work and imaging tests. Patients are usually referred to a cardiologist for management of heart failure.
During the appointment, they will listen to the heart and lungs with a stethoscope for signs of the heart not working properly or sounds of fluid buildup in the lungs. They will also measure heart rate, blood pressure, body weight, and look for swelling in the ankles, feet, legs, and veins in the neck.
Don’t Miss: Thrz Calculator
Stages Of Heart Failure
When you’re diagnosed with heart failure, your doctor will usually be able to tell you what stage it is.
The stage describes how severe your heart failure is.
It’s usually given as a class from 1 to 4, with 1 being the least severe and 4 being the most severe:
- class 1 you don’t have any symptoms during normal physical activity
- class 2 you’re comfortable at rest, but normal physical activity triggers symptoms
- class 3 you’re comfortable at rest, but minor physical activity triggers symptoms
- class 4 you’re unable to carry out any physical activity without discomfort and may have symptoms even when resting
Knowing the stage of your heart failure will help your doctors decide which treatments they think are best for you.
Page last reviewed: 26 October 2018 Next review due: 26 October 2021
Campaigning For Improved Heart Failure Care
Despite the focus on BNP testing as an important part of heart failure care, the test is still not universally or even routinely available across the UK.
That is why in 2020 we worked with healthcare professionals to produce a report and launched a campaign highlighting the main barriers to improving heart failure diagnosis and care in the UK. The report called for an improved awareness of heart failure as a long-term condition and suggested key areas for change to deliver high quality and consistent heart failure care across the UK, including equal access to BNP testing.
Also Check: Claritin Heart Racing
Clinical Recognition Can Be Challenging
Clinical recognition of HF can be challenging, especially for primary care providers.2 The diagnostic criteria for evaluating heart failure are based on parameters established by clinical experts. There are guidelines established to facilitate the decision making of providers in their routine practice. The guidelines provide up to date clinical information that can help in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with heart failure. Ultimately, decisions on individual patient care are made by the patient and their provider.1
Since the 1970s, multiple sets of diagnostic criteria have been developed with varying sensitivities. The Framingham, Duke, Gothenburg, ESC, and Boston criteria were established before noninvasive techniques for assessing systolic and diastolic dysfunction became widely available. The criteria were designed to assist in the diagnosis of heart failure. All of these criteria have proven helpful in guiding healthcare providers, particularly in diagnosing advanced or severe heart failure.4 Today, the Boston criteria are considered preferable when making a diagnosis of heart failure.5
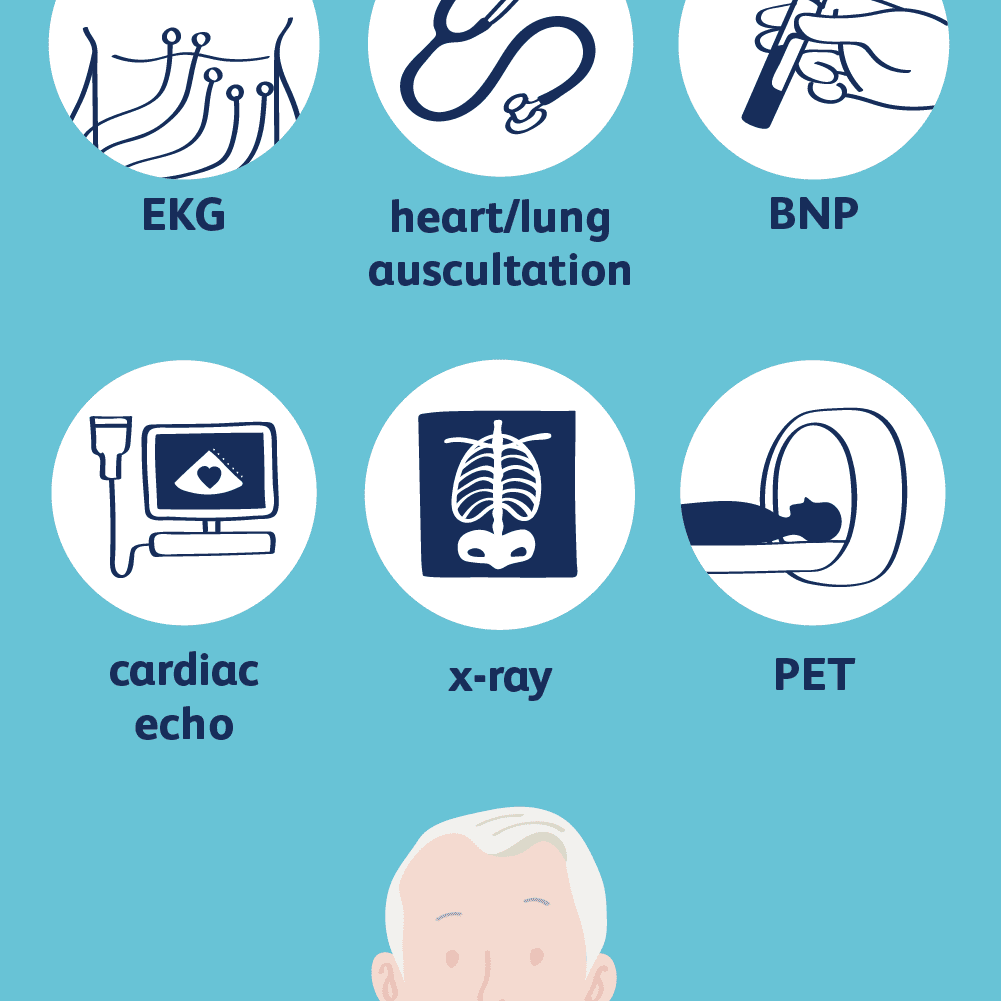
Tests For Heart Failure
Tests you may have to diagnose heart failure include:
- blood tests to check whether there’s anything in your blood that might indicate heart failure or another illness
- an electrocardiogram this records the electrical activity of your heart to check for problems
- an echocardiogram a type of ultrasound scan where sound waves are used to examine your heart
- breathing tests you may be asked to blow into a tube to check whether a lung problem is contributing to your breathlessness common tests include spirometry and a peak flow test
- a chest X-ray to check whether your heart’s bigger than it should be, whether there’s fluid in your lungs , or whether a lung condition could be causing your symptoms
You can read more about tests for heart conditions on the British Heart Foundation website.
Recommended Reading: Ibs And Heart Palpitations
