How Is Congestive Heart Failure Different From Heart Failure
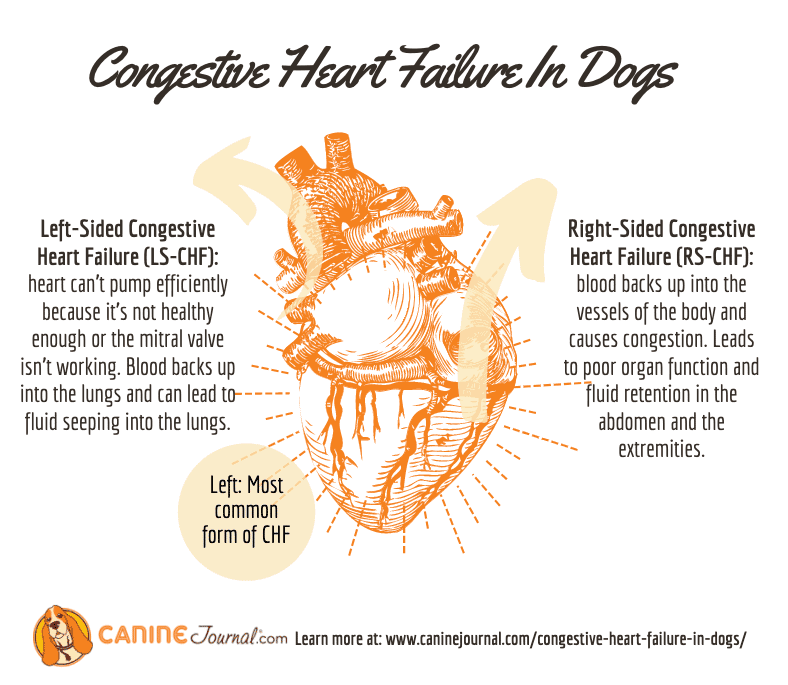
Congestive heart failure in dogs is often used to describe all canines with heart failure. However, its real definition is the fluid build-up in various body cavities, specifically the chest and abdomen.
This is brought on by the blood backing up into the lungs. As a result, proper oxygen flow throughout the body is curtailed. Other affected body organs also start to function abnormally.
Two Main Types Of Heart Failure
Typically, there are two types of heart failure.
The most common is dilated cardiomyopathy, where the heart increases in size-stretching the heart walls thin, thus decreasing the efficiency of pumping blood throughout the body.
The second, rarer kind is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, where the heart walls thicken, which also reduces the ability of the heart to sufficiently supply blood. Congestive heart failure may develop over years, months or even as short as a few weeks.
Unlike the human heart attack, the canine heart does not abruptly stop. Instead, as the heart function declines, the body relies on other organs to strain themselves to make up for the decreased heart activity. When the heart can no longer pump enough oxygenated blood to meet the body’s needs, heart failure occurs.
What Clinical Signs Should I Expect
The most common clinical sign of congestive heart failure is persistent coughing accompanied by difficulty breathing. This is due mainly to pulmonary edema or the accumulation of fluid in the lungs. The enlarged heart will also push against the trachea, causing irritation that can induce a cough.
“The most common clinical sign of congestive heart failure is persistent coughing accompanied by difficulty breathing.”
Many dogs with CHF will tire out more easily, have reduced stamina, and do not engage in playing or walking as they once did. Coughing when at rest or sleeping, excessive panting, persistent loss of appetite, a swollen belly, and pale or bluish gums are also signs associated with heart failure. The dog will develop generalized weight loss and muscle wasting due to the effects of CHF on other body systems. If any of these signs develop in a pet with a heart murmur, notify your veterinarian immediately.
Read Also: Why Does Left Arm Go Numb During Heart Attack
Causes Of Congestive Heart Failure In Dogs
There are many possible causes of congestive heart failure in dogs but the most common is myxomatous mitral valve disease , also called chronic mitral valve disease, degenerative mitral valve disease, mitral insufficiency, or endocardiosis.
The mitral valve, also known as the bicuspid or left atrioventricular valve, is on the left side of the heart and acts as the doorway between the left atrium and the left ventricle. MMVD occurs when the doorway fails to close, which results in blood leaking through this valve. Over time, it results in left-sided congestive heart failure due to a decreased ability for the left side of the heart to pump oxygen-rich blood to the body. The cause of mitral valve disease is unknown, but there does seem to be a strong genetic component. Many small-breed dogs have a genetic predisposition for mitral valve disease as a cause of congestive heart failure.
In large-breed dogs, the most common inherited form of heart disease is dilated cardiomyopathy , characterized by the heart muscle becoming weak and unable to properly contract. This causes the heart to dilate. Some examples of dogs predisposed to DCM include Doberman Pinschers, Boxers and Great Danes.
Other causes of CHF in dogs include:
-
Heart valve disease
Nutrition For Chf In Dogs

Nutritional management and diet may be used in addition to medical therapies. Nutrition tailored to your dogs underlying heart condition may help slow the progression of heart disease and improve quality of life. Nutritional goals, diet recommendations and supplements should always be discussed with your primary veterinarian, veterinary cardiologist or potentially a veterinary nutritionist.
Specific dietary supplements such as fish oil/omega fatty acids, taurine and L-carnitine may be considered to decrease inflammation, help manage arrhythmias and improve heart function.
Other recommendations may include weight management, maintaining muscle mass and eating a balanced diet. Again, your veterinarian, cardiologist, and/or veterinary nutritionist should be consulted prior to any diet changes or addition of any supplements.
Also Check: Why Would My Heart Rate Be High
How Long Can Dogs Live With Heart Failure
The prognosis for heart failure in dogs is poor. On average, dogs with this condition can survive for an average of 612 months.
But early detection and treatment of heart failure in dogs can extend the lives of affected canines. Some dogs were able to live for 3 years after being diagnosed with heart failure.
ukadmin
Signs Symptoms And Treatment For Dilated Cardiomyopathy In Dogs
January 20th, 2015 | Posted in Medical Articles
Summary:
Dilated cardiomyopathy is a disease of predominantly large and giant breed dogs that results in progressive heart muscle dysfunction, chamber dilation, and eventual congestive heart failure or death of affected patients. The exact cause of the condition is unknown but genetic factors are presumed to play a role. There is no known effective preventative strategy for the condition. Treatment for affected individuals may improve their quality of life, delay the onset of heart failure symptoms, and potentially improve life expectancy. Treatment is not curative, however, and most affected individuals eventually die from the disease.
Description:
Dilated Cardiomyopathy is a condition characterized by weakness of the heart muscle that eventually leads to enlargement of the heart chambers and complications of congestive heart failure, irregular heart rhythms , and/or sudden death in affected individuals. The condition is infrequently diagnosed in dogs and is rare in cats. It is most common in large or giant breed dogs , with Cocker Spaniels being one notable exception. The prevalence in certain breeds suggests a genetic predisposition for the condition. It affects adult, usually middle-age or elderly patients.
Cause:
You May Like: How To Measure Your Heart Rate
Also Check: Dos And Don’ts After Heart Surgery
Degenerative Mitral Valve Disease
DMVD is the most common acquired heart disease in dogs. Common clinical signs and pathophysiology include:
- Heart murmur due to mitral valve regurgitation, leading to left atrial and left ventricular dilatation
- Progressive dilatation of the left ventricle, ultimately leading to systolic dysfunction
- Significant left atrial enlargement, leading to atrial arrhythmias
- Development of pulmonary hypertension, which can contribute to clinical signs, such as respiratory distress and syncope.
Not all dogs with DMVD will develop heart failure, characterized by pulmonary edema . In general, dogs with heart enlargement are at greater risk for heart failure, but only 30% of dogs with asymptomatic DMVD develop clinical signs and require heart failure therapy.
Congestive Heart Failure In Dogs: Symptoms You Dont Want To Miss
- Not a substitute for professional veterinary help.
Congestive heart failure in dogs, or CHF, occurs commonly among older pets. In fact, 2025 percent of dogs between the ages of 9 and 12 years can be affected. Fortunately, dogs dont tend to die of heart attacks like we do. Experts say that if CHF is caught early on, the prognosis can be good.
If your dog is diagnosed with CHF, identifying a cardiologist is an important next step. Your vet will help you with this process.
Recommended Reading: How Does A Heart Attack Affect The Body
How Is Chf Diagnosed In Dogs
Bruiser needed an echocardiogram , which revealed degeneration of the mitral heart valve and subsequent heart enlargement. This is common in older dogs.
A full physical examination will be needed to determine the cause and whether there is an abnormal heart size, fluid accumulation, pleural effusion, and heart defects.
Steps toward a diagnosis of congestive heart failure in dogs:
- Listening to the heart with a stethoscope
- An electrocardiogram . Sometimes an ultrasound is done as well.
How Long Will My Dog Live With Congestive Heart Failure
Once your dog has been diagnosed with congestive heart failure, its prognosis depends on a variety of factors including the severity of its disease. Your veterinarian will be able to give you a more accurate estimate of the estimated survival time for your dog.
The majority of dogs with heart failure will not live for more than 2 years. Dr. Mark Rishniw, a veterinary cardiologist, suggested that around half of dogs will die from congestive heart failure from mitral valve disease within 8 to 10 months. As this is only an average, some dogs may die within days, weeks, or months from diagnosis.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take To Lower Resting Heart Rate
Be A Detective: Ask Detailed Questions
Take time to gather information from the patients history and physical examination, including details that may help determine whether the dog has heart failure and why it may have occurred.
Does the history support heart disease and heart failure?
- Is there a history of heart disease in a relative or littermate?
- Is congenital or acquired heart disease more likely? For instance, in a middle-aged to older dog, is the murmur a relatively new finding, suggesting an acquired disease, or has it been present since the dog was a puppy, suggesting undiagnosed congenital heart disease? See Consider These Cases .
- Does the history of clinical sign progression support heart failure? Findings from the history that support heart failure are listed in Table 1. These findings, while not specific for heart failure, suggest that pulmonary edema may be present, especially when combined with signalment and abnormal findings on physical examination.
Does the physical examination support heart disease and heart failure?
- A left apical systolic murmur is a characteristic finding in dogs with mitral regurgitation from DMVD, and a loud murmur is more likely with advanced disease. See Consider These Cases .
FIGURE 2. Lead II electrocardiogram demonstrating sinus tachycardia with a regular rhythm and heart rate of 175 beats/min in a dog with CHF .
Cbd Oil From Hemp For Dogs With Congestive Heart
At The Heart Of The Matter
Although there is no cure for the common causes of Congestive Heart Failure in dogs, there are natural therapies available that can greatly improve and extend the life of your dogspecifically, botanical extracts like CBD-rich hemp oil.
Scientists are just beginning to understand the specific pharmacological mechanisms underlying Cannabidiols potential as a treatment for cancer, heart disease, seizures, anxiety,diabetes& depression and numerous other canine health disorders.
Published scientific literature has identified more than 65 molecular targets of CBD. This versatile plant cannabinoid is highly active against heart and brain ischemia by modulating many of the molecular and cellular hallmarks of systemic inflammatory immune response.
Cannabidiol from hemp and cannabis is a compound that produces many effects through multiple molecular pathways so it can affect both the structure as well as functional aspects of the heart muscle .
CBD taps into how dogs function biologically on a very deep level. CBD from full spectrum hemp can penetrate the cell membrane and bind to receptors on the nucleus which regulate gene expression and mitochondrial activity.
CBD represents the greatest advancement in veterinary science & animal welfare introduced in the last 50 years.
Read Also: How To Reverse Congestive Heart Failure
Diagnosing Heart Disease In Dogs
Oftentimes, veterinarians can detect heart disease in dogs during routine office visits which can be covered if you enroll in an ASPCA Pet Health Insurance plan with an optional preventive care option. If your dog shows any signs or symptoms during their visit, your vet may recommend one or several of the following procedures: X-rays, cardiac evaluation, electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, cardiac catheterization, or blood and urine tests.
Diagnostic testing can be expensive too, but ASPCA Pet Health Insurance can help you cover the costs. Get a quote now!
What Is Heart Disease & Heart Failure
The heart is divided into different parts to pump blood throughout the body. The right side, made up of the right atrium and ventricle, directs blood to the lungs so that the blood cells can pick up oxygen, which is then delivered back to the heart. Then the left side, which contains the left atrium and ventricle, pumps the newly oxygenated blood throughout the rest of the body through the circulatory system.
Just like with heart disease in humans, when heart disease develops in a dog, their heart must adapt or change in order to continue to work efficiently and bring oxygen to the rest of the body. These changes typically occur slowly over timeoften yearsand cause enlargement of the heart. This timeframe is known as the preclinical form of heart disease, considered as such since dogs show no obvious outward signs of heart disease.
But over time, heart disease can progress to heart failure. This stage of the disease is called the clinical stage, because this is when dogs begin to exhibit signs of heart failure . At the core, heart failureincluding congestive heart failuretypically involves a back-up of blood in the lungs or other organs, which makes it difficult for the heart to do its job efficiently.
You May Like: What Are The First Signs Of A Heart Attack
What Causes Congestive Heart Failure
The most common cause of congestive heart failure in dogs is congenital heart defects, meaning that it’s a genetic condition that can’t be prevented. Many small breeds have a genetic propensity toward CHF, says Love to Know, including toy poodles, Pomeranians, dachshunds, and cavalier King Charles spaniels. Small dogs in general tend to be more prone to developing CHF because the heart valves tend to degenerate more than in larger breeds. However, some large breeds, particularly giant breeds such as St. Bernards, Newfoundlands, and Great Danes are prone to developing CHF due to dilated heart muscles. It’s important to understand that congenital CHF typically manifests late in a dog’s life and that these dogs can live many years seemingly healthy and happy before symptoms begin to appear.
CHF can also develop in a heart that’s been weakened by other heart conditions, so it’s important to do what you can to prevent heart disease from occurring in your pet, including preventing obesity and providing heartworm prevention.
Symptoms Of Congestive Heart Failure In Dogs
Symptoms of CHF in dogs can be one or more of the following clinical signs:
-
Coughing, sometimes even coughing up foam
-
Difficulty breathing
-
Increased rate of breathing, even when resting
-
Inability to exercise
-
Distended abdomen
-
Collapse or sudden death
Seek an emergency vet immediately if your dog is experiencing any signs of respiratory distress or trouble breathing. Your dog may need hospitalization and immediate care when experiencing moderate to severe signs of congestive heart failure.
You May Like: Does Nitro Increase Heart Rate
How Dogs Can Help Prevent Heart Disease In People
The companionship of our puppy pals can put us at ease with all the tail-wagging comfort they bring. Whether its a few wet kisses, a cold nose, or warm snuggles, most pet parents can agree that the loyalty and companionship of a dog is good medicine for the heart. And now the medical field agrees!
In general, healthier people are just more likely to own pets. But according to the American Heart Association, pet ownership can help reduce the risk of heart disease. Here are a couple of reasons behind this belief:
- Puppy parents tend to be more active and get more exercise because of their dogs
- Pets provide social support to their pet parents, which helps them maintain healthy habits, like engaging in physical activities
Its important to note that pet ownership shouldnt be viewed as something done strictly for medical purposes. Instead, consider it one of the many benefits of developing a warm and trusting relationship with your furry family members.
Heart Medication For Dogs
- Diuretics like furosemide are medications used to remove excess fluid buildup from the lungs or abdomen.
- Inodilators are medications that both increase myocardial contractility and open up constricted blood vessels, reducing the workload on your dogs weakened heart. The only one available currently is Pimobendan .
- ACE inhibitors, or inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme, are a group of medications that open up constricted blood vessels.
Bruiser is on Pimobendan, Furosemide, and a drug called Sprionolactone, which is another diuretic.
Don’t Miss: How Accurate Is Fitbit Charge 2 Heart Rate
How Do You Treat Congestive Heart Failure In Dogs
The treatment for congestive heart failure in dogs includes medications to decrease fluid that has accumulated in your dogs lungs. Right-sided heart failure may require manual removal fluid from the belly every few weeks by your veterinarian.
Some medications may be given to help improve the function of the heart. The most common medications used to treat heart failure include:
Future Outlook On Canine Congestive Heart Failure

Canine Congestive Heart Failure has many possible causes with just as many potential treatment solutions. But with early detection, by focusing on proper diet & nutrition, and by providing appropriate support therapies like CBD-rich hemp extracts, many canine patients with Congestive Heart Failure can experience a preservation of life and total restoration of health.
This article was originally published February 16, 2019. Accumulating evidence now suggests that CBD is beneficial in the cardiovascular system and has direct action on isolated arteries causing both acute and time dependent vasorelaxation.
CBD protects against the vascular damage caused by a high glucose environment, inflammation or the induction of type 2 diabetes in animal models and reduces the vascular hyperpermeability associated with such environments.
A common theme throughout these studies is the antiinflammatory and antioxidant effect of CBD. In the heart, in vivo CBD treatment protects against ischaemiareperfusion damage and against cardiomyopathy associated with diabetes. Similarly, in a different model of ischaemiareperfusion, CBD has been shown to reduce infarct size and increase blood flow in animal models of stroke, sensitive to 5HT1A receptor antagonism.
Taken together, these preclinical data appear to support a positive role for CBD treatment in the heart, and in peripheral and cerebral vasculature.
Recommended Reading: How To Slow Down Your Heart Rate From Anxiety
