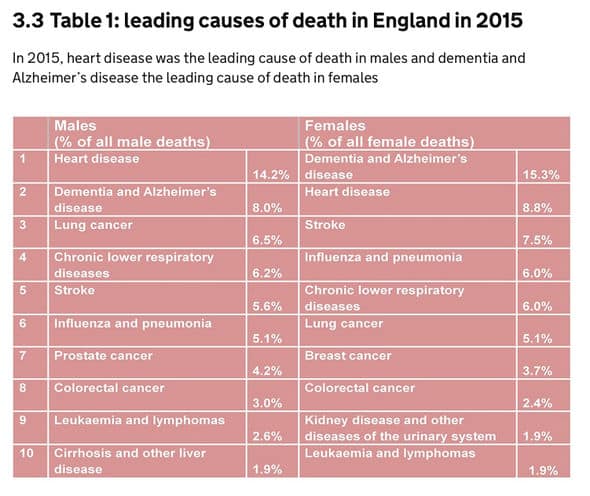
Understanding Additional Mortality Risk
According to research from The Alzheimers Society UK, a person who is diagnosed with dementia at 90+ years old, is more likely to die from an associated health problem before reaching the later stages, compared to someone diagnosed at 70. In a 2016 report by Public Health England, 38% of all dementia deaths involved respiratory disease, and 36% involved circulatory & cardiovascular disease.
What Are The 7 Stages Of Vascular Dementia
Dementia is a group of progressive diseases that cause cognitive impairment and decline over a number of years. There are several types of dementia that develop across a number of stages, including vascular dementia.
In this blog, our team of dementia specialists are going to explain more about vascular dementia and its seven stages, giving you a better insight into the condition and what you might expect if you or someone close to you has been diagnosed.
Find The Right Therapist For You
Frontal lobe dementia is also known as frontotemporal dementia , or frontotemporal degeneration, it is an overarching term for several categories of a loss of brain function. The changes to the brain are caused by an abnormal build-up of tau proteins, which stop the brain cells from functioning properly, so they die. In frontal lobe dementia parts of the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain are damaged. It was previously known as Picks disease after the doctor Arnold Pick who identified and first documented the symptoms in a patient over a hundred years ago in 1892.
Unlike the most widely diagnosed form of dementia, Alzheimers disease, frontal lobe dementia occurs at a much younger age and is partly genetic. That means while there is no certainty that if you have had a close blood relative with FLD you will get it too, your chances of developing it are much higher than for other members of the population.
There are several genes that appear to link with frontal lobe dementia, which ties in with a family history of the disease being the only known risk factor. Approximately 15% of people diagnosed have a family member with the disease. However there is no single cause for the disease.
There are three predominant forms of frontal lobe dementia:
Don’t Miss: What Can You Do For Congestive Heart Failure
Assessment Of Demographic Medical And Medication Data
Demographic data at the moment of diagnosis were obtained from SveDem and included age, sex, living situation , Mini-Mental State Examination score , and dementia type. Dementia diagnoses were coded as Alzheimer disease , vascular dementia, mixed dementia , dementia with Lewy bodies, frontotemporal dementia, Parkinson disease dementia, unspecified dementia, and other dementia types. A detailed description of the diagnostic criteria can be found elsewhere. The number of expedited drugs during the 3 months before dementia diagnosis was extracted from the Swedish Prescribed Drug Register. The medical diagnoses up until the moment of dementia diagnosis were selected from the Swedish National Patient Register and used to calculate the Charlson Comorbidity Index score .
What Are The Overall Benefits Of Hospice Care
If you or a loved one is facing a life-limiting illness, such as congestive heart failure, hospice can provide specialized medical care for patients and support services for loved ones. Here are some other lesser-known benefits of hospice.
2Miller SC, Gozalo P, Mor V. Hospice enrollment and hospitalization of dying nursing home patients. American Journal of Medicine 2001 111:38-44
Recommended Reading: When Is Heart Rate Too High
Dementia Can Complicate Heart Recovery And Treatment
Dementia is a thief. It steals a person’s memory, their ability to reason, to live independently.
As people age and face more medical challenges, it also robs them of something even more basic to survival the ability to participate in their own recovery, especially from major events such as heart attacks. And that can limit the treatments they receive.
“It interferes with adhering to a medical treatment plan, unless there is someone there to support them,” said Dr. Karen Alexander, a cardiologist and professor of medicine at Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina.
Studies show people with dementia and even those with mild cognitive impairments are less likely than those with no cognitive loss to receive invasive procedures used to treat heart disease, for example. These include cardiac catheterization, used to check for blockages in the arteries, and coronary revascularization, used to clear those blockages either with stents to prop arteries open or by rerouting blood flow to the heart using bypass surgery.
In general, dementia describes a particular group of symptoms that affects a person’s daily living, such as difficulties with memory, language, problem-solving and other thinking skills.
Dementia is more common as people grow older, affecting 1 in 3 people 85 and older, according to the National Institute on Aging.
If you have questions or comments about this story, please email .
Life Expectancy And Vascular Dementia
Repeated small strokes can damage the brain and cause vascular dementia. Its the second most common cause of the disease. The pattern of disease progression is different from the gradual deterioration of Alzheimers disease. The symptoms may be steady for a while, then suddenly get worse followed by a further period of stability. This reflects times when blood clots interrupt the blood supply to the brain, causing damage.
Because people with vascular dementia is linked to strokes, people affected often have other illnesses and may have worse general health. Research suggests that the average life expectancy is around four years. However, sudden or severe deterioration can happen when there is a further stroke.
Also Check: What Causes Left Sided Heart Failure
When To Seek Hospice Care
Even physicians have difficulty determining life expectancy for people with end-stage heart-failure. The condition can be unpredictable, and symptoms can change. However, certain signs can indicate that hospice care would be beneficial, including:
- frequent chest pain
- significant fatigue or shortness of breath
- substantial decline in ability to do daily activities, such as self-care
- The patient has already received the best possible treatment, which are no longer working well, and the patient is not a candidate for other interventions.
- The patient has received the best possible treatment and has decided to decline further specialized interventions.
People can be reluctant to start hospice, as they may worry it means theyre giving up or that it will hasten death. But such concerns are unfounded. In fact, patients and families often wish they had started hospice sooner, because it makes such a positive difference in their lives. And research shows that early admission to hospice results in greater satisfaction with care among patients and family caregivers.
Living Well With Dementia
Talking about death and dementia is difficult and distressing. The statistics can seem scary. However, each individual is different. People can live well with dementia, and you can still look forward to times of joy and togetherness. Professional home carers can help to ease the burden for family carers, supporting your loved one to continue living in their own home in comfort and safety.
You May Like: Heart Rate Smart Watch
Stage 4 Nearing Kidney Failure
Stage 4 CKD means you have an eGFR between 15 and 29. It means your kidneys are moderately or severely damaged and not working well. This stage should be taken very seriously as you are nearing kidney failure, and it can land you with dangerous complications if you are not careful.
Symptoms commonly faced by people at stage 4 kidney disease include:
- Swelling on the hand and feet
- A low number of red blood cells or anemia
At this stage, you need to consult a nephrologist regularly who comes up with a treatment plan that works for your condition. The doctor will monitor your kidney performance to ensure your disease does not deteriorate.
At this stage, the doctor will also discuss the possibility of a dialysis or kidney transplant and help you prepare for them if your kidney functions do not improve.
Life Expectancy By Sex
Along with other factors, life expectancy for kidney disease depends on the patients age and sex. For someone around 60, stage 1 stage 2 kidney disease life expectancy will be approximately 15 years. That figure falls to 13 years, 8 years, and 6 years in the second, third, and fourth stages of kidney disease, respectively. For a 60-year old woman, stage 1 life expectancy is 18 years, while stage 2 is only one year less. For stage 3 kidney disease, her life expectancy would be 11 years.
Research shows that women have a slightly greater life expectancy at all ages. But during stages 4 and 5, everything slips away, and life expectancy becomes essentially identical between the sexes.
You May Like: At What Heart Rate Should You Go To The Hospital
The Later Stage Of Dementia
Understanding the signs of late-stage dementia can help ensure a person gets the right level of care and support. For example, those living with advanced dementia are especially prone to infection, constipation, and skin ulcers which can put their life in danger if treatment is delayed.
Sometimes infection and illness can lead to delirium which can cause people to become confused, resist help, and experience hallucinations. The cause of delirium requires urgent medical attention, and some people may not recover completely from the effects. Signs of late-stage dementia include
- Speaking in single words, or repeated phrases that dont make sense
- Not being able to understand what people are saying to them, or things that are happening around them
- Needing help with most daily tasks
- Eating less because they find it difficult to swallow, or have less of an appetite
- Being unable to take part in simple physical activity such as walking, standing, or sitting upright
Is There A Test To Diagnose Pd Dementia
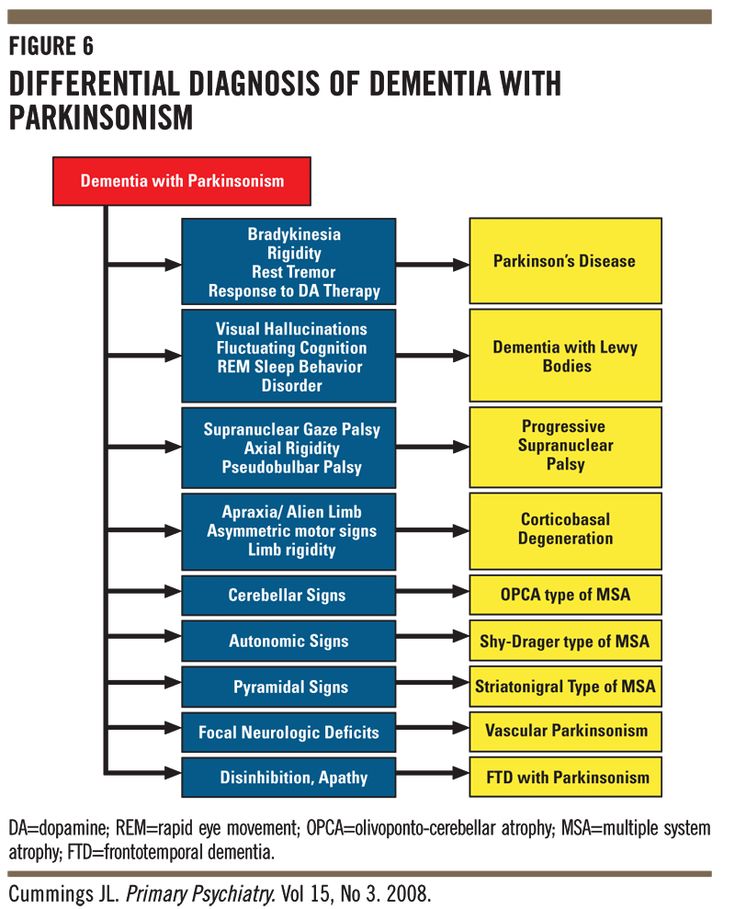
There is no single test for PDD. The diagnosis is made clinically. If you or someone you spend time with notices cognitive changes, it is important to discuss them with your care team. If you dont have a care team in place, its important to find a specialist or physician familiar with dementia or geriatric medicine. Call the Parkinsons Foundation Helpline 1-800-4PD-INFO for a referral.
Recommended Reading: Chronic Congestive Heart Failure
What Affects Life Expectancy In Dementia
The life expectancy of someone living with dementia depends on many factors. The type of dementia, the severity of dementia at the time of diagnosis, and the individuals age, sex, and their general health and wellbeing can all impact on the time they can live with the disease.
The key things that affect life expectancy include:
Michael J Fox Says Having Parkinsons Disease Sucks
We use your sign-up to provide content in ways youve consented to and to improve our understanding of you. This may include adverts from us and 3rd parties based on our understanding. You can unsubscribe at any time. More info
Its thought around one in 500 people are affected by Parkinsons disease, according to the NHS. The disease is known to affect the brain, and well-known symptoms include problems like a tremor. According to studies, taking two vitamins could help to lower your risk in later life.
You May Like: Diets For Congestive Heart Failure
Identifying Risk Factors For Parkinsons
The risk for early death increased by about 40% for every 10-year increase in age at diagnosis.
Parkinsonâs researcher Tobias Kurth, MD, agrees that identifying risk factors for early death could help clinicians better manage the disease.
Kurth is an adjunct associate professor of epidemiology at Harvard School of Public Health.
âThis is important research that adds to our understanding of the impact of specific features of Parkinsonâs disease on outcomes,â he tells WebMD.
His own study of Parkinsonâs-associated death matched Parkinsonâs patients with people without the disease who had similar non-Parkinsonâs-related illnesses.
Like the newly reported study, patients who were older when their Parkinsonâs disease was diagnosed had a greater risk for early death.
Show Sources
Treatments For Vascular Dementia
There’s currently no cure for vascular dementia and there’s no way to reverse any loss of brain cells that happened before the condition was diagnosed.
But treatment can sometimes help slow down vascular dementia.
Treatment aims to tackle the underlying cause, which may reduce the speed at which brain cells are lost.
This will often involve:
- taking medicines, such as those used to treat high blood pressure, lower cholesterol or prevent blood clots
Other treatments, including physiotherapy, occupational therapy, dementia activities and psychological therapies, can help reduce the impact of any existing problems.
Also Check: Entresto Heart Failure Guidelines
Associations Between Dementia Disorders And Hf Types
Table22 presents odds ratios for associations between dementia disorders and types of HF. For example, on crude analysis, the odds ratio for association between vascular dementia and HFREF was 1.23 . When adjusted for selected baseline characteristics, the odds ratio was 1.23 and after adjusting for all covariates it was 1.38 . None of the associations between dementia disorders and types of HF reached statistical significance.
What Are The Symptoms Of Vascular Dementia
The symptoms of vascular dementia depend on the location and amount of brain tissue involved. Vascular dementia symptoms may appear suddenly after a stroke, or gradually over time. Symptoms may get worse after another stroke, a heart attack, or major surgery. These are signs and symptoms of vascular dementia
- Increased trouble carrying out normal daily activities because of problems with concentration, communication, or inability to carry out instructions
- Memory problems, although short-term memory may not be affected
- Confusion, which may increase at night
- Stroke symptoms, such as sudden weakness and trouble with speech
- Personality changes
- Mood changes, such as depression or irritability
- Stride changes when walking too fast, shuffling steps
- Problems with movement and/or balance
- Urinary problems, such as urgency or incontinence
Recommended Reading: How Do You Calculate Target Heart Rate
Definition Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons syndrome is characterized by the clinical triad of rigor, tremor, and akinesia as well as possible postural instability.
Based on etiology, one can further distinguish between idiopathic Parkinsons disease, which is synonymous with Parkinsons disease, and atypical and symptomatic parkinsonism.
Idiopathic Parkinsons disease or Parkinsons disease is considered a diagnosis of exclusion, in the absence of a specific cause.
Symptomatic Parkinsonism, however, is triggered by certain identifiable factors. For example, in the context of intoxication, manganese or lead may cause the disease. Parkinsons syndrome is also triggered by medication, e.g., neuroleptics.
Parkinsons syndrome occurring in the context of other neurodegenerative diseases is referred to as atypical Parkinsonism.
Recommended Reading: Does Vitamin B12 Help Parkinsons
Life Expectancy And Frontotemporal Dementia
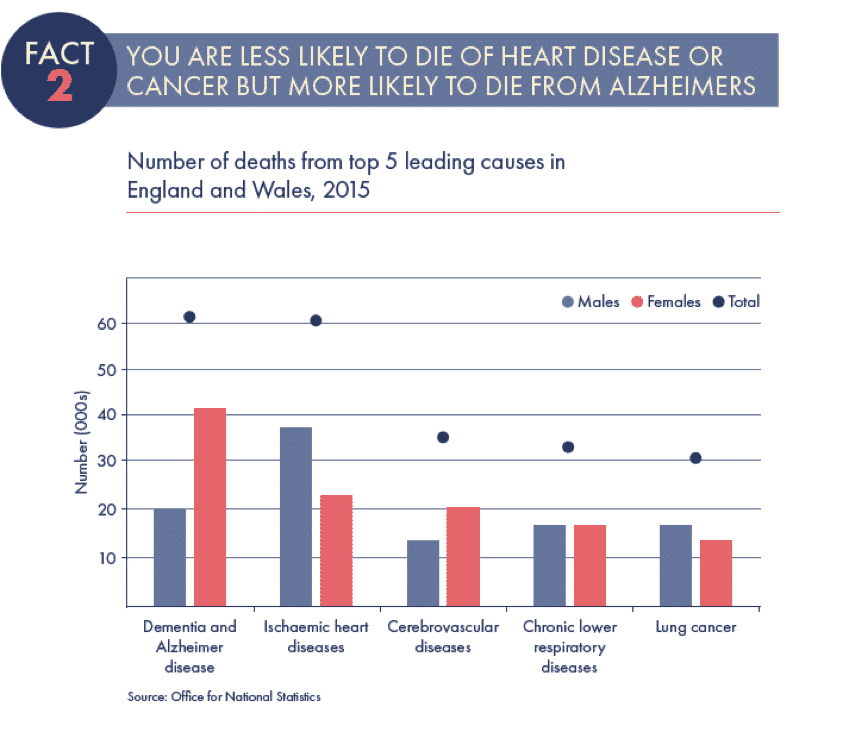
Frontotemporal dementia or Picks disease is characterised by progressive damage in the frontal and temporal lobes in the brain. This leads to personality changes, impulsiveness and problems with speech and language. Although it can affect the elderly, it is often diagnosed in younger people, between forty-five and sixty-five.
The average life span is around eight years from the time when symptoms first started, but there can be dramatic differences between individuals. Distressingly, young-onset dementia appears to progress more quickly. Someone who is diagnosed with the condition between the ages of thirty and fifty may live for two years less than someone who is diagnosed later in life.
Don’t Miss: Does Dehydration Cause Rapid Heart Rate
What Is Frontal Lobe Dementia
The frontal lobes of the brain are located as the name suggests at the front of the brain. Loosely speaking, it contains what we call the higher functions of the brain. These are the areas of the brain responsible for emotions, understanding, speech some types of movement, planning and judgement in other words the things which make you a person, and personality. Like all dementias the people who develop symptoms face a slow loss of self and those who care for them, losing the person they care for by slow degrees.
Lewy Body Dementia Prognosis
Lewy body dementia is a form of dementia characterized by the development of abnormal deposits in the brain. People with Lewy body dementia have trouble with movement as well as cognitive decline. Thinking problems generally show up before movement problems. As Lewy body dementia progresses, affected individuals may also experience visual hallucinations and sleep problems.
Life expectancy for a person with Lewy body dementia is approximately 2 to 8 years after the onset of noticeable symptoms.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Heart Attacks In Women
Are You Supporting A Person With Later
Caring for someone in the later-stages of dementia can present a lot of challenging situations and emotions. Providing support with daily tasks is one thing, but supporting a loved one with personal care, and watching their behaviour and personality change can put a lot of pressure on your relationship with them.
You may feel sadness, confusion, and perhaps anger but it can be difficult to share these feelings with friends or other family members.
Joining carers groups can connect you to support from people who understand what youre going through. There are a number of online carer communities, and you may find some in-person groups in your local area too. Local groups are particularly good at organising things like coffee mornings and day trips, and may be able to help you arrange respite care when you need a break.
To find a support group, speaking to the following people is a great place to start:
Standard Protocol Approvals Registrations And Patient Consents
Ethics permission for this study was obtained from the regional human ethics committee of Stockholm . Quality registries such as SveDem are considered an important part of the development and improvement of health and social care in Sweden. Each patient has to be informed about the registration and has the right to decline participation. Written consent is not required however, each patient has the right to obtain a copy of the information that is registered if requested and to withdraw consent.
Recommended Reading: Does Heart Rate Increase During Asthma Attack
