Influences From The Central Nervous System
Cardiovascular centres
The heart rate is rhythmically generated by the sinoatrial node. It is also influenced by central factors through sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves. Nervous influence over the heart rate is centralized within the two paired cardiovascular centres of the medulla oblongata. The cardioaccelerator regions stimulate activity via sympathetic stimulation of the cardioaccelerator nerves, and the cardioinhibitory centers decrease heart activity via parasympathetic stimulation as one component of the vagus nerve. During rest, both centers provide slight stimulation to the heart, contributing to autonomic tone. This is a similar concept to tone in skeletal muscles. Normally, vagal stimulation predominates as, left unregulated, the SA node would initiate a sinus rhythm of approximately 100 bpm.
Norepinephrine binds to the beta1 receptor. High blood pressure medications are used to block these receptors and so reduce the heart rate.
Input to the cardiovascular centres
Increased metabolic byproducts associated with increased activity, such as carbon dioxide, hydrogen ions, and lactic acid, plus falling oxygen levels, are detected by a suite of chemoreceptors innervated by the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves. These chemoreceptors provide feedback to the cardiovascular centers about the need for increased or decreased blood flow, based on the relative levels of these substances.
Exercise And Your Pulse
If you check your pulse during or immediately after exercise, it may give an indication of your fitness level. A heart rate monitor is also useful for recording your heart rate when resting and during exercise.
Aerobic activities such as walking, running and swimming are good types of exercise because they increase your heart and breathing rates.
If you haven’t exercised before, or haven’t for some time, see our Live Well section to read about the benefits of exercise and how much exercise you should be doing.
How To Check Your Heart Rate
You can check your heart rate by counting the pulse. A pulse can be felt at various sites on the body like over the sides of the neck, the wrist, and the top of the foot. To check your pulse on the wrist with the help of your middle finger and index finger, you need to:
- Keep your middle finger and your index finger over the inner part of the wrist and keep pressing gently until you can feel your pulse. The pulse is felt in your radial artery.
- After you have located your pulse, look at the watch, and start counting the beats for 30 seconds. Doubling this count will give you your heart rate. You can even count the beats for 10 seconds and multiply the number by six to get your heart rate.
If you find the rhythm of your heartbeat slightly irregular, you will have to count the beats completely until 60 seconds. You will have to visit your doctor if you keep getting a fast and irregular heart rate consistently.
Recommended Reading: Can Lexapro Cause Heart Palpitations
What Are Heart Palpitations
A heart palpitation is when you suddenly become aware of your heart beating, usually in an irregular way. Sometimes you can feel it in your ears or your chest when youre lying down. Your heart beat may feel:
- too fast or slow
- like its fluttering
- like its thudding, or pounding.
It is not unusual to feel heart palpitations occasionally and mostly they are harmless. However if youre experiencing them on a regular basis, see your doctor.
How Do You Check Your Pulse

You can measure your heart rate manually by checking your pulse. Follow these three steps.
- Find your pulse in your wrist .
- Count each beat for a total time of 30 seconds.
- Double the number of beats you counted. This is your heart rate or pulse, measured in beats per minute.
Also make a note of whether your heart beats at an even or uneven rhythm. A normal heart beats at a steady rhythm like a clock, tick tock tick tock.
Some people like to use a heart rate monitor to measure their heart rate. These monitors are often included in fitness trackers, which are now widely available in sports stores and other retail outlets. However, their accuracy depends on the quality of the device.
Read Also: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
What Are Vital Signs
Vital signs are measurements of the body’s most basic functions. The four main vital signs routinely monitored by medical professionals and health care providers include the following:
-
Body temperature
-
Pulse rate
-
Respiration rate
-
Blood pressure
Vital signs are useful in detecting or monitoring medical problems. Vital signs can be measured in a medical setting, at home, at the site of a medical emergency, or elsewhere.
Before You Measure Your Blood Pressure:
The American Heart Association recommends the following guidelines for home blood pressure monitoring:
-
Don’t smoke or drink coffee for 30 minutes before taking your blood pressure.
-
Go to the bathroom before the test.
-
Relax for 5 minutes before taking the measurement.
-
Sit with your back supported . Keep your feet on the floor uncrossed. Place your arm on a solid flat surface with the upper part of the arm at heart level. Place the middle of the cuff directly above the bend of the elbow. Check the monitor’s instruction manual for an illustration.
-
Take multiple readings. When you measure, take 2 to 3 readings one minute apart and record all the results.
-
Take your blood pressure at the same time every day, or as your healthcare provider recommends.
-
Record the date, time, and blood pressure reading.
-
Take the record with you to your next medical appointment. If your blood pressure monitor has a built-in memory, simply take the monitor with you to your next appointment.
-
When blood pressure reaches a systolic of 180 or higher OR diastolic of 110 or higher, seek emergency medical treatment.
Ask your doctor or another healthcare professional to teach you how to use your blood pressure monitor correctly. Have the monitor routinely checked for accuracy by taking it with you to your doctor’s office. It is also important to make sure the tubing is not twisted when you store it and keep it away from heat to prevent cracks and leaks.
Recommended Reading: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
High Blood Pressure Vs High Heart Rate
Some individuals confuse high blood pressure with a high heart rate. Blood pressure is the measurement of the force of the blood against the walls of arteries, while pulse rate is the number of times your heart beats per minute.
There is no direct connection in between the two, and high blood pressure does not always lead to a high pulse rate, and vice versa. Heart rate goes up during laborious activity, however a vigorous workout may just modestly enhance high blood pressure.
What Factors Can Affect Heart
Several factors can affect HRV, including age, sex, sleep quality, stress, and lifestyle choices, such as nutrition and exercise.
Fitbit Sense and Fitbit Versa 3 notify you when we detect that your heart rate is outside of your high or low thresholds while you appear to be inactive for at least 10 minutes.
You May Like: Fitbit Charge 2 Heart Rate Accuracy
Correlation With Cardiovascular Mortality Risk
| This section needs more medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. Please review the contents of the section and add the appropriate references if you can. Unsourced or poorly sourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: “Heart rate” news ·newspapers ·books ·scholar ·JSTOR |
A number of investigations indicate that faster resting heart rate has emerged as a new risk factor for mortality in homeothermic mammals, particularly cardiovascular mortality in human beings. Faster heart rate may accompany increased production of inflammation molecules and increased production of reactive oxygen species in cardiovascular system, in addition to increased mechanical stress to the heart. There is a correlation between increased resting rate and cardiovascular risk. This is not seen to be “using an allotment of heart beats” but rather an increased risk to the system from the increased rate.
Given these data, heart rate should be considered in the assessment of cardiovascular risk, even in apparently healthy individuals. Heart rate has many advantages as a clinical parameter: It is inexpensive and quick to measure and is easily understandable. Although the accepted limits of heart rate are between 60 and 100 beats per minute, this was based for convenience on the scale of the squares on electrocardiogram paper a better definition of normal sinus heart rate may be between 50 and 90 beats per minute.
What If The Second R Wave Does Not Match
Do you think I have cheated and given you the most simple example?
We know that usually on an electrocardiogram strip the second R wave does not match a thick line. The solution is a little bit tricky, but simple: We divide 300 by the number of large squares + 0.2 per small square.
Heart rate: 4 large squares + 3 small square = 65 bpm
For example: If there are 4 large squares and 3 small squares between R waves, the heart rate is 65 bpm .
If you want to avoid the hassle, you can find a heart rate calculator in our calculations section to make it easy for you.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Calculate Max Heart Rate
Lactate Threshold Heart Rate
When your muscles use oxygen to produce energy, they also churn out a variety of byproducts. One of those compounds, called lactate, is particularly important to athletes. Lactate builds up in the blood more quickly when your muscles are working hard, Hart says.
At one time, experts believed lactate primarily caused your legs to burn and your stomach to churn during hard efforts and that it was largely to blame for post-run soreness . Now, they know your body can actually use lactate for energy. In fact, the ability to do so swiftly is part of what can improve your running performance.
Your lactate threshold is the point at which your body produces lactate at the same rate it can process it its a pace you could hold for about an hour. Lab tests or field tests can pinpoint your heart rate at this amount of effort.
The closer your lactate threshold heart rate is to your maximum heart rate, the better for your running. And unlike max heart rate, which doesnt change much based on your workouts, you can train to boost your bodys ability to clear lactate and improve your lactate threshold heart rate. Tempo runs, in which you hold a comfortably challenging pace, are the most powerful way to do this.
Why Does Bradycardia Happen
The most common cause for bradycardia is a malfunction in the hearts natural pacemaker, the sinus node. It controls how quickly the top and bottom heart chambers pump blood through the body. Another cause is atrioventricular block , in which the top and bottom chambers dont communicate well and the heart rate drops as a result.
Its like having virtual electrical cables and wires inside the heart, Dr. Baez-Escudero says. And, they deteriorate as we age. Common medications that are used in older populations can also often make bradycardia more significant.
In fact, age is the most common risk factor for developing bradycardia. The condition is most common among men and women over age 65.
Illness or other conditions also may prompt it. These other causes include:
- Heart attacks due to coronary artery disease.
- Bacterial infection in the blood that attacks the heart.
- Inflammation of the heart muscle.
- Low thyroid function.
- Too much potassium in the blood.
- Certain medications, including beta blockers and antiarrhythmics.
Congenital heart defects, diabetes or long-standing high blood pressure all may make bradycardia more likely, Dr. Baez-Escudero says.
Don’t Miss: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
Why Does A Good Resting Heart Rate Matter
It’s important to know what heart rate is healthy and normal at every age in your life. Your heart rate, or pulse, can guide you to discover dangerous health conditions that need expert care, such as some heart problems. But your normal resting heart rate changes throughout your life as you age. Read this guide to learn more about your pulse through every step of your life.
When Heart Rate Or Rhythm Changes Are More Serious
Irregular heartbeats change the amount of blood that flows to the lungs and other parts of the body. The amount of blood that the heart pumps may be decreased when the heart pumps too slow or too fast.
Changes such as atrial fibrillation that start in the upper chambers of the heart can be serious, because they increase your risk of forming blood clots in your heart. This in turn can increase your risk for having a stroke or a blood clot in your lungs . People who have heart disease, heart failure, or a history of heart attack should be more concerned with any changes in their usual heart rhythm or rate.
Fast heart rhythms that begin in the lower chambers of the heart are called ventricular arrhythmias. They include ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. These types of heart rhythms make it hard for the heart to pump enough blood to the brain or the rest of the body and can be life-threatening. Ventricular arrhythmias may be caused by heart disease such as heart valve problems, impaired blood flow to the heart muscle , a weakened heart muscle , or heart failure.
Symptoms of ventricular tachycardia include palpitations, feeling dizzy or light-headed, shortness of breath, chest pain or pressure, and fainting or near-fainting. Ventricular fibrillation may cause fainting within seconds and causes death if not treated. Emergency medical treatment may include medicines and electrical shock .
Check your symptoms to decide if and when you should see a doctor.
Also Check: How Does Heart Disease Affect The Skeletal System
Is Pulse Rate And Heart Rate The Same Know More
It is a very common query among individuals whether pulse rate and heart rate are the same or not. In short, the answer is yes both of them provide the same information and can be measured the same way.
Nevertheless, there is a technical difference between pulse and heart rate. Heart rate measures the contractions of a heart, i.e. heartbeat. On the other hand, the pulse rate calculates the frequency in which palpable blood pressure surges in ones body.
Furthermore, a heartbeat pushes the blood throughout a human body. It causes a change in blood pressure and pulse rate in the main arteries. Therefore, in a healthy human being heart rate is synchronized with their pulse. Thus, there is no significant difference between heartbeat and pulse rate, apart from their definition.
As discussed above, there is no such point of difference between pulse rate and heart rate. Interested students can join our online live classes and interact with our experts and other students from around the country for a better learning session.
Additionally, they can find more study material of biology by visiting the website or the official app of Vedantu.
When To Call Your Doctor
If youre on a beta blocker to decrease your heart rate or to control an abnormal rhythm , your doctor may ask you to monitor and log your heart rate. Keeping tabs on your heart rate can help your doctor determine whether to change the dosage or switch to a different medication.
If your pulse is very low or if you have frequent episodes of unexplained fast heart rates, especially if they cause you to feel weak or dizzy or faint, tell your doctor, who can decide if its an emergency. Your pulse is one tool to help get a picture of your health.
Learn more:
Don’t Miss: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
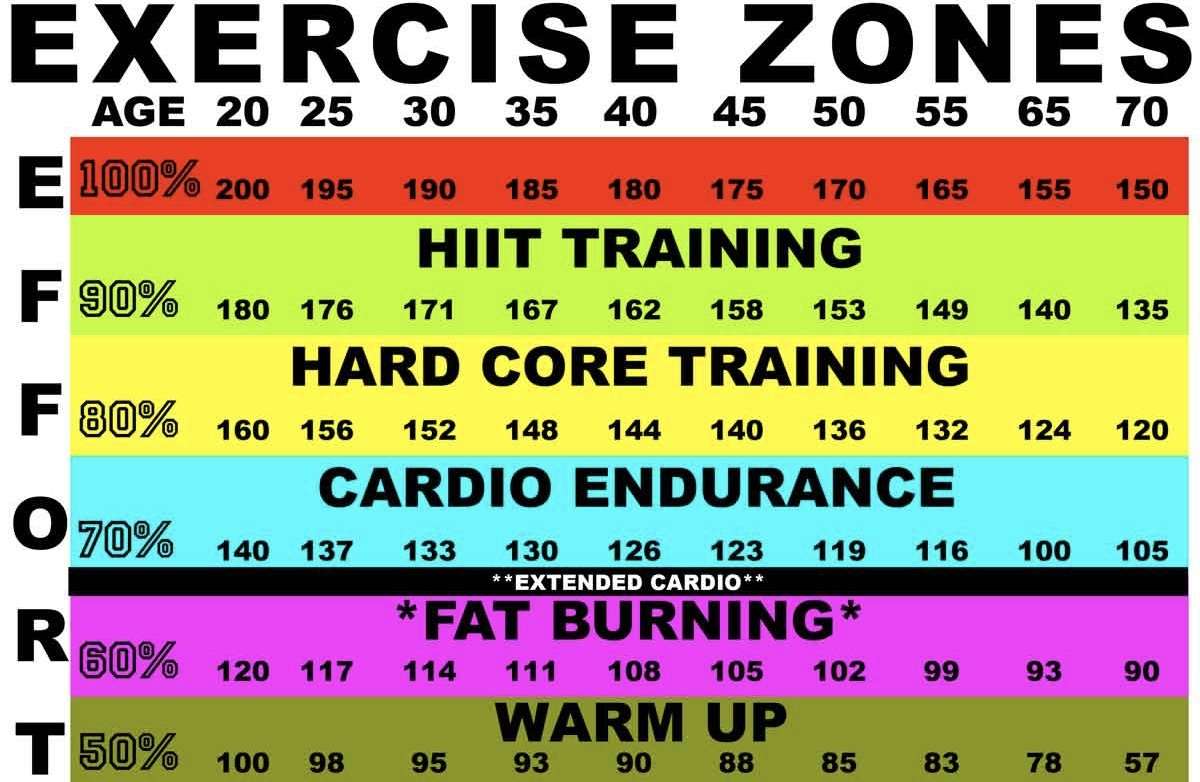
What Are The Heart
Personalized zones adjust as your fitness level or other factors change.
| Icon | |
|---|---|
|
Below Zones Below 40% of your heart rate reserve |
Below the fat burn zone, your heart beats at a slower pace. Youre at rest for now. |
|
Fat Burn Zone Between 40% and 59% of your heart rate reserve |
In the fat burn zone, youre likely in a moderate activity such as a brisk walk. Your heart rate and breathing might be elevated, but you can still carry on a conversation. |
|
Cardio Zone Between 60% and 84% of your heart rate reserve |
In the cardio zone, youre likely doing a vigorous activity such as running or spinning. |
|
Peak Zone Greater than 85% of your heart rate reserve |
In the peak zone, youre likely doing a short, intense activity that improves performance and speed such as sprinting or high-intensity interval training. |
How Does My Fitbit Device Calculate My Heart
The formula Fitbit uses to calculate your heart-rate zones is based on your device.
Fitbit personalizes your heart-rate zones using your heart rate reserve, which is the difference between your maximum heart rate* and your resting heart rate .
Heart rate reserve is an indication of your overall cardiovascular fitness. While your maximum heart rate is generally determined by age, your resting heart rate can be lowered by increasing your fitness level. By lowering your resting heart rate, you can increase your heart rate reserve.
For example, if you are 45 years old and your resting heart rate is 74 bpm, heres the math:
First, calculate your maximum heart rate and heart rate reserve.
| Metric | |
|---|---|
| Common formula of 220 – age | |
| Heart Rate Reserve |
Maximum heart rate – resting heart rate |
| Target Heart Rate Per Zone | + resting heart rate |
Next, use your heart rate reserve to calculate your personalized heart-rate zones.
| Heart-Rate Zone | |
|---|---|
| Bottom of zone: + 74 = 114 bpmTop of zone: + 74 = 134 bpm | |
| Cardio Zone |
Bottom of zone: + 74 = 135 bpmTop of zone: + 74 = 159 bpm |
| Peak Zone | Bottom of zone: + 74 = 160 bpmTop of zone: maximum heart rate |
Note that you can see your personalized heart-rate zones on the Active Zone Minutes screen in the Fitbit app.
*Occasionally during intense exercise, you might notice your heart rate go above your Fitbit-calculated maximum heart rate.
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
