Calculating Your Target Heart Rate
Your maximum heart ratethe upper limit of what your cardiovascular system can handle during physical activitycan be estimated by subtracting your age from 220. So, if you’re 35 years old, your estimated maximum heart rate is around 185 beats per minute .
It is recommended that you exercise within 55 percent to 85 percent of your maximum heart rate for at least 20 to 30 minutes to get the best results from aerobic exercise. In the example of the 35-year-old above, the target heart rate zone would be from 102 to 157 bpm.
Beta blockers can slow down your heart rate, but its effect is different for everyone . To use your resting heart rate as your guide, figure out the decrease in your heart rate as a result of the beta blocker. You will need to know what your resting heart rate was before you started taking the beta blocker.
For example, if your resting heart rate is 70 bpm without a beta blocker and 50 bpm with a beta blocker, thats a difference of 20. When calculating your target heart rate, subtract this number from the result. Thats your beta blocked target heart rate and is equivalent to what your target heart rate would be without the beta blocker. Again using the 35-year-old as an example, in this case the target heart rate zone would be reduced to between 82 and 137 bpm.
What Are Beta Blockers And How Do They Work
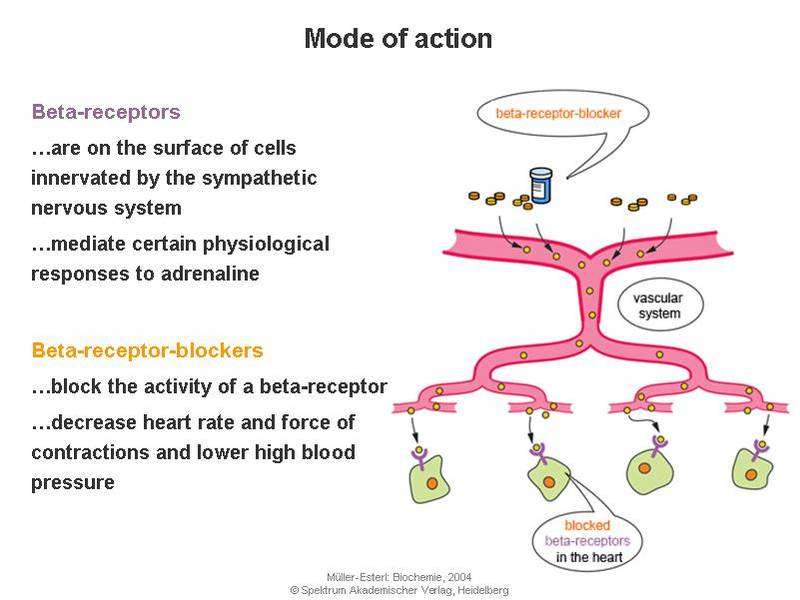
Beta blockers, also known as beta-adrenergic blocking agents, are drugs that block norepinephrine and epinephrine from binding to beta receptors on nerves. Norepinephrine and epinephrine are produced by nerves throughout the body as well as by the adrenal gland. They serve as neurotransmitters that may be active locally where they are produced, or elsewhere in the body, when they are released into the blood. There are both alpha and beta receptors in the body. There are three types of beta receptors and they control several different functions based on their location in the body.
Beta blockers primarily block 1 and 2 receptors and thereby the effects of norepinephrine and epinephrine. By blocking the effects of norepinephrine and epinephrine, beta blockers reduce heart rate; reduce blood pressure by dilating blood vessels; and may constrict air passages by stimulating the muscles that surround the air passages to contract considered an adverse side effect).
Beta Blockers: Use As Directed
When you start taking beta-blockers, your symptoms may become slightly worse for about two to three weeks as your heart adjusts to them. You might feel more tired or dizzy. Thats normal. However, youll need to check your blood pressure and heart rate to make sure they dont drop too low.
Its critical to take beta-blockers as directed. Even if you think they arent working or arent making you feel better, theyre helping prevent your heart disease from getting worse.
Its especially important to continue beta-blockers if youve been taking them long-term. Studies show that abruptly stopping them can cause chest pain and increase your risk of sudden cardiac death.
So, dont stop taking your beta-blockers unless you discuss it with your physician even if theyre causing side effects such as:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Slow, fast or irregular heartbeat.
- Swelling of feet and lower legs.
- Chest pain but contact your doctor or nurse right away.
If any of these side effects are severe or dont go away, talk to your doctor about how to control them. Sometimes your doctor can:
- Lower your beta-blocker dosage.
- Recommend alternate ways to take your beta-blocker so it doesnt interact with other medications.
You May Like: What Are The Signs Of A Heart Attack For Women
Are There Differences Amongst The Beta Blockers Available
Beta blockers differ in the type of beta receptors they block and, therefore, their effects.
- Non-selective beta blockers, for example, propranolol , block 1 and 2 receptors and, therefore, affect the heart, blood vessels, and air passages.
- Selective beta blockers, for example, metoprolol primarily block 1 receptors and, therefore, mostly affect the heart and do not affect air passages.
- Some beta blockers, for example, pindolol have intrinsic sympathomimetic activity , which means they mimic the effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine and can cause an increase in blood pressure and heart rate. Beta blockers with ISA have smaller effects on heart rate than agents that do not have ISA.
- Labetalol and carvedilol block beta and alpha-1 receptors. Blocking alpha receptors adds to the blood vessel dilating effect of labetalol and carvedilol.
Beta Blockers And Airways Disease
Beta-blockers can trigger bronchospasm and should therefore usually be avoided in patients with an established history of asthma. In the absence of a suitable alternative, it may be necessary for a patient with well-controlled asthma, or COPD;, to receive treatment with a beta-blocker for a co-existing condition .
- In this situation, a cardioselective beta-blocker should be selected and initiated at a low dose by a specialist; the patient should be closely monitored for adverse effects.
- Atenolol, bisoprolol, and metoprolol have less effect on the beta2 receptors and are, therefore, relatively cardioselective, but they are not cardiospecific. They have a lesser effect on airways resistance but are not free of this adverse effect.
Read more: Beta-adrenoceptor blocking drugs;New Zealand Formulary
Don’t Miss: How To Lower My Resting Heart Rate
What Beta Blockers Do
Tiny proteins called beta receptors sit on the outer surface of many cells. There are three main types. Beta-1 receptors are found almost exclusively in heart cells. Beta-2 receptors reside mostly in lung and blood vessel cells, though heart cells also have some. Beta-3 receptors are located on fat cells.
The job of beta receptors is to latch onto chemical messengers released by the nervous system. In response to these messengers, the heart beats faster, blood vessels constrict, the airways relax, and the kidneys increase production of a protein that boosts blood pressure.
Beta blockers subvert these processes by settling onto beta receptors and preventing the chemical messengers from binding to their receptors. That slows the heart, improves the conduction of electrical signals in the heart, relaxes blood vessels, and lowers blood pressure.
What Are Beta Blockers And Calcium Channel Blockers
Beta blockers, also called beta adrenergic blocking agents, block the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and epinephrine from binding to beta receptors on nerves, which can reduce the heart rate and reduce blood pressure by dilating blood vessels. Beta blockers are used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, angina , abnormal heart rhythms, tremors, pheochromocytoma, hypertrophic subaortic stenosis, migraine headacheprevention, hyperthyroidism, akathisia , panic disorder, anxiety, eye pressure caused by glaucoma, and aggressive behavior. Beta blockers can also prevent further heart attacks and death after a heart attack.
Calcium channel blockers dilate the arteries, reducing pressure within and making it easier for the heart to pump blood, and, as a result, the heart needs less oxygen. By reducing the heart’s need for oxygen, calcium channel blockers relieve or prevent angina . Calcium channel blockers also are used for treating high blood pressure, certain types of abnormally rapid heart rhythms, pulmonary hypertension, Raynaud’s syndrome, cardiomyopathy, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and to prevent migraineheadaches.
Also Check: How To Test Heart Rate
Do Beta Blockers Affect Exercise
Beta blockers and exercise can both be helpful to lowering blood pressure levels. If you have high blood pressure, your healthcare provider might recommend exercising more as one way to help lower it naturally. Is it safe to exercise if you have to take medication? Since most beta blockers lower your blood pressure, and slow your heart rate and cardiac output , they can affect your exercise goals.;
Whether the effect is significant enough to limit exercise is usually patient-specific, says Joanna Lewis, Pharm.D., the founder of The Pharmacists Guide. Many studies have shown that people can exercise as normal, but it really depends on the athletic state of the individual.
Your healthcare provider may recommend an exercise stress test, which checks heart blood flow during exercise and measures how hard the heart pumps on beta blockers. They can then use this information to figure out your target heart rate.;
Experts also suggest the Borg scale as a simple way to measure how hard someone is exercising. The scale matches how hard you feel youre working with numbers from six to 20. The higher the number, the harder youre working. Then, multiply the number by 10 for a rough heart rate estimate. People who take beta blockers run the risk of being unaware when theyre exercising too hard; they can use the scale to prevent overexertion.;
How To Stay In Shape While Taking Beta Blockers
People who take beta blockers can still exercise regularly and see the cardiovascular benefits of working out. Those who aim for a target heart rate should keep in mind that their new target heart rate may be different while on a beta blocker. Lewis says cardioselective beta blockers , which only block beta receptors in heart cells, may affect exercise less than the non-cardioselective kind .
Since beta blockers slow the heart rate to deceptively low levels, its important to avoid overexertion while exercising. Before starting a new workout program, talk to your healthcare provider first. Your physician can tell you what your target heart rate should be and create a custom exercise plan.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has some general exercise tips for people who havent been active in a while:;
And if youre exercising to help keep your blood pressure in check, keep in mind that are only two strategies that work. Experts also suggest eating a low-sodium diet, limiting alcohol intake, lowering stress levels, and quitting smoking.
Also Check: How To Slow Your Heart Rate
The No 1 Reason People Stop Taking Beta
The top reason patients stop using beta-blockers is admission to the hospital for various conditions, not just heart failure, Dr. Tang says. However, most people should not stop, even if they are hospitalized, unless the doctors decided that it is more harm than good.
Research shows that patients fare better when they continue taking beta-blockers while in the hospital, even with acute heart failure.
An inability to tolerate beta-blockers indicates a worsening heart condition, says Dr. Tang. Other testing may be necessary to determine if the heart is too weak for beta-blockers.
This may even apply for patients whose heart function has recovered to the normal range. Recent clinical studies have shown that, even in those with full recovery of their heart structure and function, stopping drugs like beta-blockers can reverse the recovery course and can be detrimental, he adds.
Side Effects Of Beta Blockers
Most people taking beta blockers have either no or very mild side effects that become less troublesome with time.
Contact your GP if;you’re having symptoms that bother you or last more than a few days.
Side effects commonly reported;by people taking beta blockers include:
- feeling tired, dizzy or lightheaded
- cold fingers or toes
- difficulties sleeping or nightmares
It happens rarely, but some people have serious side effects when taking beta blockers.
Tell a doctor straight away if you have:
- shortness of breath with a cough that gets worse when you exercise , swollen ankles or legs, chest pain, or an irregular heartbeat these are signs of heart problems
- shortness of breath, wheezing and tightening of your chest these can be signs of lung problems
- yellow skin or the whites of your eyes turn yellow these can be signs of liver problems
These are not all the side effects of beta blockers. For a full list, see the leaflet inside your medicine packet.
You can report suspected side effects using;the;Yellow Card Scheme.
For more information on the side effects of beta blockers, read about the specific medicine you take in our Medicines A to Z.
Don’t Miss: How Is A Heart Attack Treated
Modes Of Action And Cardiovascular Effects
- Modes of action: beta-blockers antagonise the effect of beta-adrenergic stimuli .
- Cardiovascular effects: beta-blockers reduce heart rate, cardiac contractility, and systolic blood pressure. They also have anti-arrhythmic effects since they decrease spontaneous firing of ectopic pacemakers, slow conduction, and increase the refractory period of the atrioventricular node .
- Classification: beta-blockers can be classified as non-selective or cardioselective 1-antagonists .
How Do Beta Blocker Drugs Affect Exercise

Beta blockers are a type of cardiac medication;prescribed after a heart attack;or to treat abnormal heart rhythms and other conditions. They slow down your heartbeat, and that raises a common question about them: Do they affect your ability to exercise?
The answer can vary a great deal, depending on the severity of your condition, so checking with your healthcare provider is vital. Its also important to understand how these drugs affect your heart.
You May Like: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Cautions With Other Medicines
There are some medicines that may interfere with the way that beta blockers, including beta blocker eyedrops, work.
Tell your doctor if you’re taking:
- other medicines for high blood pressure. The combination with beta blockers can sometimes lower your blood pressure too much. This may make you feel dizzy or faint
- other medicines for an irregular heartbeat such as amiodarone or flecainide
- other medicines that can lower your blood pressure. These include some antidepressants, nitrates , baclofen , medicines for an enlarged prostate gland like tamsulosin, or Parkinson’s disease medicines such as levodopa
- medicines for asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- medicines for diabetes, particularly insulin beta blockers may make it more difficult to recognise the warning signs of low blood sugar
- medicines to treat nose or sinus congestion, or other cold remedies
- medicines for allergies, such as ephedrine, noradrenaline or adrenaline
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines , such as ibuprofen. These medicines may increase your blood pressure, so it’s best to keep them to a minimum
Your Good Health: Metoprolol Can Lower Heart Rate Excessively
Dear Dr. Roach: My husband has been on metoprolol for about eight years. He was prescribed that medication right after he had a stent put in due to a clogged heart vessel. He is doing very well. His recent stress test was normal. The metoprolol took his heart rate down to a pulse of between 55 and 60 shortly after he started it. He is an active 79-year-old and in good shape. But he was told years ago, when the metoprolol lowered his pulse, that he may eventually need a pacemaker.
If the metoprolol is giving him a lower heart rate, causing a future need for a pacemaker, I would think the cardiologist would just give him a different blood pressure prescription that doesnt lower the heart rate. He does not want a pacemaker due to a medication side-effect. Do you think a replacement for the metoprolol would keep his pulse in the normal range and dismiss the thought of a future pacemaker?
N.F.
Metoprolol commonly used in patients with coronary artery blockages is a beta blocker, and it works mainly by slowing the heart rate down and by decreasing how hard it contracts. Beta blockers reduce the risk of further heart attacks and death in people with coronary artery disease, and they should be given to most people with coronary artery disease unless there is a good reason not to. They also may act to reduce rhythm disturbances by counteracting adrenaline in the blood.
D.M.
You May Like: How To Stop Heart Palpitations Due To Anxiety
Beta Blockers: Cardiac Jacks Of All Trades
Uses for beta blockers range from lowering blood pressure to improving heart failure.
The release of the first beta blocker in the early 1960s revolutionized the treatment of chest pain caused by exertion or stress . Over the following four decades, these old dogs have learned many new tricks, from protecting the heart after a heart attack to controlling heart failure. Today, millions of Americans take a beta blocker.
This medication spotlight looks at how beta blockers work, who can benefit from them, and what to expect if you take one.
Who Needs A Beta Blocker
Beta blockers are used for many reasons, including:
-
angina
-
cardiac healing after a heart attack
-
heart failure
-
heart rhythm problems such as atrial fibrillation or palpitations
-
high blood pressure
-
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
-
noncardiovascular conditions such as anxiety, essential tremor, glaucoma, migraine, and others.
Once a mainstay for treating high blood pressure, beta blockers have been elbowed aside by newer drugs, such as ACE inhibitors, and older ones, such as thiazide diuretics.
Recommended Reading: How Does Exercise Affect Heart Rate
Different Classes Of Beta
Beta-blockers that are used clinically can be divided into two classes: 1) non-selective blockers , or 2) relatively selective 1 blockers . Some beta-blockers have additional mechanisms besides beta-blockade that contribute to their unique pharmacologic profile. The two classes of beta-blockers along with specific compounds are listed in the following table. Additional details for each drug may be found at www.rxlist.com. The clinical uses indicated in the table represent both on and off-label uses of beta-blockers. For example, a given beta-blocker may only be approved by the FDA for treatment of hypertension; however, physicians sometimes elect to prescribe the drug for angina because of the class-action benefit that beta-blockers have for angina.
| ; |
While Pregnant Or Breastfeeding
Beta-blockers may affect a growingÂ;baby by slowing its heart rateÂ;and lowering its blood sugar level and blood pressure. These drugs can also pass to anÂ;infant through breast milk, causing low blood pressure, trouble breathing, and a slowÂ;heart rate.
You should tell yourÂ;doctor if you’re trying to get pregnant or you become pregnant while on beta-blockers or are breastfeeding.
Recommended Reading: Is 190 Heart Rate Bad
