Start With Resting Heart Rate
You should test your resting heart rate before measuring your training heart rate. The best time to test your resting heart rate is first thing in the morning, before youve gotten out of bed ideally after a good nights sleep.
Using the technique described above, determine your resting heart rate and record this number to share with your doctor. You might try checking your resting heart rate for a few days in a row to confirm that your measurement is accurate.
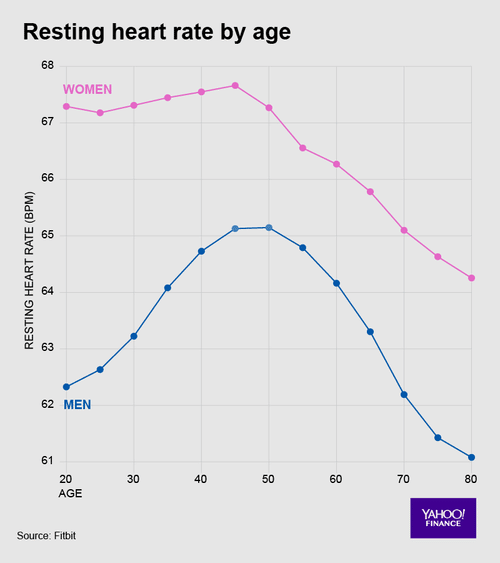
According to the American Heart Association , the average resting heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats per minute. However, this number may rise with age and is usually lower for people with higher physical fitness levels. The AHA notes that physically active people, such as athletes, may have a resting heart rate as low as 40 beats per minute.
How Do You Find Your Pulse
The easiest place to find your pulse is in your wrist.
- Turn your hand so that your palm is facing upwards.
- Now place the three middle fingers from your other hand on your wrist in the outside groove below the base of your thumb.
- Press lightly to feel the pulse under your fingers. If you can’t feel anything press slightly harder.
What Are Heart Palpitations
A heart palpitation is when you suddenly become aware of your heart beating, usually in an irregular way. Sometimes you can feel it in your ears, neck or chest when youre lying down. Your heart beat may feel:
- too fast or slow
- like its fluttering
- like its thudding, or pounding.
It is not unusual to feel heart palpitations occasionally and mostly they are harmless. However if youre experiencing them on a regular basis, see your doctor.
Also Check: What Is The Formula For Finding Your Maximum Heart Rate
How Are Arrhythmias Treated
Many arrhythmias don’t need treatment. For those that do, these options might be used:
- Medicines. Many types of prescription anti-arrhythmic medicines are available to treat arrhythmia. Sometimes, these can increase symptoms and cause side effects, so the patient will be closely watched by the doctor.
- Pacemakers. A pacemaker is a small battery-operated device implanted into the body through a surgical procedure. Connected to the heart by a wire, a pacemaker can detect if the heart rate is too slow and send electrical signals to speed up the heartbeat.
- Defibrillators. A small battery-operated implantable cardioverter defibrillator is surgically placed near the left collarbone. Wires run from the defibrillator to the heart. The ICD senses if the heart has a dangerously fast or irregular rhythm and sends an electrical signal to restore a normal heartbeat.
- Catheter ablation. A catheter is guided through a vein in the leg to the heart. Arrhythmias often are caused by microscopic defects in the heart muscle. Once the problem area of the heart is pinpointed, the catheter heats or freezes the defective muscle cells and destroys them.
- Surgery. Surgery is usually the treatment recommended only if all other options have failed. In this case, a person is put under anesthesia and a surgeon removes the tissue causing the arrhythmia.
Measuring Resting Heart Rate
Though there are a number of products, like smartwatches and heart rate monitors, that can measure resting heart rate, all you need is a watch with a second hand.
To measure your heart rate, place a finger over the radial artery or carotid artery. The radial artery is found at the base of the wrist on the side of the thumb. The carotid artery is found on the neck, to the side of the windpipe, just under the angle of the jaw.
Once you have located the artery, place your index and middle fingers over it and count the number of pulsations in one minute. A quicker method is to count the number of beats over 15 seconds and multiply this by 4 to determine beats per minute.
Read Also: What Can You Do For Congestive Heart Failure
What Is My Role In Checking Out My Fast Heart Rate
If you are concerned about an elevated heart rate, make sure you arent currently dehydrated, and that you are being treated properly for any related medical condition.
If youve accounted for common causes of an elevated heart rate including reducing or eliminating caffeine and are still experiencing symptoms, make sure to see a doctor as soon as possible.
What Is An Irregular Pulse
An irregular pulse is when the heart doesn’t beat in a regular, steady rhythm. This is also called an irregular heart rate or an arrhythmia.
If your heart rate is irregular, you may notice that your pulse:
- seems irregular or is ‘jumping around
- is racing, even when you’re at rest
- seems unusually slow some or most of the time
- seems to pause, add, or miss a beat.
Read Also: How To Slow Your Heart Rate When Nervous
Factors That Can Affect Resting Heart Rate
In addition to age, a few other factors can affect your resting heart rate.
- Temperature. Your heart rate may increase slightly when youre exposed to hot temperatures.
- Medication side effects. Medications, like beta-blockers, can lower your resting heart rate.
- Emotions. If youre anxious or excited, your heart rate may increase.
- Weight. People with obesity may have a higher resting heart rate. This is because the heart has to work harder to supply the body with blood.
- Anemia. In anemia, low levels of red blood cells can cause the heart to beat faster in order to supply your body with oxygen-rich blood.
- Endocrine or hormonal abnormalities. Abnormal levels of some hormones can influence heart rate. For example, too much thyroid hormone can increase heart rate while too little thyroid hormone can decrease heart rate.
- Postural tachycardia syndrome . This syndrome produces an abnormal increase in heart rate after sitting up or standing. In addition to heart palpitations, some typical symptoms of PoTS include dizziness and fainting.
- Body positioning. Heart rate can increase temporarily when you move from a sitting to a standing position.
- Smoking. Smokers tend to have a higher resting heart rate. Quitting smoking can help bring it back down. This is often difficult, but a doctor can help build a cessation plan that works for you.
Your maximum heart rate is a calculation that helps you figure out what your ideal target heart rate is during exercise.
Vfib And Afib: Which Is More Serious
Ventricular fibrillation is more serious than atrial fibrillation. Ventricular fibrillation frequently results in loss of consciousness and death, because ventricular arrhythmias are more likely to interrupt the pumping of blood, or undermine the hearts ability to supply the body with oxygen-rich blood.
VFib can cause sudden cardiac death . SCD accounts for about 300,000 deaths annually in the United States. SCD can kill a victim in minutes, and it can occur even in people who seem healthy.
The following risk factors are linked to ventricular fibrillation:
- previous ventricular fibrillation
- congenital heart disease, or being born with a heart defect
- electrocution or other injuries that cause heart muscle damage
Heart attack is the most common cause of ventricular fibrillation.
Don’t Miss: Did John Legend Have Heart Surgery
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose Ventricular Tachycardia
An electrocardiogram , which records your hearts electrical activity, is the most common test for diagnosing ventricular tachycardia.
Other tests may include:
- IV medications.
Nonemergency treatment for ventricular tachycardia usually includes:
- Radiofrequency catheter ablation : After pinpointing where an abnormal rhythm starts, your healthcare provider will use a catheter to destroy tissue in that area with an electrical current.
- Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator : This device monitors and controls your hearts rhythm. If it detects an episode of ventricular tachycardia, it quickly sends an electrical signal to get your heart back to a normal rhythm.
- Medications: Medications can slow your heart rate and attempt to maintain a normal rhythm. Some medications are associated with serious side effects, which your doctor will review with you prior to prescription.
Complications of the treatment
Although ablation of ventricular tachycardia has a long history of safety and success, complications can sometimes happen. Complications may include:
- Damage to your heart or blood vessel.
I’ve Been Having A Heart Rate Of 120 Bpm For The Last Hour At Rest Sitting
I’ve been having a heart rate of 120 bpm for the last hour at rest, sitting down and relaxed I’m lightheaded, no stimulus /stimulants no asthma meds, no cold, flu, fever,palpitations. The local hospital won’t let me talk triage because my doctor isn’t with the hospital I can’t drive to the er but I don’t know if I need a paramedic. I hate ambulances please what should I do?
This is where you need to talk to your doctor for guidance and where relying in the internet doesn’t work well … Although around a lot of the time, I’m not always able to answer promptly.
Most doctor’s offices have after hours doctors on call.
Thank you for that note. I’ll keep it in mind. MY heart rate finally went down 10 beats per minuts and I went to sleep. I woke up at 3 am while eating a very light snack and sitting down I got lightheaded again but today I feel better and I see my doctor today anyway.
Thank you for that note. I’ll keep it in mind. MY heart rate finally went down 10 beats per minuts and I went to sleep. I woke up at 3 am while eating a very light snack and sitting down I got lightheaded again but today I feel better and I see my doctor today anyway. My doctor office doesn’t have an after hours on call and because my doctor isn’t affiliated with the hospital I wasn’t able to speak to triage and I wasn’t able to drive across town to the er.
Ask your doctor about the situation with regard to after hours care … maybe there’s a clinic?
Also Check: When Is Heart Rate Too High
Lowering A Rapid Heart Rate
Heart rates can spike due to nervousness, stress, dehydration and overexertion. Sitting down, taking slow, deep breaths and rehydrating can help lower your heart rate in these instances.
In the long-term, maintaining a regular exercise schedule can help to lower and then maintain your resting heart rate over time. Smoking cigarettes raises the heart rate, in part due to nicotine’s effects on the circulatory systems blood vessels, so quitting smoking can also help lower one’s heart rate to a healthy range, according to Harvard Health.
To lower your heart rate in a healthy way after exercise, the AHA and Mayo Clinic recommend that you “cool down” by continuing to move for about 5 to 10 minutes, but at a slower pace and reduced intensity compared with the rest of your workout. For instance, Mayo suggests the following cool down activities:
- To cool down after a brisk walk, walk slowly for five to 10 minutes.
- To cool down after a run, walk briskly for five to 10 minutes.
- To cool down after swimming, swim laps leisurely for five to 10 minutes.
Cooling down after a workout helps gradually bring your heart rate down to pre-exercise levels, thus helping you avoid potential feelings of dizziness or nausea that can occur when the heart rate falls too rapidly. It’s unclear whether including a cool down in your workout helps to prevent muscle stiffness or soreness after exercise, but more research is needed in this area, according to the Mayo Clinic.
Slow Resting Heart Rates
On the other hand, a resting heart rate below 60 beats per minute is called bradycardia, and can cause insufficient blood flow to the brain.
“An abnormally low heart rate can lead to symptoms such as feeling tired, lightheaded, dizzy, and may even cause loss of consciousness,” says Suneet Mittal, M.D, FHRS, of the Heart Rhythm Society.
There are some conditions, such as thyroid disease, that can affect how fast your heart beats, Dr. Singh says. For people with an overactive thyroid, called hyperthyroidism, the excess amount of thyroid hormone can elevate the heart rate, he explains. Conversely, people with an underactive thyroid, called hypothyroidism, can have slower heart rates.
Some medications are also known to affect the heart rate, Dr. Singh adds. Stimulants such as pseudoephedrine, a common ingredient found in decongestants, can elevate it. Beta-blockers, which are medications used to treat high blood pressure and hyperthyroidism, can act on heart rate as well and cause it to read as lower. Electrical abnormalities in the heart’s pathways can also lower your resting heart rate.
Without overdoing it, one of the best things you can do to maintain a healthy resting heart rate is exercise. You should be incorporating both cardio and weights into your routine, for a total of 150 minutes per week, says Traynor.
Read Also: Beta Blockers In Heart Failure
Treating Supraventricular Tachycardia In Hospital
SVT is rarely life threatening. But you may need treatment in hospital if you keep having long episodes.
This may include:
- medicines to control the episodes of SVT given as tablets or through a vein
- cardioversion a small electric shock to the heart to help it get back to a normal rhythm
- catheter ablation a treatment where thin tubes are placed through a vein or artery into your heart to correct the problem with the electrical system this permanently cures the problem in most patients
Find out more about:
What Is A Target Heart Rate
According to the AHA , your target heart rate during moderate-intensity activities is about 50 to 70 percent of your maximum heart rate. Vigorous physical activity should result in about 70 to 85 percent of your maximum.
So for 35-year-olds, a goal target heart rate is between 93 and 157 bpm .
The table below shows the target heart rate range and average maximum heart rate for different ages, based on information from the AHA.
| Age |
- being an older adult
- problems with the conduction system of the heart
Borderline or occasional bradycardia may not need treatment. But prolonged bradycardia, or bradycardia thats not treated, can become more serious.
Certain underlying conditions are typically the true decider of what a dangerous heart rate is. If youre already living with heart disease, heart failure, or a history of heart disease and notice a fluctuation in your heart rate, you should go to the doctor as soon as you can, as it could be a sign of a serious complication.
You May Like: With Respect To Heart Rate, Which Of The Following Worked In Opposition To Each Other
Atria Ventricles And The Electrical Circuitry Of The Heart
The human heart consists of four chambers : the atria, which are the two upper chambers, and the ventricles, which are the two lower chambers.
The heart has a natural pacemaker, called the sinoatrial node, in the right atrium. This produces electrical impulses. Each one triggers an individual heartbeat.
As the electrical impulses leave the sinoatrial node, they cross the atria, making the atrial muscles contract. This contraction pushes blood into the ventricles.
The electrical impulses continue to the atrioventricular node, which is a cluster of cells. The AV node slows down the electrical signals, then sends them on to the ventricles.
In doing so, it allows time for the ventricles to fill with blood. When the ventricular muscles receive the electrical signals, they contract, pumping blood either to the lungs or to the rest of the body.
A problem with the electrical signals can result in a faster-than-normal heartbeat. This is tachycardia.
Tachycardia usually stems from a disruption in the normal electrical impulses that control the hearts pumping action, or the rate at which the heart pumps.
Depending on the type and cause of tachycardia, the following
- calcium channel blockers, such as diltiazem or verapamil
- beta-blockers, such as propranolol or metoprolol
- blood thinners, such as warfarin or apixaban
Elevated Heart Rate Most Likely Caused By Medical Condition
May 6, 2011
What is sinus tachycardia? What causes it? How is it treated?
Answer:
Sinus tachycardia is the term used to describe a faster-than-normal heartbeat a rate of more than 100 beats per minute versus the typical normal of 60 to 70 beats per minute. Well over 99 percent of the time, sinus tachycardia is perfectly normal. The increased heart rate doesn’t harm the heart and doesn’t require medical treatment.
The term sinus tachycardia has nothing to do with sinuses around the nose and cheeks. Rather, it comes from the sinus node, a thumbnail-sized structure in the upper right chamber of the heart. This structure controls the heart rate and is called the heart’s natural pacemaker.
The sinus node signals the heart to speed up during exercise or in situations that are stressful, frightening or exciting. For example, a 10- to 15-minute brisk walk typically elevates the heart rate to 110 to 120 beats per minute. Also, the sinus node increases the heart rate when the body is stressed because of illness. In all of these circumstances, the heart rate increase is a normal response.
Likewise, the sinus node signals the heart to slow down during rest or relaxation.
For some patients, the elevated heart rate is the only symptom. Some have a lifelong history of sinus tachycardia in the 110 beats per minute range, and they lead a normal, healthy life. And often the inappropriate sinus tachycardia will improve in time without treatment.
Don’t Miss: Reversing Congestive Heart Failure
What Is Considered A Fast Heart Rate
The definition of a fast heart rate differs depending on the age of the person experiencing it. Typically, it is defined as have a resting heart rate faster than 100 beats per minute for adults.
A fast heart rate is one that is unexpected for a certain level of physical activity. Usually, most adults resting heart rate usually lies in the range of 60-80 beats per minute, with some heart rates approaching 100 beats per minute.
