Will I Have To Take Medicine For The Rest Of My Life
If you have had a heart attack, your doctor will probably want you to take certain medicines for a long time. This can help reduce your risk of more heart problems. Your doctor can answer your questions about these medicines. He or she can tell you the benefits and risks of taking them.
- Aspirin can reduce the risk of a heart attack. A low dose of aspirin each day can keep your blood from forming clots that can eventually block the arteries. Talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of aspirin therapy.
- Antiplatelet medicines also help stop blood clots from forming. These drugs are especially important to take for at least a year if you have had a stent placed in your heart.
- Beta blockers are a group of drugs that lower the heart rate and blood pressure. They help improve blood flow to the heart.
- ACE inhibitors are a group of drugs that can help if your heart is not pumping blood well. This medicine helps open your arteries and lower your blood pressure. This improves blood flow.
- Statins are a group of drugs that are used to control cholesterol. They lower bad cholesterol levels and may help increase good cholesterol .
Stressing Out All The Time
We all have stress, and no one wants to be called a snowflake, but science is clear that chronic stress is really bad for your body. “When stress is excessive, it can contribute to everything from high blood pressure, also called hypertension, to asthma to ulcers to irritable bowel syndrome,” said Ernesto L. Schiffrin, M.D., Ph.D., professor in the Department of Medicine at McGill University. Hypertension is bad for your heart and stress leads people to engage in other unhealthy behavior that can tax your ticker, including drinking too much alcohol and stress-eating.
The Rx: Exercising, not smoking, eating a healthy diet and maintaining a healthy weight are good ways to deal with stress, said Schiffrin.
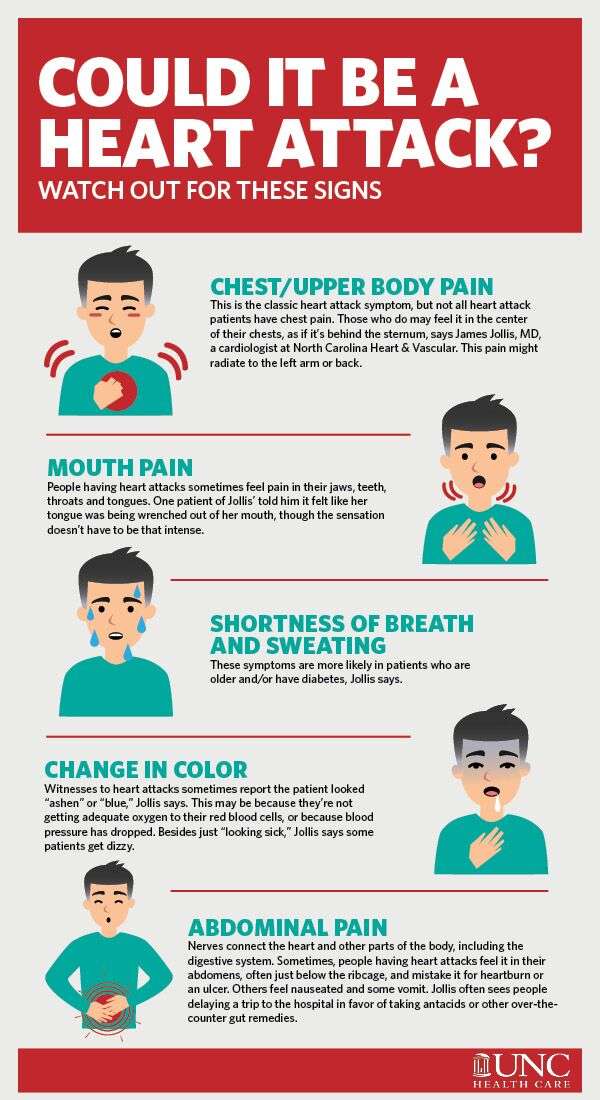
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Attack
The major symptoms of a heart attack are
- Chest pain or discomfort. Most heart attacks involve discomfort in the center or left side of the chest that lasts for more than a few minutes or that goes away and comes back. The discomfort can feel like uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain.
- Feeling weak, light-headed, or faint. You may also break out into a cold sweat.
- Pain or discomfort in the jaw, neck, or back.
- Pain or discomfort in one or both arms or shoulders.
- Shortness of breath. This often comes along with chest discomfort, but shortness of breath also can happen before chest discomfort.
Other symptoms of a heart attack could include unusual or unexplained tiredness and nausea or vomiting. Women are more likely to have these other symptoms. Learn more about women and heart disease.
Every 40 seconds, someone in the United States has a heart attack.1Learn more facts about heart attack and heart disease.
Don’t Miss: Claritin Heart Racing
Living In Lower Altitude Places
If you want to avoid experiencing a heart attack, move to the mountains! One 2017 study published in the journal Frontiers in Physiology found that those who lived in lower-altitude places had an increased risk of metabolic syndromeone of the risk factors for heart disease and heart attacks.
The Rx: If you do live in a lower altitude setting, you might not have the option of moving. However, you should be more cognizant of the other heart attack risk factors and focus on keeping them to a minimum.
What To Do If You Recognize A Heart Attack

If you think theres any chance you or someone else may be having a heart attack, you need to get medical help as quickly as possible. Even if it turns out to be something else, it is better to act quickly than risk putting your life on the line.
If you recognize the signs of a heart attack, call 9-1-1 immediately. The sooner that treatment begins, the greater likelihood that you can minimize damage to the heart.
The person having the symptoms should not drive. Always have someone else drive you to the hospital if you are not being transported by ambulance.
If the person goes unconscious, you can start cardiopulmonary resuscitation while you wait for emergency medical services . If you are in a public place, ask if there is an AED on site. An AED is a portable device that can check someone’s heart rhythm and, if necessary, deliver an electric shock to help someone who is in cardiac arrest.
Find trainings in CPR and AED use through the American Red Cross, so you are prepared if you are ever in an emergency situation.
Read Also: Where Does Blood Low In Oxygen Enter First
Treatment Of A Heart Attack
A heart attack is a medical emergency and the quicker someone is treated, the better their chances of survival.
Doctors treat a heart attack by administering oxygen, blood pressure-lowering medicines, clot-melting medicines, and cholesterol-lowering drugs. If you present to the hospital in time, your doctor may perform a procedure called percutaneous coronary intervention to repair the blocked blood vessel. This immediately improves blood flow and salvages a large chunk of your heart tissue.
However, you do not need to wait until you have a heart attack to seek treatment. If you have any of the risk factors mentioned, ensure to seek medical help in time and change your lifestyle and diet to limit your risk of a heart attack.
What Causes A Heart Attack
By definition, a heart attack is the result of blockage in an artery that supplies blood to the heart muscle. These blood vessels are called coronary arteries. Youve probably heard the term coronary artery disease, or CAD. That just means that theres plaque buildup in one or more of the hearts arteries, and that its reducing or blocking blood flow in those arteries. The plaque is a waxy substance that includes LDL cholesterol, fats, and other waste products from your bloodstream.The process of plaque building up in your arteries is called atherosclerosis. You may know it by a more familiar name: hardening of the arteries. This buildup takes place over many years.
There are some less-common heart attack causes, too. One of your coronary arteries could spasm and shut off blood flow to the heart muscle. Sometimes smoking or illicit drugs can result in coronary artery spasm. A spasm can occur in a coronary artery that isnt affected by atherosclerosis.
Also unusual, but still possible, is a tear in the inner wall of a coronary artery this is called a spontaneous coronary artery dissection. An artery has three walls or layers. When blood seeps through a tear in the inner layer, it can become trapped and bulge inward. As a result, blood flow through that artery becomes blocked.
Read Also: Flonase Chest Pain
Dont Become A Statistic
Of course, all of these life-saving treatments are of no use if you dont respond immediately to the warning signs of heart attacks.
According to a study published in Circulation , more than half of the 1.2 million people who have a heart attack or coronary death each year in the U.S. die in an ED or before reaching a hospital within an hour of the onset of symptoms.
Speed is of the essence in stopping heart attacks. Lifesaving measures are only effective for a brief period of time after symptoms begin, before heart muscle begins to die and your heart ceases to function. Heed the advice. And just. Dont. Wait.
Other Common Signs And Symptoms
Pay attention to these other possible symptoms of a heart attack:
- Breaking out in a cold sweat
- Feeling unusually tired for no reason, sometimes for days
- Nausea and vomiting
- Light-headedness or sudden dizziness
- Any sudden, new symptoms or a change in the pattern of symptoms you already have
Not everyone having a heart attack has typical symptoms. If you’ve already had a heart attack, your symptoms may not be the same for another one. However, some people may have a pattern of symptoms that recur.
The more signs and symptoms you have, the more likely it is that you’re having a heart attack.
Read Also: Low Blood Pressure Heart Failure Elderly
What Increases Your Risk
Coronary artery disease is the major cause of heart attacks. So the more risk factors you have for CAD, the greater your risk for unstable angina or a heart attack. The main risks for CAD are:
- Smoking.
- Family history of early CAD.
- Age. The risk increases in men after age 45 and in women after age 55.
Ake In Physical Activity
Being physically active will also help to prevent a heart attack. According to the American Heart Association, adults should try to get at least 150 minutes of moderate or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise every week when possible.
Adults who are already active can increase their activity levels to give themselves even better prevention against heart attacks.
Recommended Reading: Can Dehydration Cause Increased Heart Rate
Not Knowing Your Cholesterol Level
As we age, the body produces more cholesterol, which can build up in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. In women, menopause causes LDL cholesterol to rise and HDL to drop. Experts advise getting your cholesterol checked every five years, but older adults may need it done more frequently. Your total cholesterol level should be less than 200 milligrams per deciliter , with an LDL level of less than 100 mg/dL and an HDL level of 60 mg/dL or higher.
The Rx: To keep your levels in a healthy range, eat a diet low in saturated fat and trans fats, get exercise and maintain an ideal weight.
Why The First Hours Are Critical
For anyone having a heart attack, getting rapid medical attention is absolutely critical. Both the short-term and the long-term consequences of a heart attack are largely determined by how much of the heart muscle dies. With rapid and aggressive medical treatment, the blocked artery can usually be opened quickly, thus preserving most of the heart muscle.
If treatment is delivered within three or four hours, much of the permanent muscle damage can be avoided. But if treatment is delayed beyond five or six hours, the amount of heart muscle that can be saved drops off significantly. After about 12 hours, the damage is often irreversible.
Cardiac arrests can occur within the first few hours of a heart attack or during recovery. If a cardiac arrest occurs in the hospital, there is an excellent chance it can be treated. Unfortunately, the risk of sudden cardiac arrest is heightened after a heart attack, especially within the first year.
Also Check: Can Acetaminophen Raise Blood Pressure
How Is A Heart Attack Treated
Heart attack treatment begins immediately. The goal of treatment is to treat you quickly and limit heart muscle damage.
Medications
The goals of medication therapy are to break up or prevent blood clots, prevent platelets from gathering and sticking to the plaque, stabilize the plaque, and prevent further ischemia. These medications must be given as soon as possible to decrease the amount of damage to the heart muscle. The longer the delay in starting these drugs, the more damage that occurs and the less benefit they can provide.
Thrombolytic medications are used to break up clots blocking the artery
Medications given right after the start of a heart attack may include:
- Other antiplatelet drugs
- Any combination of the above
Other drugs, given during or after a heart attack lessen your heart’s work, improve the functioning of the heart, widen or dilate your blood vessels, decrease your pain, and guard against any life-threatening heart rhythms. Your doctor will prescribe the appropriate medications for you.
Interventional Procedures
During or shortly after a heart attack, you may go to the cardiac catheterization laboratory to directly evaluate the status of your heart, arteries and the amount of heart damage. In some cases, procedures are used to open up your narrowed or blocked arteries. These procedures may be combined with thrombolytic therapy to open up the narrowed arteries, as well as to break up any clots that are blocking them.
Coronary artery bypass surgery
How Do Doctors Know What Kind Of Heart Attack Youve Had
You cant predict the outcome of a heart attack by your symptoms or how severe they are. Thats why symptoms that suggest a possible heart attack should never be ignored.
How well you fare after a heart attack depends on how quickly you act, Dr. Campbell says. The sooner you get emergency care, the better the chance you will suffer less permanent damage to your heart.
If you go to the ER with heart-attack symptom, youll be treated right away. Your blood will be examined for any enzymes indicating theres been damage to your hearts muscle. And a noninvasive echocardiogram is performed to see how well your heart is pumping.
Still it may take several hours to determine whether youve had a heart attack and what kind of treatment is needed. That means, if youre not sure what your symptoms mean, the thought of spending several hours in the ER might discourage you from seeking care. Dont let it! Dr. Campbell advises that its much wiser to err on the safe side.
Its better you spend several hours in the ER than learn the damage has been done, and your heart cant be fixed, he says.
Recommended Reading: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
Ambulance And Emergency Room
Treatment begins in the ambulance and emergency room. You may get oxygen if you need it. You may get morphine if you need pain relief.
The goal of your health care team will be to prevent permanent heart muscle damage by restoring blood flow to your heart as quickly as possible.
Treatment includes:
- Nitroglycerin. It opens up the arteries of the heart to help blood flow back to the heart.
- Beta-blockers. These drugs lower the heart rate, blood pressure, and the workload of the heart.
You also will receive medicines to stop blood clots. These are given to prevent blood clots from getting bigger so blood can flow to the heart. Some medicines will break up blood clots to increase blood flow. You might be given:
- Aspirin, which you chew as soon as possible after calling 911.
- Antiplatelet medicine.
- Thrombolytics.
You Haven’t Asked Your Doctor About Heart Testing
Little-known fact: Standard heart tests at your annual physical and ECG and, in some cases, a stress test aren’t good at detecting clogged arteries until they’re 70 percent blocked. You could ace both tests and still be on your way to a heart attack. Luckily, more advanced imaging and blood tests are available, along with genetic screening, to uncover arterial issues before they lead to heart disease.
The Rx: Talk to your doctor about your personal and family health history to determine if it’s time for a more extensive peek under your hood.
Don’t Miss: Can Antihistamines Cause Heart Palpitations
Less Likely To Be A Heart Attack
Sensation of pain, or of pressure, tightness, squeezing, or burning
Sharp or knifelike pain brought on by breathing or coughing
Gradual onset of pain over the course of a few minutes
Sudden stabbing pain that lasts only a few seconds
Pain in diffuse area, including a constant pain in middle of chest
Pain clearly on one side of the body or the other
Pain that extends to the left arm, neck, jaw, or back
Pain that is localized to one small spot
Pain or pressure accompanied by other signs, such as difficulty breathing, a cold sweat, or sudden nausea
Pain that lasts for many hours or days without any other symptoms
Pain or pressure that appears during or after physical exertion or emotional stress or while you are at rest
Pain reproduced by pressing on the chest or with body motion
What Are The Risk Factors For Heart Attack
Several health conditions, your lifestyle, and your age and family history can increase your risk for heart disease and heart attack. These are called risk factors. About half of all Americans have at least one of the three key risk factors for heart disease: high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and smoking.2
Some risk factors cannot be controlled, such as your age or family history. But you can take steps to lower your risk by changing the factors you can control.
Learn more about risk factors for heart disease and heart attack.
Don’t Miss: Apple Watch Heart Rate Monitor Accuracy
What Makes You Worry That Chest Pain Is Serious Like A Heart Attack
When is chest pain serious? That dull burning feeling in your chest doesn’t seem to be going away, and even feels like it is getting worse. Is it a heart attack, or ?
It’s a vexing question, one that millions of people and their doctors face each year. What’s the problem? Chest pain can stem from dozens of conditions besides , from pancreatitis to pneumonia or panic attack.
Millions of Americans with chest pain are seen in hospital emergency departments every year. Only 20% of them are diagnosed with a heart attack or an episode of unstable , a warning sign that a heart attack may happen soon. A few have another potentially life-threatening problem, such as pulmonary embolism or aortic dissection . Some are experiencing “regular” angina, which occurs when part of the heart isn’t getting as much oxygen-rich blood as it needs during periods of physical exertion or emotional stress. Most of them, though, had a condition unrelated to the heart or arteries.
The other tricky problem with heart attacks is that different people experience them in different ways. Some have classic chest pain. Others have jaw pain or back pain. Still others become breathless, or extremely fatigued, or nauseated.
