End Stages Of Heart Failure In Dogs
The end stages of heart failure in dogs are the hardest for dog owners to endure. When the heart fails to pump as effectively as it should, a cascading chain of events takes place. While the body can try to compensate, and medications can help reduce strain on the heart, this will be effective only up to a certain extent. As the heart is forced to work more, a point will inevitably come where the heart is no longer able to pump correctly. Veterinary care at this point is still important. Your vet can suggest you a therapeutic plan and you should follow up to report the level of success of such intervention.
Clogged arteries leading to heart disease is mostly seen in humans.
When the Heart Fails
In dogs, congestive heart failure is mostly caused by two heart conditions, namely valve degeneration and dilated cardiomyopathy .
Congestive heart failure in dogs is a chronic condition that worsens over time. Although symptoms can be managed, there is no cure, and in time, affected dogs will unfortunately reach the final stages.
When dealing with heart failure, therefore vets aren’t really fixing anything, but just trying to relieve symptoms and delay the inevitable for as long as possible. Dogs with end stage heart failure are unfortunately on “borrowed time.”
When To Seek Hospice Care
Even physicians have difficulty determining life expectancy for people with end-stage heart-failure. The condition can be unpredictable, and symptoms can change. However, certain signs can indicate that hospice care would be beneficial, including:
- frequent chest pain
- significant fatigue or shortness of breath
- substantial decline in ability to do daily activities, such as self-care
- The patient has already received the best possible treatment, which are no longer working well, and the patient is not a candidate for other interventions.
- The patient has received the best possible treatment and has decided to decline further specialized interventions.
People can be reluctant to start hospice, as they may worry it means theyre giving up or that it will hasten death. But such concerns are unfounded. In fact, patients and families often wish they had started hospice sooner, because it makes such a positive difference in their lives. And research shows that early admission to hospice results in greater satisfaction with care among patients and family caregivers.
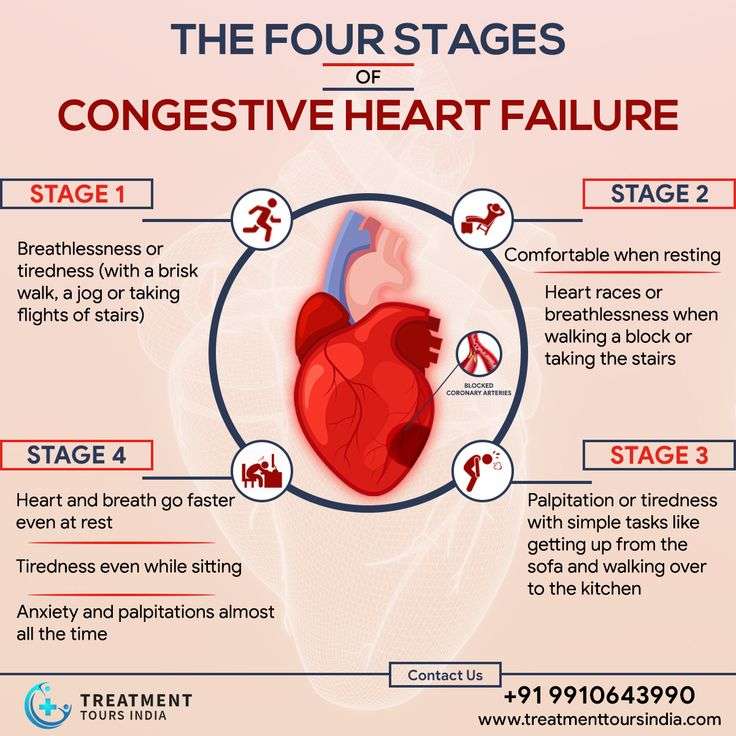
What Are The Final Stages Of Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure is essentially a stage where there is a presence of a lot of fluid buildup around the heart which inhibits the heart to pump efficiently. It is a chronic condition which progresses over time. Congestive heart failure can be fatal because the proper blood circulation throughout the body gets gravely hampered and thus fluid and blood starts accumulating in the abdomen, lungs, liver and lower torso. Medical attention in this case is an absolute necessity.
You May Like: Life Expectancy After Open Heart Surgery
What Are The Complications Of Heart Failure
Some of the complications from heart failure include:
- Irregular heartbeat.
- History of taking drugs that can damage your heart muscle, such as some cancer drugs.
Stage B
Stage B is considered pre-heart failure. It means your healthcare provider has given you a diagnosis of systolic left ventricular dysfunction but youve never had symptoms of heart failure. Most people with Stage B heart failure have an echocardiogram that shows an ejection fraction of 40% or less. This category includes people who have heart failure and reduced EF due to any cause.
Stage C
People with Stage C heart failure have a heart failure diagnosis and currently have or previously had signs and symptoms of the condition.
There are many possible symptoms of heart failure. The most common are:
- Shortness of breath.
- Need to urinate while resting at night.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats .
- A dry, hacking cough.
- A full or hard stomach, loss of appetite or upset stomach .
There may be times that your symptoms are mild or you may not have any symptoms at all. This doesn’t mean you no longer have heart failure. Symptoms of heart failure can range from mild to severe and may come and go.
Unfortunately, heart failure usually gets worse over time. As it worsens, you may have more or different signs or symptoms.Its important to let your doctor know if you have new symptoms or if your symptoms get worse.
What Is An Ejection Fraction
An ejection fraction is a measurement of the blood pumped out of your heart with each beat, expressed in a percentage. It can be measured using an echocardiogram , multigated acquisition scan, nuclear stress test, magnetic resonance imaging , or during a cardiac catheterization. A normal ejection fraction is between 50% and 70%.
You May Like: Risk Factors For Heart Attack
When To Seek Help
Patients with a life expectancy shorter than six months are eligible for hospice care. A hospice provides additional aid and resources to assist the person in living comfortably and with the highest possible quality of life. Hospice caregivers can also help patients and their families plan for future needs and circumstances. They have a unique insight into how to assist those with these difficulties.
Patients with end-stage heart failure need medical continuity throughout outpatient programs. These are just some of the symptoms that hospice care might help with. Positive inotropic drug infusions, anxiolytics, and sleeping medicines are all viable treatments. Its challenging for patients, families, and doctors caring for patients with end-stage heart failure to identify when treatment goals shift from survival to quality of life, allowing for a peaceful and dignified death.
What Is The Treatment For Congestive Heart Failure
The treatment of heart failure depends on the exact cause, but it can usually be treated effectively. The overall goals are to correct underlying causes, to relieve symptoms, and to prevent worsening of the condition. Symptoms are relieved by removing excess fluid from the body, improving blood flow, improving heart muscle function, and increasing delivery of oxygen to the body tissues. This can be done by the various congestive heart failure treatments listed in this sections.
If the underlying cause of heart failure is not correctable by surgery or catheterization procedures, medical treatment is composed of lifestyle changes and medications.
Dont Miss: Ibs And Palpitations
You May Like: How To Calculate Heart Rate
Supporting Those Around The Patient
Those close to the patient may also need emotional and practical support. They may need:
- information about heart failure to help them understand the symptoms and treatment options
- support if they’re caring for the patient
- time to relax or look after their own health.
If the patient’s heart failure is due to an inherited heart condition, their family may have concerns about their own health. Talk to them about their worries. It might be appropriate to refer immediate family members to a clinic which specialises in inherited heart conditions. This may have been done when the patient was first diagnosed.
Inherited heart conditions services offer specialist assessment and investigations, genetic counselling and testing. GPs can refer to this service.
What Can Hospice Do For The Family Of A Person With Heart Disease
Family members may have to make difficult healthcare and financial decisions, act as caregivers and provide emotional support to others. If the decision is made to stop medical support, some families experience strong emotions and feel overwhelmed.
Hospice offers comprehensive services for families of patients with heart disease:
You May Like: How To Tell If Heart Attack Is Coming
Stage B Treatment Options
While stage A CHF is managed with lifestyle changes, the treatment plan for stage B typically includes taking medications regularly. People at this stage should still make the same lifestyle changes as those appropriate for stage A. However, your doctor may also prescribe additional treatments such as:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers, if you arent taking any as part of your stage A treatment plan
- Beta blockers if youve had a heart attack and your EF is 40% or lower, if you arent taking any as part of your stage A treatment plan
- Possible surgery or intervention as a treatment for coronary artery blockage, heart attack, valve disease, or congenital heart disease
Prognosis By Ejection Fraction
Ejection fraction is a measure of how much blood is pumped out of your heart each time it contracts. A healthy heart has an EF of between about 55 percent to 75 percent.
Some people with CHF have a reduced EF. This means their heart is pumping less blood out to the rest of their body than a healthy heart. Studies have shown that people who have CHF and a reduced EF have a more challenging outlook than people with CHF who do not have a reduced EF.
The exact survival rates varied among studies, but have shown that EF has an impact on prognosis. Your doctor will have the best information about how your ejection fraction can affect your prognosis.
Don’t Miss: Does Olmesartan Lower Heart Rate
Symptoms Of Heart Failure
Common symptoms of heart failure include:
- breathlessness either when resting or being active
- swelling of legs, ankles, feet, abdomen or around the lower back area
Patients with heart failure may find it difficult to move around, do daily activities, work and do hobbies. This can affect how they feel, and lead to worries about money or losing their independence.
If someone has symptoms of heart failure and they have not been diagnosed with heart failure, it’s important that they speak to their GP or another healthcare professional.
Both Are Chronic And Have Periodic Flare
Each of these conditions is chronic and cannot be cured. But you can have periods of relative stability when symptoms are not too bothersome. At times, though, the symptoms can worsen or flare-up. This is called an exacerbation.
The difference is what causes these exacerbations. With COPD, triggers are often environmentally-related:
- Exposure to germs that cause respiratory infections
- Breathing in cold dry air
- Exposure to air pollution
- Inhaling strong fumes or smoke
With CHF, factors that cause flare-ups are often more related to lifestyle or other health issues.
- Eating the wrong foods, for example, too many salty foods
- Drinking too much water
- Having a heart attack or stroke
In both cases, exacerbations can also occur when medications are not taken as prescribed.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Stemi Heart Attack
Hospice And Congestive Heart Failure
When a heart failure patient has been diagnosed with six months or less to live, the added support of hospice care helps them remain in their home until end of life.
Crossroads Hospice & Palliative Care provides a team of nurses, aides, social workers, volunteers, and chaplains to support the patient and their family through the final stages of congestive heart failure symptoms. To learn more about referring your patient to hospice, please call Crossroads at 1-888-564-3405.
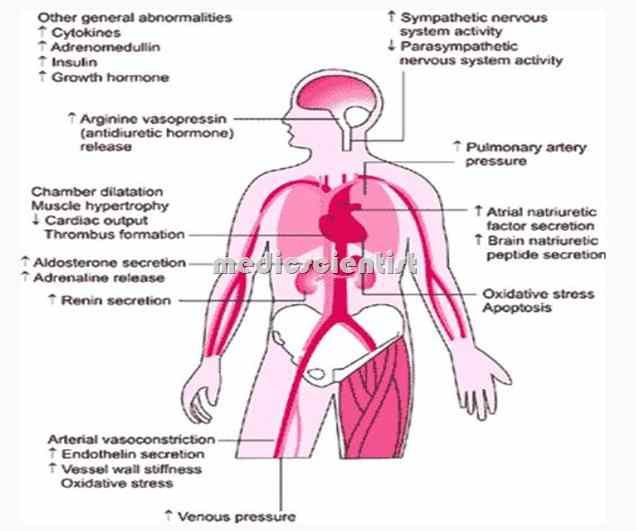
What Happens If You Have Heart Failure
People with heart failure have weak hearts that dont work as well as they should. Over time, the illness causes significant damage to the body.
In the first stages, the heart is less effective. It stretches, grows bigger, and pumps faster to compensate for the lack of strength. The body also changes, with arteries getting smaller and blood being directed away from certain body parts. Many people with heart failure dont know they have a problem in these early stages.
Towards the end stages of CHF, symptoms will worsen even if lifestyle changes are made, and the body will be unable to compensate for the loss of blood flow. As soon as that happens, the person may start to feel tired, have trouble breathing, and have other problems.
People can get help managing their end stages congestive heart failure symptoms and slowing down the progress of their condition with a variety of treatments. Its a long-term condition that cant be cured, as well as heart failure. People will eventually reach the end stages of heart failure.
Even when the person is lying down, they feel a shortness of breath. Their symptoms can change rapidly over a short period of time.
Recommended Reading: How To Rule Out Heart Attack At Home
Caring For Someone With Heart Failure Towards The End Of Life
Please be aware – this information is for healthcare professionals.
You can use our My Learning form to reflect on how this page has helped with your continuing professional development.
If you’re a patient, or a family member or friend, you can find more information on heart failure from the British Heart Foundation .
Heart failure means the heart is not pumping blood around the body as well as it should. People with heart failure may have symptoms such as fatigue, breathlessness and oedema . Here, we’ll talk about knowing when a patient with heart failure is near the end of life, and how to support them.
This information is about supporting adults with advanced heart failure.
On this page:
What Do Symptoms Of End Stage Congestive Heart Failure Look Like
Dyspnea
Dyspnea or shortness of breath can occur both during activity and rest. This is the symptom that often sends patients racing to the hospital late at night. Work with your hospice or palliative care team to manage symptoms at home and avoid these stressful hospital trips.
Chronic Cough
When the heart cannot keep up with the supply of blood moving between it and the lungs, fluid can build up in the lungs. This results in a chronic cough or wheezing that can produce white or pink mucus.
Edema
As the hearts ability to pump slows down, fluid can build up in the body. This creates swelling in the extremities particularly the feet, ankles, legs, or abdomen.
Lack of Appetite
As the digestive system receives less blood, patients may feel full or nauseous. Not wanting to eat is a natural part of the body shutting down, but families often find this distressing. Learn more about why it is okay for your loved one to stop eating and drinking at end of life.
High Heart Rate
In response to a loss in pumping capacity, the heart begins to beat faster. The patient experiences this as a racing or throbbing heartbeat.
Confusion
When the heart stops working effectively, it can change sodium levels in the blood. This leads to memory loss, confusion, and a general feeling of disorientation.
You May Like: What Does Heart Rate Mean
New Moms And Heart Failure Risk
A study published in January 2018 in the journal Circulation: Heart Failure found that women are most at risk for heart failure within the first six weeks after delivery, also known as the postpartum period.
The research supports the notion that at-risk women need closer observation postpartum.
The researchers also say that because many women are discharged from hospital care just a couple of days after they give birth and arent given a follow-up until about six weeks later, the way doctors regard women who might be at risk of heart failure needs to change.
They call for comprehensive discharge health education, with emphasis on signs and symptoms to look for and when or where to seek immediate care.
What You Can Do For Your Loved One
In addition to symptom management, its important for the family caregiver to learn how to recognize the end-of-life signs for CHF, and when they should contact hospice. Hospice care will be able to address the specific needs of CHF patients in their final days, and help them to get the most out of what time they have left.
Also Check: What Does Heart Failure Mean
Cardiac Cachexia Or Anorexia
Cardiac cachexia happens when a patient loses fat and muscle tissue. Patients with cachexia may lose their appetite and significant amounts of weight.
Speak to a dietitian about managing cachexia and anorexia. They may suggest eating small, frequent meals or taking high calorie, high protein food and supplement drinks. Patients may need to avoid some fruit juices and food supplements, which can affect their medication.
Management Of End Stage Cardiac Failure
Palliative care can be used for anyone who is in the advanced stages of an illness, including end stage heart failure. While it does not suspend any treatment of the illness, it does help an individual improve his or her quality of life by focusing on finding relief from the symptoms and stress caused by the illness. Palliative care is provided by a team of doctors, nurses and other health care specialists who work together with a patients primary physician to give an ailing loved one the support services he or she requires.
You May Like: Which Arm Is Heart Attack Sign
Section I: Cancer Diagnoses
Note: Certain cancers with poor prognoses may be hospice eligible without fulfilling the other criteria in this section.
I Decline In Clinical Status Guidelines
These changes in clinical variables are listed in order of their likelihood to predict poor survival, the most predictive first and the least predictive last. No specific number of variables must be met, but fewer of those listed first and more of those listed last would be expected to predict longevity of six months or less.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Heart Attack Pain Last
