How Does The Blood Circulatory System Work
The blood circulatory system delivers nutrients and oxygen to all cells in the body. It consists of the heart and the blood vessels running through the entire body. The arteries carry blood away from the heart the veins carry it back to the heart. The system of blood vessels resembles a tree: The trunk the main artery branches into large arteries, which lead to smaller and smaller vessels. The smallest arteries end in a network of tiny vessels known as the capillary network.
There isn’t only one blood circulatory system in the human body, but two, which are connected: The systemic circulation provides organs, tissues and cells with blood so that they get oxygen and other vital substances. The pulmonary circulation is where the fresh oxygen we breathe in enters the blood. At the same time, carbon dioxide is released from the blood.
Blood circulation starts when the heart relaxes between two heartbeats: The blood flows from both atria into the ventricles , which then expand. The following phase is called the ejection period, which is when both ventricles pump the blood into the large arteries.
How Can You Prevent Heart Attacks And Strokes
According to the American Heart Association, no matter what age you are, your heart can benefit from a healthy diet and adequate physical activity. Tthere are numerous specific suggestions about how you can decrease your risk for heart disease. For example:
- Lower cholesterol .
- Lower tryglicerides.
How The Healthy Heart Works
The normal heart is a strong, hard-working pump made of muscle tissue. It’s about the size of a person’s fist.
The heart has four chambers. The upper two chambers are the atria, and the lower two are the ventricles . The chambers are separated by a wall of tissue called the septum. Blood is pumped through the chambers, aided by four heart valves. The valves open and close to let the blood flow in only one direction.
Congenital defects may involve a valve, a chamber, the septum, an artery or blood flow issues.
The four heart valves are:
Each valve has a set of “flaps” . The mitral valve normally has two flaps the others have three.
Recommended Reading: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Pressure Relationships In The Venous System
Although vessel diameter increases from the smaller venules to the larger veins and eventually to the venae cavae , the total cross-sectional area actually decreases. The individual veins are larger in diameter than the venules, but their total number is much lower, so their total cross-sectional area is also lower.
Also notice that, as blood moves from venules to veins, the average blood pressure drops, but the blood velocity actually increases. This pressure gradient drives blood back toward the heart. Again, the presence of one-way valves and the skeletal muscle and respiratory pumps contribute to this increased flow. Since approximately 64 percent of the total blood volume resides in systemic veins, any action that increases the flow of blood through the veins will increase venous return to the heart. Maintaining vascular tone within the veins prevents the veins from merely distending, dampening the flow of blood, and as you will see, vasoconstriction actually enhances the flow.
How Does The Nervous System Work With The Circulatory System
The bones of your skull and spine protect your brain and spinal cord, but your brain regulates the position of your bones by controlling your muscles. The circulatory system provides your brain with a constant supply of oxygen-rich blood while your brain regulates your heart rate and blood pressure.
Recommended Reading: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
About The Heart And Circulatory System
The circulatory system is composed of the heart and blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries. Our bodies actually have two circulatory systems: The pulmonary circulation is a short loop from the heart to the lungs and back again, and the systemic circulation sends blood from the heart to all the other parts of our bodies and back again.
The heart is the key organ in the circulatory system. As a hollow, muscular pump, its main function is to propel blood throughout the body. It usually beats from 60 to 100 times per minute, but can go much faster when necessary. It beats about 100,000 times a day, more than 30 million times per year, and about 2.5 billion times in a 70-year lifetime.
The heart gets messages from the body that tell it when to pump more or less blood depending on an individuals needs. When were sleeping, it pumps just enough to provide for the lower amounts of oxygen needed by our bodies at rest. When were exercising or frightened, the heart pumps faster to increase the delivery of oxygen.
The heart has four chambers that are enclosed by thick, muscular walls. It lies between the lungs and just to the left of the middle of the chest cavity. The bottom part of the heart is divided into two chambers called the right and left ventricles, which pump blood out of the heart. A wall called the interventricular septum divides the ventricles.
Arterial walls have three layers:
Blood Flow During Exercise
Blood flow within muscles fluctuates as they contract and relax. During contraction, the vasculature within the muscle is compressed, resulting in a lower arterial inflow with inflow increased upon relaxation. The opposite effect would be seen if measuring venous outflow.
This rapid increase and decrease in flow is observed over multiple contractions. If the muscle is used for an extended period, mean arterial inflow will increase as the arterioles vasodilate to provide the oxygen and nutrients required for contraction. Following the end of contractions, this increased mean flow remains to resupply the muscle tissue with required nutrients and clear inhibitory waste products, due to the loss of the inhibitory contractile phase.
Don’t Miss: What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
What Does The Heart Do
The heart is a pump, usually beating about 60 to 100 times per minute. With each heartbeat, the heart sends blood throughout our bodies, carrying oxygen to every cell. After delivering the oxygen, the blood returns to the heart. The heart then sends the blood to the lungs to pick up more oxygen. This cycle repeats over and over again.
Pretty Cool It’s My Pulse
Even though your heart is inside you, there is a cool way to know it’s working from the outside. It’s your pulse. You can find your pulse by lightly pressing on the skin anywhere there’s a large artery running just beneath your skin. Two good places to find it are on the side of your neck and the inside of your wrist, just below the thumb.
You’ll know that you’ve found your pulse when you can feel a small beat under your skin. Each beat is caused by the contraction of your heart. If you want to find out what your heart rate is, use a watch with a second hand and count how many beats you feel in 1 minute. When you are resting, you will probably feel between 70 and 100 beats per minute.
When you run around a lot, your body needs a lot more oxygen-filled blood. Your heart pumps faster to supply the oxygen-filled blood that your body needs. You may even feel your heart pounding in your chest. Try running in place or jumping rope for a few minutes and taking your pulse again now how many beats do you count in 1 minute?
Recommended Reading: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Research For Your Health
The NHLBI is part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health the Nations biomedical research agency that makes important scientific discoveries to improve health and save lives. We are committed to advancing science and translating discoveries into clinical practice to promote the prevention and treatment of heart, lung, blood, and sleep disorders, including heart conditions. Learn about current and future NHLBI efforts to improve health through research and scientific discovery.
Improving Health With Current Research
Learn about the following ways the NHLBI continues to translate current research and science into improved health for people who have heart conditions. Research on this topic is part of the NHLBI’s broader commitment to advancing heart and vascular disease scientific discovery.
Learn about some of the pioneering research contributions we have made over the years that have improved clinical care.
Also Check: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
How Your Body Controls Heart Rate And Blood Pressure
How fast and hard your heart beats is controlled by signals from your bodys nervous system, as well as by hormones from your endocrine system. These signals and hormones allow you to adapt to changes in the amount of oxygen and nutrients your body needs. For example, when you exercise, your muscles need more oxygen, so your heart beats faster. When you sleep, your heart beats slower.
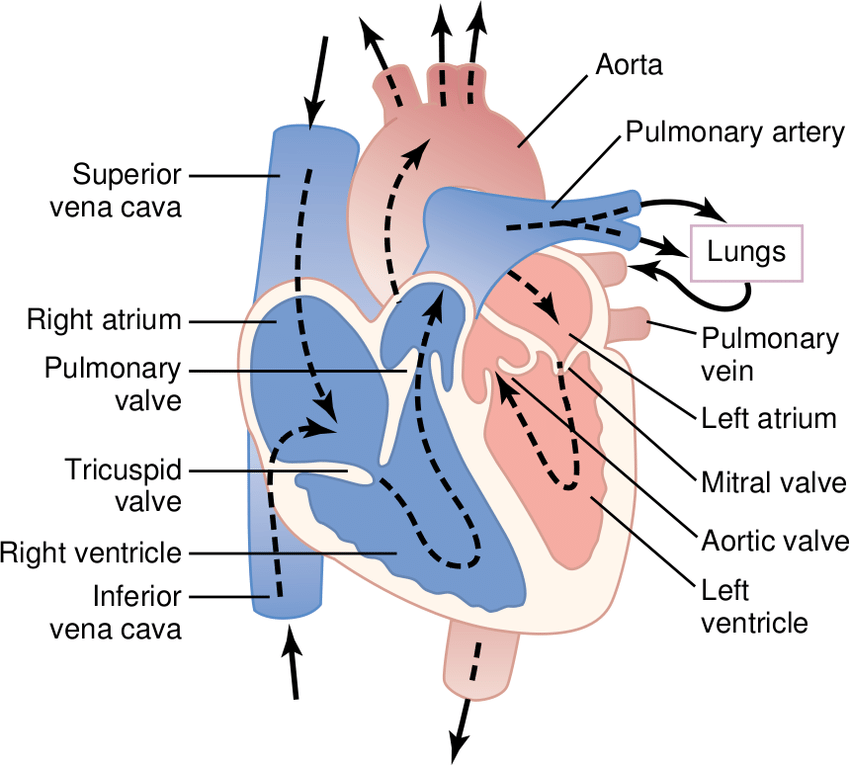
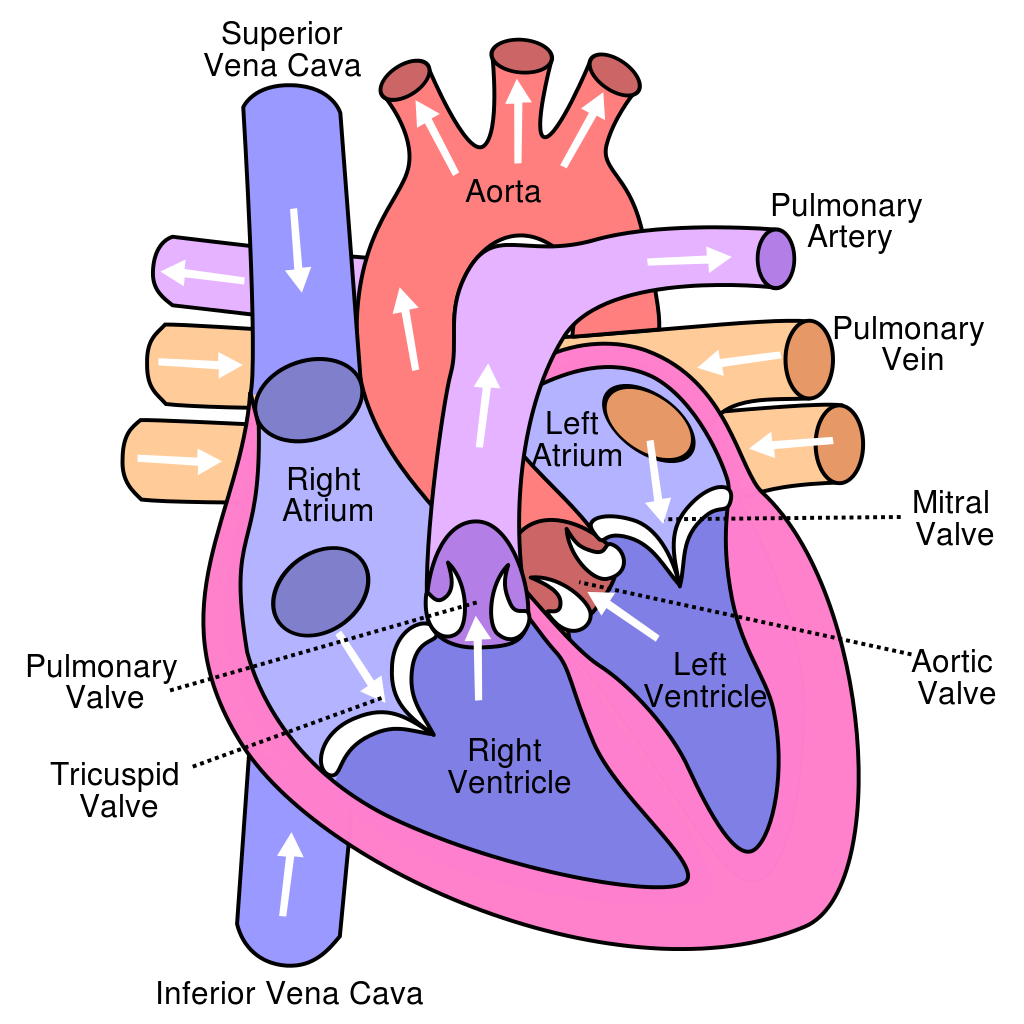
How Does Blood Flow Through The Heart
The right and left sides of the heart work together. The pattern described below is repeated over and over, causing blood to flow continuously to the heart, lungs, and body.
Right side
- Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium.
- As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your right atrium into your right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve.
- When the ventricle is full, the tricuspid valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the atria while the ventricle contracts.
- As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the pulmonic valve, into the pulmonary artery and to the lungs where it is oxygenated.
Left side
- The pulmonary vein empties oxygen-rich blood from the lungs into the left atrium.
- As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your left atrium into your left ventricle through the open mitral valve.
- When the ventricle is full, the mitral valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the atrium while the ventricle contracts.
- As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the aortic valve, into the aorta and to the body.
Don’t Miss: Heart Palpitations Prednisone
How Does The Heart Beat
The atria and ventricles work together, alternately contracting and relaxing to make the heart beat and pump blood. The electrical system of your heart is the power source that makes this possible.
Your heartbeat is triggered by electrical impulses that travel down a special pathway through your heart.
- The impulse starts in a small bundle of specialized cells called the SA node , located in the right atrium. This node is known as the heart’s natural pacemaker. The electrical activity spreads through the walls of the atria and causes them to contract.
- A cluster of cells in the center of the heart between the atria and ventricles, the AV node is like a gate that slows the electrical signal before it enters the ventricles. This delay gives the atria time to contract before the ventricles do.
- The His-Purkinje network is a pathway of fibers that sends the impulse to the muscular walls of the ventricles, causing them to contract.
At rest, a normal heart beats around 50 to 99 times a minute. Exercise, emotions, fever, and some medications can cause your heart to beat faster, sometimes to well over 100 beats per minute.
The Cardiac Cycle Includes All Blood Flow Events The Heart Accomplishes In One Complete Heartbeat
The muscular wall of the heart powers contraction and dilation. Each contraction and relaxation is a heartbeat. Ventricular contractions, called systole, force blood out of the heart through the pulmonary and aortic valves. Diastole occurs when blood flows from the atria to fill the ventricles.
Recommended Reading: Does A Higher Heart Rate Burn More Calories
What Is General Circulation In The Body
The systemic circulation provides the functional blood supply to all body tissue. It carries oxygen and nutrients to the cells and picks up carbon dioxide and waste products. Systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle, through the arteries, to the capillaries in the tissues of the body.
Regulation Of The Heart
The contraction of the muscle fibers in the heart is very organized and highly controlled. Rhythmic electrical impulses flow through the heart in a precise manner along distinct pathways and at a controlled speed. The impulses originate in the heart’s natural pacemaker , which generates a tiny electrical current.
Recommended Reading: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
How Does The Heart Work
The heart provides the bodys organs and tissues with a constant supply of blood and with it vital oxygen and nutrients. You can think of the heart as a central pump that keeps the blood circulating around the body.
At rest, an adult heart beats about 60 to 80 times a minute. Each time the heart beats it pumps blood through the body. When we exert ourselves physically, our heart beats faster. This increases the speed at which blood flows through our body. The blood can then absorb more oxygen from the lungs per minute in order to supply the body’s cells with more oxygen.
Your heart is about the same size as your fist and weighs around 300 g . In people who do endurance sports, it can weigh up to 500 g . The heart is located more or less in the middle of the chest, slightly to the left, behind the breastbone . You can normally feel someones heart beat if you put your hand on their chest.
The heart is a hollow muscle. A wall through the middle divides it into two halves. Each half has two chambers called the atrium and ventricle. The left ventricle pumps oxygen-rich blood out of the heart and into the body through an artery called the aorta. The first blood vessels that branch off from the aorta are the coronary arteries. They go straight to the muscle of the heart itself, and supply the heart with oxygen and nutrients.
The flow of blood in the heart
The curved flaps ensure that the blood flows in only one direction
The Atria Are The Hearts Entryways For Blood
The left atrium and right atrium are the two upper chambers of the heart. The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood returning from other parts of the body. Valves connect the atria to the ventricles, the lower chambers. Each atrium empties into the corresponding ventricle below.
Don’t Miss: Can Benadryl Cause Arrhythmias
Each Heart Beat Is A Squeeze Of Two Chambers Called Ventricles
The ventricles are the two lower chambers of the heart. Blood empties into each ventricle from the atrium above, and then shoots out to where it needs to go. The right ventricle receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium, then pumps the blood along to the lungs to get oxygen. The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium, then sends it on to the aorta. The aorta branches into the systemic arterial network that supplies all of the body.
What Heart Rate Is Too High
Maximum heart rate and Target Heart Rate
Going beyond your maximum heart rate is not healthy for you. Your maximum heart rate depends on your age. This is how you can calculate it:
- Subtracting your age from the number 220 will give you your maximum heart rate. Suppose your age is 35 years, your maximum heart rate is 185 beats per minute. If your heart rate exceeds 185 beats per minute during exercise, it is dangerous for you.
- Your target heart rate zone is the range of heart rate that you should aim for if you want to become physically fit. It is calculated as 60 to 80 percent of your maximum heart rate.
- Your target heart rate helps you to know if you are exercising at the right intensity.
- It is always better to consult your doctor before starting any vigorous exercise. This is especially important if you have diabetes, heart disease, or you are a smoker. Your doctor might advise you to lower your target heart rate by 50 percent or more.
Also Check: Ibs Heart Palpitations
The Heart Is A Muscle
Your heart is really a muscle. It’s located a little to the left of the middle of your chest, and it’s about the size of your fist. There are lots of muscles all over your body in your arms, in your legs, in your back, even in your behind.
But the heart muscle is special because of what it does. The heart sends blood around your body. The blood provides your body with the oxygen and nutrients it needs. It also carries away waste.
Your heart is sort of like a pump, or two pumps in one. The right side of your heart receives blood from the body and pumps it to the lungs. The left side of the heart does the exact opposite: It receives blood from the lungs and pumps it out to the body.
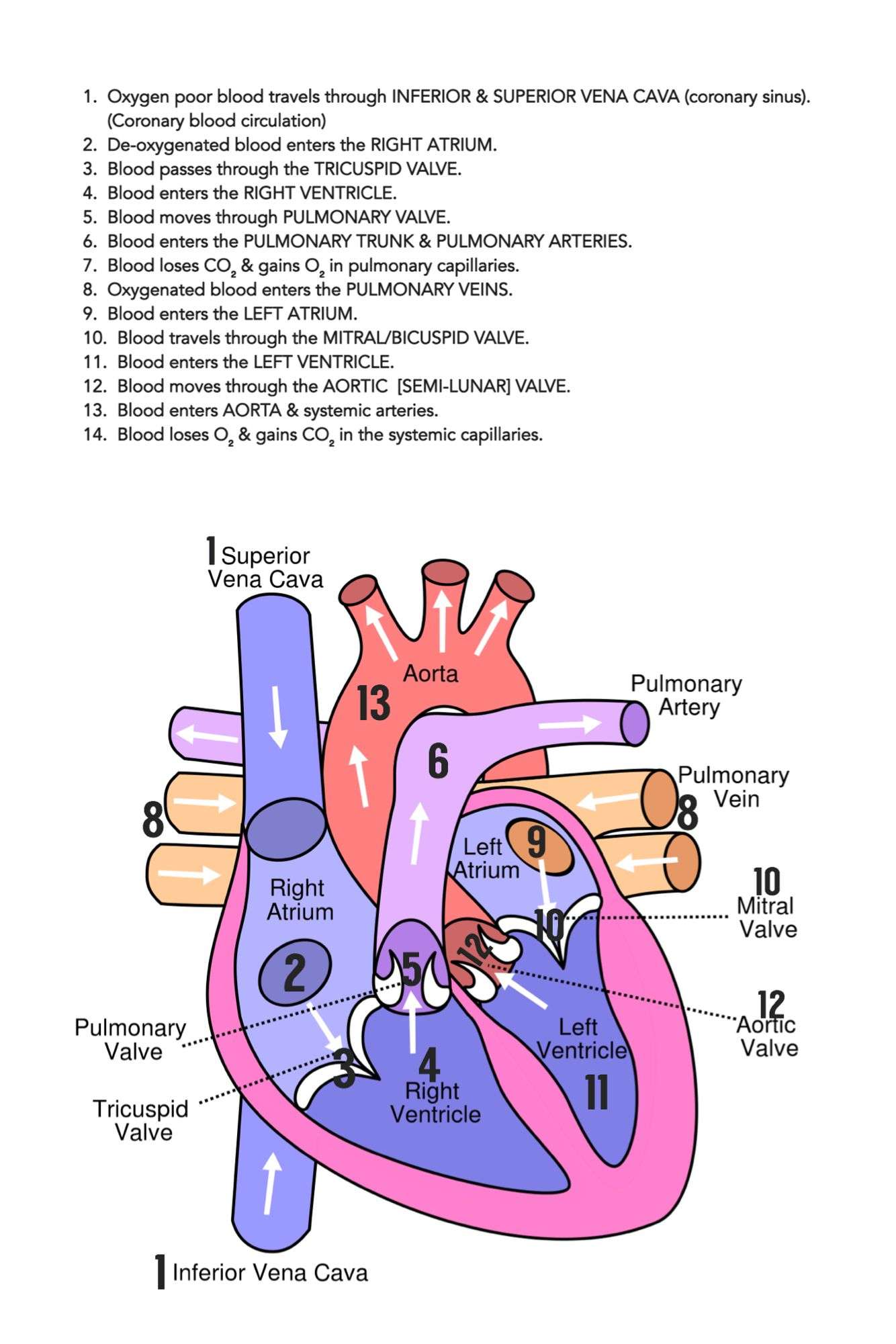
Right Side Of The Heart
Goal: to get the blood RIGHTto the lungs so it can become oxygenated.
1. The un-oxygenated blood enters the heart through the SUPERIOR AND INFERIOR VENA CAVA.
2. Blood enters into the RIGHT ATRIUM
3. Then it is squeezed through the TRICUSPID VALVE
4. Blood then enters into the RIGHT VENTRICLE
5. Then it is squeezed into the PULMONIC VALVE
6. Blood is then shot up through the PULMONARY ARTERY and then enters into the lungs for some oxygen
Study Tip: Since the goal of the right side is to get blood to the lungs always remember that the pulmonic valve and pulmonary artery will be on the right side since it is associated with the lungs. Remember in medical terminology pulmon means lungs. This will help you keep from getting confused with the left side of the heart.
You May Like: Benadryl Arrhythmia
