Outlook For Heart Failure
Heart failure is a serious long-term condition that’ll usually continue to get slowly worse over time.
It can severely limit the activities you’re able to do and is often eventually fatal.
But it’s very difficult to tell how the condition will progress on an individual basis.
It’s very unpredictable. Lots of people remain stable for many years, while in some cases it may get worse quickly.
Even Mild Lung Disease Affects The Heart
You may be surprised to learn that lung and heart diseases are closely intertwined. A recent study found that even mild lung disease can affect the hearts ability to pump blood. It suggests that a larger subset of heart failure may be due to lung disease, said Dr. R. Graham Barr, assistant professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University Medical Center. It has been known for a while that chronic obstructive pulmonary disease negatively affects the heart, however, this new study shows that even a mild decrease in lung function affects heart function, according to Dr. Barr.
How Is Chf Diagnosed
After reporting your symptoms to your doctor, they may refer you to a heart specialist, or cardiologist.
The cardiologist will perform a physical exam, which will involve listening to your heart with a stethoscope to detect abnormal heart rhythms.
To confirm an initial diagnosis, a cardiologist might order certain diagnostic tests to examine your hearts valves, blood vessels, and chambers.
There are a variety of tests used to diagnose heart conditions. Because these tests measure different things, your doctor may recommend a few to get a full picture of your current condition.
Don’t Miss: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
What Does Covid Do To Lungs
COVID-19 can cause lung complications such as pneumonia and, in the most severe cases, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or ARDS. , another possible complication of COVID-19, can also cause lasting harm to the lungs and other organs.
As we have learned more about SARS-CoV-2 and resulting COVID-19, we have discovered that in severe COVID-19, a significant pro-inflammatory condition can result in several critical diseases, complications and syndromes, Galiatsatos says.
Treatments For Heart Failure
Treatment for heart failure usually aims to control the symptoms for as long as possible and slow down the progression of the condition.
Common treatments include:
- lifestyle changes including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and stopping smoking
- medicine a range of medicines can help many people need to take 2 or 3 different types
- devices implanted in your chest these can help control your heart rhythm
- surgery such as a or a heart transplant
Treatment will usually be needed for life.
A cure may be possible when heart failure has a treatable cause. For example, if your heart valves are damaged, replacing or repairing them may cure the condition.
Also Check: Can Ibs Cause Heart Palpitations
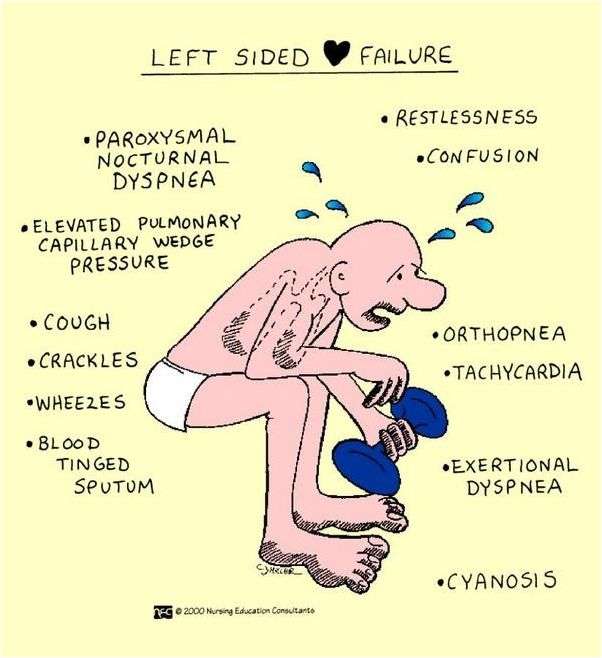
Symptoms Of Heart Failure
Symptoms of heart failure include:
- new or worsening shortness of breath
- difficulty lying flat at night
- fainting or passing out
- weight gain
- muscular fatigue, tiredness
- swelling of ankles or legs
- swelling of abdomen
- heart palpitations
- chest pain or discomfort in parts of the upper body
- unexplained coughing and wheezing
- constipation.
Types Of Heart Failure
The types of heart failure are classified by the ejection fraction , which is the percentage of blood pumped out by the heart with each beat and is a measure of how well the heart is pumping. A normal left ventricle ejects about 55 to 60% of the blood in it.
In heart failure with reduced ejection fraction :
-
The heart contracts less forcefully and pumps out a lower percentage of the blood that is returned to it. As a result, more blood remains in the heart. Blood then accumulates in the lungs, veins, or both.
In heart failure with preserved ejection fraction :
-
The heart is stiff and does not relax normally after contracting, which impairs its ability to fill with blood. The heart contracts normally, so it is able to pump a normal proportion of blood out of the ventricles, but the total amount pumped with each contraction may be less. Sometimes the stiff heart compensates for its poor filling by pumping out an even higher proportion of the blood than it normally does. However, eventually, as in systolic heart failure, the blood returning to the heart accumulates in the lungs or veins.
Heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction is a newer concept that includes people whose ejection fraction is somewhere between preserved and reduced ejection fraction.
Don’t Miss: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Signs Symptoms And Complications
Symptoms of respiratory failure depend on its cause, the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your blood, and whether respiratory failure developed slowly over time or suddenly. You may start out with mild symptoms such as shortness of breath or rapid breathing, which may get worse over time. Acute respiratory failure can be a life-threatening emergency. Respiratory failure may cause damage to your lungs and other organs, so it is important to get treated quickly.
What Is Congestive Heart Failure
Heart failure describes the inability or failure of the heart to meet the needs of organs and tissues for oxygen and nutrients. This decrease in cardiac output, the amount of blood that the heart pumps, is not adequate to circulate the blood returning to the heart from the body and lungs, causing the fluid to leak from capillary blood vessels. This leads to symptoms that may include shortness of breath, weakness, and swelling.
Understanding blood flow in the heart and body
The right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs while the left side pumps blood to the rest of the body. Blood from the body enters the right atrium through the vena cava. It then flows into the right ventricle where it is pumped to the lungs through the pulmonary artery, which carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs. In the lungs, oxygen is loaded onto red blood cells and returns to the left atrium of the heart via the pulmonary veins. Blood then flows into the left ventricle where it is pumped to the organs and tissues of the body. Oxygen is downloaded from red blood cells into the various organs while carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, is added to be removed in the lungs. Blood then returns to the right atrium to start the cycle again. The pulmonary veins are unusual in that they carry oxygenated blood, while the pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood. This is a reversal of duties versus the roles of veins and arteries in the rest of the body.
You May Like: What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
The Perception Of Exertional Dyspnoea And Leg Fatigue In Heart Failure
Patients with heart failure stop exercise because of either intolerable exertional dyspnoea, leg fatigue/discomfort or both, at a point where there is apparent cardiopulmonary reserve . Although studies conducted on large populations of patients with cardiorespiratory disorders have showed that leg discomfort is the most frequent exercise-limiting symptom in heart failure , severe dyspnoea is also frequently reported . The precise mechanisms underlying the choice, by a given patient with heart failure, to describe either dyspnoea or fatigue as their main limiting symptom remain unclear, but accumulating research tend to show that these two symptoms may, in fact, be inter-related .
In the general setting of peripheral muscle failure , a greater central motor command output is required for a given contractile force generation . The accompanying increased central corollary discharge to the sensory cortex gives rise to a sense of increased contractile effort that can become intolerable if it exceeds a certain sensory threshold that will vary among individuals . In addition, local alterations in the metabolic milieu due to excessive metabolite accumulation in the working muscles may alter afferent inputs from multiple muscle mechanosensors , which can project directly to the sensory cortex where they are perceived as an unpleasant sensation of leg discomfort .
How The Lungs And Heart Work Together
When oxygen is inhaled, it travels through the lungs and into the bloodstream. The blood then travels to the heart where it is pumped to the rest of the body. If your blood isnt receiving enough oxygen from your lungs, the heart has to work harder to pump enough oxygen throughout the body. Overworking the heart for an extended period of time will wear it out more quickly. This is why many lung disease sufferers experience heart problems as the disease progresses.
Also Check: Does Benadryl Increase Your Heart Rate
Lung Function And Ventilation
The relevance of ventilatory response to exercise in heart failure lies in the fact that, as in other cardiopulmonary disorders, dyspnoea intensity rises during exercise as VE increases . Anomalies in standard spirometry and alveolar capillary gas diffusion as well as in the ventilatory response to exercise in patients with heart failure are well documented and mostly relate to an exaggerated or disproportionally high ventilatory output compared to workload or carbon dioxide production . The steepness with which VE rises with respect to VCO2 is usually increased in heart failure , signifying that while a normal subject has to ventilate almost 2025L·min1 per 1L·min1 of carbon dioxide produced, a patient with heart failure ventilates almost 3050L·min1 for the same amount of carbon dioxide produced . Although this observation has led to the development of valuable prognostic markers , its direct relationship to exertional dyspnoea remains unclear.
Are The Ventilatory Anomalies Of Patients With Heart Failure Related To Chemo
In light of these findings, therapeutic interventions aiming at improving the neurohumoral processes implicated in the ergoreflex response to exercise in heart failure patients may be expected to improve exercise tolerance and the ventilatory response to exercise in these subjects. Exercise training has been shown to improve the sympathovagal and ventilatory responses to exercise in patients with heart failure , a finding that may be mediated by a reduction of the exaggerated ergoreflex .
Taken together, these results support an important contribution of the peripheral musculature to the abnormal response to exercise in patients with heart failure, especially with regards to the ventilatory response.
Recommended Reading: 10 Second Trick To Prevent Heart Attack
What Is Ejection Fraction
Ejection fraction refers to how well your left ventricle pumps blood with each heart beat. Most times, EF refers to the amount of blood being pumped out of the left ventricle each time it contracts. The left ventricle is the heart’s main pumping chamber.
Your EF is expressed as a percentage. An EF that is below normal can be a sign of heart failure. If you have heart failure and a lower-than-normal EF , your EF helps your doctor know how severe your condition is.
Is It Normal For The Liver To Be Enlarged
The liver is an essential organ in many of the bodys functions. An enlarged liver is swollen beyond its normal size for any reason. An enlarged liver is a symptom of an underlying problem, but is not a disease itself.
An enlarged liver is swollen beyond its normal size for any reason. An enlarged liver is a symptom of an underlying problem, but is not a disease itself. An enlarged liver may occur along with other symptoms, depending on the underlying disease that is causing it.
Recommended Reading: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
ACE inhibitors relax and widen your blood vessels. This helps to improve the flow of blood around your body, which reduces the amount of work your heart has to do.
ACE inhibitors have been shown to improve the symptoms of heart failure, reduce the need for hospital admission and improve life expectancy caused by heart failure.
Your symptoms should improve within a few weeks of starting treatment.
The main side effects of ACE inhibitors are dizziness and a cough. You will need to have regular blood tests, at least once every year, while taking an ACE inhibitor.
If you are taking an ACE inhibitor, you should check with your doctor or pharmacist before taking any other medicines. In particular, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines should not be taken with an ACE inhibitor. You should also avoid products containing high levels of potassium, such as salt substitutes.
Mechanisms Of Structural And Functional Respiratory Muscle Changes In Heart Failure
Several mechanisms can be evoked to explain the prevalent inspiratory muscle weakness in patients with heart failure. First, animal models have shown that the total number of diaphragmatic actinmyosin cross-bridges is decreased in heart failure, a finding that could be modulated by exposure to angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition . Secondly, type IIb muscles fibres, which have been reported to produce 1.5 to 2.0 times more force than type I fibres , are fewer in patients with heart failure . Thirdly, the cross-sectional area of all types of fibres of the diaphragm and rrelateib cage muscles is reduced in humans with heart failure and in a pig model of heart failure . Potential mechanisms participating in the development of these histological changes include decreased regional blood flow and activation of the ubiquitinproteasome proteolytic pathway by tumour necrosis factor . Fourthly, voluntary drive to the respiratory muscles during maximal inspiratory efforts may be decreased in patients with heart failure and finally, significant oxygen desaturation can be observed in the accessory respiratory muscles of heart failure patients during exercise , a finding thought to be related to insufficient oxygen delivery to the respiratory muscles and to a greater work of breathing in the setting of increased metabolic demand in these patients .
The resting length of muscles is usually preserved and thus probably cannot explain the inspiratory muscle weakness.
You May Like: Benadryl Arrhythmia
Factors That Can Worsen Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The symptoms of heart failure can be worsened by a number of factors, including:
- anaemia
- too much salt, fluid, or alcohol in the diet
- pregnancy
- some viral and bacterial infections
- kidney diseases
Treatment for heart failure may include:
- medicines, such as
- diuretics to remove excess fluid and improve symptoms of heart failure
- mineralcortiocoid receptor antagonists are also recommended and used in most patients with heart failure to reduce mortality and hospitalisation
- ACE inhibitors to open up blood vessels, reduce blood pressure and reduce sodium retention and water retention
- certain beta-blockers to slow the heart rate and reduce its work
- aldosterone blockers to reduce blood pressure and reduce the effects of damage to the heart muscle
- ACE inhibitors, beta blockers and aldosterone blockers can increase survival and reduce the likelihood of hospitalisation.
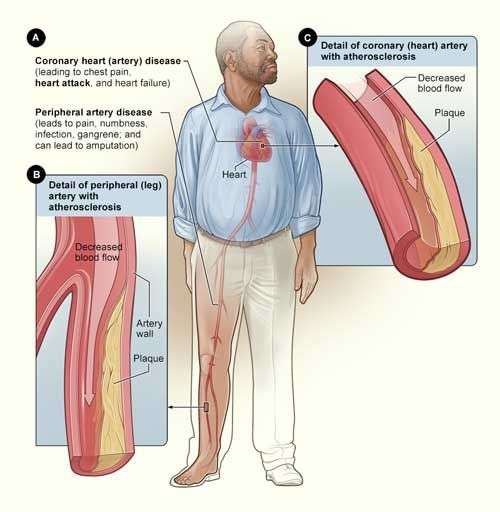
How Does Heart Disease Affect The Lungs
Before knowing the effect of heart disease, we must know at first the connection between the heart and lungs.
The functioning of the heart somewhat depends upon the lungs as it requires the amount of oxygen which is generated by the lungs to release an adequate amount of oxygen to be supplied in the blood at the time of pumping.
Thus the heart and lungs function together in order to ensure the smooth supply of oxygen-rich blood throughout the body.
The heart and lungs are connected through the two main respective loops, namely the consumptive loop and systemic loop. The consumptive loop connects the right side of the heart, whereas the systemic loop connects the left side of the heart with the lungs.
The main function of the consumptive loop is to gather the unoxidised blood from all over the body and then to pass those blood to the lungs for cleaning and oxidising.
On the other hand, the systemic loop helps the heart in receiving the oxidised blood back from the lungs and pumping the blood throughout the body.
Thus ensuring that each part receives the oxidised blood uniformly. So in a case where the heart suffers from any kind of malfunction, the lungs consequently get affected owing to its close connection.
Therefore, in the case of heart disease, the lungs also lose its ability to function. When the heart suffers from congestive heart failure, it loses its capability to pump the blood efficiently.
Read Also: Can Prednisone Cause Heart Palpitations
Stages C And D With Preserved Ef
Treatment for patients with Stage C and Stage D heart failure and reserved EF includes:
- Treatments listed in Stages A and B.
- Medications for the treatment of medical conditions that can cause heart failure or make the condition worse, such as atrial fibrillation, high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, coronary artery disease, chronic lung disease, high cholesterol and kidney disease.
- Diuretic to reduce or relieve symptoms.
YOU ARE THE MOST IMPORTANT PART OF YOUR TREATMENT PLAN!
It is up to you to take steps to improve your heart health. Take your medications as instructed, follow a low-sodium diet, stay active or become physically active, take notice of sudden changes in your weight, live a healthy lifestyle, keep your follow-up appointments, and track your symptoms. Talk to your healthcare team about questions or concerns you have about your medications, lifestyle changes or any other part of your treatment plan.
Treatment For Fluid In Lungs And Heart Failure
In recent years, more effective medications have been made available to treat fluid filled lungs. Antibiotics help get rid of the infection. Improved quality of pacemakers and implantable defibrillators help improve the function of the heart and lungs. Diuretics are usually prescribed as they help reduce the fluid in lungs. Some drugs improve the pumping capacity of the heart.
Surgery can repair blockage of the coronary arteries, a valve problem, a congenital heart defect, or a too thick pericardium. The option of heart transplant is available if the hearts ability to pump blood is permanently marred. Prompt supply of oxygen or artificial ventilation is a part of the emergency treatment. The treatment should be so designed that the fluid should not again get accumulated in the lungs.
Unhealthy eating habits and stressful lifestyle lead to heart diseases. To prevent fluid in lungs and heart failure, smoking and excessive use of alcohol should be strictly avoided. Weight control is extremely important in this case because obesity and lack of activity often contribute to congestive heart failure, either directly or indirectly.
Disclaimer: This HealthHearty article is for informative purposes only, and should not be used as a replacement for expert medical advice.
You May Like: Typical Resting Heart Rate For A Healthy Individual
