Systolic And Diastolic Failure
Systolic and diastolic heart failure each result in a decrease in stroke volume. This leads to activation of peripheral and central baroreflexes and chemoreflexes that are capable of eliciting marked increases in sympathetic nerve traffic.
Although there are commonalities in the neurohormonal responses to decreased stroke volume, the neurohormone-mediated events that follow have been most clearly elucidated for individuals with systolic heart failure. The ensuing elevation in plasma norepinephrine directly correlates with the degree of cardiac dysfunction and has significant prognostic implications. Norepinephrine, while directly toxic to cardiac myocytes, is also responsible for a variety of signal-transduction abnormalities, such as downregulation of beta1-adrenergic receptors, uncoupling of beta2-adrenergic receptors, and increased activity of inhibitory G-protein. Changes in beta1-adrenergic receptors result in overexpression and promote myocardial hypertrophy.
Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
| Heart failure |
|---|
| Acute interstitial pulmonary edema. Note enlarged heart size, apical vascular redistribution , and small bilateral pleural effusions . |
| Cardiology |
Acute decompensated heart failure is a sudden worsening of the signs and symptoms of heart failure, which typically includes difficulty breathing , leg or feet swelling, and fatigue. ADHF is a common and potentially serious cause of acute respiratory distress. The condition is caused by severe congestion of multiple organs by fluid that is inadequately circulated by the failing heart. An attack of can be caused by underlying medical illness, such as myocardial infarction, an abnormal heart rhythm, infection, or thyroid disease.
Treatment consists of reducing the fluid level with diuretics and improving heart function with nitrates, or levosimendan other treatments such as aquapheresis ultra-filtration may also be required.
What Is Diastolic Heart Failure
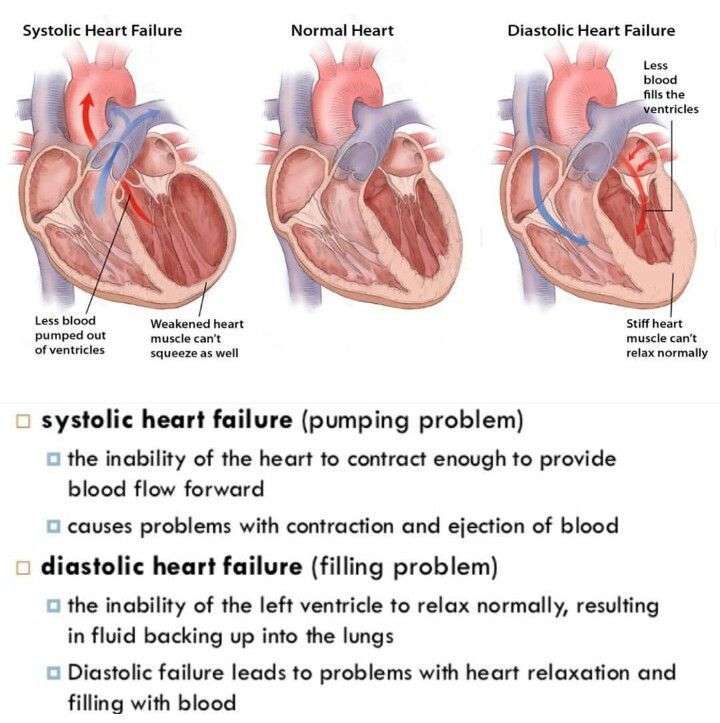
Diastolic heart failure, also known as heart failure with preserved ejection fraction , is a condition in which your hearts main pumping chamber becomes stiff and unable to fill properly.
Diastolic heart failure is one of two kinds of left-sided heart failure. The other type is systolic heart failure which reduces the pumping strength of your left ventricle.
Don’t Miss: What Side Of Your Chest Hurts For Heart Attack
Articles On Heart Failure Types & Stages
If you have diastolic heart failure, your left ventricle has become stiffer than normal. Because of that, your heart can’t relax the way it should. When it pumps, it can’t fill up with blood as it’s supposed to. Because there’s less blood in the ventricle, less blood is pumped out to your body.
When To Get Emergency Help
Heart failure is not the same thing as a heart attack. But, like a heart attack, acute heart failure can be a life threatening event. Someone with acute heart failure will typically need emergency hospital care. If your symptoms are sudden or severe, call 911 or your local emergency services for help.
If not treated, heart failure can lead to serious complications. These complications can include cardiac arrest, which is when your heart stops beating.
Some people with heart failure may have several health conditions. If thats the case, it can be hard to know whats causing your symptoms.
But when it comes to symptoms of heart failure, its best to get them checked by a doctor right away. According to a 2017 study, fast treatment of acute heart failure can lead to better outcomes.
Also Check: Do Beta Blockers Decrease Heart Rate
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you experience persistent or gradually worsening symptoms of heart failure.
Call 999 for an ambulance or go to your nearest A& E department as soon as possible if you have sudden or very severe symptoms.
A number of tests can be used to help check how well your heart is working, including blood tests, an ECG and an echocardiogram.
Acute On Chronic Diastolic Heart Failure
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- I50.33 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.33 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I50.33 – other international versions of ICD-10 I50.33 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
Read Also: How To Know If You’re Having A Heart Attack
Causes Of Systolic Heart Failure
Systolic heart failure is usually caused by another cardiovascular condition that weakens the heart muscle. For example:
- Aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the valve in the large blood vessel that branches off the heart
- Arrhythmia, an irregular heart rhythm
- Cardiomyopathy, any condition affecting the heart muscle
- Coronary artery disease, narrowing of the blood vessels that bring blood to the heart
- Heart attack, which occurs when the heart doesnt get enough blood
- High blood pressure , the force of blood pushing against arteries
- Mitral regurgitation, when a valve in the heart doesnt close tightly, allowing blood to flow backward in the heart
- Myocarditis, inflammation of the heart muscle
Systolic Vs Diastolic Heart Failure
Diastolic Heart Failure
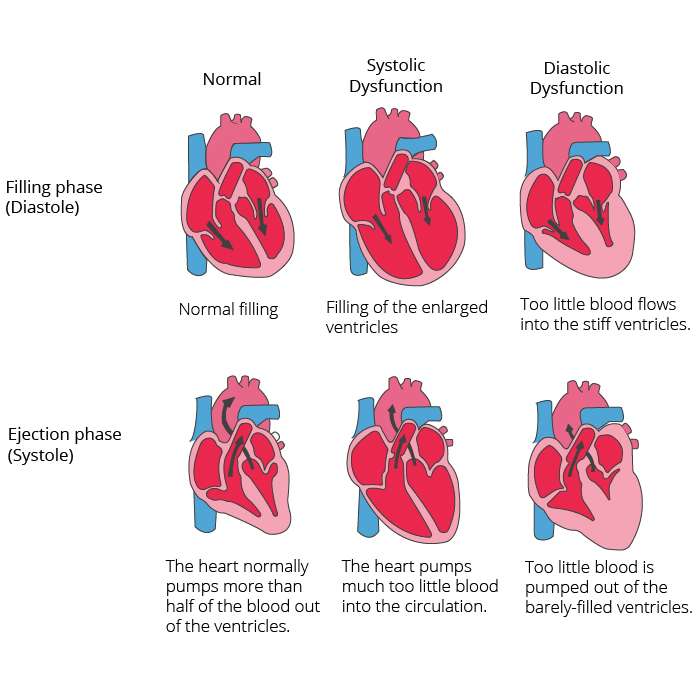
Diastolic heart failure occurs when your left ventricle can no longer rest between heartbeats because the tissues have hardened. When your heart cannot completely relax, it will not fill with blood again before the next beat.
Systolic vs Diastolic heart failure the difference is simply the Diastolic heart failure type is also called heart failure with preserved ejection fraction . In this type, your doctor can do an imaging test on your heart and determine if your EF looks fine. Your doctor will then should consider if you either have any other heart failure symptoms and if there is evidence that your heart is not functioning properly. If all those criteria are met, you may be diagnosed with diastolic heart failure.
This kind of heart failure often affects older women. It often accompanies other types of heart disease and other non-heart conditions like cancer and lung disease.
Systolic Heart Failure
Systolic vs Diastolic heart failure the difference is simply the Systolic heart failure occurs when the left ventricle of your heart does not completely contract. This means that your heart will not pump sufficiently to move your blood throughout your body in an efficient manner. It is also called heart failure with low ejection fraction .
Ejection Fraction is a measure of how much blood is released each time the heart ventricle is pumped. The more the heart pumps, the healthier it is.
Recommended Reading: Can Ibs Cause Heart Palpitations
How To Prevent Acute Heart Failure
Some risk factors, such as aging, cant be avoided. The key to preventing heart failure is to reduce the risk factors that you can control.
Many of the lifestyle measures recommended for heart failure recovery can also reduce or eliminate conditions that lead to heart failure. These conditions include high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
If youre at risk for heart failure, you should consider these measures to promote heart health:
- maintain a healthy weight, if overweight or obesity is a concern
- get regular physical activity
Definition And Classification Criteria For Diastolic Hf
Table 3 Criteria for diastolic HF according to the European Society of Cardiology .
To date, however, no certain definition of diastolic HF exists and the recognition of its existence is not unanimously accepted . Studies performed by both standard Doppler echocardiography and Tissue Doppler demonstrated how sub-clinic alterations of myocardial systolic function are already overt in diastolic HF. Because of the use of LV EF is a rather insensitive indicator of true LV myocardial contractility, the assessment of LV long-axis function by the simple M-mode of the mitral lateral annulus could help to identify initial LV systolic dysfunction . Finally, it has also to be taken into account how concomitant variables, including obesity, chronic obstructive lung disease and even myocardial ischemia, can be confounding factors leading to “false” diagnosis of diastolic HF, particularly in the elderly population .
Read Also: What Blood Tests Detect Heart Problems
Medications For Systolic Heart Failure
Depending on the severity of systolic heart failure and its underlying cause, your doctor may prescribe medications. Some of the drug options for treating systolic heart failure include:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers relax the blood vessels to lower blood pressure.
- Beta blockers make the heart beat more slowly and with less force.
- Aldosterone blockers help the body release sodium and water.
- Angiotensin receptorneprilysin inhibitors reduce excess fluid in the body and relax blood vessels, making it easier for your heart to pump blood.
How Does Diastolic Heart Failure Affect My Body
When the left side of your heart stiffens, your heart:
- Cant relax properly between beats.
- Doesnt fill up with as much blood as it should.
- Pumps out less blood to the rest of your body than a healthy heart would.
As a result, you experience symptoms of heart failure. You might feel short of breath or fatigued . Your breathing may get worse at night when you try to lay flat. You may also notice swelling in your belly or legs . These symptoms might get worse over time.
Don’t Miss: What Age Can You Have A Heart Attack
Initial Stages Of Chf
In the initial, mild stage A, there are underlying high-risk factors for CHF such as smoking or high blood pressure. However, the affected person has no symptoms or limitations at rest or with physical activity and there are no signs of CHF on evaluation by a doctor.
In stage B, the person develops mild symptoms of fatigue, shortness of breath, or heart palpitations with routine physical activity. There are minor signs of heart dysfunction on a doctors evaluation. There might also be a mild, intermittent collection of fluid, known as edema, in the ankles and feet.
Treatments For Heart Failure
Treatment for heart failure usually aims to control the symptoms for as long as possible and slow down the progression of the condition.
How you’re treated will depend on what is causing your heart failure.
Common treatments include:
- lifestyle changes including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and stopping smoking
- medicine a range of medicines can help many people need to take 2 or 3 different types
- devices implanted in your chest these can help control your heart rhythm
- surgery such as a or a heart transplant
Treatment will usually be needed for life.
A cure may be possible when heart failure has a treatable cause. For example, if your heart valves are damaged, replacing or repairing them may cure the condition.
Also Check: How To Stop Heart Palpitations During Pregnancy
Heart Failure Patients Too Optimistic
Study Shows Patients Overestimate Their Life Expectancy
A new study shows nearly two-thirds of people with congestive heart failure overestimate their remaining life expectancy by an average of 40% compared with whats realistic based on their prognosis.
Heart failure, which occurs when the heart is too weak to pump enough blood to meet the bodys needs, causes 55,000 deaths each year and indirectly contributes to 230,000 more deaths annually in the U.S.
Although there have been recent improvements in congestive heart failure treatment, researchers say the prognosis for people with the disease is still bleak, with about 50% having an average life expectancy of less than five years. For those with advanced forms of heart failure, nearly 90% die within one year.
Patient perception of prognosis is important because it fundamentally influences medical decision making regarding medications, devices, transplantation, and end-of-life care, write researcher Larry A. Allen, MD, MHS, of the Duke Clinical Research Institute and colleagues in The Journal of the American Medical Association.
What Is The Difference Between Diastolic And Systolic
Diastolic and systolic are the two numbers on a blood pressure reading. Every time your heart squeezes, it pumps out blood to the network of blood vessels known as the circulatory system. The force or pressure of that squeeze is called systolic blood pressure. When your heart rests between beats, the pressure in the arteries is the diastolic blood pressure. This is why your blood pressure has two numbers:
- The top number is the systolic blood pressure.
- The bottom number is the diastolic blood pressure.
Also Check: Can Covid Cause Heart Palpitations
History And Physical Examination
Patients with heart failure can have decreased exercise tolerance with dyspnea, fatigue, generalized weakness, and fluid retention, with peripheral or abdominal swelling and possibly orthopnea.3 Patient history and physical examination are useful to evaluate for alternative or reversible causes .3,4,8 Nearly all patients with heart failure have dyspnea on exertion. However, heart failure accounts for only 30 percent of the causes of dyspnea in the primary care setting.24 The absence of dyspnea on exertion only slightly decreases the probability of systolic heart failure, and the presence of orthopnea or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea has a small effect in increasing the probability of heart failure .21,23
The presence of a third heart sound is an indication of increased left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and a decreased LVEF. Despite being relatively uncommon findings, a third heart sound and displaced cardiac apex are good predictors of left ventricular dysfunction and effectively rule in the diagnosis of systolic heart failure .21,23
What Else Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
You may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- What can I do to prevent heart failure from progressing?
- What foods should I avoid with diastolic heart failure?
- What can I do to manage medication side effects?
- How often do I need to see my healthcare provider for diastolic heart failure?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Diastolic heart failure is one of the two types of left-sided heart failure. HFPEF is the same condition. Your risk of diastolic heart failure increases as you get older. You may also have a higher risk if you have underlying conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure. Diastolic heart failure doesnt have a cure, but you can manage the symptoms by changing your lifestyle or taking heart medications. Many people live a full and active life with diastolic heart failure.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 05/08/2022.
References
Don’t Miss: Nerve Pain After Open-heart Surgery
What Are The Symptoms Of Diastolic Heart Failure
In the earliest stages of diastolic heart failure, you may not notice any symptoms. But as the condition progresses, some of the following symptoms will likely develop:
- shortness of breath when lying down or when doing activities that you used to do with no problem
2016 study notes that diastolic heart failure is now the most common form of heart failure. It also suggests that the key to successful treatment is aggressive management of contributing factors. That means treating diastolic heart failure also involves proper treatment of any other conditions you may have, as listed above.
More specifically, treating diastolic heart failure usually involves some combination of the following therapies:
Treatment Options For Diastolic Heart Dysfunction
We work with patients to pursue a full range of treatment options, including:
- A Healthy Lifestyle this includes maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet that’s low in salt and getting regular cardiovascular exercise, either on your own or as part of a cardiac rehabilitation program.
- Medications water pills can often help to alleviate the edema that is caused by diastolic dysfunction, and other medications can help to treat underlying medical problems like high blood pressure, diabetes or other heart conditions such as atrial fibrillation.
- Left Ventricular Assist Devices UPMC cardiologists have been on the leading edge of LVAD treatment since the technology was introduced in the 1980s, and have been leaders in improving the technology since then. These implantable devices pump blood into the body just as a healthy heart would, either as a “bridge” while waiting for a heart transplant or as a permanent valve replacement.
- Heart Transplant in rare cases, a heart transplant may be considered as a treatment for diastolic dysfunction. Our physicians are leading experts in heart transplantation as part of the UPMC Thomas E. Starzl Transplantation Institute, a nationally regarded center of excellence in transplantation.
Recommended Reading: How Do They Do Heart Bypass Surgery
What Is The Treatment For Mild Congestive Heart Failure
To date, there is a lack of evidence in the management of patients with heart failure with preserved or mid-range ejection fraction. No treatment has yet been shown to reduce morbidity and mortality in these patients. The management is usually limited to optimal treatment of comorbidities such as hypertension, atrial fibrillation, and coronary artery disease.
Elevated blood pressure is an extra load on the heart. In response, the left ventricle becomes thicker and unfortunately stiffer. As the pressure rises in the heart, it also increases in the lungs, making the patient short of breath with minimal activity. There is solid evidence that improving oneâs blood pressure can lead to the regression of LVH. Some medicines such as angiotensin II receptor blockers , calcium channel blockers, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors can lead to regression of hypertrophy and return the heart to a more normal thickness and function.
Coronary artery disease where a blockage in the artery causes significantly decreased blood flow can lead to varying levels of ischemia in the myocardium. Ischemia makes the heart muscle stiff and causes the patient to be short of breath during exercise. Medicines such as nitrates, beta-blockers, calcium antagonists, ranolazine, or interventions to reopen the arteries such as coronary stenting can relieve ischemia and the patientâs symptoms.
Left Ventricular Assist Devices
These may be implanted in the chest to increase heart pumping action. Until recently, LVADs required that the patient be hooked up to a large, hospital-based console while awaiting a transplant. Miniaturized battery-powered LVAD units, however, are allowing many patients to leave the hospital. The devices may be used as a primary treatment or as a bridge to heart transplant in adults.
Read Also: What Is Maximum Heart Rate By Age
