Deterrence And Patient Education
Compliance with lifestyle modification and pharmacologic treatment and control of precipitating factors are crucial to prevent hospitalizations for heart failure exacerbation and improve the quality of life. Many of those precipitating factors are potentially under patient control. That is why patient education is an integral part of a multidisciplinary approach to decrease mortality and morbidity due to heart failure.
Heart Failure During Covid
Your heart failure nurse might have been redeployed, making it hard to have in-person appointments or check-ups. ‘The key thing is to look after yourself well, and always phone your GP or heart failure team if your symptoms change or worsen,’ says BHF nurse Lucy Martin. ‘In fact, call your GP or heart failure team if you have any concerns about your medication or care – they are there to help you.’
Your GP is qualified to answer any questions you might have. Dont worry about wasting their time this is exactly what theyre there for.
- Find out more about coronavirus and how it affects people with heart conditions at our coronavirus support hub.
What Can I Do To Manage Swelling From Extra Fluid
- Elevate your legs above the level of your heart. This will help with fluid that builds up in your legs or ankles. Elevate your legs as often as possible during the day. Prop your legs on pillows or blankets to keep them elevated comfortably. Try not to stand for long periods of time during the day. Move around to keep your blood circulating.
- Limit sodium . Ask how much sodium you can have each day. Your healthcare provider may give you a limit, such as 2,300 milligrams a day. Your provider or a dietitian can teach you how to read food labels for the number of mg in a food. He or she can also help you find ways to have less salt. For example, if you add salt to food as you cook, do not add more at the table.
- Drink liquids as directed. You may need to limit the amount of liquid you drink within 24 hours. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much liquid to have and which liquids are best for you. He or she may tell you to limit liquid to 1.5 to 2 liters in a day. He or she will also tell you how often to drink liquid throughout the day.
- Weigh yourself every morning. Use the same scale, in the same spot. Do this after you use the bathroom, but before you eat or drink. Wear the same type of clothing each time. Write down your weight and call your healthcare provider if you have a sudden weight gain. Swelling and weight gain are signs of fluid buildup.
Don’t Miss: Can Young People Get Heart Attacks
Surgery For Heart Failure
Your doctor may recommend surgery to implant a medical device that helps the heart function more effectively:
- Pacemaker, which maintains a steady heart beat in people with a slow or irregular heartbeat
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator , which monitors the heart for fast rhythm and delivers an electrical shock to reset normal rhythm
- Left ventricular assist device , which takes over the pumping action of the heart
People with advanced heart failure may be candidates for heart transplantation. A heart transplant replaces the diseased heart with a donated heart from a person who has died.
How Can You Prevent Heart Failure
Some lifestyle measures can help treat heart failure and prevent the condition from developing. Maintaining a moderate weight and exercising regularly can significantly decrease your risk of heart failure. Reducing the amount of salt in your diet can also lower your risk.
Other habits that may prevent heart failure include:
- limiting alcohol intake
You May Like: What Is Ischaemic Heart Disease
How Do I Take Care Of Myself If I Have Right
The most important thing is to make healthy lifestyle habits part of your daily routine. The more you make healthy living part of your new lifestyle, the better youll feel. Try to:
- Work with a nutritionist or dietitian to create a nutritious, filling meal plan you can stick with long-term.
- Find an exercise routine you enjoy so youll be motivated to get moving every day.
- Track and manage your symptoms. Report any changes to your healthcare provider.
- Take medications as instructed.
Life Expectancy With Congestive Heart Failure
The life expectancy of someone with congestive heart failure depends on the type of heart failure, the cause, the stage of the disease, and how effective treatment is.
When heart failure results from cardiomyopathy or coronary artery disease, a person typically has a less positive outlook than someone with heart failure in its earliest stage.
Recommended Reading: What Is Considered Heart Disease
Surgical Options To Treat Underlying Causes Of Heart Failure
- Coronary artery bypass graft to prevent and treat heart failure caused by blocked arteries. During bypass surgery, blood vessels taken from another part of the body usually the leg are attached to the clogged artery to create a detour around the blockage. This is conventionally done through open-heart surgery, but some patients may be candidates for minimally invasive CABG, an alternative offered at UCSF.
- Angioplasty, another treatment for blocked arteries. A thin flexible tube called a catheter is inserted through a small incision in the groin or neck into a blood vessel. In one procedure, a balloon is introduced through the catheter into the center of a blocked blood vessel. When the balloon is inflated, the blockage material is compressed back against the walls of the artery. A small metal device, called a stent, may be inserted through the catheter to serve as a permanent barrier to keep the plaque compressed. In another type of procedure, instruments are introduced through the catheter to remove the plaque.
- Implantation of pacemakers and other devices such as artificial heart valves
- Repairing congenital heart defects
Surgical treatments for heart failure itself include:
Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction Treatment
Treatment for anyone with heart failure should start with lifestyle modification such as:
- Diet modification, including low sodium and fluid intake
- Quitting smoking
- Increasing exercise
- Maintaining a healthy weight
Pharmacotherapy is the cornerstone of the treatment of HFrEF. The main validated heart failure medications are:
Medications are usually added based on how effective they are at managing your symptoms. Your cardiologist will likely start with a combination of an ACE inhibitor, beta-blocker, or diuretics for symptom relief. If you are still symptomatic and your LVEF is equal to or less than 35%, an MRA might be added.
If you are still symptomatic and your LVEF is equal to or less than 35%, your doctor may suggest replacing your ACE inhibitor with an angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor. Corlanor or cardiac resynchronization therapy might also be considered.
Finally, if you are still asymptomatic, digoxin, an LV assist device, or heart transplantation should be considered.
Recommended Reading: When Do Heart Attacks Occur
How Does Heart Failure Affect Quality Of Life And Lifestyle
With the right care and treatment plan, heart failure may limit your activities, but many adults still enjoy life. How well you feel depends on how well your heart muscle is working, your symptoms and how well you respond to and follow your treatment plan. This includes caring for yourself and living a healthy lifestyle .
Because heart failure is a chronic long-term illness, talk to your doctor and your family about your preferences for medical care. You can complete an advance directive or living will to let everyone involved in your care know your desires. A living will details the treatments you do or dont want to prolong your life. It is a good idea to prepare a living will while you are well in case you arent able to make these decisions at a later time.
Reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional.
References
Left Ventricular Assist Devices
Left ventricular assist devices are mechanical pumps that can help if your left ventricle isn’t working properly and medication alone isn’t helping.
They may be used as a permanent treatment if you can’t have a heart transplant, or as a temporary measure while you wait for a transplant.
In addition to the pump, LVADs also include an external battery. A wire connecting this to the pump will need to be placed under your skin during the operation.
Read more about LVADs on the British Heart Foundation website.
Also Check: What Causes A Low Heart Rate
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The main symptoms of heart failure are:
- Shortness of breath when youre active or resting, because youre not getting enough oxygen.
- Swollen feet, ankles, stomach and around the lower back area, caused by fluid build up.
- Feeling unusually tired or weak because theres not enough blood and oxygen getting to your muscles.
You should see your GP immediately if you begin to experience any of these symptoms.
Reduction Of Functional Capacity
Functional capacity in HF patients is limited by shortness of breath and fatigue on exertion. A basic pathophysiology of these symptoms can be summarized in two points :
Physiopathology of symptoms in heart failure.
Adapted from Clark with permission from BMJ Group Ltd.135
Abbreviation: HF, heart failure.
Read Also: Women Having Heart Attacks
What Are The Symptoms Of Right
The main sign of right-sided heart failure is fluid buildup. This buildup leads to swelling in your:
- Feet, ankles and legs.
- Gastrointestinal tract and liver .
Other signs include:
Where you accumulate fluid depends on how much extra fluid and your position. If youre standing, fluid typically builds up in your legs and feet. If youre lying down, it may build up in your lower back. And if you have a lot of excess fluid, it may even build up in your belly.
Fluid build up in your liver or stomach may cause:
- Bloating.
- Appetite loss.
Once right-sided heart failure becomes advanced, you can also lose weight and muscle mass. Healthcare providers call these effects cardiac cachexia.
Mood And Heart Failure
Its normal to feel low or sad from time to time. You may feel down about your symptoms and new limitations, or feel that you have a lack of control over your life.Some people find it very difficult to live with the uncertainty of having heart failure. But learning about your condition and being involved in making decisions about your treatment will all help you to feel more in control and may help to relieve anxiety. Its also important to discuss your worries with your family and close friends so they can support you.
Stress affects different people in different ways. People who dont manage their stress well may turn to unhealthy habits such as smoking, drinking alcohol, or snacking on unhealthy foods. Knowing what triggers the stress can help you to tackle the problem. Finding healthy ways of coping with stress and learning to relax can help you manage your heart failure. Read more about coping with stress.
You May Like: Why Is It Important To Know Your Resting Heart Rate
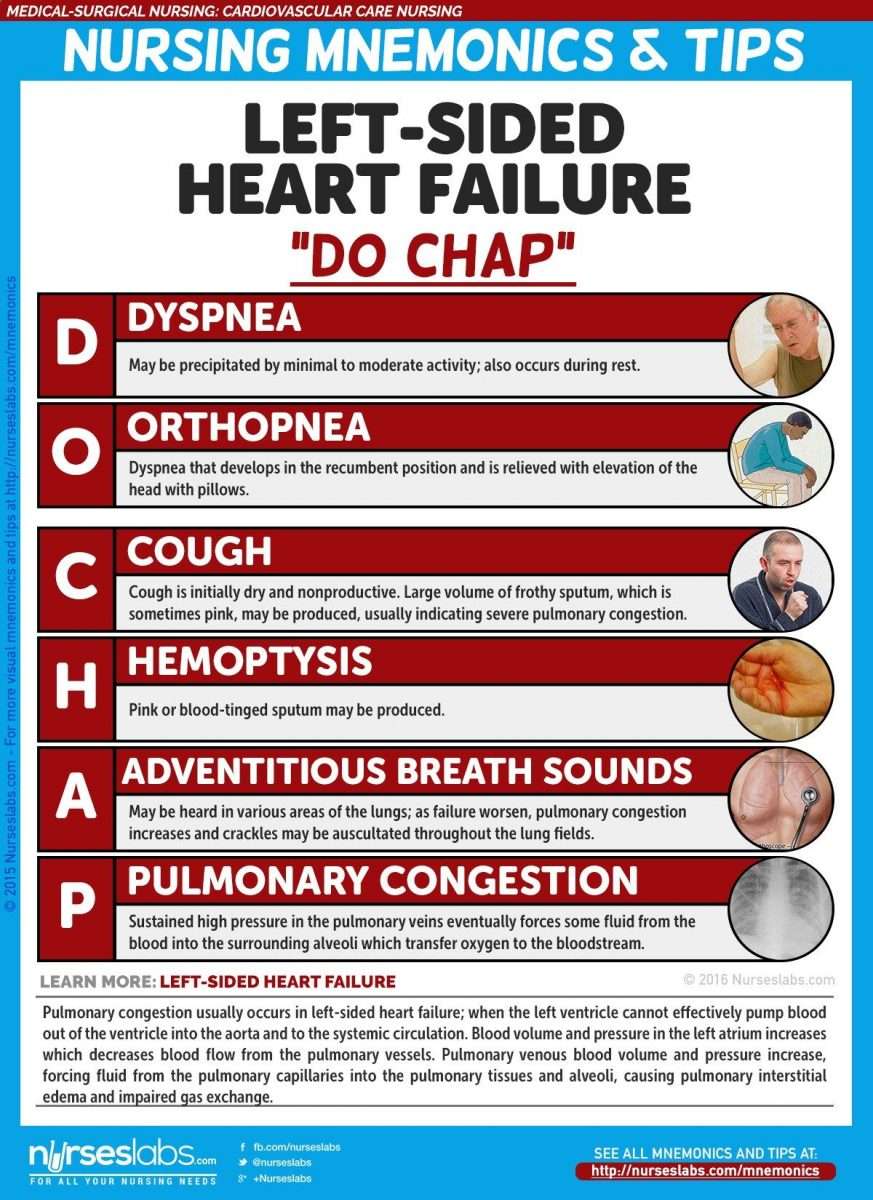
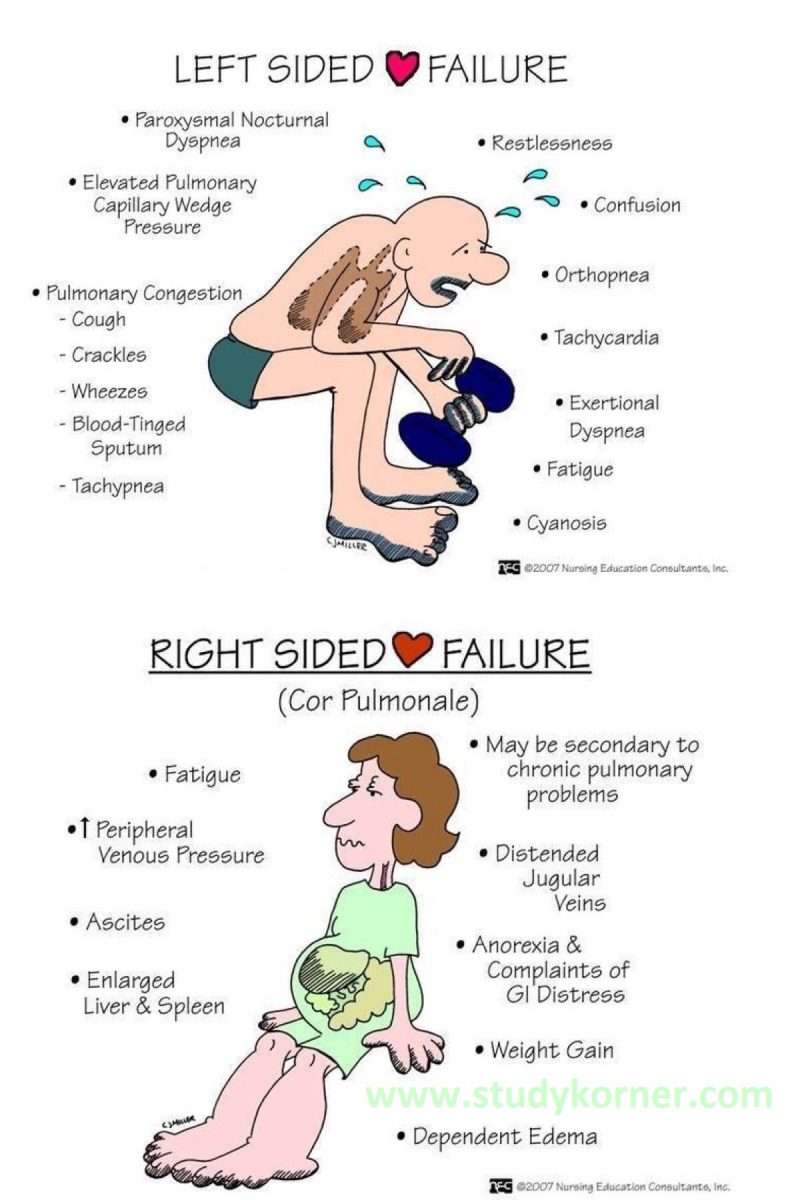
Left Sided Heart Failure
primary cause of right sided heart failure.
When the left ventricle is not working as effectively, fluid pressure increases and ends up moving back through the lungs. This can cause an overload to the heartâs right side.
Consequently, when the right side is unable to pump blood, fluid accumulates in the veins, resulting in swelling.
Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction Treatment
Diuretics are a mainstay of HFpEF treatment. For these medications to be helpful, however, you need to also make changes to your diet and overall lifestyle.
If you have HFpEF, your doctor will likely suggest you follow a treatment regimen that includes a combination of:
- Diet and lifestyle changes
- For some patients, a device to protect the heart from abnormal rhythms
Diet and Lifestyle Changes
If you have heart failure, the following lifestyle changes may help you manage your symptoms:
- Regular low-intensity aerobic exercise to strengthen the heart
- Cutting back on salt
- Limiting your alcohol consumption
- Quitting smoking
Reducing your salt intake is especially important. Too much salt in your diet can cause fluid retention. This will counteract the drugs that help relieve fluid accumulation.
The effectiveness of medication in the treatment of diastolic heart failure is inconclusive. Therefore, the best way to manage HFpEF is to treat its underlying cause, such as hypertension, diabetes, or coronary artery disease.
SGLT2 inhibitor medications are antidiabetic drugs that may be used to treat HFpEF in people with or without diabetes. In people with heart failure, taking this medication can help prevent heart failure episodes. Your doctor can determine whether you are able to use an SGLT2 inhibitor.
Management by Stage
The American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association recommend that cardiologists manage heart failure by stage.
Also Check: Can Teenagers Have Heart Attacks
Enlargement Of The Heart
Another important compensatory mechanism is enlargement of the muscular walls of the ventricles . When the heart must work harder, the hearts walls enlarge and thicken, as biceps muscles enlarge after months of weight training. At first, the enlargement allows the heart to maintain the amount of blood it pumps out . However, the enlarged and/or thickened heart eventually becomes stiff, causing or worsening heart failure. Also, the enlargement can stretch the heart valve openings, causing them to malfunction, which causes more pumping problems.
What Is The Difference Between Left And Right
Heart failure can occur in the left side of the heart, the right side of the heart or on both sides. The major difference between left-sided heart failure and right-sided heart failure is in the side of the heart that is weakened. In left-sided heart failure, the left side of the heart is weakened and results in reduced ability for the heart to pump blood into the body. In right-sided heart failure, the right side of the heart is weakened and results in fluid in your veins, causing swelling in the legs, ankles, and liver.
To understand these conditions, it is important to know a little about how blood flows through the heart.
The heart is made up of four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria and the lower chambers are called ventricles. Each side of the heart has paired upper and lower chambers. Blood returns from the body and enters the right atrium. From there it moves to the right ventricle, which pumps it to the lungs where it is oxygenated. Blood moves from the lungs into the left atrium, down to the left ventricle and then out to the body to supply organs and tissues with oxygen and nutrients.
Also Check: What Causes Heart Rate To Drop Suddenly
Left Side Of The Heart
The job of the heart muscle is to transport oxygenated blood coming from the lungs to the left atrium and on through to the left ventricle. The left ventricle is the main pumping portion of the heart. It is larger than the other chambers and plays a fundamental role in normal heart function. When there is HF on the left side of the heart, the heart muscle has to work harder to squeeze out the same volume of blood. This is referred to as left ventricular heart failure. It is the most common type of HF.1
What Are The Symptoms Of Left Ventricular Failure
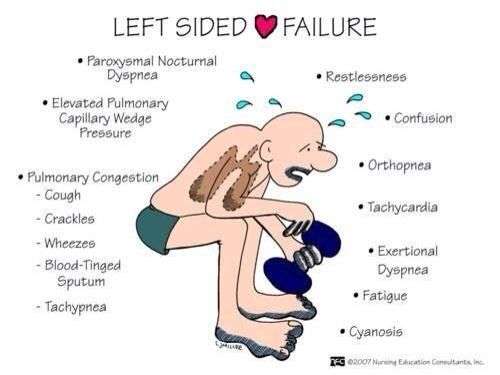
There are a number of different left-sided heart failure symptoms. As we mentioned earlier, shortness of breath occurs because of fluid backing up into the lungs. This shortness of breath often gets worse at night, so some sufferers have to sleep upright. As time goes on, left-sided heart failure can cause shortness of breath at any time of day even when resting.
Here are the other common symptoms of left ventricular failure:
Some of the symptoms described here are due to forward failure, which means the heart isnt pumping enough of the blood out to other parts of the body. Fatigue, chest discomfort, and a decrease in urine are caused by forward failure.
Other symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, coughing with blood, and weight gain are a result of backward failure, which occurs when the heart isnt receiving enough blood.
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Congestive Heart Failure
Risk Factors Associated With Left
As you may have guessed, there are people who are more prone to left-sided heart failure than others. Some of the left-sided heart failure risk factors are out of our control, while others are an indication of how important it is to pay attention to our overall health since we can have influence over it.
Here are some of the common risk factors:
- Blood clots: Clots in the lungs are known to lead to left-sided heart failure
- Chronic diseases: HIV, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, diabetes, or a build-up of protein or iron can lead to left-sided heart failure.
- Congenital heart defects: These can prevent proper blood flow from the heart.
- Aortic stenosis: Blood flow slows and then the heart weakens when the aortic valve opening narrows.
- Cardiomyopathy: This is a hereditary condition that can lead to heart damage.
- Irregular heartbeats: Abnormal heart rhythms can weaken the heart muscle.
- Myocarditis: This is a condition that is caused by inflammation of the heart
- Pericardial constriction: This is inflammation that creates a sac covering the heart, which can scar and tighten the heart muscle.
- Previous heart attack: In some cases, this can impact the pumping of blood
- Medications: Some chemotherapy and diabetes medications may increase risk.
- Valvular heart disease: Damage to one of the four heart valves can prevent the heart from pumping blood properly.
- Viral infection: Some viral infections have the potential to damage heart muscle.
