What Are The Symptoms Of Left Ventricular Failure
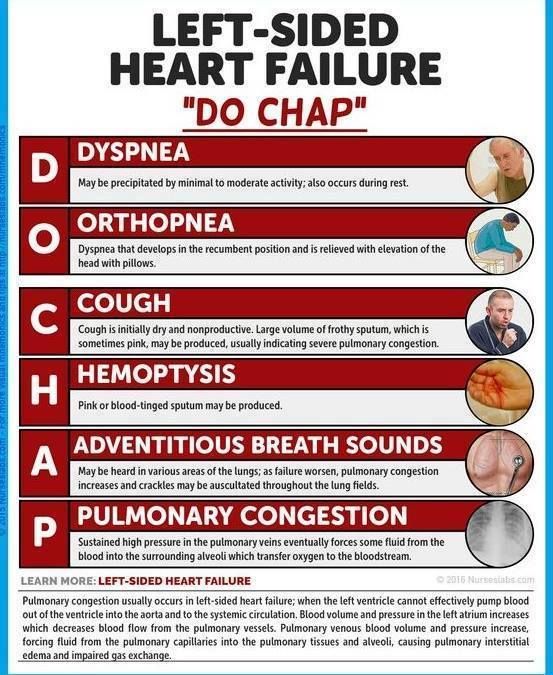
There are a number of different left-sided heart failure symptoms. As we mentioned earlier, shortness of breath occurs because of fluid backing up into the lungs. This shortness of breath often gets worse at night, so some sufferers have to sleep upright. As time goes on, left-sided heart failure can cause shortness of breath at any time of day even when resting.
Here are the other common symptoms of left ventricular failure:
Some of the symptoms described here are due to forward failure, which means the heart isnt pumping enough of the blood out to other parts of the body. Fatigue, chest discomfort, and a decrease in urine are caused by forward failure.
Other symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, coughing with blood, and weight gain are a result of backward failure, which occurs when the heart isnt receiving enough blood.
Essay On Fluid Transport
pressure. Filtration will occur until the equilibrium is reached. If the two hydrostatic pressures between the compartments are equal, then filtration will not occur. An example of filtration would be edema caused by right sided heart failure. In said diagnosis, there is right-sided hypertrophy due to it having to work harder than normal. Not enough blood is pushed out of the right side, so it backs up into the venous system where the hydrostatic pressure will continue to rise which causes capillary
Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
To make a diagnosis of HFpEF, your healthcare provider looks for:
- The clinical signs and symptoms of heart failure, and
- Evidence that the left ventricle contracts normally, or near normally, and that it pumps out greater than 50% of the blood it contains with each beat, and
- Evidence of reduced diastolic function seen on an echocardiogram
A diagnosis of diastolic heart dysfunction can also be measured invasively, using a catheter, or non-invasively, using doppler imaging techniques. Exercise tests can also help your healthcare provider diagnose your condition.
There are multiple conditions that can contribute to HFpEF, but the most common are:
- High blood pressure
Don’t Miss: How Do They Do Open Heart Surgery
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide And B
ANP and BNP are endogenously generated peptides activated in response to atrial and ventricular volume/pressure expansion. ANP and BNP are released from the atria and ventricles, respectively, and both promote vasodilation and natriuresis. Their hemodynamic effects are mediated by decreases in ventricular filling pressures, owing to reductions in cardiac preload and afterload. BNP, in particular, produces selective afferent arteriolar vasodilation and inhibits sodium reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule. It also inhibits renin and aldosterone release and, therefore, adrenergic activation. ANP and BNP are elevated in chronic heart failure. BNP especially has potentially important diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications.
For more information, see the Medscape Drugs & Diseases article Natriuretic Peptides in Congestive Heart Failure.
What Can I Do To Manage Swelling From Extra Fluid
- Elevate your legs above the level of your heart. This will help with fluid that builds up in your legs or ankles. Elevate your legs as often as possible during the day. Prop your legs on pillows or blankets to keep them elevated comfortably. Try not to stand for long periods of time during the day. Move around to keep your blood circulating.
- Limit sodium . Ask how much sodium you can have each day. Your healthcare provider may give you a limit, such as 2,300 milligrams a day. Your provider or a dietitian can teach you how to read food labels for the number of mg in a food. He or she can also help you find ways to have less salt. For example, if you add salt to food as you cook, do not add more at the table.
- Drink liquids as directed. You may need to limit the amount of liquid you drink within 24 hours. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much liquid to have and which liquids are best for you. He or she may tell you to limit liquid to 1.5 to 2 liters in a day. He or she will also tell you how often to drink liquid throughout the day.
- Weigh yourself every morning. Use the same scale, in the same spot. Do this after you use the bathroom, but before you eat or drink. Wear the same type of clothing each time. Write down your weight and call your healthcare provider if you have a sudden weight gain. Swelling and weight gain are signs of fluid buildup.
Don’t Miss: How To Lower Heart Rate Anxiety
What Are The Types Of Left
There are two types of left-sided heart failure: systolic heart failure and diastolic heart failure.
- Systolic heart failure: Also called reduced ejection fraction , it happens when the left ventricle cant contract forcefully. Less oxygen-rich blood gets pumped out to the body when you have systolic heart failure. Instead, it flows back into the organs, leading to fluid build-up in the lungs as well as swelling in certain parts of the body.
- Diastolic heart failure: Also referred to as preserved ejection fraction , this is when the heart muscle actually contracts normally but the ventricles are stiff or thick and dont relax, so the amount of blood pumped out to the body is reduced.
Ejection fraction is the term thats used to measure the amount of blood that pumps through the ventricles. A hearts normal ejection fraction is between 50 and 70 percent. A measurement of 40 percent or under is usually a sign of heart failure. Sometimes, people can have a normal ejection fraction reading and still have heart failure. An echocardiogram is the most common test used for measuring EF.
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The symptoms of heart failure depend on which side of your heart is affected and how serious your condition has become. Most symptoms are caused by reduced blood flow to your organs and fluid buildup in your body.
Fluid buildup happens because the flow of blood through your heart is too slow. As a result, blood backs up in the vessels that return the blood to your heart. Fluid may leak from the blood vessels and collect in the tissues of your body, causing swelling and other problems.
Symptoms of heart failure may include:
- Feeling short of breath when you do things like climbing stairs. This may be one of the first symptoms you notice.
- Fatigue or weakness even after rest.
Also Check: How Is A Heart Attack Treated
What Raises My Risk For Heart Failure
Many things can raise your risk of heart failure. Some things you can control, such as your lifestyle habits, but many others are out of your control, including your age, race, or ethnicity. Your risk of heart failure goes up if you have more than one of the following.
Heart failure is common in both men and women, although men often develop heart failure at a younger age than women. Women more commonly have heart failure with preserved ejection fraction , which is when the heart does not fill with enough blood. Men are more likely to have heart failure with reduced ejection fraction , . Women often have worse symptoms than men.
What Is The Difference Between Diastolic And Systolic
Diastolic and systolic are the two numbers on a blood pressure reading. Every time your heart squeezes, it pumps out blood to the network of blood vessels known as the circulatory system. The force or pressure of that squeeze is called systolic blood pressure. When your heart rests between beats, the pressure in the arteries is the diastolic blood pressure. This is why your blood pressure has two numbers:
- The top number is the systolic blood pressure.
- The bottom number is the diastolic blood pressure.
Also Check: Where Does Oxygenated Blood Enter The Heart
Types Of Heart Failure
In heart failure, the heart can no longer pump enough blood around the body. The heart muscle is either too weak or not elastic enough. Different parts of the heart may be affected too. The type of medication people use for the treatment of heart failure will depend on the type of heart failure they have.
Heart failure often only affects the left or right side of the heart, but can affect both. Doctors differentiate between three types of heart failure, accordingly:
- Left-sided heart failure: The left ventricle of the heart no longer pumps enough blood around the body. As a result, blood builds up in the pulmonary veins . This causes shortness of breath, trouble breathing or coughing especially during physical activity. Left-sided heart failure is the most common type.
- Right-sided heart failure: Here the right ventricle of the heart is too weak to pump enough blood to the lungs. This causes blood to build up in the veins . The increased pressure inside the veins can push fluid out of the veins into surrounding tissue. This leads to a build-up of fluid in the legs, or less commonly in the genital area, organs or the abdomen .
- Biventricular heart failure: In biventricular heart failure, both sides of the heart are affected. This can cause the same symptoms as both left-sided and right-sided heart failure, such as shortness of breath and a build-up of fluid.
Coronary Angiography And Cardiac Catheterization
A coronary angiography and cardiac catheterization are two diagnostic procedures often used to identify problems with the heart. They involve a surgical procedure in which a small incision is made into the groin, arm, or neck and into a large blood vessel. A catheter is fed through the blood vessel, via the incision, to the heart.
The coronary angiography portion of this procedure involves the administration of a contrast dye . After you are given the contrast dye, the healthcare provider can take X-rays, which allow them to watch where the dye goes and observe its flow through the blood vessels and heart. This is helpful in identifying any blockages.
Other things can be done through a cardiac catheterization. Biopsies of tissue can be taken, stents can be placed to open up blockages, and the pressure of blood flow through the heart can be measured.
These tests are invasive procedures and are usually able to be done on a same-day surgery basis. Depending on where your incision is made and what is done during the procedure, you may need to lay flat for a period of time following your cardiac catheterization. You should follow your practitioner’s or nurse’s instructions precisely during your recovery period.
You May Like: How To Determine Max Heart Rate
Left Heart Failure Research Paper
Nursing 281 Research Paper Professor White27 September 2015Introduction: The human body is a wonderful machine, but sometimes it can have mechanical break downs Within it. One of the many break downs is the Left Heart Failure this disease is a very progressive disorder and once it starts, anything short of a transplant is hard to fix. The Left Heart Failure which is the injury to the heart will cause a lot of damage to the cardiovascular
How Is Diastolic Heart Failure Diagnosed

Your healthcare provider asks you about your symptoms and family health history. Your provider also conducts a physical exam and listens to your heart with a stethoscope.
You may have specific tests to diagnose heart failure, such as:
- Chest X-ray to take images of your chest and heart.
- Electrocardiogram , a record of the electrical activity in your heart.
- Echocardiogram, using sound waves to evaluate the structure and function of your heart muscle and valves.
- Exercise stress test, increasing your heart rate with medicine or as you walk on a treadmill to see how your heart responds.
- Cardiac catheterization, using a catheter to measure your hearts pressure and blood flow.
Don’t Miss: Low Heart Rate When Sleeping
Classification Based On Course Of The Disease
Heart failure can develop suddenly, for instance after a heart attack or due to certain heart rhythm problems. This is known as acute heart failure.
But it usually develops gradually over time as a result of a different medical problem, such as permanently high blood pressure. This is known as chronic heart failure.
What Are The Symptoms
Your feet, legs, and ankles will likely to swell because blood is backing up in your veins. This symptom is called edema.
- If it backs up into your stomach or liver, you may notice that your abdomen is distended, too.
- You might find that you have to go to the bathroom more, especially at night. This is caused by fluid buildup, too.
As your heart failure gets worse, you may also see some of these symptoms:
- Itâs hard to breathe.
- Your neck veins are swollen.
- Your pulse is fast or feels âoff.â
- Your chest hurts.
- Youâre gaining weight from excess fluid.
- You donât feel like eating.
- Your skin is cold and sweaty.
- Youâre very tired.
Also Check: Heart Ablation Surgery For Afib
The Flow Of Blood Through Your Heart
To understand the different types of heart failure, it helps to know how your heart pumps blood:
Precipitating Causes Of Heart Failure
A previously stable, compensated patient may develop heart failure that is clinically apparent for the first time when the intrinsic process has advanced to a critical point, such as with further narrowing of a stenotic aortic valve or mitral valve. Alternatively, decompensation may occur as a result of the failure or exhaustion of the compensatory mechanisms but without any change in the load on the heart in patients with persistent, severe pressure or volume overload. In particular, consider whether the patient has underlying coronary artery disease or valvular heart disease.
The most common cause of decompensation in a previously compensated patient with heart failure is inappropriate reduction in the intensity of treatment, such as dietary sodium restriction, physical activity reduction, or drug regimen reduction. Uncontrolled hypertension is the second most common cause of decompensation, followed closely by cardiac arrhythmias . Arrhythmias, particularly ventricular arrhythmias, can be life threatening. Also, patients with one form of underlying heart disease that may be well compensated can develop heart failure when a second form of heart disease ensues. For example, a patient with chronic hypertension and asymptomatic LV hypertrophy may be asymptomatic until an MI develops and precipitates heart failure.
- Profound anemia
- Nutritional deficiencies
You May Like: How To Lower Your Heart Rate Fast
Essay About Dreams Come True
Besides dreams and faith, listening to our hearts also guides us towards our distinct destinies. When I was a little boy, I had difficulties when it came to making decisions. I would do things because somebody said I should do them and when I was finally asked why I did what I did, I would point a finger and sayI did it because he said I should do it. My mother said to me: you do not do things because somebody said you should do them, listen to your heart and you will never go wrong. Since then
What Are The Symptoms Of Left
Symptoms may be mild at first or you may think it’s a cold or allergy. You might not even notice them. But as heart functioning worsens, you may experience:
- Constant coughing.
- Shortness of breath with walking or bending over.
- Waking up short of breath or unable to lie flat at night.
- Swelling in your ankles, legs or abdomen.
Over time, the heart works harder to do its job. This causes complications that may include:
- Abnormal heart rates and rhythms .
You May Like: Can You Live With Heart Failure
Systolic And Diastolic Failure
Systolic and diastolic heart failure each result in a decrease in stroke volume. This leads to activation of peripheral and central baroreflexes and chemoreflexes that are capable of eliciting marked increases in sympathetic nerve traffic.
Although there are commonalities in the neurohormonal responses to decreased stroke volume, the neurohormone-mediated events that follow have been most clearly elucidated for individuals with systolic heart failure. The ensuing elevation in plasma norepinephrine directly correlates with the degree of cardiac dysfunction and has significant prognostic implications. Norepinephrine, while directly toxic to cardiac myocytes, is also responsible for a variety of signal-transduction abnormalities, such as downregulation of beta1-adrenergic receptors, uncoupling of beta2-adrenergic receptors, and increased activity of inhibitory G-protein. Changes in beta1-adrenergic receptors result in overexpression and promote myocardial hypertrophy.
What Are The Treatments For Heart Failure
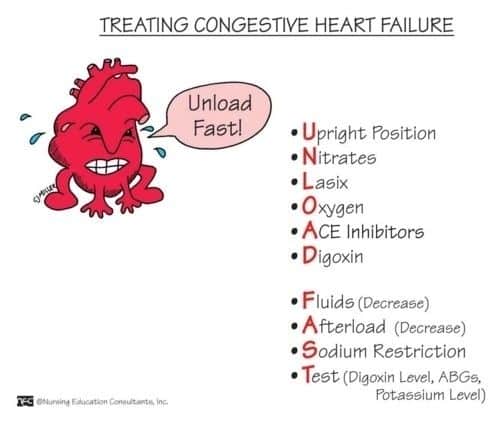
Your treatment will depend on the type of heart failure you have and how serious it is. There’s no cure for heart failure. But treatment can help you live longer with fewer symptoms.
Even with treatment, heart failure usually gets worse over time, so you’ll likely need treatment for the rest of your life.
Most treatment plans include:
You may need heart surgery if:
- You have a congenital heart defect or damage to your heart that can be fixed.
- The left side of your heart is getting weaker and putting a device in your chest could help. Devices include:
- A biventricular pacemaker .
- A mechanical heart pump or a total artificial heart).
As part of your treatment, you’ll need to pay close attention to your symptoms, because heart failure can worsen suddenly. Your provider may suggest a cardiac rehabilitation program to help you learn how to manage your condition.
Don’t Miss: Open Heart Surgery Recovery Timeline
