How Does Strength Training Exercise Affect Your Heart
Strength training exercise works the heart in a completely different way. At any given moment, certain muscles are contracting and relying predominantly on type two muscle fibers, which are responsible for giving us a great looking body and making us stronger.
As the muscles contractsay the arm muscles during a bicep curlthey press and close the blood vessels that flow through them. This leads to increased blood pressure in the rest of the body and the heart has to fight against a stronger force to push blood out.
The heart adapts to this by increasing the thickness of the left ventricle wall. This thickness derived from chronic weight training is healthy, whereas the thickness from chronic high blood pressure is not.
What’s the difference? The healthy heart only has to work under pressure for two to three hours of strength training per week, whereas the heart with high blood pressure has to work 24 hours a day, seven days a week. The second heart may exhaust, whereas the healthy heart becomes stronger with a lower resting heart rate.
Exercise also stimulates the production of new blood vessels. As we make more blood vessels, there are more places for blood to flow, which results in more efficient circulation. Cardiovascular exercise increases the number of new blood vessels while resistance training increases the size of those blood vessels.
Increase your metabolism and tone up faster. Find afitness class.
Measuring Your Heart Rate
Watch any medical drama on TV and the first thing youll see the doctor do is measure the patients heart rate. Firstly because yes, it means theyre alive! Secondly, because our heart rate reveals so much about our general health and fitness. For example, a weak pulse or a racing heart rate can be a sign to a medical professional that something is not right.
So what exactly are they checking? By definition, your heart rate means the number of times your heart beats in a minute. The two most common ways to describe heart rate are:
- In beats per minute .
- As a percentage of your maximum heart rate .
What Is The Best Exercise For Heart Rate
While interval-style exercise training is a popular choice for people who are time-poor, the intermittent nature of the exercise means heart rate will fluctuate, providing not much more benefit than traditional steady-state exercise.
Read more:Health Check: high-intensity micro workouts vs traditional regimes
From a scientific perspective, athletes typically use heart-rate ranges to train at specific intensities during aerobic exercise, like cycling or long-distance running.
Exercising at certain intensities are known to elicit adaptive responses from the body, for example, exercising at or below the lactate threshold.
These intensities are called training zones and are expressed relative to HRmax. For instance, a light aerobic training session would be prescribed below 75% HRmax, while training at threshold will induce physiological change.
Overall, some exercise is better than no exercise for your cardiovascular health. Accumulating 150 minutes of exercise per week is the minimum requirement for health benefit. Exercising at your maximal heart rate is not necessary to achieve these benefits. Athletes can use training zones, relative to HRmax, to achieve optimal adaptation and enhance endurance performance.
Don’t Miss: How To Calculate Resting Heart Rate
Exercise Makes Your Heart More Efficient
Typical resting heart rate can vary quite substantially between people and even within an individual. Around 60-80 beats per minute for adults is common.
Improving your aerobic fitness reduces your resting heart rate, as the heart becomes more efficient with each beat. An athletes resting heart rate, for instance, is typically around 40 BPM.
In fact, evidence suggests that long-term exercise training increases the size of the heart, specifically the left ventricle, a phenomenon known as Athletes Heart. A bigger heart means more blood can be pumped with each beat, and fewer beats per minute are required to maintain blood flow around the body. This is a beneficial physiological adaptation allowing athletes to exercise at higher intensities for longer.
Effects Of Exercise On Rhr By Considering Different Types Of Sports/exercise

The mean baseline and post-interventional RHR according to the different forms of sports and/or exercise are presented in . Under consideration of all comparisons, the RHR significantly decreased more in the exercising groups compared to the control groups . The meta-analyses on specific types of sports and exercise also revealed significant higher decreases in RHR in the intervention compared to the corresponding control groups for endurance training , yoga , strength training , and combined endurance and strength training .
Read Also: How Do You Calculate Max Heart Rate
Too Much Body Fat Is Linked To A
variety of health problems, including CVD, cancer, and type Healthy body composition can be difficult to
achieve and maintain because a diet that contains all essential nutrients can be relatively high in calories, especially for someone who is sedentary. are stored in the body as fat. Excess calories
Resting Heart Rate And Fitness
Your resting heart rate is the number of times your heart beats per minute while at complete rest. It is an indicator of your physical fitness. Your resting heart rate will decrease as your heart becomes stronger through aerobic exercise training.
A low resting heart rate indicates better fitness in people who are in athletic training or a workout program, but it can have other health significance for people who are not physically fit .
Recommended Reading: Which Of The Following Signs Is Commonly Observed In Patients With Right-sided Heart Failure
Why Has Your Resting Heart Rate Increased After Exercise
Its one thing for your heart rate after exercise to be a bit elevated, but its a little different if your resting heart rate has experienced an increase after youve worked out.
Before we look at why this happens, its worth explaining what a resting heart rate is. Basically, your resting heart rate is how many times your heart beats per minute when your body is resting.
A healthy resting heart rate for adults is 60 to 100 beats per minute. An athlete will have a heart rate thats much lower than this, though sometimes around 40 beats per minute. This is as a result of how a lower resting heart rate is a sign of healthy cardiovascular function.
If youve been putting your body through strenuous exercise but not giving your body the time it needs to rest, then you might experience your heart rate increasing even when youre at rest. This is just a sign from your body that you need more chill time. Make sure you always have some time for your body to repair after a workout.
There are other things that could contribute to your resting heart rate being elevated, such as if its hot and you havent been drinking enough water, or if youre feeling stressed.
Heart Rate Response To Exercise
The primary purpose of the cardiorespiratory system is to deliver adequate amounts of oxygen and remove waste from body tissues . The purpose of cardiovascular regulation is maintaining adequate blood flow to all body tissues. In addition, the circulatory system transports nutrients and aids in temperature regulation. During exercise, the demand for oxygen to the muscles is 15 to 25 times greater than at rest. The heart cannot accomplish this by itself, and does not work in isolation. The respiratory system and the circulatory system function together as a coupled unit delivering the bodys oxygen and nutrients and taking away carbon dioxide and wastes to maintain homeostasis.
During exercise, there is an increase in oxygen demand on body tissues and many things happen in the body such as an increase in blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate. To meet the demand for oxygen, two major adjustments of blood flow are made, and increase in the amount of blood being pumped per minute by the heart or the cardiac output, and a redistribution of blood flow from inactive organs to the active skeletal muscle.
Recommended Reading: How Does Heart Disease Affect The Skeletal System
Possible Relevance Of Exercise
Recently, Aune et al. calculated that an increase of the RHR by 10 bpm increases all-cause mortality by 17%. The evidence regarding negative influence of elevated RHR on cardiovascular and thus all-cause death is constantly increasing. The mechanisms of this relationship are still not completely known. Possible mechanisms may be endothelial dysfunction, reduced artery compliance and distensibility, and consequently increased arterial wall stress and elevated pulsed wave velocity, which is further associated with increased after load and ultimately systemic hypertension . However, the RHR does not fulfil all criteria for being an independent risk factor, as scientific evidence proving that treating an elevated RHR reduces mortality is still lacking . Thus, it cannot be excluded that the relationship between the RHR and mortality may be non-causative. If there is a causative relationship assuming a persistently reduced RHR due to lifelong enduranceaccording to the results of our meta-analysisexercise and yoga could reduce mortality by about 4.4% to 8.9% and about 6.0% to 8.7%, respectively, depending on the sex of the athlete.
How Long And How Hard
To achieve a lower resting heart rate from exercise, you should exercise at least 150 minutes a week in your aerobic zone. If you are just starting an exercise program, slowly build up your exercise time by a little bit each day. You can enjoy great health benefits and an even lower resting heart rate by exercising for a longer time or at a more vigorous level, such as at 65 percent to 85 percent of your maximum heart rate.
You May Like: Can Acid Reflux Cause Palpitations
What Is A Normal Resting Heart Rate
For a well-trained athlete, their resting heart rate will usually be around 40 beats per minute.
For adults, a normal RHR ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute, although most people who are relaxed and healthy should be below 90. For a well-trained athlete, their RHR will usually be below this, around 40 beats per minute. This is because a lower RHR is often a sign of good cardiovascular fitness and efficient heart function.
However, you shouldnt compare your RHR with someone elses. Youre unique and beautiful and thats how it should be. While your neighbors RHR might be lower than yours, it might be for a dozen different reasons.
Instead of comparing yourself to others, youre better off monitoring how your RHR is changing over time. When your resting heart rate decreases as a result of training, its a sign that your aerobic fitness has improved.
Take that, neighbor.
Concluding Remarks And Remaining Questions To Be Addressed
Overview of major cardiovascular effects of exercise. Abbreviations: HR, heart rate LV, left ventricle eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase NO, nitric oxide VSM, vascular smooth muscle BP, blood pressure HDL, high density lipoprotein LDL, low density lipoprotein VLDL, very low density lipoprotein TG, triglycerides EPC, endothelial progenitor cell.
Don’t Miss: How Accurate Is Fitbit Charge 2 Heart Rate
How Do I Measure My Resting Heart Rate
A heart rate sensor is the most accurate way to measure your RHR. Discover how to monitor your RHR when using this technology with our guide to measuring your resting heart rate.
Also known as your basal heart rate because it is your base measurement
If you dont have a heart rate sensor, you can try measuring it yourself by checking your pulse. You can choose between your carotid artery or your radial artery .
You should never use your thumb to take this measurement as it has its own pulse, which could cause you to miscount. Instead, place your index and third fingers on either your neck or wrist. Count the number of beats in 15 seconds and then times this number by four to calculate the beats per minute.
The American Heart Association recommends checking your RHR first thing in the morning before getting out of bed. The caffeine in your morning coffee or tea will cause heart palpitations, so make sure you measure your RHR before making your heart rate rise.
Dont attempt to measure your resting heart rate after exercise or a stressful event. Leave it an hour as your RHR is high after a workout or any strenuous activity. Allow your resting heart rate recovery time just like the rest of your body.
Want to work out max heart rate? Use our calculator.
Normal Cardiac And Skeletal Muscle Energy Metabolism
Heart muscle must maintain blood circulation in states of both rest and high peripheral demand such as that triggered by exercise. A trained athlete is able to rapidly increase cardiac output as much as 6-fold from rest to high activity levels . The work done by the heart and hence energy yield must then be permanent, adaptable, rapidly regulated, and highly efficient.
Another recent issue in energy metabolism concerns the transcriptional regulation and signaling pathways involved in the maintenance of energy homeostasis and mitochondrial biogenesis . Mitochondrial biogenesis depends on the coordinated function of mitochondrial and nuclear genomes. The mitochondrial transcription factor is encoded by the nuclear genome and activates transcription and replication of the mitochondrial DNA. MtTFA expression is controlled by nuclear respiratory factors that additionally stimulate expression of numerous nuclear-encoded mitochondrial proteins. NRFs expression and transcriptional activity are under the control of the transcriptional co-activator PGC-1 gamma) . PGC-1 coordinates mitochondrial protein expression with substrate utilization by co-activating respectively PPAR that regulates fatty acid oxidation, and NRFs that activate transcription of nuclear and mitochondria-encoded proteins . Creatine kinases are highly modulated in response to physiological stimuli, but surprisingly little is known concerning their transcriptional regulation in muscle cells .
Recommended Reading: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
Exercises To Improve Your Cardiorespiratory Endurance
These exercises may help you to improve your cardiorespiratory endurance. You dont need a lot of equipment, so they can be done anytime and anywhere. You can even try doing 510 minutes of these exercises a few times per day if you dont have large blocks of time available for exercise.
The exercises can help to burn fat, develop muscle, and get your heart pumping. Its also important that you breathe deeply while doing the exercises.
Try to do each exercise for at least a minute. You can take a 30-second break in between each exercise. They require a certain amount of endurance, so you can gradually increase the duration and intensity of your workouts.
Understanding Target Heart Rate Why Does It Matter
Target heart rate is a heart rate range that ensures you stay safe when exercising.
Its based on 60 to 80 percent of your maximum heart rate, and will vary depending on your age. Its not just about safety, though. Focusing on your target heart rate ensures that you can take advantage of various benefits.
For example, by keeping your heart rate in the lower range, youll be able to exercise for longer periods at a time and boost your weight loss. On the other hand, if you keep your heart rate in the higher range, youll experience improved cardiorespiratory fitness.
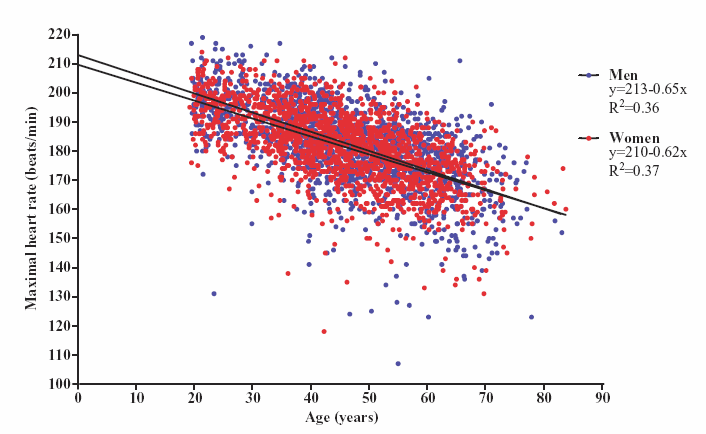
If youre 20 years old and your heart rate is 120 beats per minute, thats 60 percent of your heartbeat. On the other hand, 70 percent will be 140 beats and 80 percent will be 160 beats.
For example, when youre 35, youll release 111 heartbeats at 60 percent of your heart rate, 130 beats at 70 percent, and 148 at 80 percent. This happens because ones maximum heart rate decreases with age.
Also Check: Tylenol Heart Rate
Why Train With Heart Rate
Your heart rate is a useful tool for understanding and improving your fitness level and performance. Training with heart rate allows you to monitor and control the intensity of your workouts, allowing for variation in your training plan.
The best part of training with heart rate means that every second of your workout counts. By monitoring your heart rate during exercise, youll enhance both your fitness and recovery time, which combined will improve your overall performance.
Whats An Ideal Target Heart Rate
Your target heart rate during exercise should be between 50% to 85% of your MHR, depending on what type of exercise you are doing and for what purpose.
For example, if you want to improve your endurance, you should do long training sessions at low intensity. If your aim is to improve your cardiovascular health, then high-intensity interval training is what you should try.
Read Also: Acid Reflux Heart Fluttering
How Does Cardiovascular Exercise Affect Your Heart
When performing cardio, blood flow is directed toward working muscles and away from areas that aren’t doing much . There is increased blood flow, and blood volume returning to the heart.
As the heart registers a larger blood volume, over time the left ventricle adapts and enlarges. This larger cavity can hold more blood, and ejects more blood per beat, even at rest.
More: Calculate your Target Heart Rate.
Over time, with chronic cardio training, our resting heart rate drops because each beat delivers a bigger burst of blood, and fewer beats are needed. This takes work off your heart and is why cardio exercise is recommended for heart health.
However, cardiovascular exercise can also produce stress. If we get into over-training, we may hit a point where we are drowning in cortisol. This eventually leads to immune-suppression and fat gain around the abdomen and face.
People who spend a significant part of their day in stress, who have poor digestion or other sources of physiological stress, should not further their stress levels by overtraining. Always think of your goals, moderate your exercise if necessary, and work to reduce your stress levels.
